爬虫综合大作业
相信很多人都有书荒的时候,想要找到一本合适的书籍确实不容易,所以这次利用刚学习到的知识爬取豆瓣网的各类书籍,传送门https://book.douban.com/tag/?view=cloud。
首先是这个程序的结构,html_downloader是html下载器,html_outputer是导出到Excel表,html_parser是解析页面,make_wordcloud是制作词云,spided_main是程序入口,url_manager是URL管理器,有兴趣的童鞋可以去慕课网看paython基础爬虫课程。
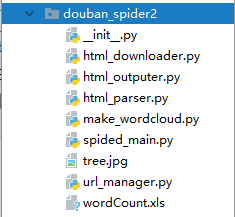
主要实现思路是先请求下载需要的html,解析得到目标URL并存储到URL管理器中,再从URL管理器中获取得到URL,发送请求,解析得到需要的信息内容,导出到Excel表格,再重Excel表中获取数据进行分析得到词云。
html_downloader:
在这里我使用的是urllib.request进行请求,之前有试过用request进行请求,但是爬取了几百页就被封了ip,所以弃用request。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-import urllib.requestfrom urllib.parse import quoteimport stringclass HtmlDownloader(object): def download(self,url): if url is None: return None s = quote(url, safe=string.printable) #url里有中文需要添加这一句,不然乱码 response = urllib.request.urlopen(s) if response.getcode()!= 200: return None return response.read() #返回内容 |
通过分析豆瓣网的结构,可以看到,我们首先传进去的是总的图书分类,但是我们需要的是每一个分类里面的图书信息。所以我们需要得到每一个分类的url,即base_url,再通过这个base_url去获取图书url,即detail_url。
url_manager:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-class UrlManage(object): def __init__(self): self.base_urls = set() #基本分类的URL self.detail_urls = set() #详细内容页的URL self.old_base_urls = set() #已经爬取过的url self.old_detail_urls = set()#已经爬取过的url |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
<br> #添加单个url def add_base_url(self,url): if url is None: return if url not in self.base_urls and url not in self.old_base_urls: self.base_urls.add(url) def add_detail_url(self,url): if url is None: return if url not in self.detail_urls and url not in self.old_detail_urls: self.detail_urls.add(url) # print(self.detail_urls) # 添加多个url def add_new_detail_urls(self, urls): if urls is None or len(urls) == 0: return for url in urls: self.add_detail_url(url) def add_new_base_urls(self, urls): if urls is None or len(urls) == 0: return for url in urls: self.add_base_url(url)<br> #判断是否还有url def has_new_detail_url(self): return len(self.detail_urls)!=0 def has_new_base_url(self): return len(self.base_urls)!=0<br> #得到一个新的url def get_base_url(self): new_base_url = self.base_urls.pop() self.old_base_urls.add(new_base_url) return new_base_url def get_detail_url(self): new_detail_url = self.detail_urls.pop() self.old_detail_urls.add(new_detail_url) return new_detail_url |
解析器 html_parser:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-import refrom urllib.parse import urlparsefrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupclass HtmlParser(object): def soup(cont): soups = BeautifulSoup(cont, 'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8') return soups<br> #得到具体的data数据 def get_new_data(soup): dict = {} if (soup.select('.subject-list')[0].contents): li = soup.select('.subject-list')[0].select('.subject-item') di = {} for i in li: bookname = i.select('.info')[0].select('a')[0].attrs['title'] # 书名 comment = i.select('.clearfix')[0].select('.pl')[0].text comment = re.findall('\d+', comment)[0] di[bookname] = comment if di: # 返回的字典不为空的时候 dict.update(di) return dict # 得到详细内容的url def get_detail_url(base_url): detail_urls = set() for k in range(0, 501, 20): if (k == 0): urls = base_url # print(urls) else: urls = base_url + '?start={}&type=T'.format(k) # print(urls) detail_urls.add(urls) return detail_urls # 得到所有的baseurl def get_all_base_urls(soup): links = soup.select('.tagCol')[0].select('a') base_urls = set() for link in links: new_full_url = 'https://book.douban.com{}'.format(link.attrs['href']) # HtmlParser.get_detail_url(new_full_url) base_urls.add(new_full_url) return base_urls def parser(cont): soup = BeautifulSoup(cont, 'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8') base_urls = HtmlParser.get_all_base_urls(soup) return base_urls |
spided_main:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-from douban_spider2 import url_manager, html_downloader, html_parser, html_outputerclass SpiderMain(object): def __init__(self): self.urls = url_manager.UrlManage() self.downloader = html_downloader.HtmlDownloader() self.htmlparser = html_parser.HtmlParser self.outputer = html_outputer.HtmlOutputer() def craw(self,root_url): count = 1 dictdata = {} cont = self.downloader.download(root_url) base_urls = self.htmlparser.parser(cont) self.urls.add_new_base_urls(base_urls) while self.urls.has_new_base_url(): try: base_url = self.urls.get_base_url() detail_urls = self.htmlparser.get_detail_url(base_url) self.urls.add_new_detail_urls(detail_urls) except: print('craw failed') while self.urls.has_new_detail_url(): try: detail_url = self.urls.get_detail_url() print ('crow %d : %s'%(count,detail_url)) html_cont = self.downloader.download(detail_url) soup = self.htmlparser.soup(html_cont) dict = self.htmlparser.get_new_data(soup) dictdata.update(dict) if count == 1000: #因为之前有被封过ip,所以这里先爬取前1000条detail_url的内容 break count = count + 1 except: print ('craw failed') self.outputer.output_excel(dictdata)<br>#程序入口if __name__=="__main__": url = 'https://book.douban.com/tag/?view=cloud' obj_spider = SpiderMain() obj_spider.craw(url) |
html_outputer:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-import xlwt #写入Excel表的库class HtmlOutputer(object): def __init__(self): self.datas =[] def output_excel(self, dict): di = dict wbk = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8') sheet = wbk.add_sheet("wordCount") # Excel单元格名字 k = 0 for i in di.items(): sheet.write(k, 0, label=i[0]) sheet.write(k, 1, label=i[1]) k = k + 1 wbk.save('wordCount.xls') # 保存为 wordCount.xls文件 |
导出的Excel表格格式为,一共导出15261条记录
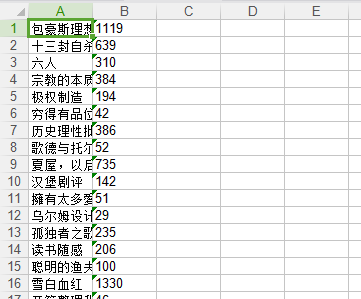
make_wordcloud:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-from wordcloud import WordCloudimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport xlrdfrom PIL import Image,ImageSequenceimport numpy as npfile = xlrd.open_workbook('wordCount.xls')sheet = file.sheet_by_name('wordCount')list = {}for i in range(sheet.nrows): rows = sheet.row_values(i) tu = {} tu[rows[0]]= int(rows[1]) list.update(tu)print(list)image= Image.open('./08.png')graph = np.array(image)wc = WordCloud(font_path='./fonts/simhei.ttf',background_color='white',max_words=20000, max_font_size=50, min_font_size=1,mask=graph, random_state=100)wc.generate_from_frequencies(list)plt.figure()# 以下代码显示图片plt.imshow(wc)plt.axis("off")plt.show() |
爬过的坑:
当定义的类有构造函数时候,调用时一定要加上括号,如 f = html_downloader.HtmlDownloader().download(),而不是 f= html_downloader.HtmlDownloader.download(),不然就会一直报错,类似于TypeError: get_all_base_urls() takes 1 positional argument but 2 were given。
生成词云的背景图片我选用的是
最后的做出由15261本书形成的词云

本次爬虫只是针对图书类热门评论而做出的词云,可以看到涵盖所有分类的书籍里最热门评论的有解忧杂货店,白夜行等,据此我们可以选取比较热门的图书进行阅读,也可以根据此结果再做进一步的分析,获取热门书籍中的评论进行分析人们对于某本书的评价关键词,从而进一步的了解这本图书所描述的内容。




