深入理解系统调用
1. 找一个系统调用,系统调用号为学号最后2位相同的系统调用:

本次实验选择84号系统调用:rmdir。该系统调用的作用是删除文件夹。
#include <unistd.h> int rmdir( const char *pathname ); 返回值:若成功则返回0,若出错则返回-1
2. 通过汇编指令触发该系统调用:
首先使用c库函数触发rmdir系统调用:
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> int main(){ int flag; char *dir = "test"; flag = rmdir(dir); if (flag == 0) { printf("删除成功\n"); }else { printf("删除失败\n"); } return 0; }
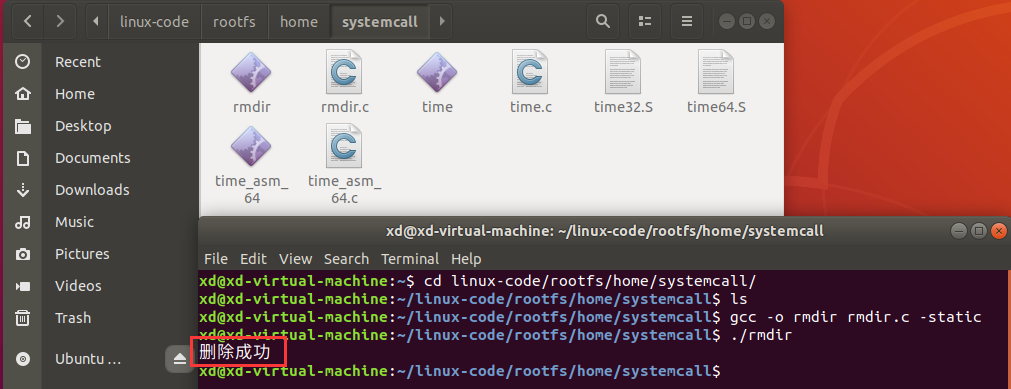
通过反汇编发现通过%rdi传递参数,通过%eax传递系统调用号:
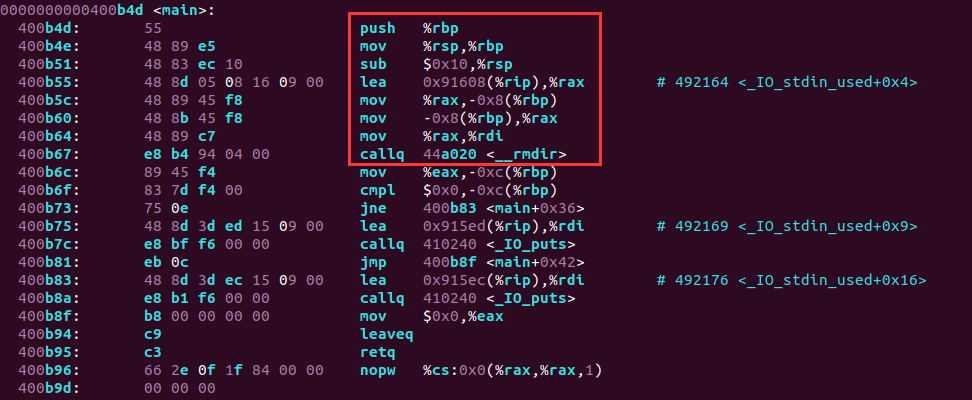
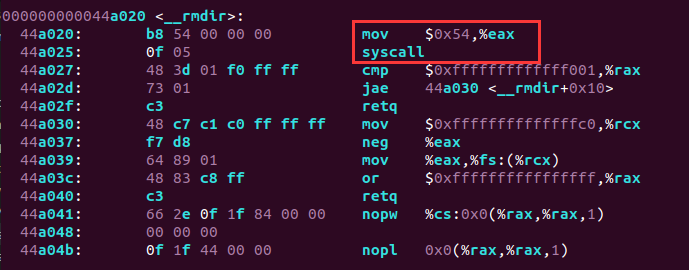
下面使用嵌入式汇编来代替libc提供的rmdir()函数,并触发rmdir系统调用:
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> int main(){ int flag; char *dir = "test"; asm volatile( "movq %1, %%rdi\n\t" "movq $0x54, %%rax\n\t" "syscall\n\t" "movq %%rax,%0\n\t" :"=m"(flag) :"b"(dir) ); if (flag == 0) { printf("Delete succeeded\n"); }else { printf("Delete unsucceeded\n"); } return 0; }
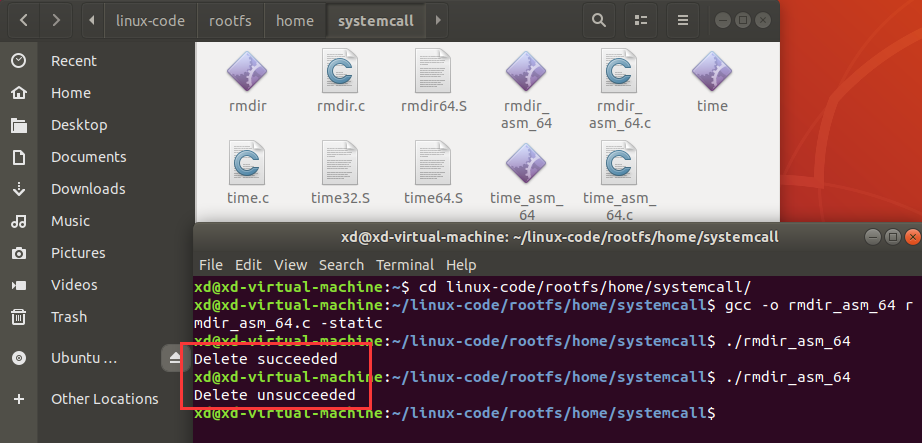
通过实验验证了改写成功,能够通过嵌入式汇编触发rmdir系统调用:
3. 通过gdb跟踪该系统调用的内核处理过程:
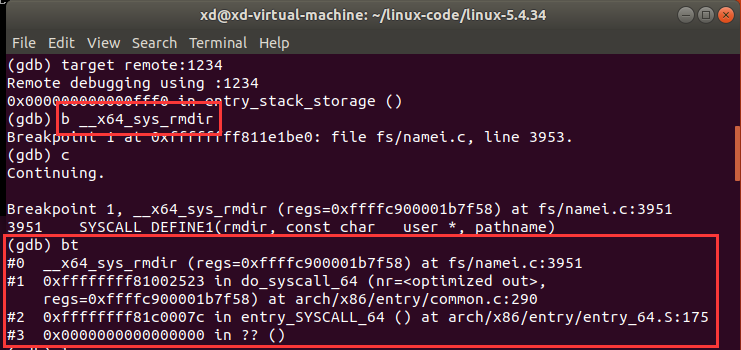
通过bt查看函数调用栈,结合课上所学知识和本次实验,绘制了两幅系统调用的宏观图:
64位嵌入式汇编:

32位libc提供的rmdir()函数:

由于gdb无法追踪entry_SYSCALL_64处的汇编代码,因此我们只能把断点设在do_syscall_64()和__x64_sys_rmdir()函数处,通过以下调试代码可以看到:
首先gdb跟踪到了do_syscall_64 (nr=84, regs=0xffffc90000033f58) 处,然后进入函数体内,在执行到 regs->ax = sys_call_table[nr](regs) 时,根据系统调用号和参数跳转到 __x64_sys_rmdir() 函数处,执行完对应的内核处理函数后,依次返回到do_syscall_64 函数中执行 syscall_return_slowpath(regs) ,再返回到 entry_SYSCALL_64 中,在这段汇编的末尾,我们跟踪到了 USERGS_SYSRET64 这条语句,它相当于做了swapgs和sysretq,对应恢复现场和中断返回,接着继续执行用户态的代码。
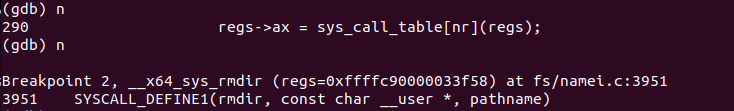

Breakpoint 1, do_syscall_64 (nr=84, regs=0xffffc90000033f58) at arch/x86/entry/common.c:279 279 { (gdb) l 274 prepare_exit_to_usermode(regs); 275 } 276 277 #ifdef CONFIG_X86_64 278 __visible void do_syscall_64(unsigned long nr, struct pt_regs *regs) 279 { 280 struct thread_info *ti; 281 282 enter_from_user_mode(); 283 local_irq_enable(); (gdb) n 283 local_irq_enable(); (gdb) n 284 ti = current_thread_info(); (gdb) n 285 if (READ_ONCE(ti->flags) & _TIF_WORK_SYSCALL_ENTRY) (gdb) n 288 if (likely(nr < NR_syscalls)) { (gdb) n 289 nr = array_index_nospec(nr, NR_syscalls); (gdb) n 290 regs->ax = sys_call_table[nr](regs); (gdb) n Breakpoint 2, __x64_sys_rmdir (regs=0xffffc90000033f58) at fs/namei.c:3951 3951 SYSCALL_DEFINE1(rmdir, const char __user *, pathname) (gdb) n do_rmdir (dfd=-100, pathname=0x492164 "test") at fs/namei.c:3893 3893 { (gdb) n 3900 unsigned int lookup_flags = 0; (gdb) n 3893 { (gdb) n 3902 name = filename_parentat(dfd, getname(pathname), lookup_flags, (gdb) n 3904 if (IS_ERR(name)) (gdb) n 3902 name = filename_parentat(dfd, getname(pathname), lookup_flags, (gdb) n 3904 if (IS_ERR(name)) (gdb) n 3907 switch (type) { (gdb) n 3919 error = mnt_want_write(path.mnt); (gdb) n 3920 if (error) (gdb) n 3923 inode_lock_nested(path.dentry->d_inode, I_MUTEX_PARENT); (gdb) n 3924 dentry = __lookup_hash(&last, path.dentry, lookup_flags); (gdb) n 3926 if (IS_ERR(dentry)) (gdb) n 3924 dentry = __lookup_hash(&last, path.dentry, lookup_flags); (gdb) n 3926 if (IS_ERR(dentry)) (gdb) n 3928 if (!dentry->d_inode) { (gdb) n 3935 error = vfs_rmdir(path.dentry->d_inode, dentry); (gdb) n 3937 dput(dentry); (gdb) n 3939 inode_unlock(path.dentry->d_inode); (gdb) n 3940 mnt_drop_write(path.mnt); (gdb) n 3942 path_put(&path); (gdb) n 3945 lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_REVAL; (gdb) n 3942 path_put(&path); (gdb) n 3943 putname(name); (gdb) n 3944 if (retry_estale(error, lookup_flags)) { (gdb) n 3949 } (gdb) n do_syscall_64 (nr=180688, regs=0xffffc90000033f58) at arch/x86/entry/common.c:300 300 syscall_return_slowpath(regs); (gdb) n 301 } (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:184 184 movq RCX(%rsp), %rcx (gdb) n 185 movq RIP(%rsp), %r11 (gdb) n 187 cmpq %rcx, %r11 /* SYSRET requires RCX == RIP */ (gdb) n 188 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 205 shl $(64 - (__VIRTUAL_MASK_SHIFT+1)), %rcx (gdb) n 206 sar $(64 - (__VIRTUAL_MASK_SHIFT+1)), %rcx (gdb) n 210 cmpq %rcx, %r11 (gdb) n 211 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 213 cmpq $__USER_CS, CS(%rsp) /* CS must match SYSRET */ (gdb) n 214 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 216 movq R11(%rsp), %r11 (gdb) n 217 cmpq %r11, EFLAGS(%rsp) /* R11 == RFLAGS */ (gdb) n 218 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 238 testq $(X86_EFLAGS_RF|X86_EFLAGS_TF), %r11 (gdb) n 239 jnz swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 243 cmpq $__USER_DS, SS(%rsp) /* SS must match SYSRET */ (gdb) n 244 jne swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode (gdb) n 253 POP_REGS pop_rdi=0 skip_r11rcx=1 (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:259 259 movq %rsp, %rdi (gdb) n 260 movq PER_CPU_VAR(cpu_tss_rw + TSS_sp0), %rsp (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:262 262 pushq RSP-RDI(%rdi) /* RSP */ (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:263 263 pushq (%rdi) /* RDI */ (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:271 271 SWITCH_TO_USER_CR3_STACK scratch_reg=%rdi (gdb) n 273 popq %rdi (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:274 274 popq %rsp (gdb) n entry_SYSCALL_64 () at arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S:275 275 USERGS_SYSRET64 (gdb) n 0x0000000000400b83 in ?? ()
最后我们发现do_syscall_64函数执行到结尾处调用了syscall_return_slowpath(regs),无论执行哪个系统调用内核处理函数,执行完之后都会调用syscall_return_slowpath(regs),这是进程调度和进程切换的时机,进一步跟踪可以跟踪到schedule()函数和do_signal()函数,这就与理论上进程调度发生在系统调用结束时对应上了。





