异步编程之委托
前言:
项目中由于大量的数据读取操作,导致每次加载界面都需要长时间等待,因此决定使用异步来获取数据,实现更好的用户体验。
趁此机会,也好好的补充一下自己在异步编程方面的知识!
先从委托开始说起!
委托的定义:
委托是一个类,它定义了方法的类型,使得可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递。
委托的特点:
委托类似于 C++ 函数指针,但它们是类型安全的。
委托允许将方法作为参数进行传递。
委托可用于定义回调方法。
方法不必与委托签名完全匹配。
委托的声明:
(1). delegate
delegate我们常用到的一种声明
Delegate至少0个参数,至多32个参数,可以无返回值,也可以指定返回值类型。
例:public delegate int MethodtDelegate(int x, int y);表示有两个参数,并返回int型。
(2). Action
Action是无返回值的泛型委托。
Action 表示无参,无返回值的委托
Action<int,string> 表示有传入参数int,string无返回值的委托
Action<int,string,bool> 表示有传入参数int,string,bool无返回值的委托
Action<int,int,int,int> 表示有传入4个int型参数,无返回值的委托
Action至少0个参数,至多16个参数,无返回值。
例:
public void Test<T>(Action<T> action,T p)
{
action(p);
}
(3). Func
Func是有返回值的泛型委托
Func<int> 表示无参,返回值为int的委托
Func<object,string,int> 表示传入参数为object, string 返回值为int的委托
Func<object,string,int> 表示传入参数为object, string 返回值为int的委托
Func<T1,T2,,T3,int> 表示传入参数为T1,T2,,T3(泛型)返回值为int的委托
Func至少0个参数,至多16个参数,根据返回值泛型返回。必须有返回值,不可void
例:
public int Test<T1,T2>(Func<T1,T2,int>func,T1 a,T2 b)
{
return func(a, b);
}
(4) .predicate
predicate 是返回bool型的泛型委托
predicate<int> 表示传入参数为int 返回bool的委托
Predicate有且只有一个参数,返回值固定为bool
例:public delegate bool Predicate<T> (T obj)
委托的使用:
(1).Delegate的使用
public delegate int MethodDelegate(int x, int y);
private static MethodDelegate method;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
method = new MethodDelegate(Add);
Console.WriteLine(method(10,20));
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
结果:
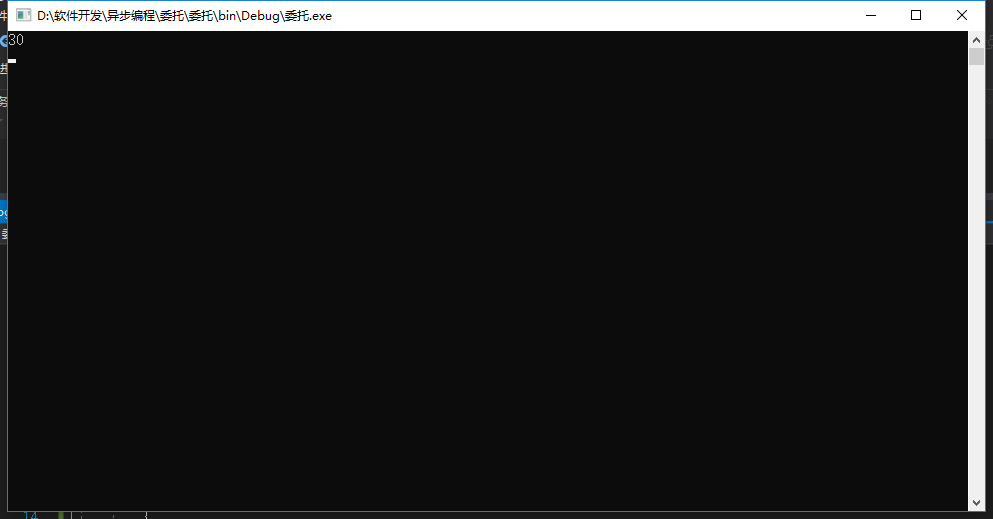
个人想法:委托就像一个统一的类,可以把所有参数和返回值相同的方法统一起来进行调用。
(2).Action的使用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test<string>(Action,"Hello World!");
Test<int>(Action, 1000);
Test<string>(p => { Console.WriteLine("{0}", p); }, "Hello World");//使用Lambda表达式定义委托
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void Test<T>(Action<T> action, T p)
{
action(p);
}
private static void Action(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
private static void Action(int s)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
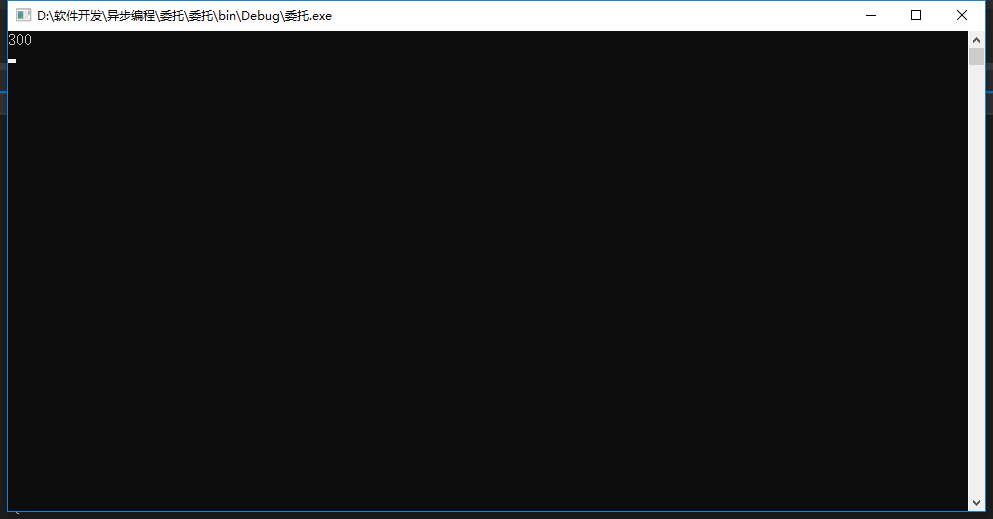
结果:

(3).Func的使用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Test<int,int>(Fun,100,200));
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static int Test<T1, T2>(Func<T1, T2, int> func, T1 a, T2 b)
{
return func(a, b);
}
private static int Fun(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
结果:
(4). predicate的使用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point point1 = new Point() { X = 100, Y = 200 };
Point point2 = new Point() { X = 1000, Y = 200 };
Console.WriteLine(Test<Point>(ProductGT10,point1));
Console.WriteLine(Test<Point>(ProductGT10, point2));
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static bool Test<T>(Predicate<T> predicate, T p)
{
return predicate(p);
}
private static bool ProductGT10(Point p)
{
if (p.X * p.Y > 100000)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
结果:
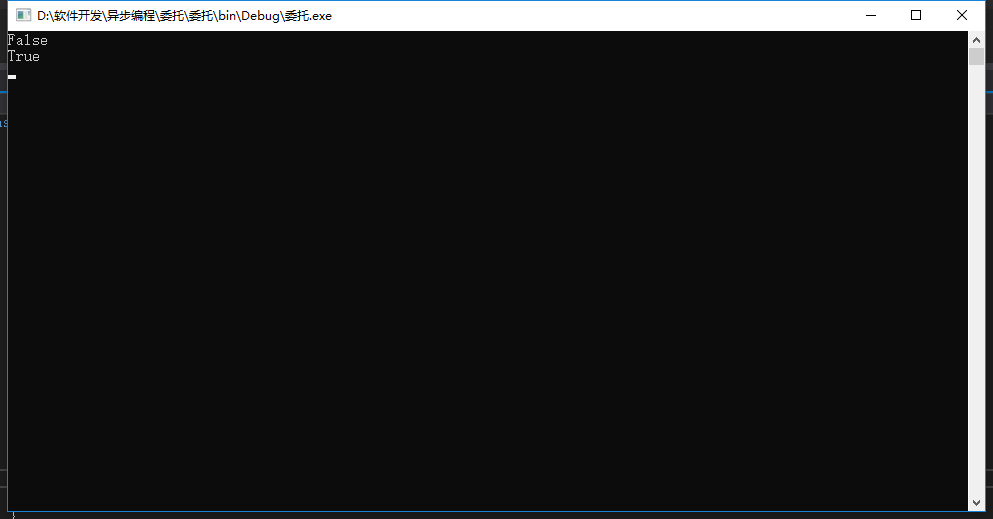
参考链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/akwwl/p/3232679.html



