MySQL——优化详解
1.MySQL简介
-
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQLAB公司开发,目前属于Oracle公司。
-
Mysql是开源的,可以定制的,采用了GPL协议,你可以修改源码来开发自己的Mysql系统。
-
MySQL使用标准的SQL数据语言形式。
-
Mysql可以允许于多个系统上,并且支持多种语言。这些编程语言包括C、C++、Python、Java、Perl、PHP、Eiffel、Ruby和Tcl等。
-
MySQL支持大型数据库,支持5000万条记录的数据仓库,32位系统表文件最大可支持4GB,64位系统支持最大的表文件为8TB。
1.1 修改字符集
1.1.1 常用命令
| SQL语句 | 描述 | 备注 |
| showdatabases | 列出所有数据库 | |
| create database 库名 | 创建一个数据库 | |
| create database 库名 character set utf8 | 创建数据库,顺便执行字符集为 utf-8 |
|
| show create database 库名 | 查看数据库的字符集 | |
| showv ariableslike‘%char%’ | 查询所有跟字符集相关的信息 | |
| set [字符集属性] =utf8 | 设置相应的属性为utf8 | 只是临时修改,当前有效。服务重启后, 失效。 |
| alter database 库名 character set 'utf8' | 修改数据库的字符集 |
1.1.2 字符集乱码原因
如果在建库建表的时候,没有明确指定字符集,则采用默认的字符集latin1,其中是不包含中文字符的。查看默认的编码字符集:
mysql> show variables like '%char%';
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| character_set_client | utf8 |
| character_set_connection | utf8 |
| character_set_database | latin1 |
| character_set_filesystem | binary |
| character_set_results | utf8 |
| character_set_server | latin1 |
| character_set_system | utf8 |
| character_sets_dir | /usr/share/mysql/charsets/ |
| validate_password_special_char_count | 1 |
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------+1.1.3 修改已创建库、表字符集
mysql> show create database mysql_charset;
+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Database | Create Database |
+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| mysql_charset | CREATE DATABASE `mysql_charset` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */ |
+---------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> alter database mysql_charset character set 'utf8';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create database mysql_charset;
+---------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Database | Create Database |
+---------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| mysql_charset | CREATE DATABASE `mysql_charset` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */ |
+---------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)1.1.4 修改已经乱码数据
无论是修改mysql配置文件或是修改库、表字符集,都无法改变已经变成乱码的数据。只能删除数据重新插入或更新数据才可以完全解决。
1.2 设置大小写不敏感
(1)查看大小写是否敏感:show variables like '%lower_case_table_names%';
mysql> show variables like '%lower_case_table_names%';
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| lower_case_table_names | 0 |
+------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)(2)设置大小写不敏感:在my.cnf这个配置文件[mysqld]中加入lower_case_table_names=1,然后重启服务器
-
0:大小写敏感
-
1:大小写不敏感。创建的表,数据库都是以小写形式存放在磁盘上,对于sql语句都是转换为小写对表和DB进行查找。
-
2:创建的表和DB依据语句上格式存放,凡是查找都是转换为小写进行。
注意:如果要设置属性为大小写不敏感,要在重启数据库实例之前就需要将原来的数据库和表转换为小写,否则将找不到数据库名。在进行数据库参数设置之前,需要掌握这个参数带来的影响,切不可盲目设置。
2. MySQL的用户和权限管理
2.1 用户创建相关命令
| 命令 | 描述 | 备注 |
| create user zhang3 identified by '123123'; | 创建名称为zhang3的用户,密码设为123123; | |
| select host,user,select_priv,insert_priv,drop_priv from mysql.user; | 查看用户和权限的相关信 息 |
|
| set password=password('123456') | 修改当前用户的密码 | |
| update mysql.user set password=password('123456') where user='li4'; | 修改其他用户的密码 | 所有通过user表的修改,必须 用flushprivileges;命令才能生 效 |
| update mysql.user set user='li4' where user='wang5'; | 修改用户名 | 所有通过user表的修改,必须 用flushprivileges;命令才能生 效 |
| drop user li4; | 删除用户 | 不要通过delete from user where user='li4';进行删除,系 统会有残留信息保留。 |
mysql> select host,user,select_priv,insert_priv,drop_priv from mysql.user;
+-----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+
| host | user | select_priv | insert_priv | drop_priv |
+-----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+
| % | root | Y | Y | Y |
| localhost | mysql.session | N | N | N |
| localhost | mysql.sys | N | N | N |
+-----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)host:表示连接类型
-
%:表示所有远程通过TCP方式的连接
-
IP地址:如(172.168.1.2,127.0.0.1)通过制定ip地址进行的TCP方式的连接
-
机器名:通过制定i网络中的机器名进行的TCP方式的连接
-
::1:IPv6的本地ip地址等同于IPv4的127.0.0.1
-
localhost:本地方式通过命令行方式的连接,比如mysql -uxxx -p xxx方式的连接。
user:表示用户名
- 同一用户通过不同方式链接的权限是不一样的。
select_priv,insert_priv等:为该用户所拥有的权限。
2.2 权限授权
| 命令 | 描述 |
| grant 权限1,权限2,…权限n on 数据库名称.表名称 to 用户名@用户地址 identified by '连接口令' |
该权限如果发现没有该用户,则会直接新建一个用户。示例: grant select,insert,delete,drop on mysql_demo.* to li4@localhost; |
| grant all privileges on *.* to wang5@'%' identified by'123'; | 授予通过网络方式登录的wang5用户,对所有库所有表的全部权限,密码设为123. |
2.3 权限回收
| 命令 | 描述 |
| show grants | 查看当前用户权限 |
| revoke [权限1,权限2,…权限n] on 库名.表名 from 用户名@用户地址; | 收回权限命令 |
| REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGESON mysql.* FROM wang5@localhost; | 收回全库全表的所有权限 |
| REVOKE select,insert,update,delete ON mysql.* FROM wang5@localhost; | 收回mysql库下的所有表的插删改查权限 |
| 权限收回后,必须用户重新登录后,才能生效。 |
2.4 查看权限
| 命令 | 描述 |
| show grants; | 查看当前用户权限 |
| select * from user; |
mysql> show grants;
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@% |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3. MySQL逻辑架构简介
3.1 MySQL架构图
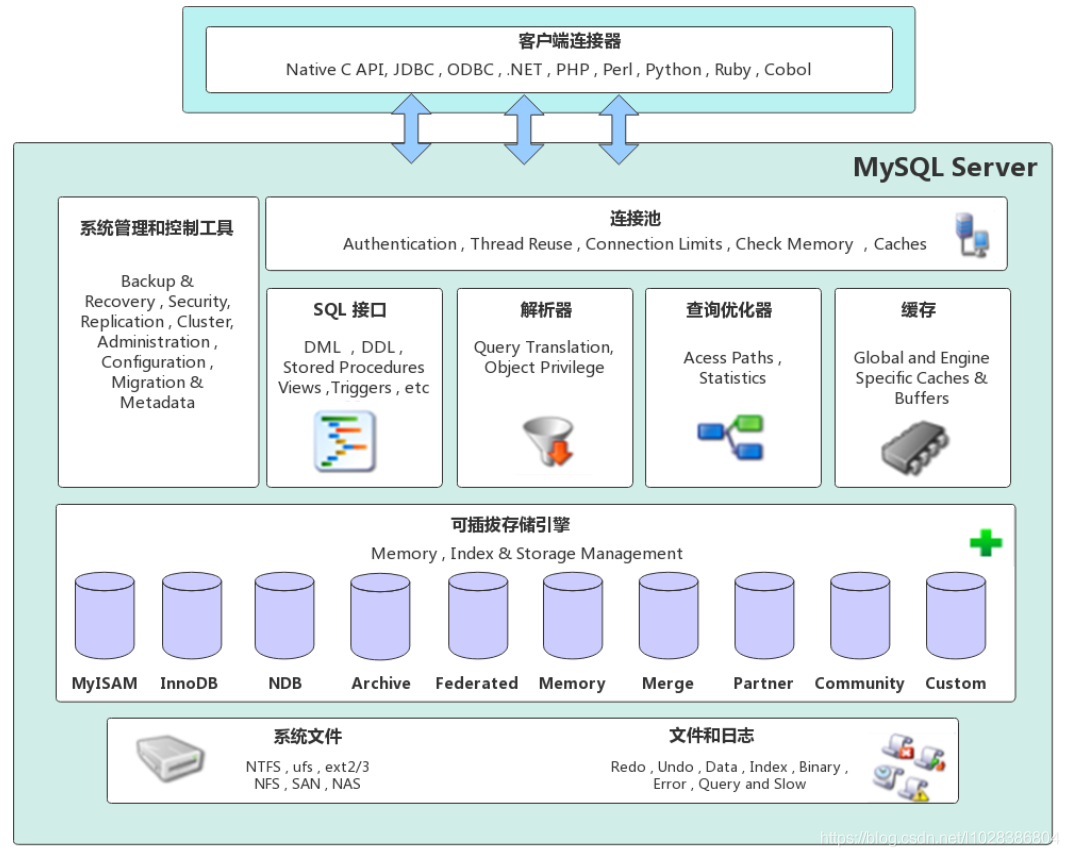
MySQL与其他数据相比,它的架构可以在多种不同场景中应用并发挥良好作用。主要体现在存储引擎的架构上,插件式的存储引擎架构将查询处理和其它的系统任务以及数据的存储提取相分离。这种架构可以根据业务的需求和实际需要选择合适的存储引擎。
3.1.1 连接层
最上层是一些客户端和连接服务,包含本地sock通信和大多数基于客户端/服务端工具实现的类似于tcp/ip的通信。主要完成一些类似于连接处理、授权认证、及相关的安全方案。在该层上引入了线程池的概念,为通过认证安全接入的客户端提供线程。同样在该层上可以实现基于SSL的安全链接。服务器也会为安全接入的每个客户端验证它所具有的操作权限。
3.1.2 服务层
| Management Serveices&Utilities | 系统管理和控制工具 |
| SQLInterface | SQL接口。接受用户的SQL命令,并且返回用户需要查询的结果。比如select from就是调用SQL Interface。 |
| Parser | 解析器。SQL命令传递到解析器的时候会被解析器验证和解析。 |
| Optimizer | 查询优化器。SQL语句在查询之前会使用查询优化器对查询进行优化,比如有where条件时,优化器来决定先投影还是先过滤。 |
| Cache和Buffer | 查询缓存。如果查询缓存有命中的查询结果,查询语句就可以直接去查询缓存中取数据。这个缓存机制是由一系列小缓存组成的。比如表缓存,记录缓存,key缓存,权限缓存等。 |
3.1.3 引擎层
存储引擎层,存储引擎真正的负责了MySQL中数据的存储和提取,服务器通过API与存储引擎进行通信。不同的存储引擎具有的功能不同,这样我们可以根据自己的实际需要进行选取。
3.1.4 存储层
数据存储层,主要是将数据存储在运行于裸设备的文件系统之上,并完成与存储引擎的交互。
3.2 show profile
利用show profile可以查看sql的执行周期!
3.2.1 开启profile
查看profile是否开启:show variables like'%profiling%';
mysql> show variables like'%profiling%';
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | OFF |
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+如果没有开启,可以执行set profiling=1开启!
mysql> set profiling=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like'%profiling%';
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | ON |
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)3.2.2 使用 profile
执行show prifiles命令,可以查看最近的几次查询。
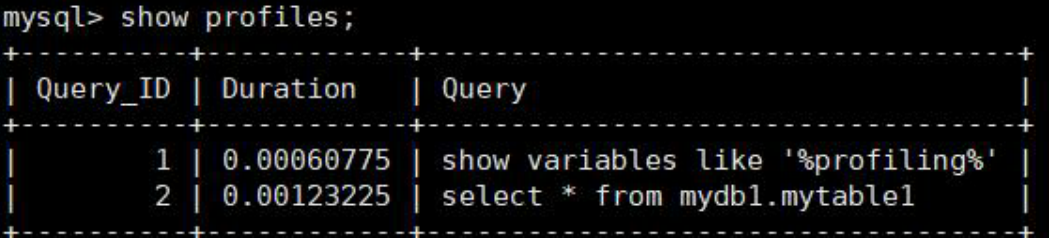
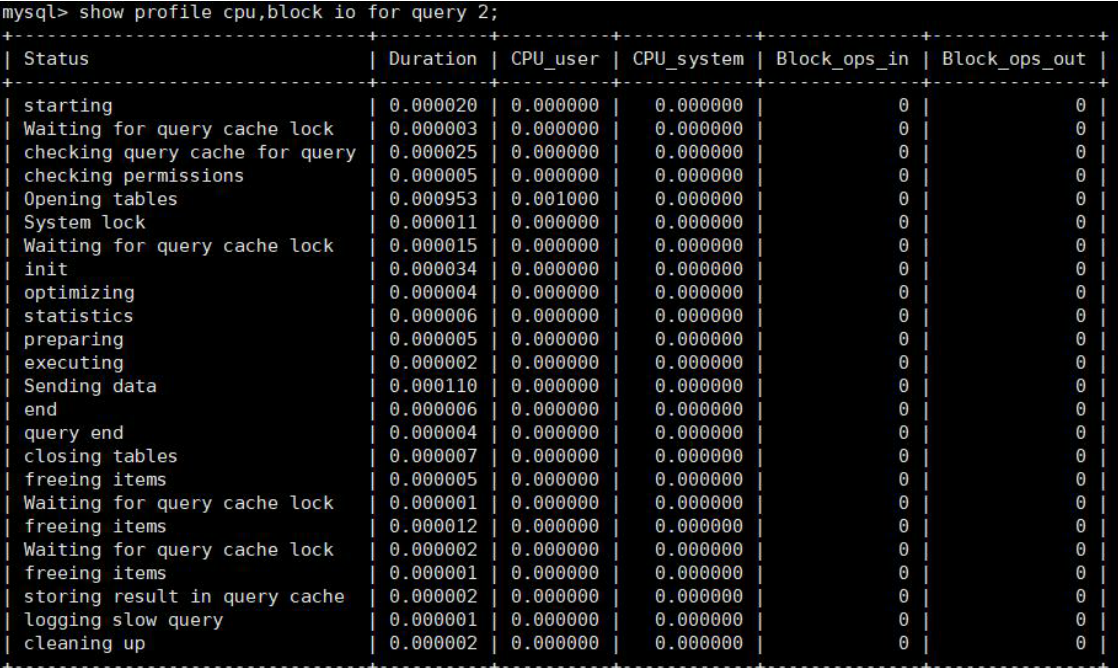
根据Query_ID,可以进一步执行show profile cpu,block io for query Query_id来查看sql的具体执行步骤。
3.3 MySQL查询流程
-
mysql客户端通过协议与mysql服务器建连接,发送查询语句,先检查查询缓存,如果命中,直接返回结果,否则进行语句解析,也就是说,在解析查询之前,服务器会先访问查询缓存(querycache)——它存储SELECT语句以及相应的查询结果集。如果某个查询结果已经位于缓存中,服务器就不会再对查询进行解析、优化、以及执行。它仅仅将缓存中的结果返回给用户即可,这将大大提高系统的性能。
-
语法解析器和预处理:首先mysql通过关键字将SQL语句进行解析,并生成一棵对应的“解析树”。mysql解析器将使用mysql语法规则验证和解析查询;预处理器则根据一些mysql规则进一步检查解析树是否合法。
-
查询优化器:当解析树被认为是合法的了,并且由优化器将其转化成执行计划。一条查询可以有很多种执行方式,最后都返回相同的结果。优化器的作用就是找到这其中最好的执行计划。
3.4 SQL执行顺序
手写SQL顺序:
SELECT DISTINCT
<select_list>
FROM
<left_table> <join_type>
JOIN <right_table> ON <join_condition>
WHERE
<where_condition>
GROUP BY
<group_by_list>
HAVING
<having_condition>
ORDER BY
<order_by_condition>
LIMIT <limit_number>优化器会分析不同执行顺序产生的性能消耗不同而动态调整执行顺序。下面是经常出现的查询顺序:
FROM <left_table>
ON <join_condition>
<join_type> JOIN <right_table>
WHERE <where_condition>
GROUP BY <group_by_list>
HAVING <having_condition>
SELECT
DISTINCT <select_list>
ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
LIMIT <limit_number>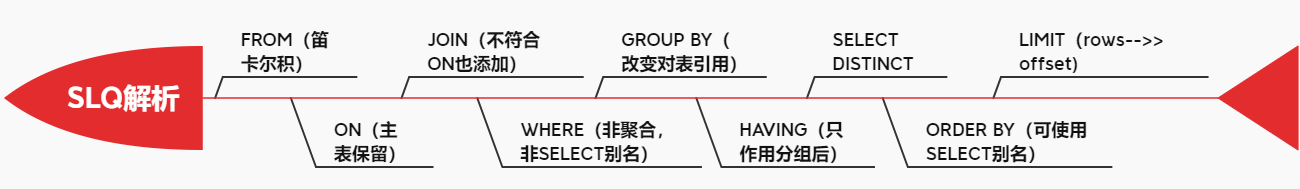 3.5 MyISAM和InnoDB
3.5 MyISAM和InnoDB
| MyISAM | InnoDB | |
| 外键 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 事务 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 行表锁 | 表锁,即使操作一条记录也会锁住整个表,不适合高并发的操作 | 行锁,操作时只锁某一行,不对其它行有影响,适合高并发的操作 |
| 缓存 | 只缓存索引,不缓存真实数据 | 不仅缓存索引还要缓存真实数据,对内存要求较高,而且内存大小对性能有决定性的影响 |
查看数据库引擎:
mysql> show engines;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+show variables like '%storage_engine%' 查看默认的数据库引擎:
mysql> show variables like '%storage_engine%' ;
+----------------------------------+--------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------------------+--------+
| default_storage_engine | InnoDB |
| default_tmp_storage_engine | InnoDB |
| disabled_storage_engines | |
| internal_tmp_disk_storage_engine | InnoDB |
+----------------------------------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)4. SQL JOIN类型
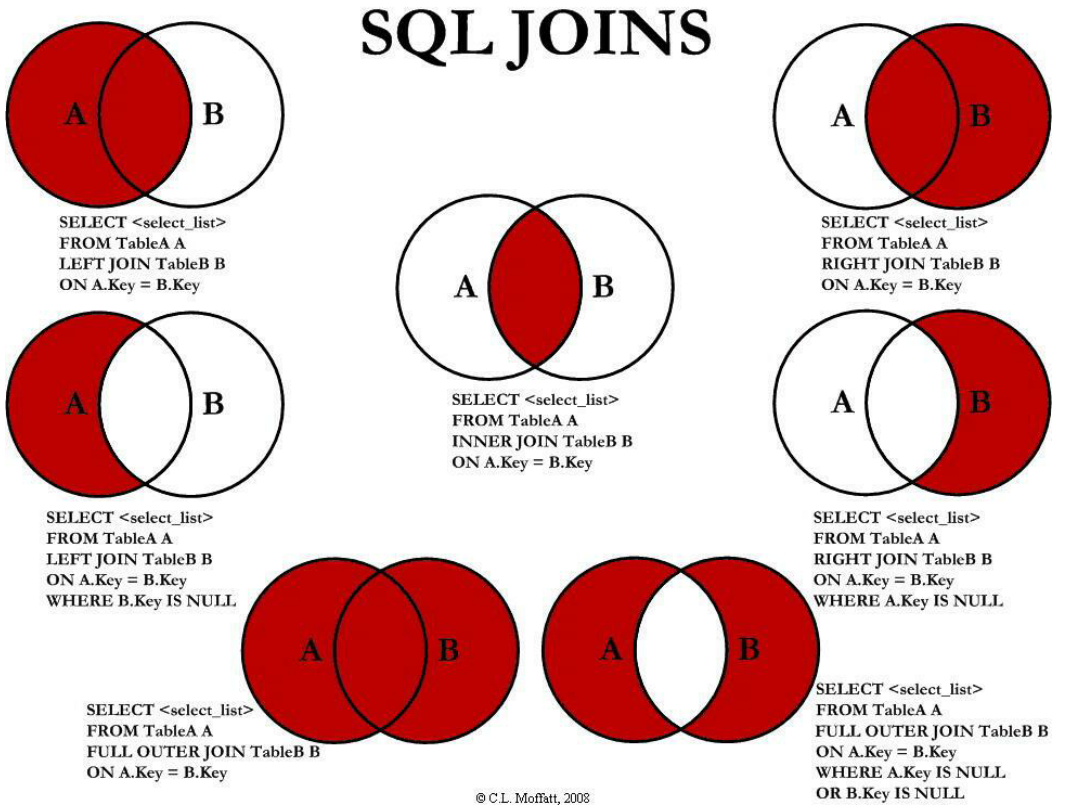
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a LEFT JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a RIGHT JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a LEFT JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id WHERE b.id is null;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a LEFT JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id WHERE a.id is null;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a INNER JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a FULL OUTER JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id;
-
SELECT <select_list> FROM tableA a FULL OUTER JOIN TableB b on a.id=b.id WHERE a.id is null or b.id is null;
JOIN示例:创建员工和部门表
CREATE TABLE `tbl_dept` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`deptName` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`locAdd` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_emp` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`deptId` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fk_dept_id` (`deptId`),
KEY `index_name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=9 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) values('RD',11);
insert into tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) values('HR',12);
insert into tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) values('MK',13);
insert into tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) values('MIS',14);
insert into tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) values('FD',15);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('z3',1);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('z4',1);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('z5',1);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('w5',2);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('w6',2);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('s7',3);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('s8',4);
insert into tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) values('s9',51);mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td ;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 |
| 2 | HR | 12 |
| 3 | MK | 13 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 |
| 5 | FD | 15 |
+----+----------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_emp te ;
+----+------+--------+
| id | name | deptId |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 7 | s8 | 4 |
| 8 | s9 | 51 |
+----+------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td inner join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is NULL ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where td.id is NULL ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is null union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId where td2.id is null ;
SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 | 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 3 | MK | 13 | 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 | 7 | s8 | 4 |
| 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 | 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 3 | MK | 13 | 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 | 7 | s8 | 4 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 |
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is NULL ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is NULL ;
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where td.id is NULL ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td right join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where td.id is NULL ;
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 |
+------+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td inner join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td inner join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId ;
+----+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+----+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 | 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 3 | MK | 13 | 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 | 7 | s8 | 4 |
+----+----------+--------+----+------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.01 sec)SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId;
+------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 | 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 1 | RD | 11 | 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 2 | HR | 12 | 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 3 | MK | 13 | 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 | 7 | s8 | 4 |
| 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 |SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is null union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId where td2.id is null ;
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is null union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId where td2.id is null ;
+------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId |
+------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+
| 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 |
+------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+5. 索引优化分析
5.1 索引是什么?
MySQL官方对索引的定义为:索引(Index)是帮助MySQL高效获取数据的数据结构。即索引的本质:数据结构。可以简单理解为排好序的快速查找数据结构。
在数据之外,数据库系统还维护着满足特定查找算法的数据结构,这些数据结构以某种方式引用(指向)数据,这样就可以在这些数据结构上实现高级查找算法。这种数据结构,就是索引。下图就是一种可能的索引方式示例:
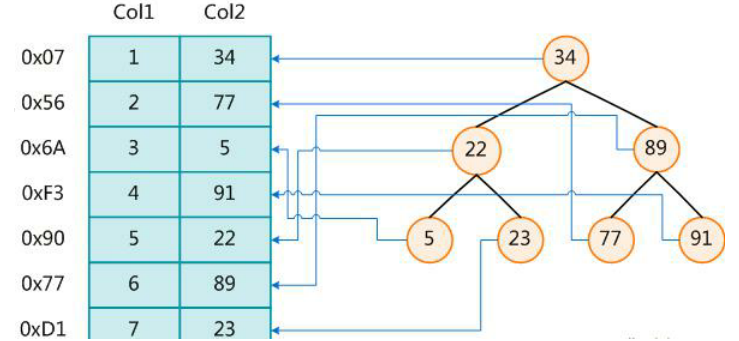
左边是数据表,一共有两列七条记录,最左边的是数据记录的物理地址。为了加快Col2的查找,可以维护一个右边所示的二叉查找树,每个节点分别包含索引键值和一个指向对应数据记录物理地址的指针,这样就可以运用二叉查找在一定的复杂度内获取到相应数据,从而快速的检索出符合条件的记录。
一般来说索引本身也很大,不可能全部存储在内存中,因此索引往往以索引文件的形式存储的磁盘上。
索引的优缺点:
(1)优势:
-
提高数据检索的效率,降低数据库的IO成本。
-
通过索引列对数据进行排序,降低数据排序的成本,降低了CPU的消耗。
(2)劣势:
- 虽然索引大大提高了查询速度,同时却会降低更新表的速度,如对表进行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE。因为更新表时,MySQL不仅要保存数据,还要保存一下索引文件每次更新添加了索引列的字段,都会调整因为更新所带来的键值变化后的索引信息。
- 实际上索引也是一张表,该表保存了主键与索引字段,并指向实体表的记录,所以索引列也是要占用空间的。
5.2 MySQL索引
5.2.1 B-tree索引
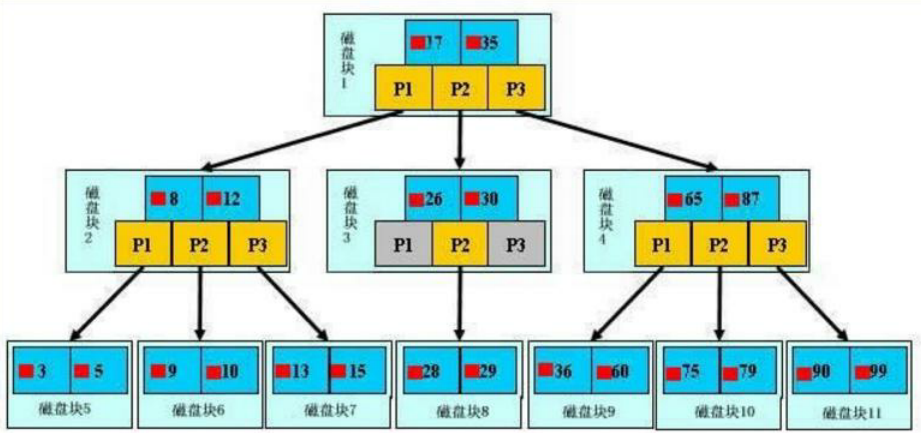
浅蓝色部分:表示磁盘块;深蓝色部分:表示数据项;黄色部分:表示指针。如磁盘块1包含数据项17和35,包含指针P1、P2、P3。
P1表示小于17的磁盘块,P2表示在17和35之间的磁盘块,P3表示大于35的磁盘块。真实的数据存在于叶子节点,即3、5、9、10、13、15、28、29、36、60、75、79、90、99。非叶子节点不存储真实的数据,只存储指引搜索方向的数据项,如17、35并不真实存在于数据表中。
数据查找过程:查找数据项29
(1)首先会把磁盘块1由磁盘加载到内存,此时发生一次IO,在内存中用二分查找确定29在17和35之间,锁定磁盘块1的P2指针,内存时间因为非常短(相比磁盘的IO)可以忽略不计。
(2)通过磁盘块1的P2指针的磁盘地址把磁盘块3由磁盘加载到内存,发生第二次IO,29在26和30之间,锁定磁盘块3的P2指针。
(3)通过指针加载磁盘块8到内存,发生第三次IO,同时内存中做二分查找找到29,结束查询,总计三次IO。
真实的情况是,3层的b-树可以表示上百万的数据,如果上百万的数据查找只需要三次IO,性能提高将是巨大的,如果没有索引,每个数据项都要发生一次IO,那么总共需要百万次的IO,显然成本非常非常高。
5.2.2 B+tree索引
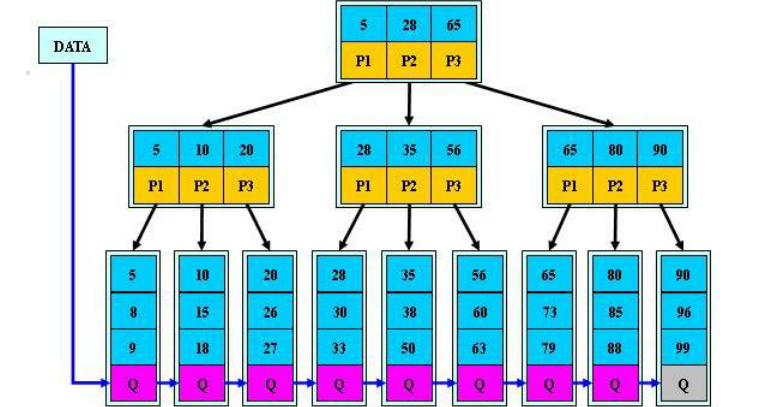
B+Tree与B-Tree的区别
1)B-树的关键字和记录是放在一起的,叶子节点可以看作外部节点,不包含任何信息;B+树的非叶子节点中只有关键字和指向下一个节点的索引,记录只放在叶子节点中。
2)在B-树中,越靠近根节点的记录查找时间越快,只要找到关键字即可确定记录的存在;而B+树中每个记录的查找时间基本是一样的,都需要从根节点走到叶子节点,而且在叶子节点中还要再比较关键字。从这个角度看B-树的性能好像要比B+树好,而在实际应用中却是B+树的性能要好些。因为B+树的非叶子节点不存放实际的数据,这样每个节点可容纳的元素个数比B-树多,树高比B-树小,这样带来的好处是减少磁盘访问次数。尽管B+树找到一个记录所需的比较次数要比B-树多,但是一次磁盘访问的时间相当于成百上千次内存比较的时间,因此实际中B+树的性能可能还会好些,而且B+树的叶子节点使用指针连接在一起,方便顺序遍历(例如查看一个目录下的所有文件,一个表中的所有记录等),这也是很多数据库和文件系统使用B+树的缘故。
为什么B+树比B-树更适合实际应用中操作系统的文件索引和数据库索引?
(1)B+树的磁盘读写代价更低
B+树的内部结点并没有指向关键字具体信息的指针,因此其内部结点相对B-树更小。如果把所有同一内部结点的关键字存放在同一磁盘块中,那么同一磁盘块所能容纳的关键字数量也越多。一次性读入内存中的需要查找的关键字也就越多。相对来说IO读写次数也就降低了。
(2)B+树的查询效率更加稳定
由于非终结点并不是最终指向文件内容的结点,而只是叶子结点中关键字的索引。所以任何关键字的查找必须走一条从根结点到叶子结点的路。所有关键字查询的路径长度相同,导致每一个数据的查询效率相当。
5.2.3 聚簇索引和非聚簇索引
聚簇索引并不是一种单独的索引类型,而是一种数据存储方式。术语‘聚簇’表示数据行和相邻的键值聚簇的存储在一起。如下图,左侧的索引就是聚簇索引,因为数据行在磁盘的排列和索引排序保持一致。
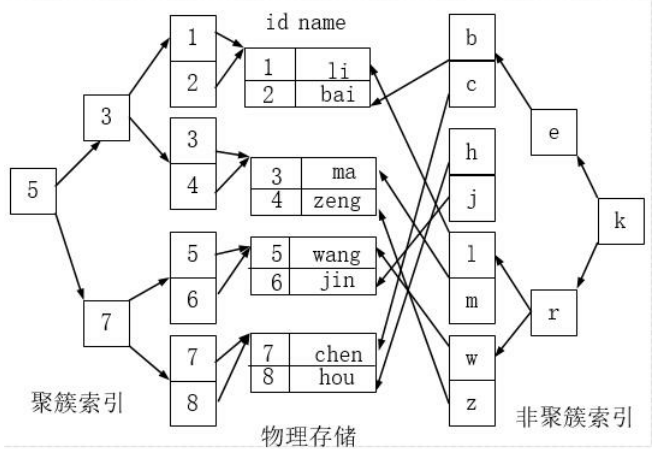
聚簇索引的好处:
按照聚簇索引排列顺序,查询显示一定范围数据的时候,由于数据都是紧密相连,数据库不不用从多个数据块中提取数据,所以节省了大量的io操作。
聚簇索引的限制:
对于mysql数据库目前只有innodb数据引擎支持聚簇索引,而Myisam并不支持聚簇索引。由于数据物理存储排序方式只能有一种,所以每个Mysql的表只能有一个聚簇索引。一般情况下就是该表的主键。为了充分利用聚簇索引的聚簇的特性,所以innodb表的主键列尽量选用有序的顺序id,而不建议用无序的id,比如uuid这种。
5.3 MySQL索引分类
创建索引基本语法:
| 操作 | 命令 |
| 创建 | CREATE [UNIQUE] INDEX (index_name) ON table_name(column); |
| 删除 | DROP INDEX [index_name] on table; |
| 查看 | SHOW INDEX FROM table_name; |
| 使用Alter命令 | ALTER TABLE table_name ADD PRIMARY KEY(column_list);添加一个主键,索引的值唯一且不能为null。 |
| ALTER TABLE bl_name ADD INDEX index_name(column_list);添加普通索引,索引值可出现多次。 | |
| ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD FULLTEXT index_name(column_list);该语句指定了索引为FULLTEXT,用于全文索引。 |
5.3.1 单值索引
单值索引:即一个索引只包含单个列,一个表可以有多个单列索引。
#建表是创建索引
CREATE TABLE `customer`(`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, customer_no VARCHAR(200), customer_name VARCHAR(200), PRIMARY KEY(id), KEY(customer_name) );
#单独创建索引
CREATE INDEX idx_customer_name ON customer(customer_name);
#删除索引
ALTER TABLE mysql_demo.customer DROP INDEX customer_name;mysql> show index from customer;
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| customer | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| customer | 0 | idx_customer_no | 1 | customer_no | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| customer | 1 | idx_customer_name | 1 | customer_name | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+5.3.2 唯一索引
唯一索引:索引列的值必须唯一,但允许有空值。
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_customer_no ON customer(customer_no);mysql> show index from customer;
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| customer | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| customer | 0 | idx_customer_no | 1 | customer_no | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| customer | 1 | idx_customer_name | 1 | customer_name | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+----------+------------+-------------------+--------------+---------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+5.3.3 主键索引
主键索引:设定为主键后数据库会自动建立索引,innodb为聚簇索引。
#随表一起创建索引
CREATE TABLE `customer`(`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, customer_no VARCHAR(200), customer_name VARCHAR(200), PRIMARY KEY(id) );
#单独创建索引
ALTER TABLE customer add PRIMARY KEY customer(customer_no);
#删除建主键索引:
ALTER TABLE customer drop PRIMARY KEY;
#修改建主键索引
必须先删除掉(drop)原索引,再新建(add)索引。
5.3.4 复合索引
复合索引:即一个索引包含多个列。
#建表是创建索引
CREATE TABLE `customer`(`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, customer_no VARCHAR(200), customer_name VARCHAR(200), PRIMARY KEY(id), KEY(customer_name),KEY(customer_no,customer_name) );
#单独创建索引
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_customer_no_name ON customer(customer_no,customer_name);
覆盖索引(Covering index)(索引覆盖):SELECT 的数据列只用从索引中就能取得,不必读取行,MySQL可以利用索引返回select列表中的字段,而不必根据索引再次读取文件,换句话说就是查询列要被所建的索引覆盖。
注意:如果要使用覆盖索引,一定要注意 SELECT列表中只取出需要的列,不可写 SELECT * ...,因为如果将所有字段一起做索引会导致索引文件过大,导致查询性能下降。
5.4 索引创建的场景
5.4.1 适合创建索引场景
-
主键自动建立唯一索引;
-
频繁作为查询条件的字段应该创建索引;
-
查询中与其他表关联的字段,外键关系建立索引;
-
单键/组合索引的选择问题,组合索引性价比更高;
-
查询中排序的字段,排序字段若通过索引去访问将大大提高排序速度;
-
查询中统计或者分组字段。
5.4.2 不合适创建索引的情况
-
表记录太少;
-
经常进行增删改的表或者字段;
-
where条件里用不到的字段不用创建索引;
-
过滤性不好的不适合创建索引。
6. Explain 性能分析
使用EXPLAIN关键字可以模拟优化器执行SQL查询语句,从而知道MySQL是如何处理你的SQL语句的。分析你的查询语句或是表结构的性能瓶颈。
Explain 用法:Explain+SQL语句。
Explain执行返回信息:
id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra
Explain能干什么?
-
查看表的读取顺序
-
数据读取操作的操作类型
-
哪些索引可以使用
-
哪些索引实际被使用
-
表之间的引用
-
每张表有多少行被优化器查询
6.1 id
select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行 select 子句或操作表的顺序。
(1)id 相同,执行顺序由上至下。
mysql> explain SELECT * from tbl_dept td ,tbl_emp te where td.id = te.deptId ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | td | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | te | NULL | ALL | fk_dept_id | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 20.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)(2)id 不同,如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id值越大,优先级越高,会被优先执行。
mysql> explain SELECT * from tbl_emp te where EXISTS (SELECT 1 from tbl_dept td where te.deptId = td.id );
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | te | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | td | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | mysql_demo.te.deptId | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)(3)id 有相同也有不同,id如果相同,可以认为是一组,从上往下顺序执行;在所有组中,id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行,衍生=DERIVED。
mysql> explain SELECT * from tbl_dept td left join tbl_emp te on td.id = te.deptId where te.deptId is null union SELECT * from tbl_dept td2 right join tbl_emp te2 on td2.id = te2.deptId where td2.id is null ;
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | td | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | PRIMARY | te | NULL | ALL | fk_dept_id | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 12.50 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
| 2 | UNION | te2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | UNION | td2 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 20.00 | Using where; Not exists; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
| NULL | UNION RESULT | <union1,2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary |
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
6.2 查询类型(select_type)
| select_type属性 | 含义 |
| SIMPLE | 简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者UNION |
| PRIMARY | 查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为Primary |
| SUBQUERY | 在SELECT或WHERE列表中包含了子查询 |
| DERIVED | 在FROM列表中包含的子查询被标记为DERIVED(衍生),MySQL会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放在临时表里。 |
| UNION | 若第二个SELECT出现在UNION之后,则被标记为UNION;若UNION包含在FROM子句的子查询中,外层SELECT将被标记为:DERIVED |
| UNION RESULT | 从UNION表获取结果的SELECT |
| UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY | 无法使用缓存的子查询 |
| DEPEDENT SUBQUERY | 在SELECT或WHERE列表中包含了子查询,子查询基于外层 |
(1)SIMPLE
explain select * from tbl_emp;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_emp | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)(2)PRIMARY
查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为Primary。
(3)DERIVED
在FROM列表中包含的子查询被标记为DERIVED(衍生),MySQL会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放在临时表里。
6.3 table
显示查询的数据是基于哪张表。
6.4 type
type是查询的访问类型。是较为重要的一个指标,结果值从最好到最坏依次是:
system>const>eq_ref>ref>range>index>all
system>const>eq_ref>ref_or_null>index_merge>unique_subquery>index_subquery>range>index>all
一般来说,查询至少要保证达到range级别,最好能达到ref。
6.4.1 system
表只有一行记录(等于系统表),这是const类型的特列,平时不会出现,这个也可以忽略不计。
6.4.2 const
表示通过索引一次就找到了,const用于比较primary key或者unique索引。因为只匹配一行数据,所以很快。如将主键置于where列表中,MySQL就能将该查询转换为一个常量。
6.4.3 eq_ref
唯一性索引扫描,对于每个索引键,表中只有一条记录与之匹配。常见于主键或唯一索引扫描。
6.4.4 ref
非唯一性索引扫描,返回匹配某个单独值的所有行。本质上也是一种索引访问,它返回所有匹配某个单独值的行,然而,它可能会找到多个符合条件的行,所以他应该属于查找和扫描的混合体。
6.4.5 range
只检索给定范围的行,使用一个索引来选择行。key列显示使用了哪个索引一般就是在你的where语句中出现了between、<、>、in等的查询,这种范围扫描索引扫描比全表扫描要好,因为它只需要开始于索引的某一点,而结束语另一点,不用扫描全部索引。
6.4.6 index
出现index是sql使用了索引但是没用通过索引进行过滤,一般是使用了覆盖索引或者是利用索引进行了排序分组。
6.4.7 all
FullTableScan,将遍历全表以找到匹配的行。
6.5 possible_keys 和 key
possible_keys:显示可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个。查询涉及到的字段上若存在索引,则该索引将被列出,但不一定被查询实际使用。
key:实际使用的索引。如果为NULL,则没有使用索引。
6.6 key_len
表示索引中使用的字节数,可通过该列计算查询中使用的索引的长度。key_len字段能够帮你检查是否充分的利用上了索引。key_len越长,说明索引使用的越充分。
key_len长度计算:
-
先看索引上字段的类型+长度,比如int=4;varchar(20)=20;char(20)=20。
-
如果是varchar或者char这种字符串字段,视字符集要乘不同的值,比如utf-8要乘3,GBK要乘2。
-
varchar这种动态字符串要加2个字节。
-
允许为空的字段要加1个字节。
6.7 ref
显示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的话,是一个常数。哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值。
6.8 rows
rows列显示MySQL认为它执行查询时必须检查的行数。越少越好!
6.9 Extra
包含不适合在其他列中显示但十分重要的信息。
6.9.1 Using filesort
说明mysql会对数据使用一个外部的索引排序,而不是按照表内的索引顺序进行读取。MySQL中无法利用索引完成的排序操作称为“文件排序”。
6.9.2 Using temporary
使了用临时表保存中间结果,MySQL在对查询结果排序时使用临时表。常用于排序order by和分组查询group by。
6.9.3 Using index
Using index表示相应的select操作中使用了覆盖索引(Covering Index),避免访问了表的数据行,效率不错!如果同时出现using where,表明索引被用来执行索引键值的查找;如果没有同时出现using where,表明索引只是用来读取数据而非利用索引执行查找。
6.9.4 Using where
表明使用了where过滤。
6.9.5 Using oin buffer
使用了连接缓存。
6.9.6 impossible where
where子句的值总是false,不能用来获取任何元组。select able soptimized away
7. 关联查询优化
7.1 单表优化
新建表:aticle
CREATE TABLE `article` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`author_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`category_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`views` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`comments` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`title` varbinary(255) NOT NULL,
`content` text NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_article_ccv` (`category_id`,`comments`,`views`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;插入数据:
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0x31, '1');
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0x32, '2');
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(3, 1, 1, 3, 3, 0x33, '3');
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0x31, '1');
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(5, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0x32, '2');
INSERT INTO mysql_demo.article
(id, author_id, category_id, views, comments, title, content)
VALUES(6, 1, 1, 3, 3, 0x33, '3');创建索引:
mysql> show index from article;
+---------+------------+-----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+---------+------------+-----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| article | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 6 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| article | 1 | idx_article_ccv | 1 | category_id | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| article | 1 | idx_article_ccv | 2 | comments | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| article | 1 | idx_article_ccv | 3 | views | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+---------+------------+-----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)explain SELECT * from article where category_id =1 AND comments > 1 order by views DESC limit 1;
mysql> explain SELECT * from article where category_id =1 AND comments > 1 order by views DESC limit 1;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | range | idx_article_ccv | idx_article_ccv | 8 | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Using index condition; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)explain SELECT * from article where category_id =1 AND comments = 1 order by views DESC limit 1;
mysql> explain SELECT * from article where category_id =1 AND comments = 1 order by views DESC limit 1;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | ref | idx_article_ccv | idx_article_ccv | 8 | const,const | 2 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)#结论:
type 变成了 range,这是可以忍受的。但是 extra 里使用 Using filesort 仍是无法接受的
#但是我们已经建立了索引,为啥没用呢?
这是因为按照 BTree 索引的工作原理先排序 category_id,如果遇到相同的 category_id 则再排序 comments,如果遇到相同的 comments 则再排序 views。当 comments 字段在联合索引里处于中间位置时,因comments > 1 条件是一个范围值(所谓 range),MySQL 无法利用索引再对后面的 views 部分进行检索,即 range 类型查询字段后面的索引无效。
查询优化:
删除原有索引:idx_article_ccv,新建索引:
CREATE index idx_article_cv on article_1(category_id,views);查看索引:
mysql> show index from article_1 ;
+-----------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-----------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| article_1 | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| article_1 | 1 | idx_article_cv | 1 | category_id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| article_1 | 1 | idx_article_cv | 2 | views | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-----------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)查看执行结果:
mysql> explain SELECT * from article_1 where category_id =1 AND comments > 1 order by views DESC limit 1;
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | article_1 | NULL | ref | idx_article_cv | idx_article_cv | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)结论:type 变为了 ref,Extra 中的 Using filesort 也消失了,结果非常理想。
7.2 两表关联查询优化
新建:calss,book两张表
CREATE TABLE `class` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`card` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=21 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `book` (
`bookid` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`card` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`bookid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=21 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;执行:inner join/right join/left join
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c inner join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 10.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c left join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c right join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)type: all
添加索引优化(索引加在:calss表还是book表?不知道)。
(1)假设在“book”表中添加索引“idx_card”。
create index idx_card on book(card);查看索引:
mysql> show index from book;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| book | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | bookid | A | 20 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| book | 1 | idx_card | 1 | card | A | 16 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)执行SQL查询语句,查看explain执行结果:
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c left join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.c.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain SELECT * from class c right join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | index | NULL | idx_card | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)mysql> explain SELECT * from class c inner join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.c.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)执行结果:left join和inner join中有使用到了索引,type为ref,MySQL执行查询时必须检查的行数变为1。而right join则和优化之前没有发生变化。
结论:
①在优化关联查询时,只有在被驱动表上建立索引才有效!
②left join时,左侧的为驱动表,右侧为被驱动表!
(2)把表“book”中的索引去掉,在“class”表中添加“idx_card”索引,然后查看执行结果,进行对比分析。
#删除book中的索引
DROP index idx_card on book;
#在class表中创建索引
ALTER TABLE class ADD index idx_card (card);
#查看索引
show index from class;
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| class | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 20 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| class | 1 | idx_card | 1 | card | A | 13 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)执行SQL查询语句,查看explain执行结果:
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c left join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | index | NULL | idx_card | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c inner join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.b.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c right join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.b.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)从执行结果可以看出,当索引加在“class”表时,执行 inner join和right join时优化结果较为明显,type值为ref,影响行数rows由20变为1行。
这是由于左连接和右连接的特性决定的,LEFT JOIN条件用于确定如何从右表搜索行,左边一定有,所以右边是关键点,一定需要建立索引。而RIGHT JOIN则与LEFT JOIN相反,RIGHT JOIN条件用于确定如何从左边表搜索行,右边一定有,所以左边是关键点,一定需要建立索引。
结论:
①inner join:mysql会自动将小结果集的表选为驱动表。
②right join:效果和inner join一样,但是会强制将左侧作为驱动表!
对比一下两种写法(此时索引建在“class”表中)的执行结果:
mysql> explain SELECT * from book b left join class c on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.b.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from class c left join book b on c.card = b.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | c | NULL | index | NULL | idx_card | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | b | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)结论:执行“LEFT JOIN”查询语句时,将建有索引的表写在右边同样达到优化的目的。同理,执行“RIGHT JOIN”查询语句时,将建有索引的表写在左边。
7.3 多表关联查询优化
创建表:“phone”,将“class”表和“book”表中创建的索引删除。
CREATE TABLE `phone` (
`phoneid` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`card` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`phoneid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=21 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;执行SQL查询语句:SELECT * from class class left join book book on class.card = book.card left join phone phone on book.card = phone.card ;
查看代码
mysql> SELECT * from class class left join book book on class.card = book.card left join phone phone on book.card = phone.card ;
+----+------+--------+------+---------+------+
| id | card | bookid | card | phoneid | card |
+----+------+--------+------+---------+------+
| 2 | 8 | 19 | 8 | 1 | 8 |
| 3 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 2 | 18 |
| 9 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 2 | 18 |
| 13 | 17 | 1 | 17 | 4 | 17 |
| 16 | 17 | 1 | 17 | 4 | 17 |
| 3 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 6 | 18 |
| 9 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 6 | 18 |
| 15 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 7 | 12 |
| 15 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 7 | 12 |
| 2 | 8 | 19 | 8 | 9 | 8 |
| 3 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 11 | 18 |
| 9 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 11 | 18 |
| 11 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 13 | 2 |
| 8 | 16 | 2 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 8 | 16 | 4 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 19 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 19 | 14 |
| 19 | 14 | 16 | 14 | 19 | 14 |
| 6 | 13 | 8 | 13 | 20 | 13 |
| 1 | 7 | 9 | 7 | NULL | NULL |
| 4 | 7 | 9 | 7 | NULL | NULL |
| 7 | 7 | 9 | 7 | NULL | NULL |
| 12 | 1 | 13 | 1 | NULL | NULL |
| 14 | 1 | 13 | 1 | NULL | NULL |
| 18 | 1 | 13 | 1 | NULL | NULL |
| 5 | 19 | 14 | 19 | NULL | NULL |
| 10 | 4 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 17 | 11 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 20 | 4 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+------+--------+------+---------+------+explain查看执行计划,执行过程中使用了全表扫描:
mysql> explain SELECT * from class class left join book book on class.card = book.card left join phone phone on book.card = phone.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
| 1 | SIMPLE | phone | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
表查询优化,在“book”表和“phone”表中分别创建索引“idx_card”。
mysql> explain SELECT * from class class left join book book on class.card = book.card left join phone phone on book.card = phone.card ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.class.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | phone | NULL | ref | idx_card | idx_card | 4 | mysql_demo.book.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-----------------------+------+----------+-------------+
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)结论:添加索引之后,book、phone表中的type都是ref,且总rows由20变为1,即优化效果较好。
总结:
-
尽可能减少 join 语句中的 NestedLoop 的循环总次数,优先优化 NestedLoop 的内层循环;
-
永远用小结果集驱动大的结果集;
-
保证 join 语句中被驱动表上 join 条件字段已经被索引;
- 当无法保证被驱动表的 join 条件字段被索引且内存资源充足的前提下,不要吝啬 JoinBuffer 的设置。
8 索引失效
创建“staffs”员工表,并创建索引 idx_name_age_pos` (`name`,`age`,`pos`)。
CREATE TABLE `staffs` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '年龄',
`pos` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位',
`add_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '入职时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_name_age_pos` (`name`,`age`,`pos`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表';8.1 全值匹配
全值匹配:查询的字段按照顺序在索引中都可以匹配到。SQL中查询字段的顺序,跟使用索引中字段的顺序没有关系。优化器会在不影响SQL执行结果的前提下自动地优化。
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name = 'July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 74 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name = 'July' and age = 23;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 78 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name = 'July' and age = 23 and pos = 'dev';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 140 | const,const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8.2 最佳左前缀法则
如果索引添加了多列,要遵守最左前缀法则。指的是查询从索引的最左前列开始并且不跳过索引中的列。
例如:explain SELECT * from staffs where age = 23 and pos = 'dev'; 该SQL跳过了索引中的第一列 name,此时索引失效,type值为all。
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where age = 23 and pos = 'dev';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)如果跳过中间列时,后面的索引列失效:
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name = 'July' and pos = 'dev';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 74 | const | 1 | 33.33 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8.3 不在索引列上做任何操作 (计算、函数、(自动or手动)类型转换)
在索引上使用函数或者自动类型转换时,会导致索引失效而转向全表扫描。
(1)索引列使用函数导致索引失效。
mysql> select * from staffs where left(name,4) = 'July';
+----+------+-----+-----+---------------------+
| id | name | age | pos | add_time |
+----+------+-----+-----+---------------------+
| 2 | July | 23 | dev | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
+----+------+-----+-----+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from staffs where left(name,4) = 'July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
8.4 索引列上不做范围查询
范围之后索引全失效,即“age > 23”导致“pos ”列索引失效。将可能做范围查询的字段的索引顺序放在最后。
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name = 'July' and age > 23 and pos = 'dev';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | range | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 78 | NULL | 1 | 33.33 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)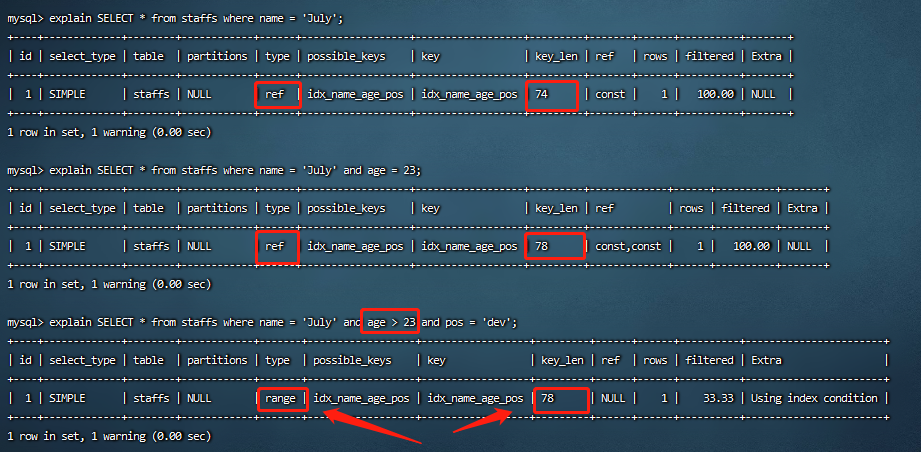
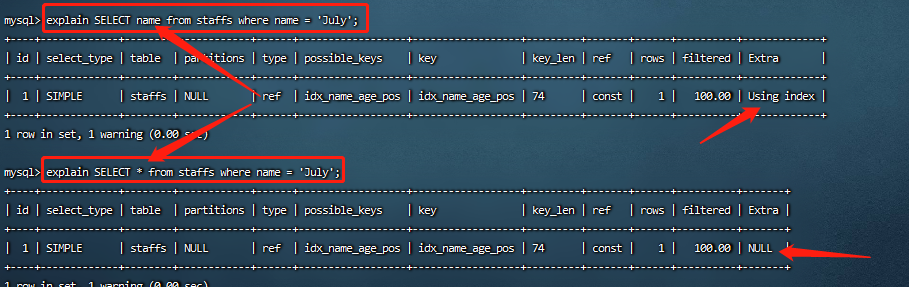
8.5 尽量使用覆盖索引(索引列和查询列一致),减少select *
即查询列和索引列一致,不要写select*。
explain SELECT name,age,pos from staffs where name = 'July' and age = 23 and pos = 'dev'; SELECT列中指定所需的查询列(与创建索引的列相同)时,Extra处使用了Using index,即使用索引去读取数据而非通过索引去查找数据,因此效率更好。
mysql> explain SELECT name,age,pos from staffs where name = 'July' and age = 23 and pos = 'dev';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 140 | const,const,const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------------+
8.6 使用不等于(!= 或者<>)导致索引失效
mysql在使用不等于(!=或者<>)时,有时会无法使用索引会导致全表扫描。
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name != 'July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_pos | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 66.67 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name <> 'July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_pos | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 66.67 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)从中可以看出type值为ALL,key值为null,即索引失效,导致全表扫描。
8.7 is null ,is not null 导致索引失效
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name is null;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Impossible WHERE |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name is not null;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_pos | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 66.67 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8.8 like 前后模糊(%abc/%abc%)查询导致索引失效
like 前后模糊(%abc/%abc%)查询导致索引失效造成全表扫描,like % 写右边不会导致索引失效。
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name like '%July%';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name like '%July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT * from staffs where name like 'July%';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | range | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 74 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+------------------+------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)某些场景下必须要使用通配符%开头:“%name%”,如何解决索引失效的问题?——覆盖索引!
新建:“tbl_user ”表,创建索引之前执行SQL并查看EXPLAIN执行结果:
mysql> SELECT * from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
+----+------+------+-----------+
| id | name | age | email |
+----+------+------+-----------+
| 1 | 1aa1 | 21 | b@163.com |
| 2 | 2aa2 | 222 | a@163.com |
| 3 | 3aa3 | 265 | c@163.com |
| 4 | 4aa4 | 21 | d@163.com |
+----+------+------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT name from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)创建索引:idx_name_age
mysql> show index from tbl_user ;
+----------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+----------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| tbl_user | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| tbl_user | 1 | idx_name_age | 1 | name | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| tbl_user | 1 | idx_name_age | 2 | age | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+----------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)使用覆盖索引,并以通配符“%”开头进行模糊查:
mysql> explain SELECT name,age from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_user | NULL | index | NULL | idx_name_age | 68 | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)由结果可知该查询使用了索引,即使用通配符“%”开头进行模糊查时索引没有失效。且以下SQL语句都不会导致索引失效。
explain SELECT id from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
explain SELECT name from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
explain SELECT age from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
explain SELECT name,age from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';
explain SELECT id,name,age from tbl_user where name LIKE '%aa%';8.9 字符串不加单引号索引失效
mysql> select * from staffs;
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | pos | add_time |
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
| 1 | z3 | 22 | manager | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
| 2 | July | 23 | dev | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
| 3 | 2000 | 23 | dev | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from staffs where name = 2000;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_pos | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from staffs where name = '2000';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | idx_name_age_pos | idx_name_age_pos | 74 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)8.10 使用“or”导致索引失效
mysql> select * from staffs where name = 'z3' or name = 'July';
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | pos | add_time |
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
| 1 | z3 | 22 | manager | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
| 2 | July | 23 | dev | 2022-11-23 22:10:52 |
+----+------+-----+---------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from staffs where name = 'z3' or name = 'July';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_pos | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 66.67 | Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)使用unionall或者union来替代。
9. 子查询优化
9.1 小表驱动大表(in/exist)
小表驱动大表:即小的数据集驱动大的数据集。
当A表的数据集大于B表的数据集时,用 in 优于 exist。
#对A查询涉及id,使用索引,故A表效率高,可使用大表,即使用“in”时外大内小。
select * from A where id in (select id from B);
等价于:
for select id from B
for select * from A where A.id = B.id当A表的数据集小于B表的数据集时,用 exists 优于 in。
#对B表查询涉及id,使用索引,故B表效率高,可用大表,即使用“exists”时外小内大。
select * from A where id exists (select 1 from B where A.id = B.id);
等价于:
for select id from A
for select * from B where A.id = B.id注意:A表和B表的ID字段应建立索引。
select* from table where exists (subquery):将主查询的数据放到子查询中做条件验证,根据验证结果(true/false)来决定查询的数据结果是否得以保留。
提示:exists(subquery) 只返回true或false,因此子查询中的 select * 也可以是 select 1 或者其他,实际执行是会忽略 select 清单。
*** EXISTS 和 IN 的区别*** :
(1)exists是对外表做loop循环,每次loop循环再对内表(子查询)进行查询,因为对内表的查询使用的索引(内表效率高,故可用大表),而外表有多大都需要遍历,不可避免(尽量用小表),故内表大的使用exists,可加快效率;
(2)in是把外表和内表做hash连接,先查询内表,再把内表结果与外表匹配,对外表使用索引(外表效率高,可用大表),而内表多大都需要查询,不可避免,故外表大的使用in,可加快效率。
(3)如果查询的两个表大小相当,那么用in和exists差别不大。如果两个表中一个较小,一个是大表,则子查询表大的用exists,子查询表小的用in。
案例演示:
mysql> select count(*) from tbl_emp A;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 8 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from tbl_dept B;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from tbl_emp A where deptId in (select id from tbl_dept B);
+----+------+--------+
| id | name | deptId |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 7 | s8 | 4 |
+----+------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from tbl_emp A where exists (select 1 from tbl_dept B where B.id = A.deptId);
+----+------+--------+
| id | name | deptId |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 7 | s8 | 4 |
+----+------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tbl_emp A where deptId in (select id from tbl_dept B);
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_dept | NULL | index | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 5 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_emp | NULL | ALL | fk_dept_id | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 20.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) |
+----+-------------+----------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tbl_emp A where exists (select 1 from tbl_dept B where B.id = A.deptId);
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+---------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+---------------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | A | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | B | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | mysql_demo.A.deptId | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+---------------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
filtered
filtered 表示某个表经过搜索条件过滤后剩余记录条数的百分比,如果使用的是索引执行的单表扫描,那么计算时需要估计出满足除使用到对应索引的搜索条件外的其他搜索条件的记录有多少条。
10. 排序、分组优化
10.1 排序优化
MySQL支持两种方式的排序:
-
FileSort:文件排序
-
Index:索引排序
Index效率高,Index指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。FileSort方式效率较低。Order By子句尽量使用index方式排序,避免使用FileSet方式排序。
Order By满足以下两种情况会使用Index方式排序:
-
Order By语句使用索引最左前列。
-
使用where子句与Order By子句条件列组合满足最左前列。
如果不在索引列上,filesort有两种算法:
-
双路排序:MySQL4.1之前是使用双路排序,字面意思就是两次扫描磁盘,最终得到数据,读取行指针和order by列,对他们进行排序,然后扫描已经排序好的列表,按照列表中的值重新从列表中读取对应的数据输出。从磁盘取排序字段,在buffer进行排序,再从磁盘取其他字段。
-
单路排序:从磁盘读取查询需要的所有列,按照order by列在buffer对它们进行排序,然后扫描排序后的列表进行输出,它的效率更快一些,避免了第二次读取数据。并且把随机IO变成了顺序IO,但是它会使用更多的空间,因为它把每一行都保存在内存中了。使用单路排序的前提是排序的字段大小要小于max_length_for_sort_data。
注:单路排序可能会存在以下问题
在sort_bufer中,方法B比方法A要多占用很多空间,因为方法B是把所有字段都取出,所以有可能取出的数据的总大小超出了sort_bufer的容量,导致每次只能取sort_bufer容量大小的数据,进行排序(创建tmp文件,多路合并),排完再去取sort_bufer容量大小,再排......从而多次I/O。本来想省一次I/O操作,反而导致了大量的I/O操作,反而得不偿失。
优化策略:
-
增大sort_buffer_size参数:不管用哪种算法,提高这个参数都会提高效率。此要根据系统的能力去提高,因为这个参数是针对每个进程的1M~8M之间调整。
-
增大max_length_for_sort_data参数:提高这个参数,会增加使用改进算法的概率。但是如果设的太高,数据总容量超出sort_bufer_size的概率就增大,其明显症状是高的磁盘I/O活动和降低的处理器使用率。其值大小设置范围:1024~8192M之间调整。
如何提高Order By的速度?
-
只查询需要的字段,Order by 时禁止使用 select *,因为 select * 会导致以下两点:
-
当Query的字段总和小于max_length_for_sort_data,而且排序字段不是TEXT|BLOB类型时,会使用单路排序算法,否则使用多路排序算法。
-
两种算法的数据都有可能超出sort_bufer的容量,超出之后,会创建tmp文件进行合并排序,导致多次I/O,但是用单路排序算法的风险会更大一些,所以要提高sort_bufer_size。
-
-
尝试提高sort_bufer_size的值;
-
尝试提高max_length_for_sort_data的值。
*****order by 使用索引情况,KEY a_b_c (a, b, c)*****
order by 能使用索引最左前缀
-ORDER BY a
-ORDER BY a,b
-ORDER BY a b,c
-ORDER BY a DESC, b DESC, C DESC
如果WHERE使用索引的最左前缀定义为常量,则order by能使用索引
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY b,c
- WHERE a = const AND b = const ORDER BY C
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY b, c
-WHERE a = const AND b > const ORDER BY b, c
不能使用索引进行排序
- ORDER BY a AsC, b DESC,C DESC /* 排序不一致,要么同升,要么同降*/
- WHERE g = const ORDER BY b, c /*丢失a索引,即最左前缀*/
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY C /*丢失b索引*/
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY a, d /* d 不是索引的一部分 */
-WHERE a in (...) ORDER BY b. c /*对于排序来说,多个相等条件也是范围查询 */
案例演示:新建表“tblA”,创建索引“idx_A_ageBirth”。
CREATE TABLE `tblA` (
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`birth` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
KEY `idx_A_ageBirth` (`age`,`birth`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
mysql> SELECT * from tblA;
+------+---------------------+
| age | birth |
+------+---------------------+
| 22 | 2022-11-23 22:11:18 |
| 23 | 2022-11-23 22:11:18 |
| 24 | 2022-11-23 22:11:18 |
+------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show index from tblA;
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| tblA | 1 | idx_A_ageBirth | 1 | age | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| tblA | 1 | idx_A_ageBirth | 2 | birth | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)执行以下SLQ并查看结果:
explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by age;
explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by age,birth ;
explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by birth ;
explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by birth,age;
explain select * from tblA order by birth;
explain select * from tblA where birth > '2022-11-23 22:11:18.0' order by birth;
explain select * from tblA where birth > '2022-11-23 22:11:18.0' order by age ;
explain select * from tblA order by age ASC ,birth DESC ;mysql> explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by age;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | idx_A_ageBirth | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by age,birth ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | idx_A_ageBirth | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by birth ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | idx_A_ageBirth | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA where age > 20 order by birth,age;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | idx_A_ageBirth | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+----------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA order by birth;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | NULL | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA where birth > '2022-11-23 22:11:18.0' order by birth;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | NULL | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA where birth > '2022-11-23 22:11:18.0' order by age ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | NULL | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from tblA order by age ASC ,birth DESC ;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tblA | NULL | index | NULL | idx_A_ageBirth | 9 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
案例2:新建表“test03”
CREATE TABLE `test03` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`c1` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`c2` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`c3` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`c4` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`c5` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `index_test03_c1234` (`c1`,`c2`,`c3`,`c4`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;创建索引:
mysql> show index from test03 ;
+--------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+--------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| test03 | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| test03 | 1 | index_test03_c1234 | 1 | c1 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| test03 | 1 | index_test03_c1234 | 2 | c2 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| test03 | 1 | index_test03_c1234 | 3 | c3 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| test03 | 1 | index_test03_c1234 | 4 | c4 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
+--------+------------+--------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)执行SQL查看结果:
explain select * from test03 where c1='al' and c2='a2' and c4>'a4' and c3='a3';
explain select * from test03 where c4='a4' and c3>'a3' and c2='a2' and c1='al';
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' and c3>'a3' and c4='a4';
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2'and c4='a4' order by c3;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' order by c4;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' order by c3;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c2,c3;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3,c2;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3,c4;
explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c4,c3;查看代码
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='al' and c2='a2' and c4>'a4' and c3='a3';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | range | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 124 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c4='a4' and c3>'a3' and c2='a2' and c1='al';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | range | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 93 | NULL | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' and c3>'a3' and c4='a4';
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | range | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 93 | NULL | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+-------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2'and c4='a4' order by c3;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 62 | const,const | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' order by c4;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 62 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c2='a2' order by c3;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 62 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 31 | const | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition; Using where; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c2,c3;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 31 | const | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition; Using where |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3,c2;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 31 | const | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition; Using where; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from test03 where c1='a1' and c5='a5' order by c3,c4;
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | test03 | NULL | ref | index_test03_c1234 | index_test03_c1234 | 31 | const | 1 | 20.00 | Using index condition; Using where; Using filesort |
+----+-------------+--------+------------+------+--------------------+--------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)10.2 分组优化
Group By:实质是先排序后进行分组,遵照索引建的最佳左前缀。
当无法使用索引列时,增大max_length_for_sort_data和sort_buffer_size参数值进行优化。
where高于having,能写在where限定的条件就不要去用having进行限定。
11. 慢查询日志
11.1 什么是慢查询日志?
MySQL的慢查询日志是MySQL提供的一种日志记录,它用来记录在MySQL中响应时间超过阀值的语句,具体指运行时间超过long_query_time值的SQL,则会被记录到慢查询日志中。long_query time的默认值为10,大于10秒以上的SQL语句会被记录到慢查询日志中。
默认情况下,MySQL数据库没有开启慢查询日志,需要我们手动来设置这个参数。如果不是调优需要的话,一般不建议启动该参数,因为开启慢查询日志会或多或少带来一定的性能影响。慢查询日志支持将日志记录写入文件。
11.2 如何查看是否开启慢查询日志?
mysql> show variables like '%query%';
+------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| binlog_rows_query_log_events | OFF |
| ft_query_expansion_limit | 20 |
| have_query_cache | YES |
| long_query_time | 5.000000 |
| query_alloc_block_size | 8192 |
| query_cache_limit | 1048576 |
| query_cache_min_res_unit | 4096 |
| query_cache_size | 1048576 |
| query_cache_type | OFF |
| query_cache_wlock_invalidate | OFF |
| query_prealloc_size | 8192 |
| slow_query_log | ON |
| slow_query_log_file | /var/lib/mysql/huangdh-9930-slow.log |
+------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
13 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+
| slow_query_log | OFF |
| slow_query_log_file | /var/lib/mysql/huangdh-9930-slow.log |
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)其中,/var/lib/mysql/huangdh-9930-slow.log 表示慢查询日志文件位置。
11.3 开启慢查询日志
使用 set global slow_query_log = 1 开启慢查询日志,只针对当前数据库有效,如果MySQL重启则会失效。
mysql> set global slow_query_log = 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+
| slow_query_log | ON |
| slow_query_log_file | /var/lib/mysql/huangdh-9930-slow.log |
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+如果要永久生效,就必须修改配置文件my.cnf。
在[mysqld]下增加或修改参数:slow_query_log 和slow query log file,并设置参数为:
slow query log =1
slow query log file=/var/lib/mysql/hostName-slow.log(如果没有指定参数的话,系统默认会给一个缺省的文件hostName-slow.log)
然后重启MySQL服务器。
修改慢查询阈值为3秒: set global long_query_time = 3;
mysql> set global long_query_time = 3;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+----------+
| long_query_time | 3.000000 |
+-----------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)如果修改阈值之后使用命令:show variables like '%long_query_time%' 查看值没有发生变化时,则需要新开一个会话窗口进查看。
mysql> set global long_query_time = 5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+----------+
| long_query_time | 3.000000 |
+-----------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%long_query_time%';
+-----------------+----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+----------+
| long_query_time | 5.000000 |
+-----------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)模拟慢查询:select sleep(6);,并查看日志记录:show global status like '%slow_queries%';
mysql> select sleep(6);
+----------+
| sleep(6) |
+----------+
| 0 |
+----------+
1 row in set (6.00 sec)
mysql> show global status like '%slow_queries%';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Slow_queries | 9 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)12. Show Profile
Show profile是什么?
show profile是mysql提供可以用来分析当前会话中语句执行的资源消耗情况。可以用于SQL的调优的测量。 默认情况下,参数处于关闭状态,并保存最近15次的运行结果。看看当前的mysql版本是否支持:show variables like 'profiling'。
mysql> show variables like 'profiling';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| profiling | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
开启功能,默认是关闭:set profiling = on。
mysql> set profiling = on;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like 'profiling';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| profiling | ON |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
运行SQL并查看结果:show profiles。
mysql> show profiles;
+----------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 0.00168575 | show variables like 'profiling' |
| 2 | 0.00005575 | ls |
| 3 | 0.00050675 | show databases |
| 4 | 0.00018875 | SELECT DATABASE() |
| 5 | 0.00028525 | show databases |
| 6 | 0.00019000 | show tables |
| 7 | 0.00033300 | show tables |
| 8 | 0.23495875 | select count(*) from emp |
| 9 | 1.13139000 | select * from emp |
| 10 | 0.00046550 | SELECT * from tbl_emp te where EXISTS (SELECT 1 from tbl_dept td where te.deptId = td.id ) |
+----------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
10 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
SQL诊断:show profile cpu,block io for query。
mysql> select sleep(6);
+----------+
| sleep(6) |
+----------+
| 0 |
+----------+
1 row in set (6.00 sec)
mysql> show profiles;
+----------+------------+-----------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+-----------------+
| 1 | 6.00039075 | select sleep(6) |
+----------+------------+-----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show profile cpu,block io for query 1;
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| starting | 0.000055 | 0.000023 | 0.000024 | 0 | 0 |
| Opening tables | 0.000014 | 0.000007 | 0.000007 | 0 | 0 |
| System lock | 0.000062 | 0.000030 | 0.000031 | 0 | 0 |
| checking permissions | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 |
| Opening tables | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| init | 0.000011 | 0.000005 | 0.000006 | 0 | 0 |
| optimizing | 0.000005 | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 |
| executing | 0.000009 | 0.000004 | 0.000005 | 0 | 0 |
| User sleep | 6.000078 | 0.002907 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 |
| end | 0.000027 | 0.000017 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| query end | 0.000007 | 0.000007 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| closing tables | 0.000005 | 0.000004 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| freeing items | 0.000021 | 0.000022 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| logging slow query | 0.000007 | 0.000006 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| Opening tables | 0.000013 | 0.000013 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| System lock | 0.000061 | 0.000061 | 0.000000 | 0 | 8 |
| cleaning up | 0.000012 | 0.000011 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
17 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)show profile * for query,其中“*”可用参数值如下:
ALL:显示所有的开销信息;
BLOCK IO:显示块IO相关开销;
CONTEXT SWITCHES:上下文切换相关开销;
CPU:显示CPU相关开销信息;
IPC:显示发送和接收相关开销信息;
MEMORY:显示内存相关开销信息;
PAGE FAULTS:显示页面错误相关开销信息;
SOURCE:显示和Source function,Source file,Source line相关的开销信息;
SWAPS:显示交换次数相关开销的信息。
SQL诊断结果中的参数及表示意思:
converting HEAP to MyISAM:查询结果太大,内存都不够用了往磁盘上搬了。
Creating tmp table:创建临时表,拷贝数据到临时表,用完再删除。
Copying to tmp table on disk:把内存中临时表复制到磁盘。
SQL优化总结:
-
开启慢查询并捕获SQL
-
explain + 慢 SQL 分析
-
show frofile 查询SQL在MySQL服务器里面的执行细节和生命周期情况
-
SQL数据库服务器参数调优





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本