7.队列:在线程池等有限资源池中的应用
队列(queue)
先进者先出,这就是典型的“队列”
栈有基本操作入栈push()和出栈pop()
队列也有两个基本操作入队enqueue(),放一个数据到队列的尾部;出队dequeue(),从队列头部取一个元素。
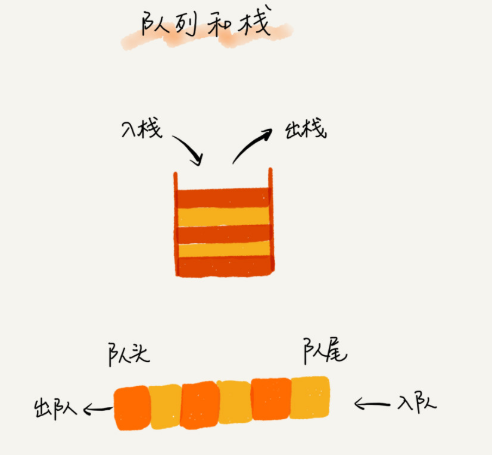
所以,队列和栈一样,也是一种操作受限的线性表数据结构。
顺序队列和链式队列
用数组实现的队列叫顺序队列,用链表实现的队列叫链式队列。
用java实现顺序队列
1 // 用数组实现的队列 2 3 public class ArrayQueue { 4 5 // 数组:items,数组大小:n 6 7 private String[] items; 8 9 private int n = 0; 10 11 // head 表示队头下标,tail 表示队尾下标 12 13 private int head = 0; 14 15 private int tail = 0; 16 17 18 19 // 申请一个大小为 capacity 的数组 20 21 public ArrayQueue(int capacity) { 22 23 items = new String[capacity]; 24 25 n = capacity; 26 27 } 28 29 30 31 // 入队 32 33 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 34 35 // 如果 tail == n 表示队列已经满了 36 37 if (tail == n) return false; 38 39 items[tail] = item; 40 41 ++tail; 42 43 return true; 44 45 } 46 47 48 49 // 出队 50 51 public String dequeue() { 52 53 // 如果 head == tail 表示队列为空 54 55 if (head == tail) return null; 56 57 // 为了让其他语言的同学看的更加明确,把 -- 操作放到单独一行来写了 58 59 String ret = items[head]; 60 61 ++head; 62 63 return ret; 64 65 } 66 67 }
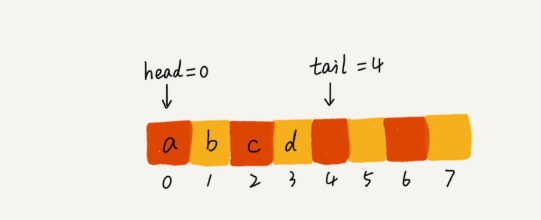
对于栈来说,只要一个栈顶指针就可以了,但队列需要两个指针一个是head指针,指队头,一个是tail指针,指队尾。
入队a,b,c,d后
调用两次出队操作后
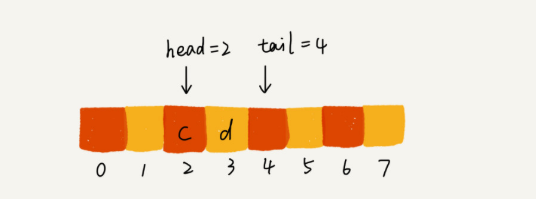
随着不断地入队、出队操作,head和tail会不断向后边移动,当tail移动到最右边时,即使数组还有空闲空间,也无法继续往队列里添加数据了。
解决办法
1.想数组删除数据一样,每一次出队就进行数据搬移,但每次出队操作时间复杂度会为O(n)。
2.只在没空间入队的时候,进行一次数据搬移,出队函数dequeue()保持不变,只要稍加改造下enqueue()。
1 // 入队操作,将 item 放入队尾 2 3 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 4 5 // tail == n 表示队列末尾没有空间了 6 7 if (tail == n) { 8 9 // tail ==n && head==0,表示整个队列都占满了 10 11 if (head == 0) return false; 12 13 // 数据搬移 14 15 for (int i = head; i < tail; ++i) { 16 17 items[i-head] = items[i]; 18 19 } 20 21 // 搬移完之后重新更新 head 和 tail 22 23 tail -= head; 24 25 head = 0; 26 27 } 28 29 30 31 items[tail] = item; 32 33 ++tail; 34 35 return true; 36 37 }
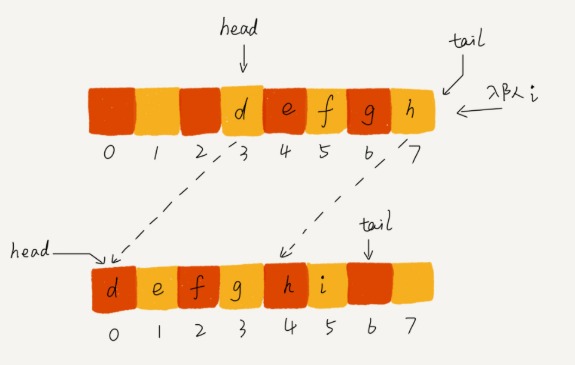
链表队列
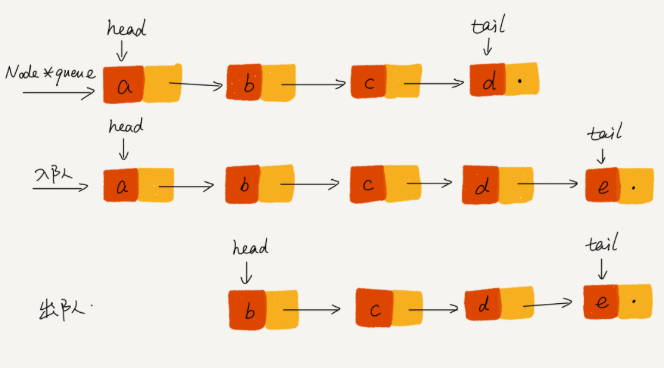
1 public class QueueBasedOnLinkedList { 2 3 4 5 // 队列的队首和队尾 6 7 private Node head = null; 8 9 private Node tail = null; 10 11 12 13 // 入队 14 15 public void enqueue(String value) { 16 17 if (tail == null) { 18 19 Node newNode = new Node(value, null); 20 21 head = newNode; 22 23 tail = newNode; 24 25 } else { 26 27 tail.next = new Node(value, null); 28 29 tail = tail.next; 30 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 36 37 // 出队 38 39 public String dequeue() { 40 41 if (head == null) return null; 42 43 44 45 String value = head.data; 46 47 head = head.next; 48 49 if (head == null) { 50 51 tail = null; 52 53 } 54 55 return value; 56 57 } 58 59 60 61 public void printAll() { 62 63 Node p = head; 64 65 while (p != null) { 66 67 System.out.print(p.data + " "); 68 69 p = p.next; 70 71 } 72 73 System.out.println(); 74 75 } 76 77 78 79 private static class Node { 80 81 private String data; 82 83 private Node next; 84 85 86 87 public Node(String data, Node next) { 88 89 this.data = data; 90 91 this.next = next; 92 93 } 94 95 96 97 public String getData() { 98 99 return data; 100 101 } 102 103 } 104 105 106 107 }
循环队列
用数组实现队列的时候,tail = n时,会有数据搬移操作,循环队列可以解决这个问题。
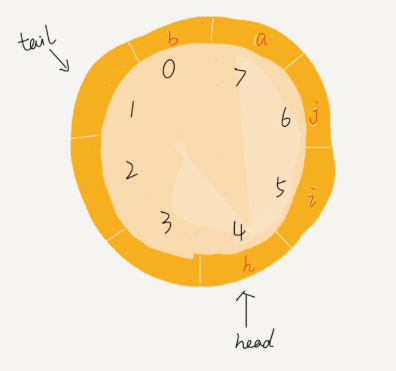
插入a,再插入b
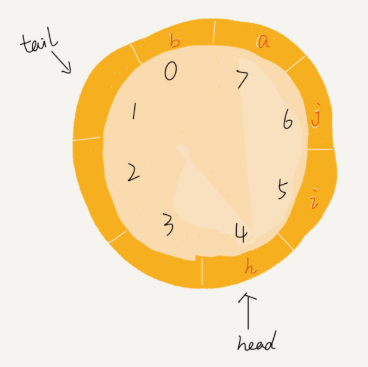
但要实现好循环队列的代码,一定要确定好队空和队满的判定条件。
数组实现的非循环队列中,队满:tail == n ,队空: head == tail。
而在循环队列里,队列为空的判断他条件依然为:head == tail
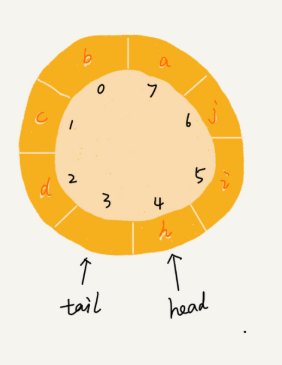
但队满就复杂些了,如下图中,tail = 3 ,head = 4 ,n = 8, 总结规律就是(3 + 1)%8 = 4
多次试验后你就会发现,队满时,(tail + 1) % n = head。
但要注意的是,队满时tail 指向的位置实际上市没有存储空间的,所以,循环队列会蓝给付一个数组的存储空间。
1 public class CircularQueue { 2 3 // 数组:items,数组大小:n 4 5 private String[] items; 6 7 private int n = 0; 8 9 // head 表示队头下标,tail 表示队尾下标 10 11 private int head = 0; 12 13 private int tail = 0; 14 15 16 17 // 申请一个大小为 capacity 的数组 18 19 public CircularQueue(int capacity) { 20 21 items = new String[capacity]; 22 23 n = capacity; 24 25 } 26 27 28 29 // 入队 30 31 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 32 33 // 队列满了 34 35 if ((tail + 1) % n == head) return false; 36 37 items[tail] = item; 38 39 tail = (tail + 1) % n; 40 41 return true; 42 43 } 44 45 46 47 // 出队 48 49 public String dequeue() { 50 51 // 如果 head == tail 表示队列为空 52 53 if (head == tail) return null; 54 55 String ret = items[head]; 56 57 head = (head + 1) % n; 58 59 return ret; 60 61 } 62 63 } 64 65
阻塞队列和并发队列
阻塞对垒其实就是在碎裂基础之上增加了阻塞的操作,队列空,从队头取数据会阻塞直到有数据,队列满,插入被阻塞直到有空闲位置。
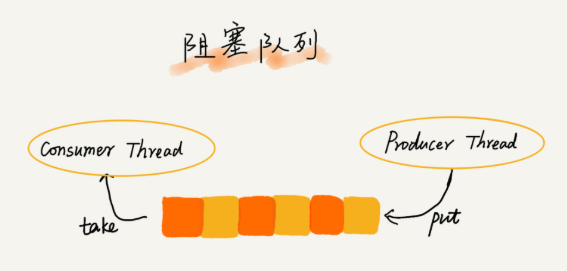
实际上这样就用对了实现了一个“生产者-消费者”模型,甚至可以
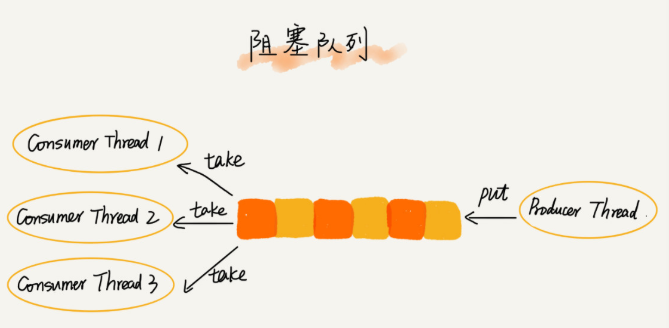
多个线程同时操作队列,就会存在线程安全问题,而线程安全的队列,我们叫做并发队列。最简单直接的实现方式就是在enqueue()和dequeue()上加锁,但是锁的粒度大并法度会比较低,同一时刻仅允许一个存或取操作。
基于数组的循环队列,利用CAS原子操作,可以实现非常高效的并发队列,因此循环队列应用地比链式队列更广泛。
开篇解答
线程池没有空闲线程,又有新任务请求,何处处理?
1.非阻塞处理。直接拒绝请求。
2.阻塞处理。若是希望公平处理每个排队请求,先进先服务,非常适合用队列来存储排队请求。
基链表实现,可实现一个无限排队的无界队列(unbounded queue),但坑内导致请求排队过长,响应处理时间过长,不适合队响应时间敏感的系统。
基于数组实现,可实现一个有界队列(bounded queue),队列有大小,超过范围便会拒绝,对响应时间敏感的系统,就更加合适,但队列过大会导致等待请求过多,过小hi导致无法充分利用系统资源,发挥最大性能。

