20230430 28. 访问者模式 - 男女对比
介绍
访问者模式(Visitor),表示一个作用于某对象结构中的各元素的操作。它使你可以在不改变各元素的类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作
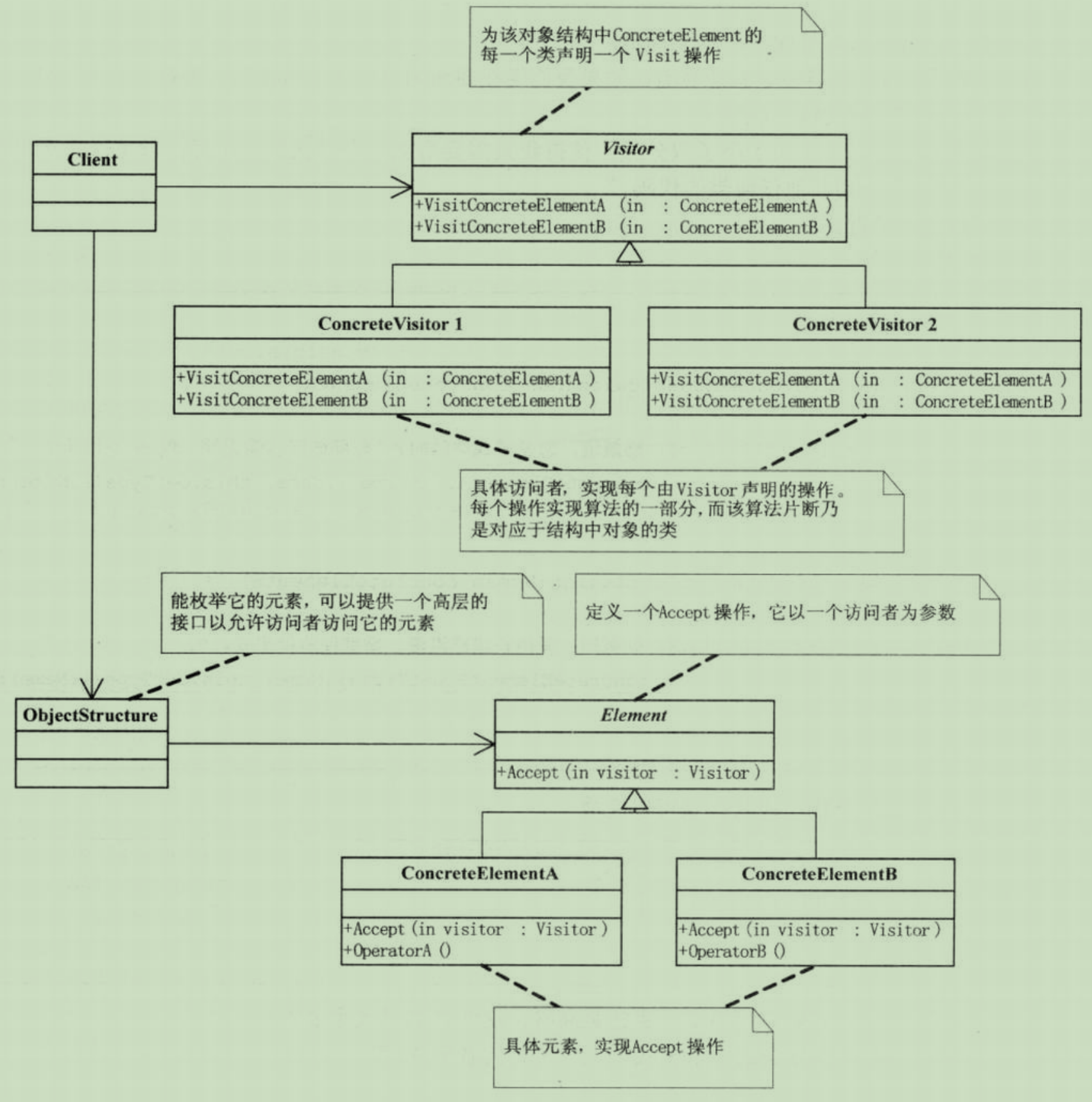
访问者模式适用于数据结构相对稳定的系统
访问者模式把数据结构和作用于结构上的操作之间的耦合解脱开,使得操作集合可以相对自由地演化。
访问者模式的目的是要把处理从数据结构分离出来。很多系统可以按照算法和数据结构分开,如果系统有比较稳定的数据结构,又有易于变化的算法的话,使用访问者模式就是比较合适的,因为访问者模式使得算法操作的増加变得容易。
访问者模式的优点就是增加新的操作很容易,因为增加新的操作就意味着增加一个新的访问者。访问者模式将有关的行为集中到一个访问者对象中。
访问者的缺点其实也就是使增加新的数据结构变得困难了。
访问者模式的能力和复杂性是把双刃剑,只有当你真正需要它的时候,才应该考虑使用它
代码示例
Element
public abstract class Person {
public abstract void accept(Action action);
}
Element 实现类
public class Man extends Person {
@Override
public void accept(Action action) {
action.getManConclusion(this);
}
}
public class Woman extends Person {
@Override
public void accept(Action action) {
action.getWomanConclusion(this);
}
}
Visitor
public abstract class Action {
public abstract void getManConclusion(Man man);
public abstract void getWomanConclusion(Woman woman);
}
Visitor 实现类
public class Success extends Action {
@Override
public void getManConclusion(Man man) {
System.out.println(man.getClass().getSimpleName()
+ " " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "时,背后多半有一个伟大的女人。");
}
@Override
public void getWomanConclusion(Woman woman) {
System.out.println(woman.getClass().getSimpleName()
+ " " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "时,背后多半有一个伟大的女人。");
}
}
public class Failing extends Action {
@Override
public void getManConclusion(Man man) {
System.out.println(man.getClass().getSimpleName()
+ " " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "时,闷头喝酒,谁也不用劝。");
}
@Override
public void getWomanConclusion(Woman woman) {
System.out.println(woman.getClass().getSimpleName()
+ " " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "时,眼泪汪汪,谁也劝不了。");
}
}
对象结构
public class ObjectStructure {
private List<Person> elements = new ArrayList<>();
public void add(Person person) {
elements.add(person);
}
public void remove(Person person) {
elements.remove(person);
}
public void accept(Action action) {
for (Person person : elements) {
person.accept(action);
}
}
}
客户端
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectStructure objectStructure = new ObjectStructure();
objectStructure.add(new Man());
objectStructure.add(new Woman());
objectStructure.accept(new Success());
System.out.println("*************************");
objectStructure.accept(new Failing());
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具
2018-06-22 JavaScript中的arguments详解