20200930 9. TCP 粘包和拆包 及解决方案
TCP 粘包和拆包 及解决方案
TCP 粘包和拆包基本介绍
- TCP是面向连接的,面向流的,提供高可靠性服务。收发两端(客户端和服务器端)都要有一一成对的 socket,因此,发送端为了将多个发给接收端的包,更有效的发给对方,使用了优化方法(Nagle算法),将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据,合并成一个大的数据块,然后进行封包。这样做虽然提高了效率,但是接收端就难于分辨出完整的数据包了,因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的
- 由于TCP无消息保护边界, 需要在接收端处理消息边界问题,也就是我们所说的粘包、拆包问题, 看一张图
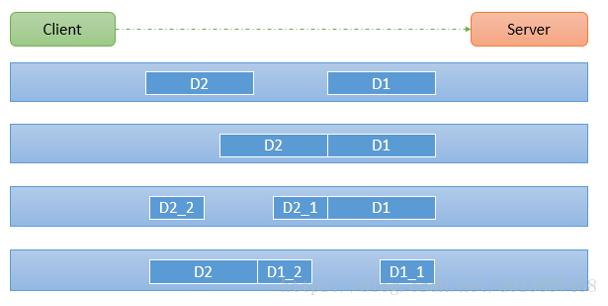
假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包D1和D2给服务端,由于服务端一次读取到字节数是不确定的,故可能存在以下四种情况:
-
服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,没有粘包和拆包
-
服务端一次接受到了两个数据包,D1和D2粘合在一起,称之为TCP粘包
-
服务端分两次读取到了数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1包和D2包的部分内容,第二次读取到了D2包的剩余内容,这称之为TCP拆包
-
服务端分两次读取到了数据包,第一次读取到了D1包的部分内容D1_1,第二次读取到了D1包的剩余部分内容D1_2和完整的D2包。
TCP 粘包和拆包解决方案
- 使用 自定义协议 + 编解码器 来解决
- 关键就是要解决 服务器端每次读取数据长度的问题, 这个问题解决,就不会出现服务器多读或少读数据的问题,从而避免的TCP 粘包、拆包 。
看一个具体的实例:
- 要求客户端发送 5 个 Message 对象, 客户端每次发送一个 Message 对象
- 服务器端每次接收一个Message, 分5次进行解码, 每读取到 一个Message , 会回复一个Message 对象 给客户端.
代码实例
MyServer
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7005).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyServerInitializer
public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder());//解码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder());//编码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
}
MyServerHandler
//处理业务的handler
@Slf4j
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol> {
private int count;
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
//接收到数据,并处理
int len = msg.getLen();
byte[] content = msg.getContent();
log.info("\n\n\n");
log.info("服务器接收到信息如下");
log.info("长度=" + len);
log.info("内容=" + new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
log.info("服务器接收到消息包数量=" + (++this.count));
//回复消息
String responseContent = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
int responseLen = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8").length;
byte[] responseContent2 = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8");
//构建一个协议包
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(responseLen);
messageProtocol.setContent(responseContent2);
ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol);
}
}
MyClient
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new MyClientInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 7005).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyClientInitializer
public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder()); //加入编码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder()); //加入解码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
}
MyClientHandler
@Slf4j
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol> {
private int count;
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//使用客户端发送10条数据 "今天天气冷,吃火锅" 编号
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String mes = "今天天气冷,吃火锅";
byte[] content = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8"));
int length = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")).length;
//创建协议包对象
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(length);
messageProtocol.setContent(content);
ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol);
}
}
// @Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
int len = msg.getLen();
byte[] content = msg.getContent();
log.info("客户端接收到消息如下");
log.info("长度=" + len);
log.info("内容=" + new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
log.info("客户端接收消息数量=" + (++this.count));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
log.info("异常消息=" + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
MessageProtocol
//协议包
public class MessageProtocol {
private int len; //关键
private byte[] content;
public int getLen() {
return len;
}
public void setLen(int len) {
this.len = len;
}
public byte[] getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(byte[] content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
MyMessageEncoder
@Slf4j
public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<MessageProtocol> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
log.info("MyMessageEncoder encode 方法被调用");
out.writeInt(msg.getLen());
out.writeBytes(msg.getContent());
}
}
MyMessageDecoder
@Slf4j
public class MyMessageDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
log.info("MyMessageDecoder decode 被调用");
//需要将得到二进制字节码-> MessageProtocol 数据包(对象)
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] content = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(content);
//封装成 MessageProtocol 对象,放入 out, 传递下一个handler业务处理
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(length);
messageProtocol.setContent(content);
out.add(messageProtocol);
}
}




