2.2多线程(java学习笔记)线程状态及线程操作的相关方法
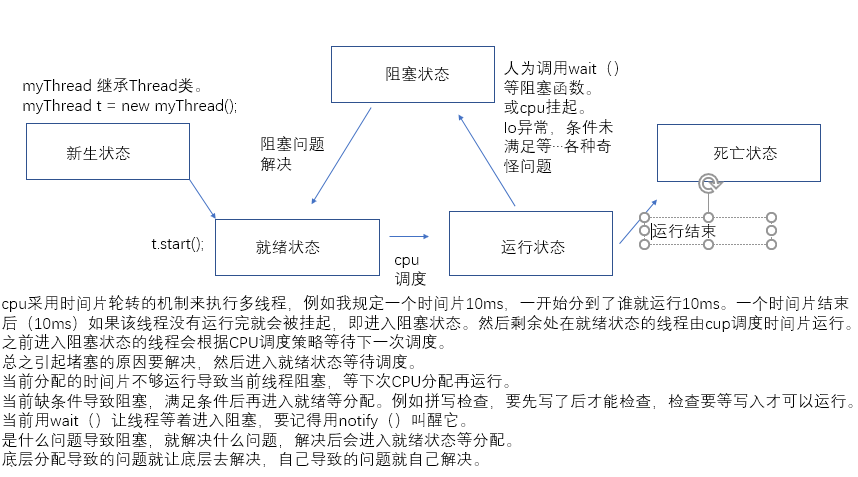
一、线程的状态
线程一般具有五种状态,即创建、就绪、运行、阻塞、终止。
它们之间的关系:
二、线程操作相关方法
1.设置和取得线程名称。
如果不设置线程名称,系统会自动分配线程名,一般格式为Thread-Xx
获取当前线程用Thread.currentThread.getName();
线程名称的设置,Thread类中已经建好了各种构造器。
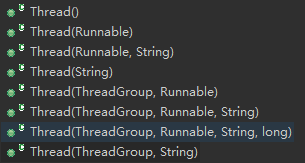
中间带有String的基本都是设置线程名称的,大家可以自行看下。
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 Thread t2 = new Thread(s, "线程t2"); 6 Thread t3 = new Thread(s); 7 8 t1.start(); 9 t2.start(); 10 t3.start(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 15 public void run(){ 16 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); 18 } 19 } 20 }
运行结果: 线程t1 i:0 Thread-0 i:0 线程t2 i:0 Thread-0 i:1 线程t1 i:1 Thread-0 i:2 线程t2 i:1 Thread-0 i:3 线程t1 i:2 Thread-0 i:4 线程t2 i:2 线程t1 i:3 线程t1 i:4 线程t2 i:3 线程t2 i:4
2.判断线程是否启动
判断当前线程是否“”活着“”,可能大家对于线程活着这个定义不是很清楚。说明点就是线程启动了,而且也没有死亡就称之为活着。
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 Thread t2 = new Thread(s, "线程t2"); 6 System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); //false 7 System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); //false 8 t1.start(); 9 System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); //ture 10 System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); //flase 11 t2.start(); //着这里加个延迟几秒就会发现下面会打印false。 12 System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); //这里的状态是不定的,假如指向到这t1和t2没有执行完,那么就是true 13 System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); //如果已经执行完毕进入死亡状态,这里就是false 14 } 15 } 16 17 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 18 public void run(){ 19 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); 21 } 22 } 23 }
false false true false true true 线程t1 i:0 线程t1 i:1 线程t1 i:2 线程t1 i:3 线程t1 i:4 线程t2 i:0 线程t2 i:1 线程t2 i:2 线程t2 i:3 线程t2 i:4
当现场处于就绪状态和运行状态都是true,可能又会有疑问那处于堵塞状态了。
我们接下里就测试下处于堵塞状态下isAlive();
public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(s, "线程t2"); System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); t1.start(); System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); t2.start(); System.out.println(t1.isAlive()); System.out.println(t2.isAlive()); } } class TestSleep implements Runnable{ synchronized public void run(){ try { this.wait(); //当前线程等待,即进堵塞状态 } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); } } }
运行结果: false false true false true true
可以发现最后两个线程都堵塞了,但最后打印的状态还是true,处于堵塞状态的线程也是存活的。
3.线程的强制加入
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 t1.start(); 6 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 7 if(i == 5){ 8 try { 9 t1.join(); //当i为5时,强制加入线程t1 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 } 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 21 synchronized public void run(){ 22 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); 24 } 25 } 26 }
main0 main1 main2 main3 main4 线程t1 i:0 线程t1 i:1 线程t1 i:2 线程t1 i:3 线程t1 i:4 main5 main6 main7 main8 main9
强制加入的线程运行完毕后才会让出资源。
4.线程的休眠
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 t1.start(); 6 } 7 } 8 9 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 10 synchronized public void run(){ 11 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(1000); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); 19 } 20 } 21 }
sleep(填入的数字代表毫秒),上图中填入的是1000代表休眠1s,运行后我们会发现每隔一秒打印一次线程名+ i的值。
5.线程的中断。
可以使用interrupt()方法中断线程的运行。
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 t1.start(); 6 t1.interrupt(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 11 public void run(){ 12 System.out.println("开始休眠10s"); 13 try { 14 Thread.sleep(10000); 15 System.out.println("完成休眠"); 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 18 System.out.println("当前线程被中断,休眠失败"); 19 }
20 System.out.println("run正常运行结束"); 21 } 22 }
如上代码没有被中断应是线程进入run中“开始休眠10s”,10s后会打印出“休眠完成”,"正常运行结束。"
运行我们会发现一运行就出现了“开始休眠10s”,"当前线程被中断,休眠失败",说明执行t1.interrupt()后t1线程被中断了执行。
运行结果:
开始休眠10s
当前线程被中断,休眠失败
6.线程的礼让
1 public class TestThread { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestSleep s = new TestSleep(); 4 Thread t1 = new Thread(s, "线程t1"); 5 t1.start(); 6 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ 7 if(i == 5){ 8 System.out.println("开始礼让:"); 9 Thread.currentThread().yield(); 10 } 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 16 class TestSleep implements Runnable{ 17 public void run(){ 18 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i:" + i ); 20 } 21 } 22 }
用yield()可以让当前线程暂停,暂时让其他线程来运行。
是暂时让一会不是一直让,只让一会就不让了,具体调度要看CPU。
运行结果: main0 main1 main2 main3 main4 开始礼让: 线程t1 i:0 main5 main6 main7 main8 线程t1 i:1 main9 线程t1 i:2 线程t1 i:3 线程t1 i:4



