Mybatis学习笔记
Mybatis学习笔记04
一、复杂查询语句
1.多对一查询
案例:每个学生都对应一个老师(实体类的属性中有一个是对象)
我们需要查询所有学生的信息以及对应的老师的信息
方式1:按照我们编写的SQL语句输出来的结果嵌套处理
<select id="getStudent2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.id tid,t.name tname
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
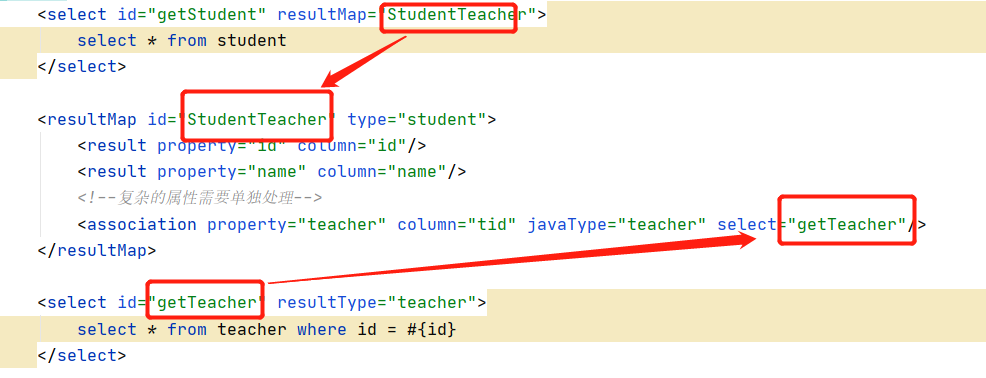
方式二:先查询所有学生信息再根据查询出来的tid查询对应的老师
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from student
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<!--复杂的属性需要单独处理-->
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="teacher">
select * from teacher where id = #{id}
</select>
2.一对多查询
案例:一个老师有多个学生(实体类的属性中有一个是集合)
我们需要查询这个老师的信息以及该老师对应的学生的信息

方式1:按照我们编写的SQL语句输出来的结果嵌套处理
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tid
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<!--复杂属性单独处理 对象:association 集合:collection-->
<!--javaType="" 指定的属性类型 而集合中泛型信息使用ofType获取-->
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
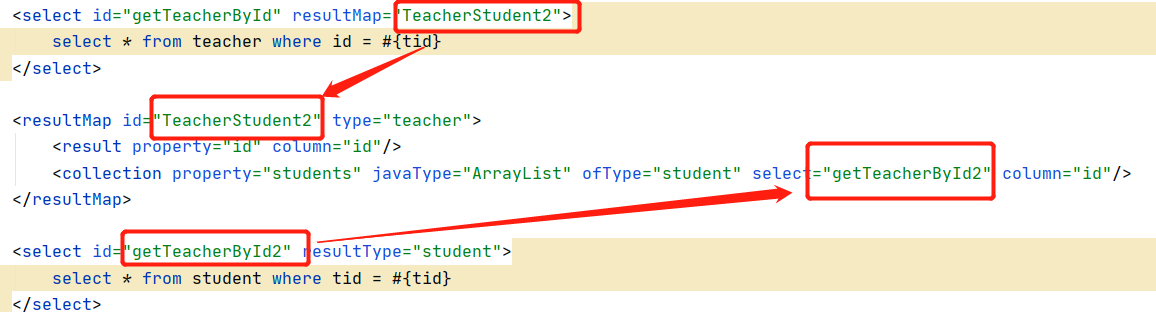
方式二:子查询
<select id="getTeacherById" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">
select * from teacher where id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="teacher">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="student" select="getTeacherById2" column="id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacherById2" resultType="student">
select * from student where tid = #{tid}
</select>
3.小结
多对一:关联association
一对多:集合collection
javaType:用来指定实体类中属性的类型
ofType:用来指定映射到List或集合中的pojo类型泛型中的约束条件
二、动态SQL
根据不同的条件生成不同的且可以实现不同功能的SQL语句
只在Mapper.xml使用
常用标签有if choose(when otherwise) trim(where set) foreach
select * from blog
<where>
<if test="title != null">
and title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<select id="queryBlogChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
and views = #{views}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map">
update blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title},
</if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<select id="queryBlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from blog
<where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or">
id = #{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
在测试类中传入不同参数可以得到不同的结果
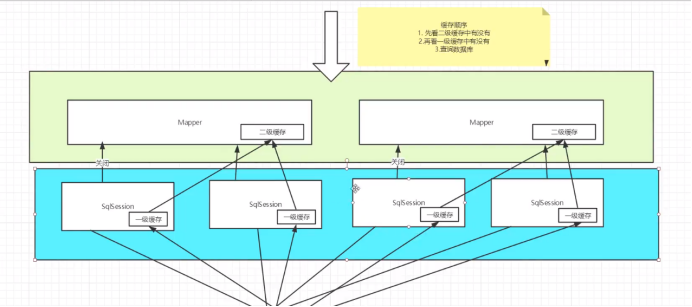
三、Mybatis缓存
经常查询并且不经常改变的数据可以使用缓存
1.一级缓存:
sqlSession级别,一级缓存是默认开启的
2.二级缓存
二级缓存也称为全局缓存,作用域大于一级缓存
二级缓存是基于namespace级别的缓存一个名称空间对应了一个二级缓存
工作机制:
①一个会话查询一条数据这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中
②如果当前会话关闭这个会话对应的一级缓存就没了,但是我们想要的是,会话关闭了一级缓存中的数据被保存到二级缓存中
③新的会话查询信息就可以从二级缓存中获取内容
④不同的mapper查出的数据回放在自己对应的缓存map中
步骤:
开启二级缓存


3.总结

注意点:记得将实体类序列化
4.缓存原理