《Vue.js设计与实现》 第八章 挂载与更新
8.1 挂载子节点和元素的属性
1. 挂载子节点
// 子节点为数组
const vnode = {
type: "div",
children: [
{
type: "p",
children: "hello",
},
],
};
// 支持多个子节点的挂载方法
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
const el = createElement(vnode.type);
if (typeof vnode.children === "string") {
setElementText(el, vnode.children);
} else if (Array.isArray(vnode.children)) {
// 如果 children 是数组,则遍历每一个子节点,并调用 patch 函数挂载它们
vnode.children.forEach((child) => {
patch(null, child, el);
});
}
insert(el, container);
}
2. 设置元素的属性
// 有属性的节点
const vnode = {
type: "div",
// 使用 props 描述一个元素的属性
props: {
id: "foo",
},
children: [
{
type: "p",
children: "hello",
},
],
};
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
const el = createElement(vnode.type);
// 省略 children 的处理
// 如果 vnode.props 存在才处理它
if (vnode.props) {
// 遍历 vnode.props
for (const key in vnode.props) {
// 1. 调用 setAttribute 将属性设置到元素上
el.setAttribute(key, vnode.props[key]);
// 2. 或者 通过 DOM 对象直接设置
// el[key] = vnode.props[key];
}
}
insert(el, container);
}
ps: 实际上,无论是使用 setAttribute 函数,还是直接操作 DOM 对象,都存在缺陷。
8.2 HTML Attributes 与 DOM Properties
HTML Attributes 指的就是定义在 HTML 标签上的属性,例如:
<input id="my-input" type="text" value="foo" />
DOM Properties 指的就是 DOM 对象下的属性,例如:
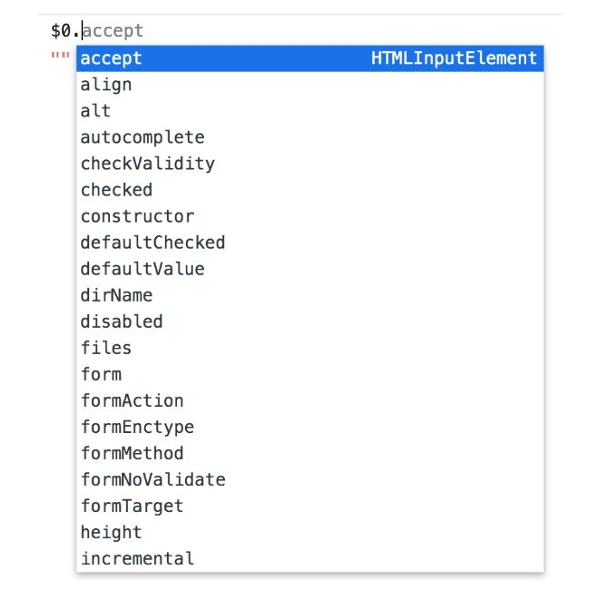
很多 HTML Attributes 在DOM 对象上有与之同名的 DOM Properties,例如
id="my-input" 对应 el.id,
type="text" 对应 el.type,
value="foo" 对应el.value 等。
但 DOM Properties 与 HTML Attributes 的名字不总是一模一样的,例如:
<div class="foo"></div>
class="foo" 对应的 DOM Properties 则是 el.className
并不是所有 HTML Attributes 都有与之对应的 DOM Properties,例如:
<div aria-valuenow="75"></div>
aria-* 类的 HTML Attributes 就没有与之对应的 DOM Properties。
类似地,也不是所有 DOM Properties 都有与之对应的 HTML Attributes,例如:
可以用 el.textContent 来设置元素的文本内容,
但并没有与之对应的 HTML Attributes 来完成同样的工作。
HTML Attributes 与 DOM Properties 具有相同名称(例如 id)的属性,看作直接映射
HTML Attributes 的作用是设置与之对应的 DOM Properties 的初始值。
<input value="foo" />
// 当用户修改输入框文本内容为 bar 时
el.getAttribute('value') // 仍然是 'foo'
el.value // 'bar'
el.defaultValue // 'foo'
这说明一个 HTML Attributes 可能关联多个 DOM Properties
8.3 正确地设置元素属性
- 有些元素属性需要特殊处理,才能正确设置。
例如1:
<button disabled>Button</button>
像这种,只指定属性没有指定具体值的模板。
例如2:
<form id="form1"></form>
<input form="form1" />
像这种,DOM Properties 是 el.form,但el.form 是只读的,因此我们只能够通过 setAttribute 函数来设置它。
- 平台无关考虑。el.xxx 、setAttribute 等方法需要抽象成 patchProps() 方法传入。
8.4 class 的处理
设置class样式的时候需要特殊处理,因为Vue.js对class进行了增强,除了支持string,还支持:
- 对象
- 数组
在底层的实现上,需要做正常化处理,正常化的过程是有性能代价的。
8.5 卸载操作
<!-- 新 vnode 为 null,意味着卸载之前渲染的内容 -->
renderer.render(null, document.querySelector('#app'))
卸载操作不能简单的移除节点内容,还需要:
- 容器的内容可能是由某个或多个组件渲染的,当卸载操作发生时,应该正确地调用这些组件的生命周期函数。
- 有的元素存在自定义指令,我们应该在卸载操作发生时正确执行对应的指令钩子函数。
- 找到对应真实DOM从父元素中移除。因为innerHTML 清空容器元素,不会移除绑定在 DOM 元素上的事件处理函数。
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
// 让 vnode.el 引用真实 DOM 元素
const el = (vnode.el = createElement(vnode.type));
if (typeof vnode.children === "string") {
setElementText(el, vnode.children);
} else if (Array.isArray(vnode.children)) {
vnode.children.forEach((child) => {
patch(null, child, el);
});
}
if (vnode.props) {
for (const key in vnode.props) {
patchProps(el, key, null, vnode.props[key]);
}
}
insert(el, container);
}
function render(vnode, container) {
if (vnode) {
patch(container._vnode, vnode, container);
} else {
if (container._vnode) {
// 根据 vnode 获取要卸载的真实 DOM 元素
const el = container._vnode.el;
// 获取 el 的父元素
const parent = el.parentNode;
// 调用 removeChild 移除元素
if (parent) parent.removeChild(el);
}
}
container._vnode = vnode;
}
重构,由于卸载操作是比较常见操作,所以我们应该将它封装到 unmount 函数中
function unmount(vnode) {
const parent = vnode.el.parentNode;
if (parent) {
parent.removeChild(vnode.el);
}
}
function render(vnode, container) {
if (vnode) {
patch(container._vnode, vnode, container);
} else {
if (container._vnode) {
// 调用 unmount 函数卸载 vnode
unmount(container._vnode);
}
}
container._vnode = vnode;
}
将卸载操作封装到 unmount 中,还能够带来两点额外的好处。
- 在 unmount 函数内,我们有机会调用绑定在 DOM 元素上的指令钩子函数,例如beforeUnmount、unmounted 等。
- 当 unmount 函数执行时,我们有机会检测虚拟节点 vnode 的类型。如果该虚拟节点描述的是组件,则我们有机会调用组件相关的生命周期函数。
8.6 区分 vnode 的类型
在patch时,需要进行vnode类型的判断,如果是DOM执行DOM的更新逻辑,如果是组件执行组件更新逻辑
function patch(n1, n2, container) {
// 如果有旧节点,并且新旧节点类型不同,则卸载旧节点
if (n1 && n1.type !== n2.type) {
unmount(n1);
n1 = null;
}
// 代码运行到这里,证明 n1 和 n2 所描述的内容相同
const { type } = n2;
// 如果 n2.type 的值是字符串类型,则它描述的是普通标签元素
if (typeof type === "string") {
if (!n1) {
mountElement(n2, container);
} else {
patchElement(n1, n2);
}
} else if (typeof type === "object") {
// 如果 n2.type 的值的类型是对象,则它描述的是组件
} else if (type === "xxx") {
// 处理其他类型的 vnode
}
}
8.7 事件的处理
1. 如何在虚拟DOM中描述事件
事件可以视作一种特殊的属性,因此我们可以约定,在 vnode.props 对象中,凡是以字符串 on 开头的属性都视作事件。
const vnode = {
type: "p",
props: {
// 使用 onXxx 描述事件
onClick: () => {
alert("clicked");
},
},
children: "text",
};
2. 如何添加事件到DOM
在 patchProps 中调用 addEventListener 函数来绑定事件即可
patchProps(el, key, prevValue, nextValue) {
// 匹配以 on 开头的属性,视其为事件
if (/^on/.test(key)) {
// 根据属性名称得到对应的事件名称,例如 onClick ---> click
const name = key.slice(2).toLowerCase()
// 绑定事件,nextValue 为事件处理函数
el.addEventListener(name, nextValue)
} else if (key === 'class') {
// 省略部分代码
} else if (shouldSetAsProps(el, key, nextValue)) {
// 省略部分代码
} else {
// 省略部分代码
}
}
3. 如何更新事件
- 一般实现方式
先移除之前的事件处理函数,再将新的事件处理函数绑定到DOM
<代码略>
- 性能更优的实现方式
在绑定事件时,我们可以绑定一个伪造的事件处理函数 invoker,然后把真正的事件处理函数设置为 invoker.value属性的值。
这样当更新事件的时候,我们将不再需要调用removeEventListener 函数来移除上一次绑定的事件,只需要更新invoker.value 的值即可
<代码略>
- 考虑绑定多个时间处理程序问题
8.8 事件冒泡与更新时机问题
需要解决的问题:
更新早于事件冒泡,带来的逻辑上还未绑定事件的父元素,触发事件问题。
解决方式:
当一个事件触发时,目标元素上还没有绑定相关的事件处理函数,我们可以根据这个特点来解决问题:屏蔽所有绑定时间晚于事件触发时间的事件处理函数的执行。
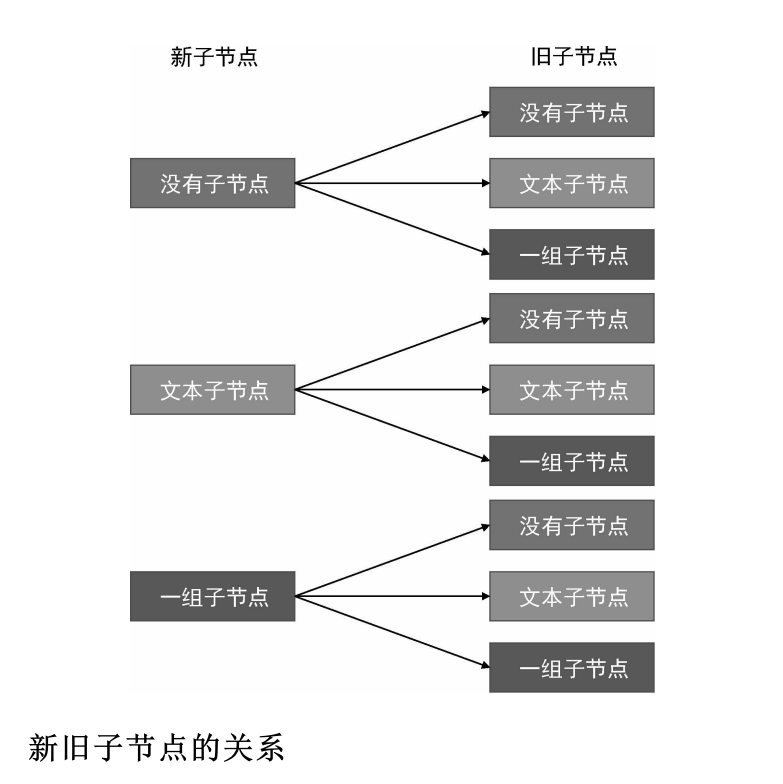
8.9 更新子节点
子节点的类型是规范化的,才有利于我们编写更新逻辑。因此,在具体讨论如何更新子节点之前,我们有必要先规范化vnode.children。
1. 子节点的类型(归类为以下三种)
<!-- 没有子节点 -->
<div></div>
<!-- 文本子节点 -->
<div>Some Text</div>
<!-- 单个或多个子节点 -->
<div>
<p/>
<p/>
</div>
2. 更新时的节点情况
既然一个vnode 的子节点可能有三种情况,那么当渲染器执行更新时,新旧子节点都分别是三种情况之一。所以,我们可以总结出更新子节点时全部九种可能。
3. 代码实现
落实到代码层面并不需要完全覆盖这九种可能。
function patchElement(n1, n2) {
const el = n2.el = n1.el
const oldProps = n1.props
const newProps = n2.props
// 第一步:更新 props
for (const key in newProps) {
if (newProps[key] !== oldProps[key]) {
patchProps(el, key, oldProps[key], newProps[key])
}
}
for (const key in oldProps) {
if (!(key in newProps)) {
patchProps(el, key, oldProps[key], null)
}
}
// 第二步:更新 children
patchChildren(n1, n2, el)
}
// 更新子节点
function patchChildren(n1, n2, container) {
// 判断新子节点的类型是否是文本节点
if (typeof n2.children === 'string') {
// 旧子节点的类型有三种可能:没有子节点、文本子节点以及一组子节点
// 只有当旧子节点为一组子节点时,才需要逐个卸载,其他情况下什么都不需要做
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach((c) => unmount(c))
}
// 最后将新的文本节点内容设置给容器元素
setElementText(container, n2.children)
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
// 说明新子节点是一组子节点
// 判断旧子节点是否也是一组子节点
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
// 代码运行到这里,则说明新旧子节点都是一组子节点,这里涉及核心的 Diff 算法
} else {
// 此时:
// 旧子节点要么是文本子节点,要么不存在
// 但无论哪种情况,我们都只需要将容器清空,然后将新的一组子节点逐个挂载
setElementText(container, '')
n2.children.forEach(c => patch(null, c, container))
}
} else {
// 代码运行到这里,说明新子节点不存在
// 旧子节点是一组子节点,只需逐个卸载即可
if (Array.isArray(n1.children)) {
n1.children.forEach(c => unmount(c))
} else if (typeof n1.children === 'string') {
// 旧子节点是文本子节点,清空内容即可
setElementText(container, '')
}
// 如果也没有旧子节点,那么什么都不需要做
}
}
8.10 文本节点和注释节点
<div><!-- 注释节点 -->我是文本节点</div>
如何用虚拟节点标识文本节点和注释节点
注释节点与文本节点不同于普通标签节点,它们不具有标签名称,所以我们需要人为创造一些唯一的标识。
// 文本节点的 type 标识
const Text = Symbol()
const newVNode = {
// 描述文本节点
type: Text,
children: '我是文本内容'
}
// 注释节点的 type 标识
const Comment = Symbol()
const newVNode = {
// 描述注释节点
type: Comment,
children: '我是注释内容'
}
文本节点的渲染
// 渲染文本节点
function patch(n1, n2, container) {
if (n1 && n1.type !== n2.type) {
unmount(n1)
n1 = null
}
const { type } = n2
if (typeof type === 'string') {
if (!n1) {
mountElement(n2, container)
} else {
patchElement(n1, n2)
}
} else if (type === Text) { // 如果新 vnode 的类型是 Text,则说明该 vnode 描述的是文本节点
// 如果没有旧节点,则进行挂载
if (!n1) {
// 使用 createTextNode 创建文本节点
const el = n2.el = document.createTextNode(n2.children)
// 将文本节点插入到容器中
insert(el, container)
} else {
// 如果旧 vnode 存在,只需要使用新文本节点的文本内容更新旧文本节点即可
const el = n2.el = n1.el
if (n2.children !== n1.children) {
el.nodeValue = n2.children
}
}
}
}
跨平台支持
patch 函数依赖浏览器平台特有的 API,即 createTextNode 和 el.nodeValue。为了保证渲染器核心的跨平台能力,我们需要将这两个操作 DOM 的 API 封装到渲染器的选项中
// 添加渲染器选项
const renderer = createRenderer({
createElement(tag) {
// 省略部分代码
},
setElementText(el, text) {
// 省略部分代码
},
insert(el, parent, anchor = null) {
// 省略部分代码
},
createText(text) {
return document.createTextNode(text)
},
setText(el, text) {
el.nodeValue = text
},
patchProps(el, key, prevValue, nextValue) {
// 省略部分代码
}
})
// 重写patch方法
function patch(n1, n2, container) {
if (n1 && n1.type !== n2.type) {
unmount(n1)
n1 = null
}
const { type } = n2
if (typeof type === 'string') {
if (!n1) {
mountElement(n2, container)
} else {
patchElement(n1, n2)
}
} else if (type === Text) {
if (!n1) {
// 调用 createText 函数创建文本节点
const el = n2.el = createText(n2.children)
insert(el, container)
} else {
const el = n2.el = n1.el
if (n2.children !== n1.children) {
// 调用 setText 函数更新文本节点的内容
setText(el, n2.children)
}
}
}
}
8.11 Fragment
Fragment(片断)是 Vue.js 3 中新增的一个 vnode 类型。
用于支持多根节点模板
vnode实现代码
const Fragment = Symbol()
const vnode = {
type: Fragment,
children: [
{ type: 'li', children: 'text 1' },
{ type: 'li', children: 'text 2' },
{ type: 'li', children: 'text 3' }
]
}
渲染
Fragment 本身并不会渲染任何内容,渲染器只会渲染 Fragment 的子节点
patch
function patch(n1, n2, container) {
if (n1 && n1.type !== n2.type) {
unmount(n1)
n1 = null
}
const { type } = n2
if (typeof type === 'string') {
// 省略部分代码
} else if (type === Text) {
// 省略部分代码
} else if (type === Fragment) { // 处理 Fragment 类型的 vnode
if (!n1) {
// 如果旧 vnode 不存在,则只需要将 Fragment 的 children 逐个挂载即可
n2.children.forEach(c => patch(null, c, container))
} else {
// 如果旧 vnode 存在,则只需要更新 Fragment 的 children 即可
patchChildren(n1, n2, container)
}
}
}
unmount
当卸载 Fragment 类型的虚拟节点时,由于 Fragment 本身并不会渲染任何真实 DOM,所以只需要遍历它的 children 数组,并将其中的节点逐个卸载即可。
function unmount(vnode) {
// 在卸载时,如果卸载的 vnode 类型为 Fragment,则需要卸载其 children
if (vnode.type === Fragment) {
vnode.children.forEach(c => unmount(c))
return
}
const parent = vnode.el.parentNode
if (parent) {
parent.removeChild(vnode.el)
}
}