Feign踩坑源码分析 -- 请求参数分号变逗号
一.案例
1.1.Post请求:
http://localhost:8250/xx/task/test json格式参数: { "string": "a;b;c;d" }
1.2.controller代码:
@Autowired DataSourceClientService dataSourceClientService; @RequestMapping("/test") @ResponseBody public void test(@RequestBody String string) { System.out.println(string); String result = dataSourceClientService.test(string); System.out.println(result); }
1.3.feign代码:
@FeignClient( value = "zz") public interface DataSourceClientService { @RequestMapping(value = "/dataSource/test",method = RequestMethod.POST,produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") String test(@RequestParam("str") String str); }
1.4服务提供方代码:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public String test(@RequestParam String str) {
System.out.println(str);
String result = "success;";
return result;
}
1.5发起请求后控制台打印结果:
请求方控制台: 用户[null]开始调用web接口:http://localhost:8250/xx/task/test { "string": "a;b;c;d" } 服务提供方控制台: 用户[null]开始调用web接口:http://localhost:8247/zz/dataSource/test { "string": "a,b,c,d" }
二.解决办法
2.1.在请求方对参数进行编码:
string = UriUtils.encode(string, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String test = dataSourceClientService.test(string);
2.2.服务提供方@RequestParam改成@RequestBody;
三.分析
3.1.需求
服务提供方需要的字符串是包含“;”而不是“,”,因为实际传递的是一个JSONObject的字符串,导致JSONUtil.parse转换成对象失败,导致业务失败;
3.2请求方法参数@RequestParam而传参不加密
3.2.1 请求方源码探究
通过一步步debug代码调试,发现调用 dataSourceClientService.test(string) 是jdk动态代理,调用链接到
feign.ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler#invoke
-->feign.SynchronousMethodHandler#invoke
-->feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#create
-->feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#resolve
-->feign.RequestTemplate#resolve(java.util.Map<java.lang.String,?>)
-->feign.template.QueryTemplate#expand
-->feign.template.QueryTemplate#queryString
static final String COLLECTION_DELIMITER = ";"; private String queryString(String name, String values) { if (this.pure) { return name; } /* covert the comma separated values into a value query string */ List<String> resolved = Arrays.stream(values.split(COLLECTION_DELIMITER)) .filter(Objects::nonNull) .filter(s -> !UNDEF.equalsIgnoreCase(s)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); if (!resolved.isEmpty()) { return this.collectionFormat.join(name, resolved, this.getCharset()).toString(); } /* nothing to return, all values are unresolved */ return null; }

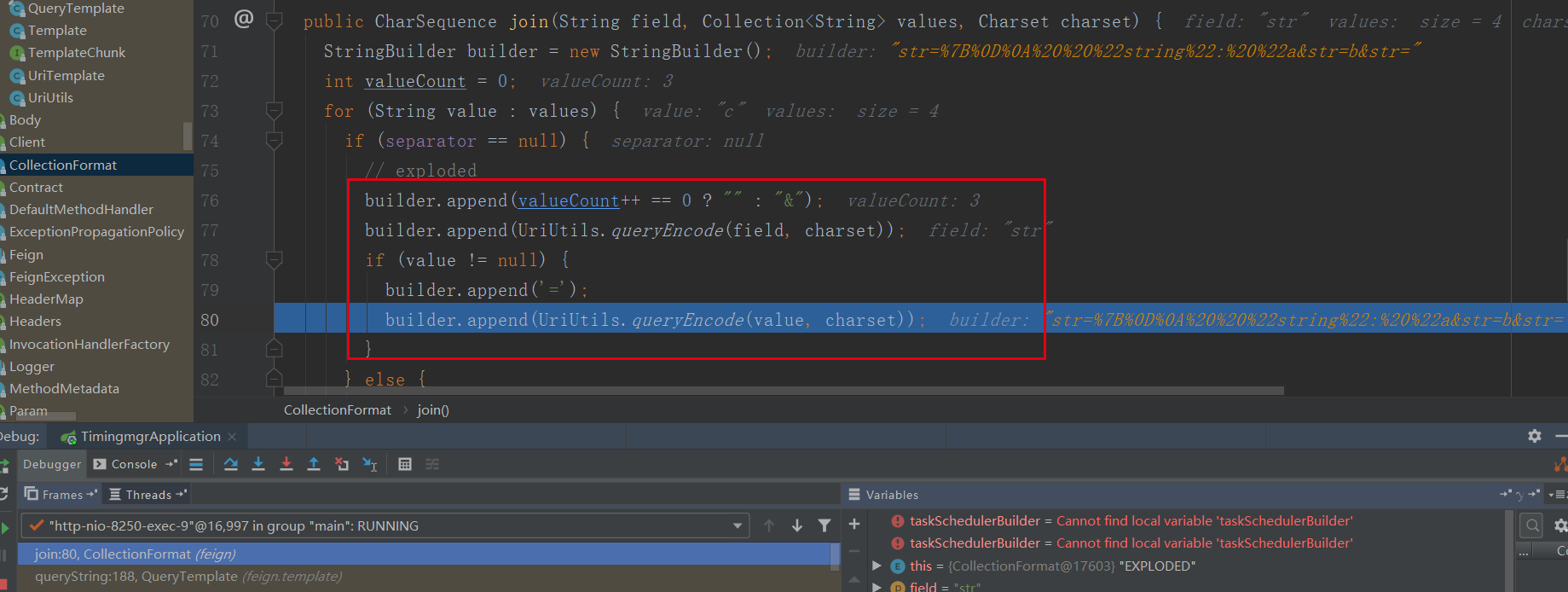
从上面可以看到,一个参数字符串“a;b;c;d”被分割处理成了一个数组,然后重新组合成字符串(Collection)传递给服务提供方,服务提供方接收参数是一个string字符串,会用逗号给拼接成字符串。
也就是说,feign预设了使用者如果是用传参带了分号过来的,会认为你传的是Collection,而不是String。
3.2.1 服务提供方源码探究
下面是服务提供方接收的参数详情:
org.springframework.web.method.annotation.AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument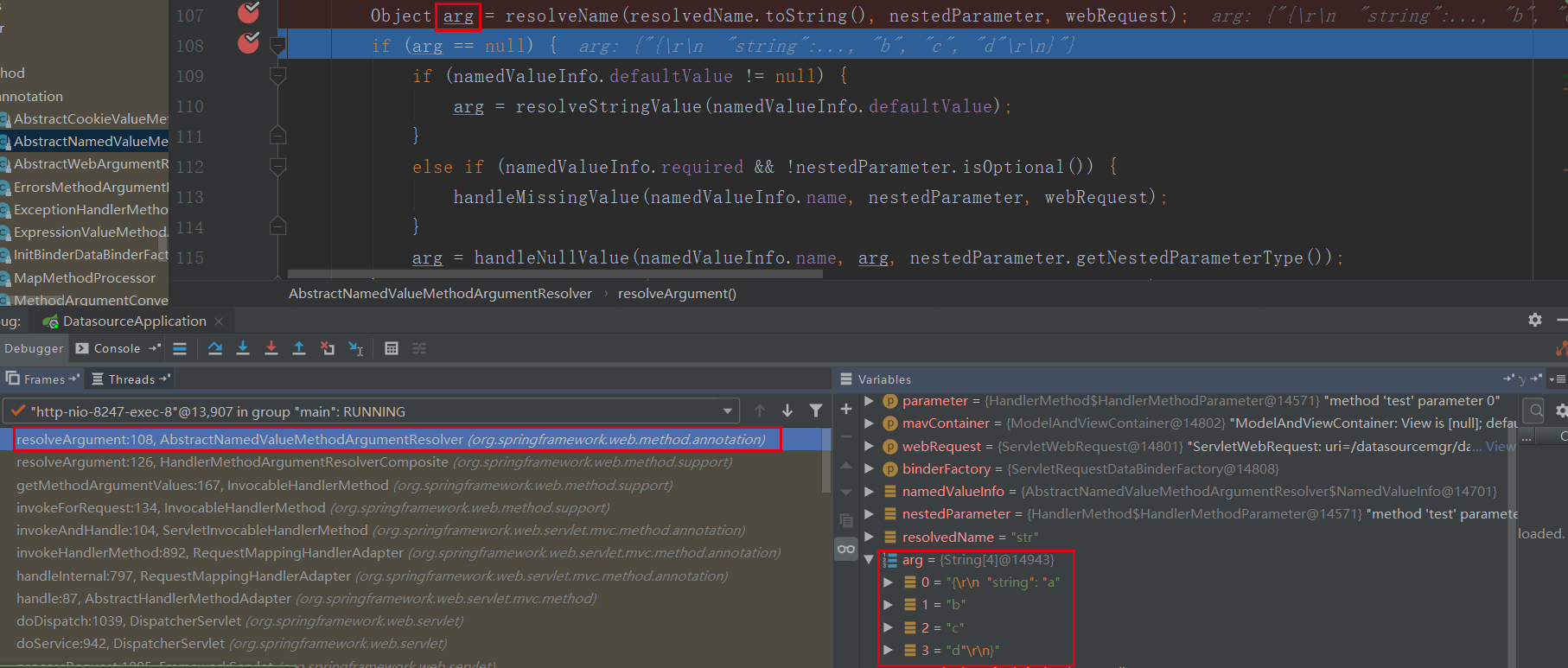
从上面可以看出,请求解析出来是一个字符串数组,在
org.springframework.core.convert.support.CollectionToStringConverter#convert 中用逗号拼接起来:
3.2.1 调用服务提供方方法前参数编码:
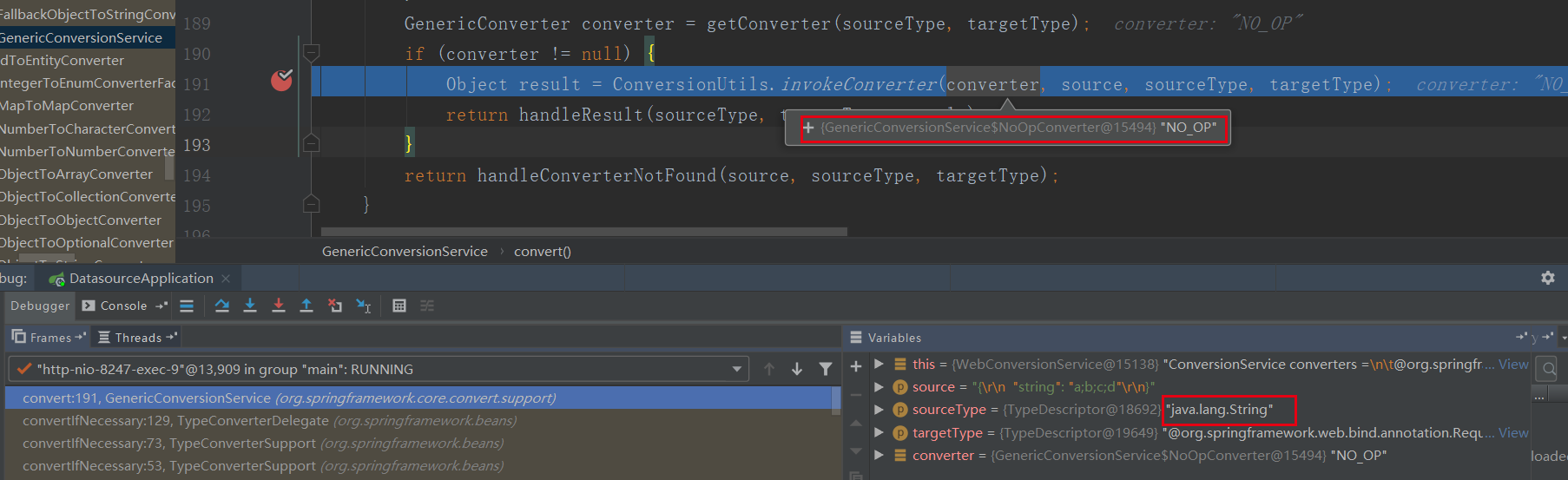
当没有编码前,org.springframework.core.convert.support.GenericConversionService#convert(java.lang.Object, org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor, org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor) 调用链进入的是org.springframework.core.convert.support.CollectionToStringConverter#convert 中用逗号拼接起来,因为参数类型是字符串数组
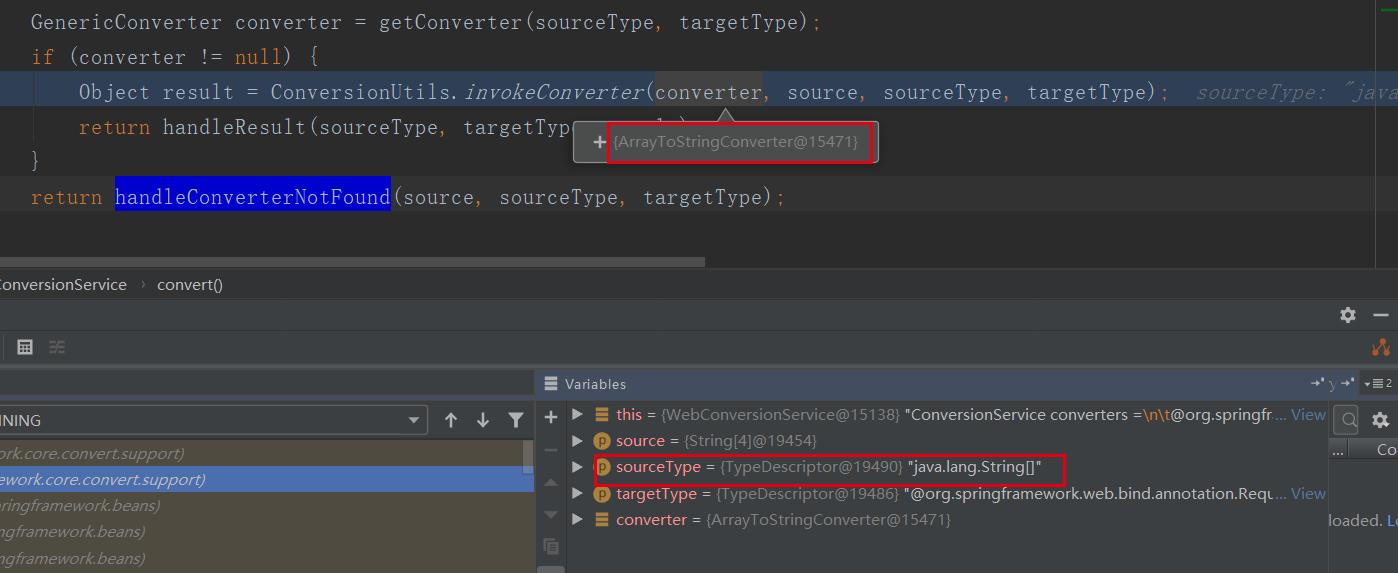
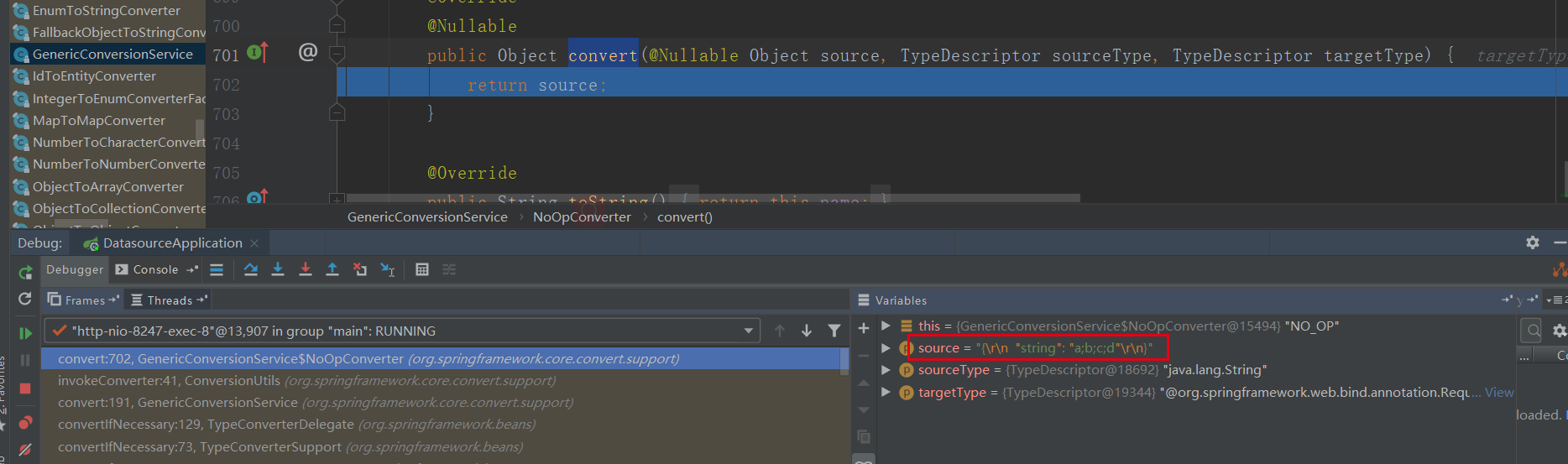
当编码后,进入的是org.springframework.core.convert.support.GenericConversionService.NoOpConverter#convert,直接返回字符串:
参数值的获取在org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver#resolveName 中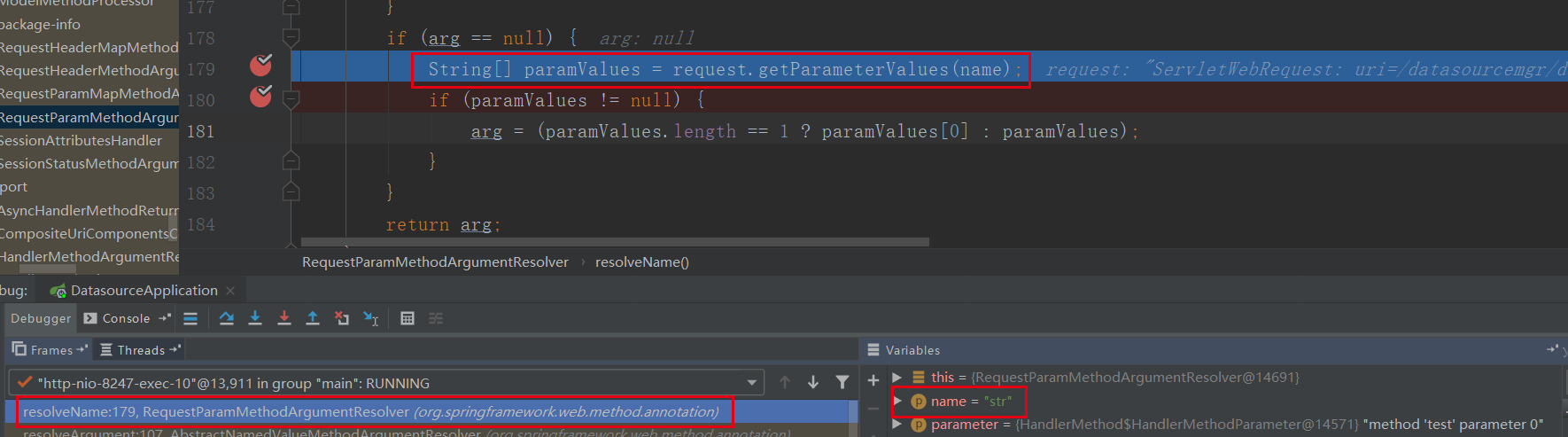
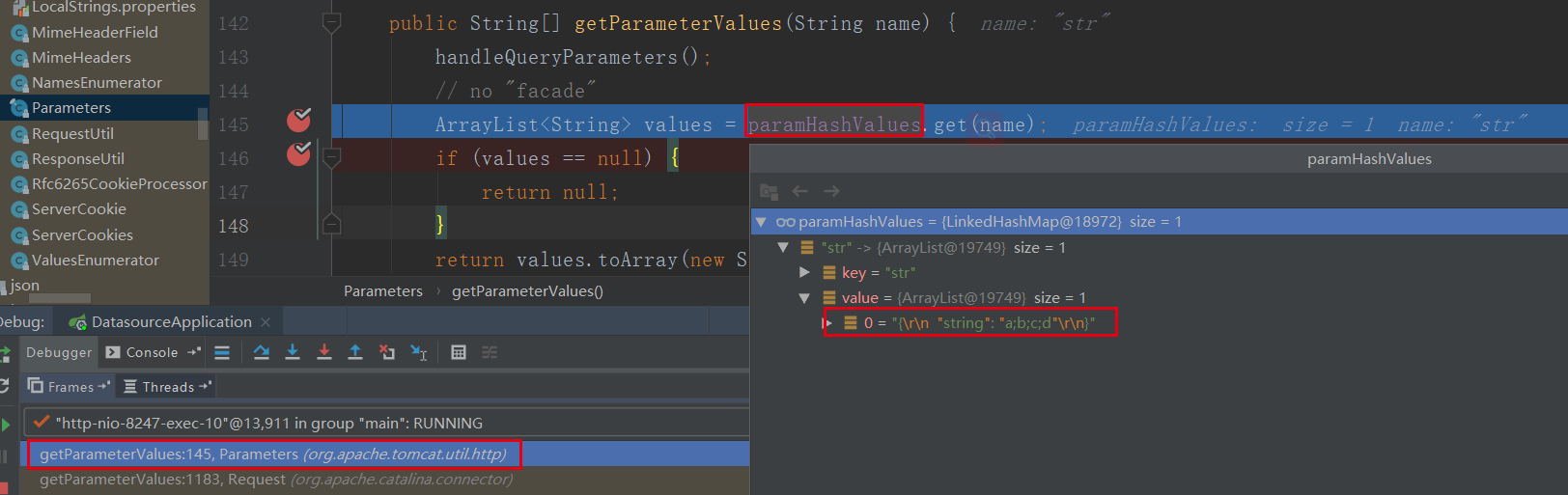
参数的解码方法在org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#processParameters(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset)中进入
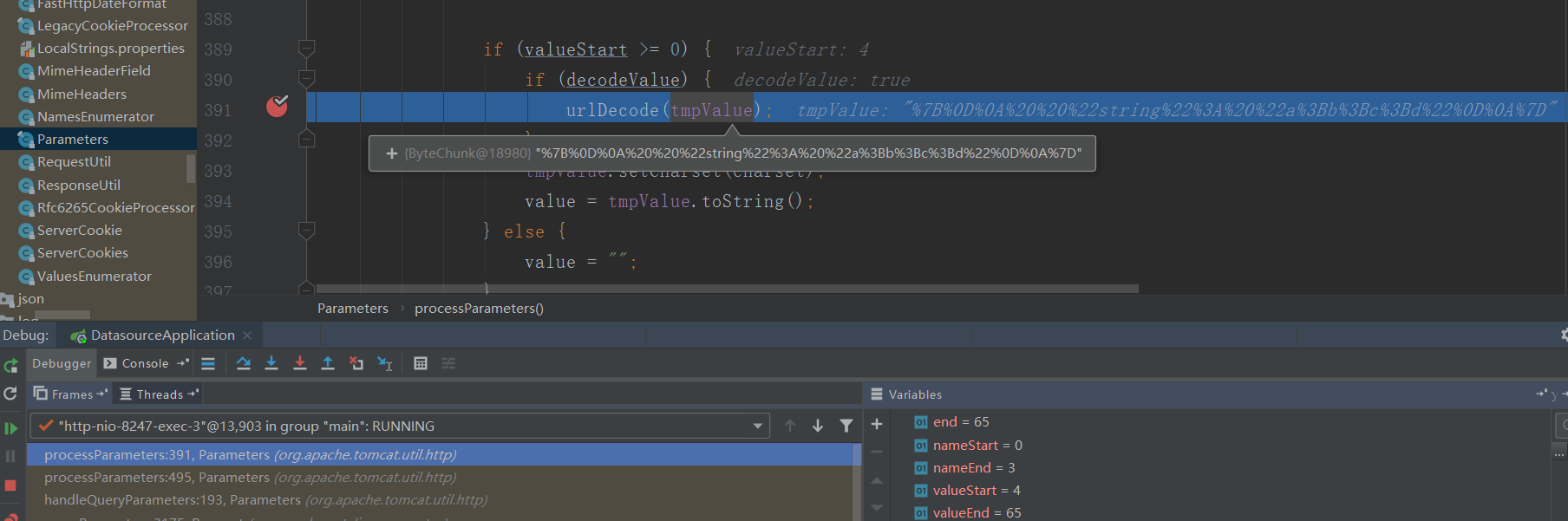
在org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#urlDecode进行解码
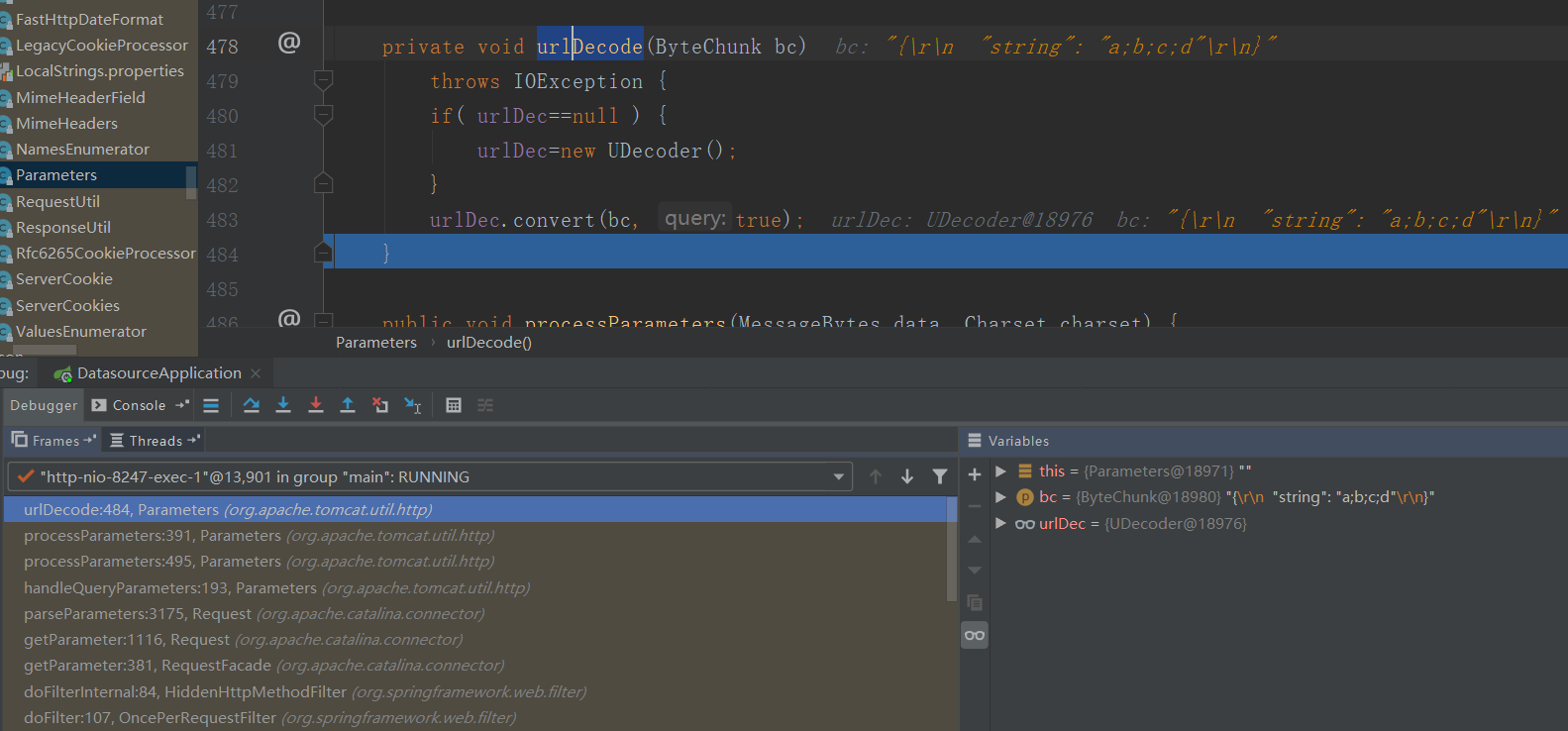
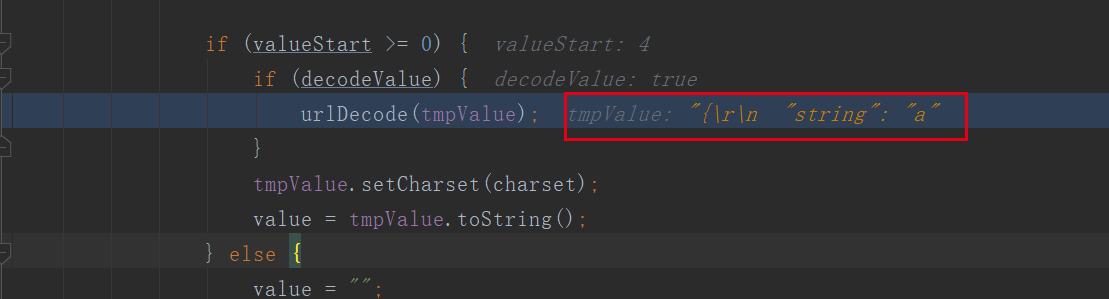
前面的是参数进行编码后解码,因为编码成一个字符串,所以解码的也是字符串,当没有进行编码,传递的会认为是一个collection,所以会遍历解码:
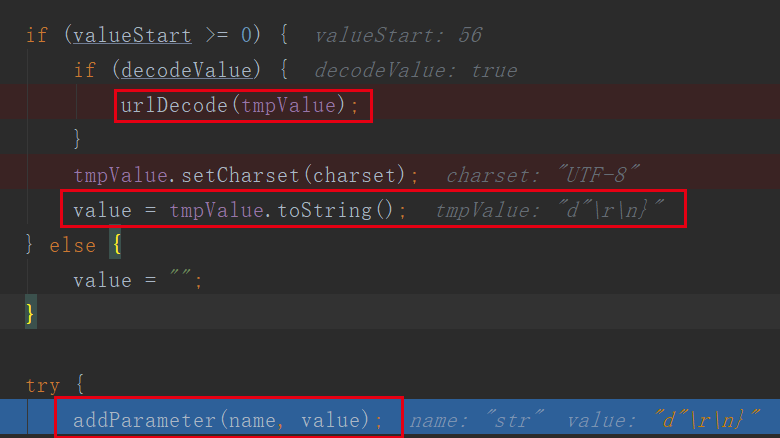
然后加入到数组中:
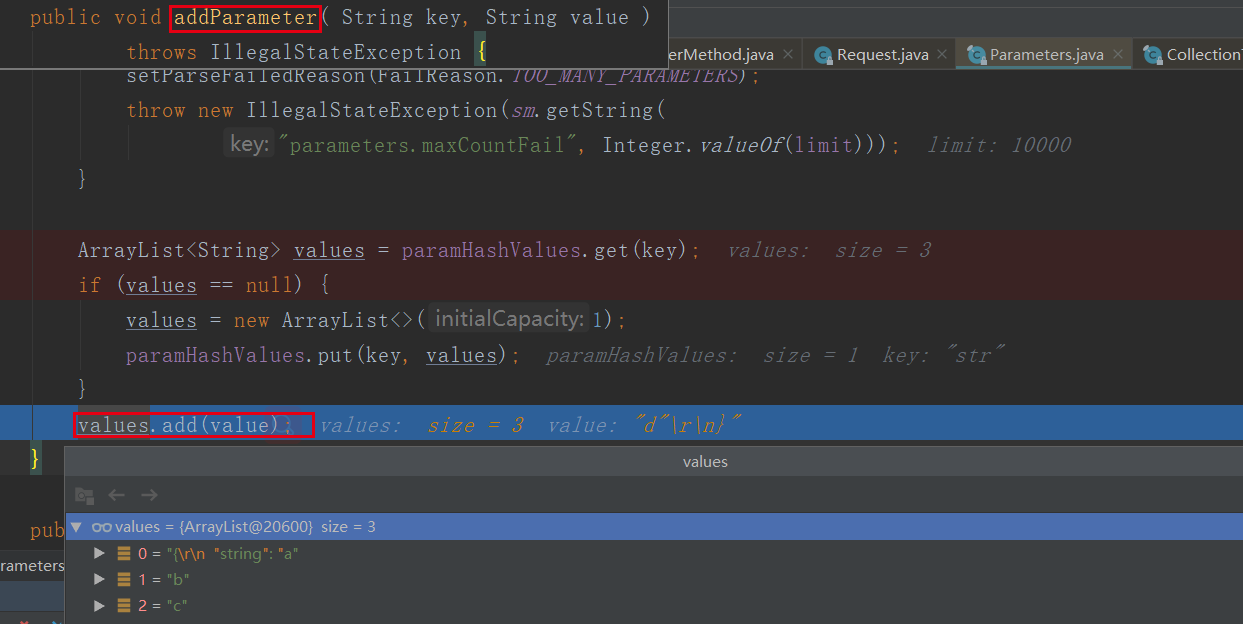
3.3请求方法参数改成@RequestBody
3.3.1服务提供方
当请求方法是@RequestBody时,获取参数在org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor#resolveArgument:

直接从httprequest请求中获取body参数值:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.AbstractMessageConverterMethodArgumentResolver#readWithMessageConverters(org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage, org.springframework.core.MethodParameter, java.lang.reflect.Type)
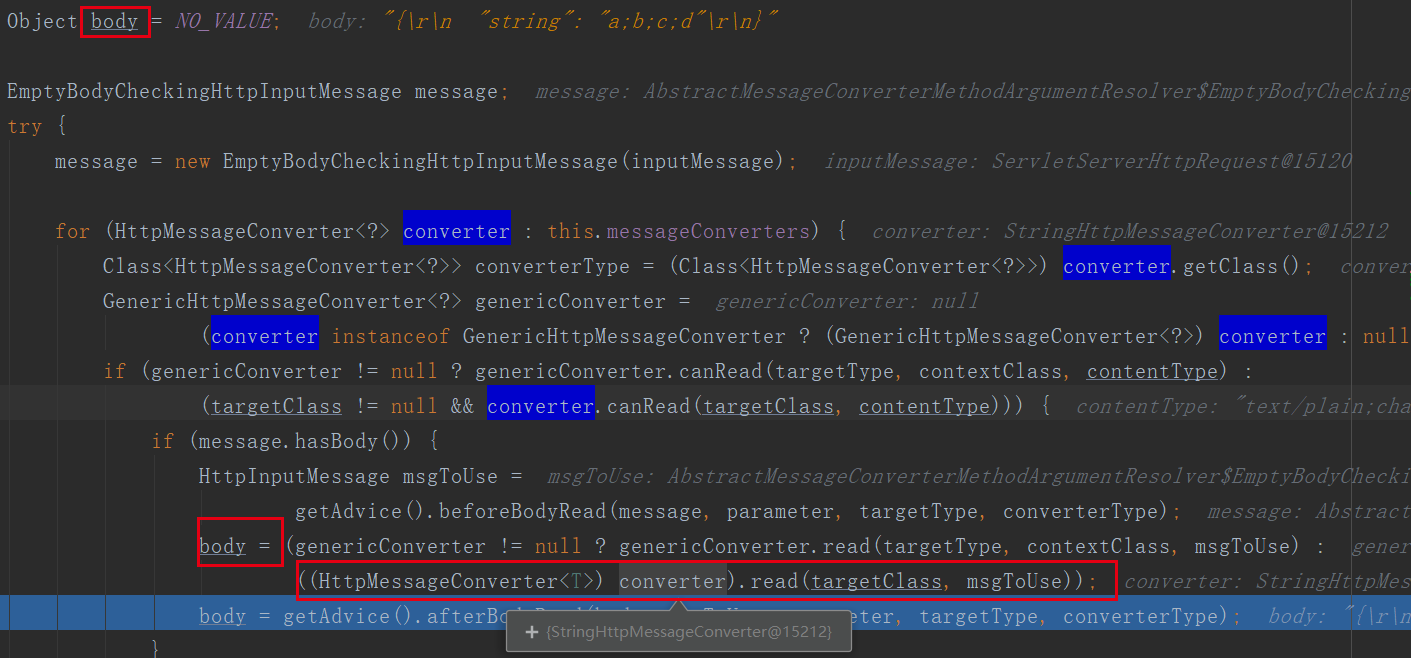
3.3.2请求方
参数直接封装到body中:
feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#create
--> feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildEncodedTemplateFromArgs#resolve
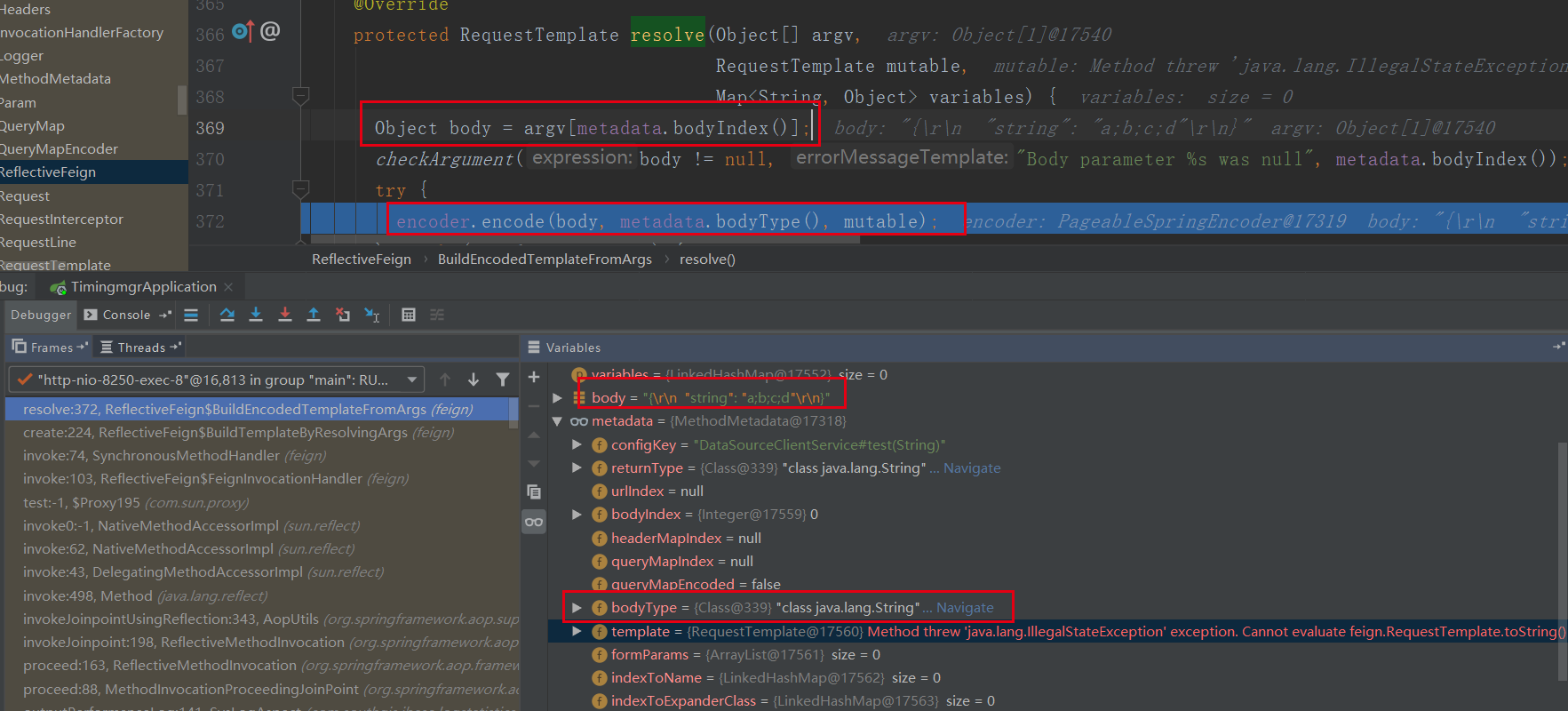
对比3.2.1流程会发现,body不会进行字符串的切割,当然拉,也跟参数的请求类型不一致有关,一个是query,一个是body,下面是3.2.1流程
-->feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#create
-->feign.ReflectiveFeign.BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs#resolve
-->feign.RequestTemplate#resolve(java.util.Map<java.lang.String,?>)
-->feign.template.QueryTemplate#expand
-->feign.template.QueryTemplate#queryString
四.扩展
4.1.get请求
get请求的参数类型是query,所以走的是3.2.1流程,所以string的传参中包含“;”也会被转换成“,”;
@FeignClient( value = "zz") public interface DataSourceClientService { @RequestMapping(value = "/dataSource/testGet",method = RequestMethod.GET,produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") String testGet(@RequestParam("str") String str); } @RequestMapping(value = "/testGet") @ResponseBody public String testGet(String str) { System.out.println(str); String result = "success"; return result; } 服务提供方控制台输出: 用户[null]开始调用web接口:http://localhost:8247/zz/dataSource/testGet a,b,c,d
ps:当请求参数字符串存在特殊符号比如“+”时,会被转义为空格
http://localhost:8250/xx/task/test2?string=a+b 请求方控制台输出: 用户[null]开始调用web接口:用户[null]开始调用web接口:http://localhost:8250/xx/task/test2 a b
通过debug调试发现当发起请求时在org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod#invokeForRequest中获取参数:

继续调用链:
-->org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite#resolveArgument
-->org.springframework.web.method.annotation.AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver#resolveArgument
-->org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver#resolveName
-->org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletWebRequest#getParameterValues
-->org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade#getParameterValues
-->org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#getParameterValues
-->org.apache.coyote.Request#getParameters
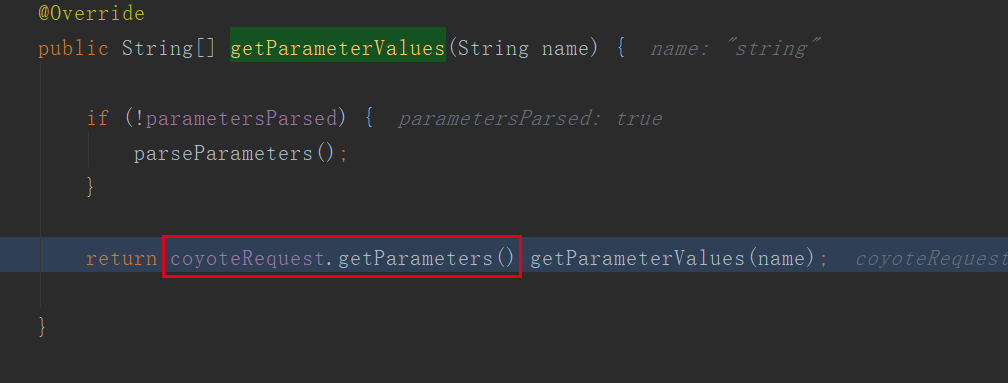

从上面可以得知参数在parameters中,并且特殊符号已经被处理过了,那接下来找下什么时候放进来和怎么被处理的;在org.apache.catalina.connector.Request中看见了parseParameters方法,可以看出是对参数的解析方法,在里面打下断点重新跑下:
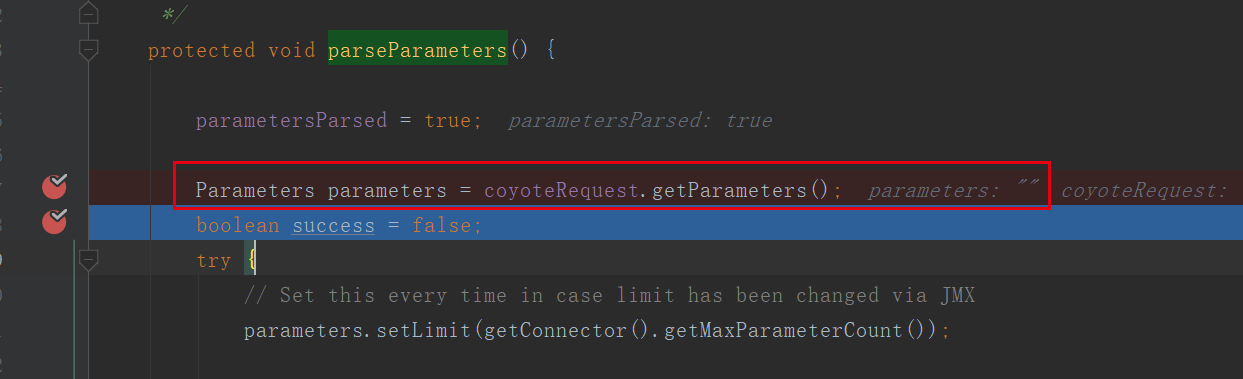
从下面可以看出这里是真正进行参数解析处理的:

org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#handleQueryParameters:
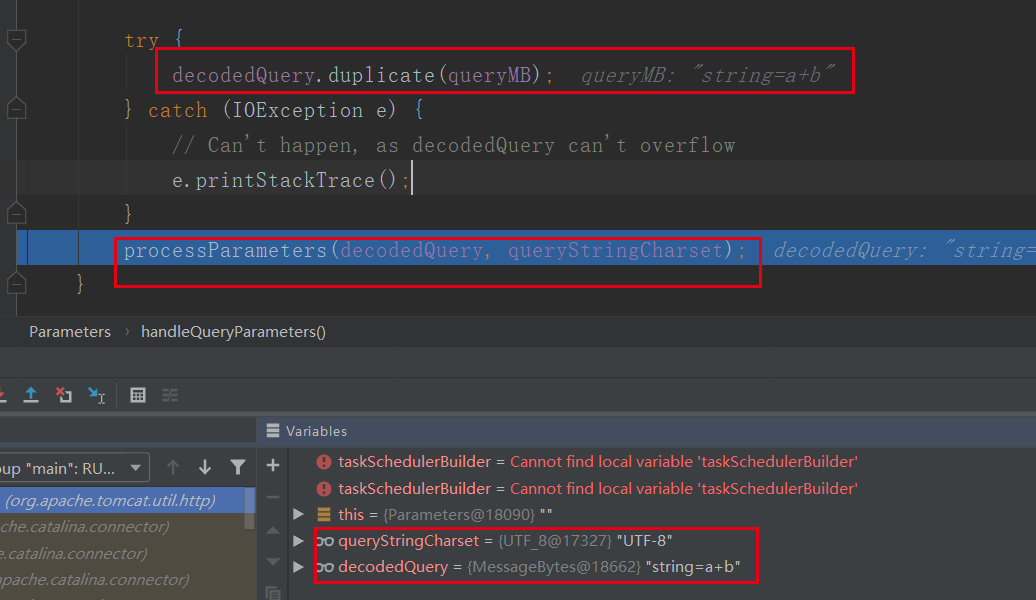
-->org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#processParameters(org.apache.tomcat.util.buf.MessageBytes, java.nio.charset.Charset)
-->org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#processParameters(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset)
-->org.apache.tomcat.util.http.Parameters#urlDecode
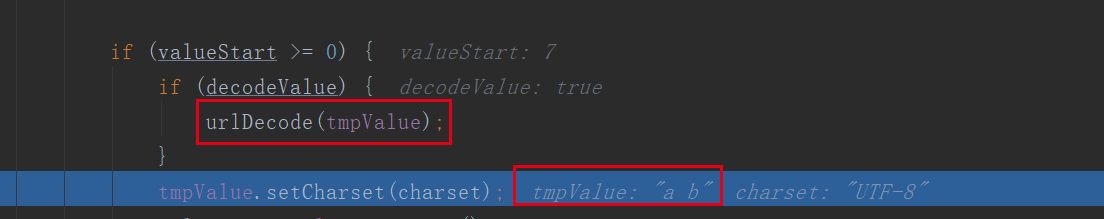
从上面可以看到,是在进行解码时将“+”去除掉的;
继续debug发现在下面的代码中,可以清晰的看到对“+”替换成空格;
-->org.apache.tomcat.util.buf.UDecoder#convert(org.apache.tomcat.util.buf.ByteChunk, boolean)
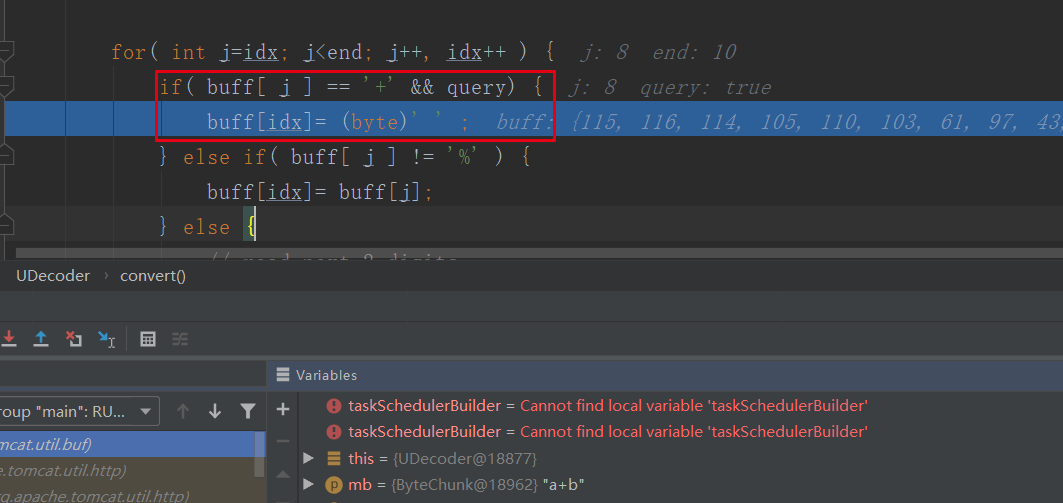
解决办法为:
1)对参数“a+b”进行编码;
2)改成post请求;
4.2.header参数
在网上看见一篇文章,在这里收藏下《FeignClient传入的header中带逗号引发的401问题》
五.总结
1.@RequestParam参数的";"会被QueryTemplate#queryString进行分割组成Collection字符串;
然后在服务提供方CollectionToStringConverter#convert 中用逗号拼接起来;
2.当没有编码前进入的是CollectionToStringConverter#convert,当编码后进入的是GenericConversionService.NoOpConverter#convert;
3.参数值的获取在RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver#resolveName 中;
4.@RequestBody获取参数在RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor#resolveArgument中,直接从body中读取然后返回;
5.请求参数字符串存在特殊符号比如“+”时,在参数编码过程中UDecoder#convert会被转义为空格;
如果,您希望更容易地发现我的新博客,不妨点击一下左下角的【关注我】。
如果,您对我的博客所讲述的内容有兴趣,请继续关注我的后续博客,我是【码猿手】。














