15天玩转redis —— 第十篇 对快照模式的深入分析
我们知道redis是带有持久化这个能力了,那到底持久化成到哪里,持久化成啥样呢???这篇我们一起来寻求答案。
一:快照模式
或许在用Redis之初的时候,就听说过redis有两种持久化模式,第一种是SNAPSHOTTING模式,还是一种是AOF模式,而且在实战场景下用的最多的
莫过于SNAPSHOTTING模式,这个不需要反驳吧,而且你可能还知道,使用SNAPSHOTTING模式,需要在redis.conf中设置配置参数,比如下面这样:
# Save the DB on disk: # # save <seconds> <changes> # # Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given # number of write operations against the DB occurred. # # In the example below the behaviour will be to save: # after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed # after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed # after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed # # Note: you can disable saving completely by commenting out all "save" lines. # # It is also possible to remove all the previously configured save # points by adding a save directive with a single empty string argument # like in the following example: # # save "" save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000
上面三组命令也是非常好理解的,就是说900指的是“秒数”,1指的是“change次数”,接下来如果在“900s“内有1次更改,那么就执行save保存,同样
的道理,如果300s内有10次change,60s内有1w次change,那么也会执行save操作,就这么简单,看了我刚才说了这么几句话,是不是有种直觉在
告诉你,有两个问题是不是要澄清一下:
1. 上面这个操作应该是redis自身进行的同步操作,请问是否可以手工执行save呢?
当然可以进行手工操作,redis提供了两个操作命令:save,bgsave,这两个命令都会强制将数据刷新到硬盘中,如下图:
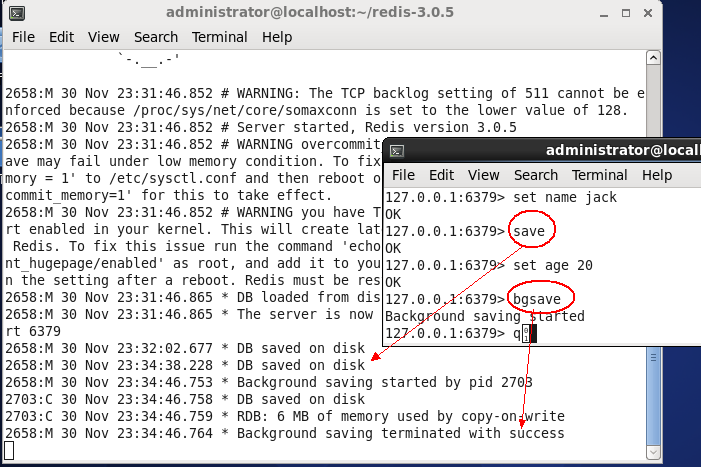
2. 看上面的图,貌似bgsave是开启单独线程的,请问是吗?
确实如你所说,bgsave是开启次线程进行数据刷新的,不信的话我们来看看代码,它的代码是在rdb.c源文件中,如下:
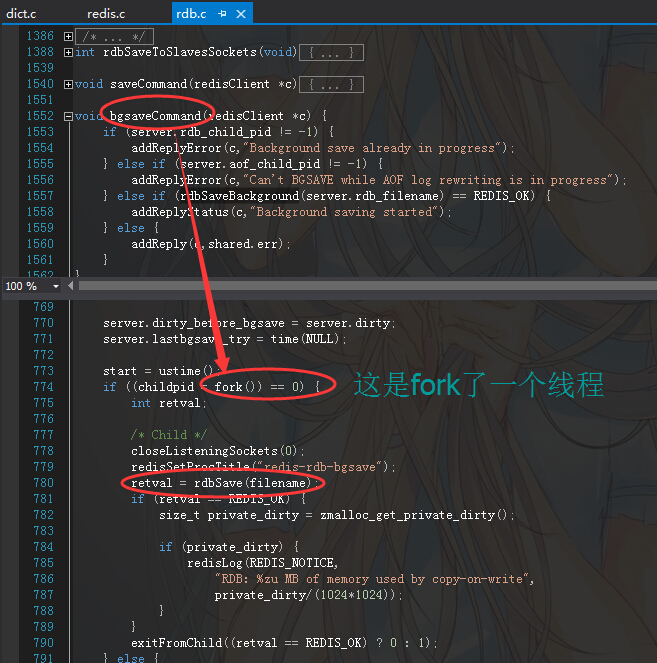
从上面的代码中,有没有看到一个重点,那就是fork方法,它就是一些牛人口中说的什么fork出一个线程,今天你也算终于看到了,其实redis并不是单纯
的单线程服务,至少fork告诉我们,它在一些场景下也是会开启工作线程的,然后可以看到代码会在工作线程中执行同步的bgsave操作,就这么简单。
3. 能简单说下saveparams参数在redis源码中的逻辑吗?
可以的,其实在redis中有一个周期性函数,叫做serverCron,它会周期性启动,大概会做七件事情,如redis注释所说:
/* This is our timer interrupt, called server.hz times per second. * Here is where we do a number of things that need to be done asynchronously. * For instance: * * - Active expired keys collection (it is also performed in a lazy way on * lookup). * - Software watchdog. * - Update some statistic. * - Incremental rehashing of the DBs hash tables. * - Triggering BGSAVE / AOF rewrite, and handling of terminated children. * - Clients timeout of different kinds. * - Replication reconnection. * - Many more... * * Everything directly called here will be called server.hz times per second, * so in order to throttle execution of things we want to do less frequently * a macro is used: run_with_period(milliseconds) { .... } */ int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
上面的红色字体就是做了我们所关心的save操作,看过方法的注释,接下来我们来找一下具体逻辑。
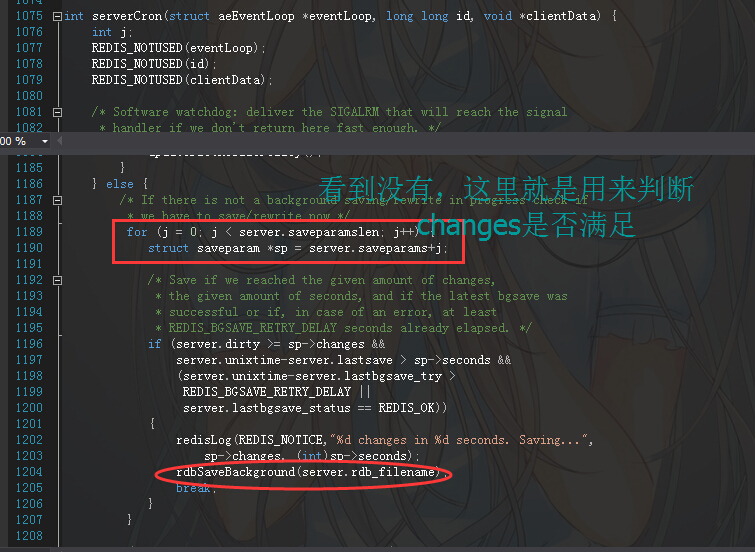
从上面这段代码逻辑,你应该可以发现以下几点:
<1>. saveparams参数是在server对象下面,而server对象正好是redisServer类型,如下图:
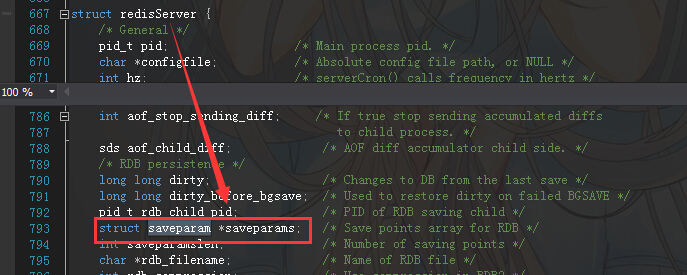
从上面图中 *saveparams 的注释上来看,你应该知道*saveparams是saveparam类型的数组,那现在是不是有强烈的好奇心想看一下saveparam
类型是怎么定义的的呢??? 如下图:

可以看到,saveparam参数里面有两个参数,seconds就是保存秒数,changes就是改变量,而这二个参数就对应着我们配置文件中的900 0 这样的
配置节,想起来的没有哈~~~
<2> 然后我们通过if发现,如果终满足,就会最终调用rdbSaveBackground来持久化我们的rdb文件,简单吧。。。
好了,大概就这样了,希望对你有帮助。


