Python进阶学习
Python中的访问限制

1 ''' 2 私有属性是以双下划线'__'开头的属性,在类的外部访问私有属性将会抛出异常,提示没有这个属性。 3 ''' 4 5 class Animal: 6 __location='china' 7 def __init__(self,name,age): 8 self.name=name 9 self.__age=age 10 11 #__location是类的私有属性,在class外部无法直接访问 12 print(Animal.__location) 13 dog=Animal('dog',3) 14 print(dog.name) 15 #__age是对象的私有属性,在class外部无法直接访问 16 print(dog.__age)
Python中的类方法

1 ''' 2 类方法: 3 1、类方法需要使用@classmethod来标记为类方法,否则定义的还是实例方法 4 2、类方法的第一个参数将传入类本身,通常将参数名命名为 cls 5 ''' 6 class Animal: 7 __count=0 #私有的类属性,每创建一个实例对象,该值就加1 8 def __init__(self): 9 Animal.__count+=1 10 11 @classmethod 12 def get_count(cls): 13 return cls.__count 14 @classmethod 15 def set_count(cls,count): 16 cls.__count=count 17 18 Animal.set_count(0) 19 dog1=Animal() 20 dog2=Animal() 21 dog3=Animal() 22 dog4=Animal() 23 print(Animal.get_count())
Python判断类型

1 s = 'this is a string.' 2 print(isinstance(s, int) )#False 3 print(isinstance(s, str) )#True
Python的多重继承

1 ''' 2 python支持多重继承 3 ''' 4 class First(object): 5 def __init__(self): 6 super(First, self).__init__() 7 print("first init...") 8 9 class Second(object): 10 def __init__(self): 11 super(Second, self).__init__() 12 print("second init...") 13 14 class Third(First, Second): 15 def __init__(self): 16 super(Third, self).__init__() 17 print("third init...") 18 19 Third() 20 ''' 21 输出结果: 22 second init... 23 first init... 24 third init... 25 '''
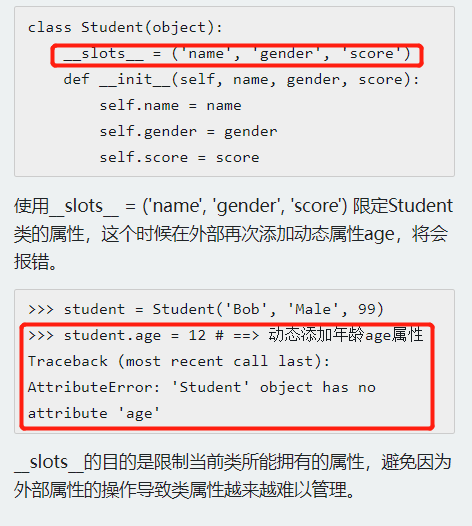
Python类的__slots__方法
Python类的__call__方法

1 ''' 2 如果把一个类的实例也变成一个可调用对象,可以实现一个特殊的方法__call__() 3 ''' 4 class Person(object): 5 def __init__(self, name, gender): 6 self.name = name 7 self.gender = gender 8 9 def __call__(self, friend): 10 print('My name is {}...'.format(self.name)) 11 print('My friend is {}...'.format(friend)) 12 13 p=Person('zhangsan','nan') 14 p('lisi') 15 16 ''' 17 输出的结果为: 18 My name is zhangsan... 19 My friend is lisi... 20 '''
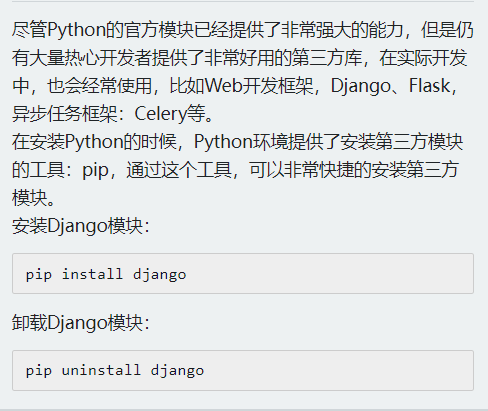
Python安装第三方模块
Python读写文件

1 # input函数:通过命令行界面输入东西 2 str=input('please input biao da shi:') 3 # eval函数:将算术表达式计算出结果 4 print(eval(str)) 5 ''' 6 运行结果如下: 7 please input biao da shi:7*8 8 56 9 '''

1 ''' 2 请尝试以只读模式打开一个指定绝对路径的文本文件,并正确关闭。 3 ''' 4 def open_text_file(): 5 #默认打开的就是文本文件 6 f=open('E:\\test\\nginx.conf','r') 7 print(type(f)) 8 f.close() 9 10 ''' 11 请尝试用只读模式打开一个指定绝对路径的二进制文件,并正确关闭 12 ''' 13 def open_binary_file(): 14 f=open('E:\\test\\my_love.jpg','rb') 15 print(type(f)) 16 f.close()

1 ''' 2 读取文件的内容,文件的内容被原样打印出来 3 ''' 4 def read_text_file(): 5 #默认打开的就是文本文件 6 f=open('E:\\test\\nginx.conf','r',encoding='utf8') 7 #readlines()会读到换行符\n,且该函数返回的结果是list 8 for line in f.readlines(): 9 line=line.strip('\n') #去调换行符\n 10 print(line) 11 f.close()

1 ''' 2 请从test.txt文件读取以上内容,并将每一行字符串反转,写入test1.txt文件 3 test.txt文件中的原内容: 4 Hello World 5 Hello Python 6 Hello Imooc 7 test1.txt文件中的预期内容: 8 dlroW olleH 9 nohtyP olleH 10 coomI olleH 11 ''' 12 def write_text_file(src_file,dest_file): 13 f1=open(src_file,'r',encoding='utf8') 14 f2=open(dest_file,'w',encoding='utf8') 15 lines=f1.readlines() #lines为['Hello World\n','Hello Python\n','Hello Imooc'] 16 num=0 #用来记录行数 17 for line in lines: 18 #读一行,行数记录加1 19 num+=1 20 line=line.strip('\n')[::-1] # 去掉\n后反转字符串 21 f2.write(line) 22 #最后一行的后面不写换行符 23 if num!=len(lines): 24 f2.write('\n') 25 f1.close() 26 f2.close()

1 ''' 2 test.txt文件中的内容如下: 3 Hello World 4 Hello Python 5 Hello Imooc 6 请将文件的内容重复写一份追加到文件的尾部。 7 ''' 8 # seek()函数参数的含义如下,0:文件首部,1:当前位置,2:文件尾部 9 def append_text_file(src_file): 10 f=open(src_file,'a+') 11 f.seek(0) 12 contents=f.readlines() 13 print(contents) 14 # 本身最后一行没有换行符,先移动到文件尾部增加一个换行符 15 f.seek(2) 16 f.write('\n') 17 # 再次移动到文件的尾部 18 f.seek(2) 19 f.writelines(contents) 20 f.close()

1 ''' 2 使用with关键字: 3 with关键字对资源进行访问的场合,会确保不管在使用过程中是否发生异常,都会执行必要的“清理”的操作,释放资源,比如文件使用后自动关闭等等 4 当文件使用结束后,不需要显式的调用f.close()关闭文件。 5 ''' 6 def with_append_text_file(src_file): 7 with open(src_file,'a+') as f: 8 f.seek(0) 9 contents=f.readlines() 10 print(contents) 11 # 本身最后一行没有换行符,先移动到文件尾部增加一个换行符 12 f.seek(2) 13 f.write('\n') 14 # 再次移动到文件的尾部 15 f.seek(2) 16 f.writelines(contents)
Python网络编程
通过socket实现网络通信

1 import socket 2 ''' 3 服务端在收到消息后,也把消息原样返回给client 4 ''' 5 # 1. 新建socket 6 server = socket.socket() 7 # 2. 绑定IP和端口(其中127.0.0.1为本机回环IP) 8 server.bind(('127.0.0.1', 8999)) 9 # 3. 监听连接 10 server.listen(5) 11 # 4. 接受连接(返回一个新的socket和一个address:ip和端口号) 12 s, addr = server.accept() 13 print('connect addr:{}'.format(addr)) 14 # 5. 接收客户端的内容,并原样返回给客户端 15 while True: 16 content =s.recv(1024) 17 if str(content,encoding='utf-8')=='end': 18 break 19 if len(content)!=0: 20 print('客户端发送给我的内容:{}'.format(str(content,encoding='utf-8'))) 21 s.send(content) 22 s.close()

1 import socket 2 ''' 3 client.py可以循环接收用户输入并发送给服务端 4 ''' 5 # 1. 新建socket 6 client = socket.socket() 7 # 2. 连接服务端(注意,IP和端口要和服务端一致) 8 client.connect(('127.0.0.1', 8999)) 9 # 3. 发送内容,注意发送的是字节字符串。 10 while True: 11 content=input('>>>') 12 client.send(bytes(content, encoding='utf-8')) 13 # 当向服务端发送end字符串时,表示我要断开与服务端的连接 14 if content=='end': 15 break 16 recvStr=str(client.recv(1024),encoding='utf-8') 17 print(f'服务端返回给我的内容:{recvStr}') 18 client.close()
通过http实现网络通信

1 ''' 2 Python提供了相关的库urllib,通过urllib包里面的request,可以向其他HTTP服务器发起请求 3 ''' 4 from urllib import request 5 6 response=request.urlopen('http://baidu.com') 7 # 打印出响应头信息 8 print('响应头信息如下:') 9 for k,v in response.getheaders(): 10 print(f'{k}:{v}') 11 # 打印出响应状态码 12 print(f'响应状态码:{response.status}')

1 ''' 2 使用第三方库requests 3 ''' 4 import requests 5 6 response=requests.request(method='GET',url='https://www.imooc.com/') 7 print('响应头信息如下:') 8 print(response.headers) 9 print(f'响应状态码:{response.status_code}') 10 print('响应内容如下:') 11 content = str(response.content, encoding='utf-8') 12 print(content) 13 print('响应内容中链接含有www的内容:') 14 content_list = content.split('\n') 15 for line in content_list: 16 if 'www' in line: 17 print(line.strip())
Python函数式编程

1 import math 2 3 ''' 4 Python把函数作为参数 5 ''' 6 def add(x,y,f): 7 return f(x)+f(y) 8 print(add(4,25,math.sqrt))

1 ''' 2 map()函数: 3 map()是 Python 内置的高阶函数,它接收一个函数 f 和一个 list,并通过把函数 f依次作用在list的每个元素上 4 map()的使用方法:map(f,list) 5 map()函数会返回一个迭代器,可以依次迭代得到原来list的元素被函数f处理后的结果。 6 7 请利用map()函数,把一个list(包含若干不规范的英文名字)变成一个包含规范英文名字的list: 8 输入:['alice', 'BOB', 'CanDY'] 9 输出:['Alice', 'Bob', 'Candy'] 10 ''' 11 # 将一个字符串的首字符变成大写,其它字符变成小写 12 def f(str): 13 return str[0].upper() + str[1:].lower() 14 15 str_list=['alice', 'BOB', 'CanDY'] 16 print([item for item in map(f,str_list)])

1 ''' 2 reduce()函数: 3 reduce()函数接收的参数和 map() 类似,一个函数 f,一个list,但行为和 map()不同,reduce()传入的函数 f 必须接收两个参数,reduce()对list的每个元素反复调用函数f,并返回最终结果值 4 在python3中,reduce()函数被收录到functools包内,需要引入functools才可以使用 5 reduce()还可以接收第3个可选参数,作为计算的初始值 6 7 Python内置了求和函数sum(),但没有求积的函数,请利用recude()来求积 8 输入:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 9 输出:13579的结果 10 ''' 11 from functools import reduce 12 def f(x,y): 13 return x*y 14 list=[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 15 print(reduce(f,list))

1 ''' 2 filter()函数是 Python 内置的另一个有用的高阶函数 3 filter()函数接收一个函数 f 和一个list,这个函数 f 的作用是对每个元素进行判断,返回 True或 False, 4 filter()根据判断结果自动过滤掉不符合条件的元素,并返回一个迭代器,可以迭代出所有符合条件的元素。 5 6 请利用filter()过滤出1~100中平方根是整数的数,即结果应该是:1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100。 7 ''' 8 import math 9 def sqrt_is_int(x): 10 return int(math.sqrt(x))**2==x 11 print([item for item in filter(sqrt_is_int,range(1,101))])

1 ''' 2 sorted()函数: 3 是Python内置的函数 4 sorted()接受key参数,用来指定排序的字段,key的值是一个函数,接受待排序列表的元素作为参数,并返回对应需要排序的字段 5 如果需要倒序,指定reverse参数即可 6 7 对字符串排序时,有时候忽略大小写排序更符合习惯。请利用sorted()高阶函数,实现忽略大小写排序的算法。 8 输入:['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'] 9 输出:['about', 'bob', 'Credit', 'Zoo'] 10 ''' 11 # 方法1 12 def func1(): 13 s = ['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'] 14 print(sorted(s,key=lambda w:w.lower())) 15 16 # 方法2 17 def f(str): 18 return str.lower() 19 20 def func2(): 21 s = ['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'] 22 print(sorted(s, key=f)) 23 24 func1() 25 func2()

1 ''' 2 Python返回函数 3 请编写一个函数calc_prod(list_),它接收一个list,返回一个函数,返回函数可以计算参数的乘积。 4 ''' 5 def calc_prod(list_): 6 def product(): 7 res=1 8 for item in list_: 9 res=res*item 10 return res 11 return product 12 13 product=calc_prod([1,2,3,4]) 14 print(product())

1 ''' 2 Python的闭包 3 像这种内层函数引用了外层函数的变量(参数也算变量),然后返回内层函数的情况,称为闭包(Closure) 4 返回函数不要引用任何循环变量,或者后续会发生变化的变量 5 ''' 6 def calc_sum(list_): 7 def lazy_sum(): 8 return sum(list_) 9 return lazy_sum 10 ''' 11 请写count()函数,让它正确返回能计算1x1、2x2、3x3的函数 12 ''' 13 def count(x,y): 14 def f(): 15 return x*y 16 return f 17 18 for i in range(1,4): 19 f=count(i,i) 20 print(f())

1 ''' 2 Python的匿名函数 3 定义方式:使用lambda定义,例如lambda x: x * x,冒号前面的x表示匿名函数的参数,后面的是一个表达式 4 匿名函数有个限制,就是只能有一个表达式,不写return,返回值就是该表达式的结果 5 6 请利用sorted()高阶函数和lambda匿名函数,实现忽略大小写排序的算法。 7 输入:['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'] 8 输出:['about', 'bob', 'Credit', 'Zoo'] 9 ''' 10 print(sorted(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'],key=lambda str:str.lower()))

1 ''' 2 Python的装饰器decorator 3 本质上就是一个高阶函数,它接收一个函数作为参数,然后,返回一个新函数。 4 请编写一个@performance,它可以打印出函数调用的时间。 5 ''' 6 import time 7 8 #不带参数的装饰器performance 9 def performance(f): 10 def print_time(*args, **kwargs): 11 start=time.time() 12 print('call ' + f.__name__ + '()') 13 r=f(*args, **kwargs) 14 end=time.time() 15 print(f'函数{f.__name__}()执行的时间为:{end-start}') 16 return r 17 return print_time 18 19 #使用装饰器performance 20 @performance 21 def my_task(): 22 for i in range(1,100001): 23 print(i) 24 25 #函数调用开始 26 my_task()

1 ''' 2 带参数的装饰器:打印函数名称 3 ''' 4 def log(prefix): 5 def log_decorator(f): 6 def wrapper(*args, **kw): 7 print('[{}] {}()...'.format(prefix, f.__name__)) 8 return f(*args, **kw) 9 10 return wrapper 11 12 return log_decorator 13 14 # 使用log装饰器 15 @log('DEBUG') 16 def test(): 17 pass 18 # 函数调用 19 test() 20 21 # 另一个带参数的装饰器 22 import time 23 24 def performance(unit): 25 def perf_decorator(f): 26 def fn(*args, **kw): 27 t1 = time.time() 28 r = f(*args, **kw) 29 t2 = time.time() 30 t = (t2 - t1) * 1000 if unit == 'ms' else (t2 - t1) 31 print('call {}() in {}{}'.format(f.__name__, t, unit)) 32 return r 33 34 return fn 35 36 return perf_decorator 37 38 39 @performance('ms') 40 def my_task(): 41 print([i for i in range(1,100001)]) 42 43 #函数调用 44 my_task()

1 ''' 2 Python的偏函数 3 偏函数指的就是“创建一个调用另外一个部分参数或变量已经预置的函数”的函数的用法 4 functools.partial就是帮助我们创建一个偏函数的 5 6 在前面,我们在sorted这个高阶函数中传入自定义排序函数就可以实现忽略大小写排序。 7 请用functools.partial把这个复杂调用变成一个简单的函数 8 ''' 9 import functools 10 11 sorted_ignore_case = functools.partial(sorted, key=lambda item: item.lower()) 12 print(sorted_ignore_case(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit']))






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现