第六篇 Mysql数据库
Mysql数据库
参考资源:1 sql自学网:http://xuesql.cn/
- 前期准备
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Python_bh/article/details/109565532?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
windows简单命令:
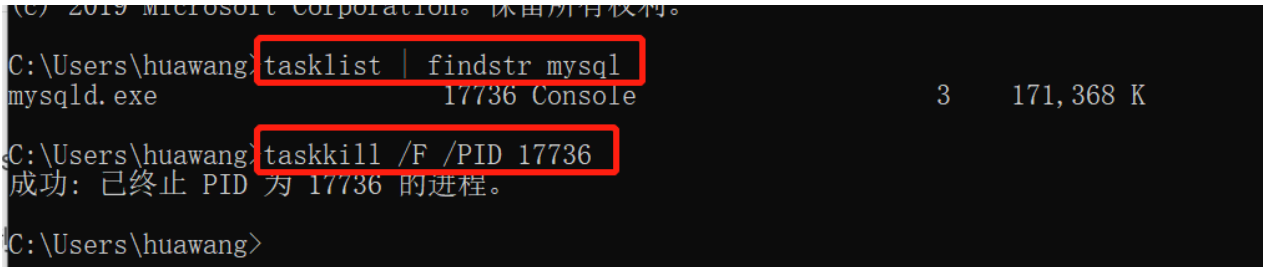
tasklist | findstr mysql 任务查找
taskkill /F /PID 17736 强制杀死任务
- mysql相关
windows安装 链接下载(msi)一键安装
1. 创建数据库&表结构并录入数据(可以自行创造数据) create database day27db default charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; use day27db; drop database day27db; drop database IF EXISTS day27db; 2.利用导入数据库命令: 导入: mysql -u root -p day27db < /Users/wupeiqi/day27db.sql 导出: # 结构+数据 mysqldump -u root -p day27db > /Users/wupeiqi/day27db2.sql #导出全部数据
mysqldump -uroot -p dbname test>db.sql # 导出test表的数据与结构 # 结构 mysqldump -u root -p -d day27db > /Users/wupeiqi/day27db3.sql
3 创建用户 luffy 并赋予此数据库的所有权限。
create user 'luffy'@'%' identified by 'root123';
如果创建失败,先执行下面两步操作,(可能未删除干净)
##drop user "root"@'localhost';
##flush privileges;
grant all privileges on day27db.* TO 'luffy'@'%';
flush privileges;
1 如果安装mysql出错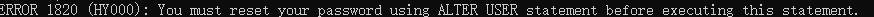
执行:

2 注意 一定要用管理员权限启动(避免错误)
3添加到用户服务(自启动) net_start_mysql
net_start_mysql注意:--install前,必须用mysql启动命令的绝对路径 # 制作MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行此命令: "c:\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\bin\mysqld" --install # 移除MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行此命令: "c:\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\bin\mysqld" --remove 注册成服务之后,以后再启动和关闭MySQL服务时,仅需执行如下命令: # 启动MySQL服务 net start mysql # 关闭MySQL服务 net stop mysql ———————————————— 版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Python_bh」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Python_bh/article/details/109565532
4 Ubuntu Server下启动/停止/重启MySQL数据库的三种方式(ubuntu 16.04)
 View Code
View Code启动mysql: 方式一:sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start 方式二:sudo service mysql start 停止mysql: 方式一:sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop 方式二:sudo service mysql stop 重启mysql: 方式一:sudo/etc/init.d/mysql restart 方式二:sudo service mysql restart
5 ubuntu root用户丢失,重新创建
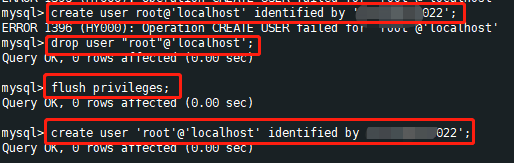
 创建root用户
创建root用户# 1 找到服务器自带默认用户 vim /etc/mysql/debian.cnf # 2 登录mysql user mysql; select * from user \G;#查看用户表 # 3 参考下面截图创建root用户
说明:localhost 应更换为“%”(方便远程连接)
 root@"%"说明
root@"%"说明Host列指定了允许用户登录所使用的IP,比如user=root Host=192.168.1.1。这里的意思就是说root用户只能通过192.168.1.1的客户端去访问。 而%是个通配符,如果Host=192.168.1.%,那么就表示只要是IP地址前缀为“192.168.1.”的客户端都可以连接。如果Host=%,表示所有IP都有连接权限。、 这也就是为什么在开启远程连接的时候,大部分人都直接把Host改成%的缘故,为了省事
6 linux修改用户密码
 skip-grant-tables
skip-grant-tablesvim /etc/mysql/mysql.cnf !includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/ !includedir /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/ [mysqld] skip-grant-tables 2 修改密码 update mysql.user set password=password("123") where user="root" and host="localhost";
方式二:
# 前面为旧密码,password后面为新密码 mysqladmin -uroot -p123456 password micagentmysql 格式化输出
# 使用G按行垂直显示结果 mysql> select * from db_archivelog\G
其他参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/mayidudu/p/5983696.html6 mysql可视化工具(navicat)
链接:https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/zrUkgSCQwFZ 密码修改-配置文件
密码修改-配置文件---相关命令: 1 tasklist |findstr mysql 2 taskkill /F /PID 10556 #强制杀死 ----windows平台mysql密码设置 #1 关闭mysql - tasklist |findstr mysql - taskkill /F /PID 10556 #强制杀死 #2 在cmd中执行:mysqld --skip-grant-tables #3 在cmd中执行:mysql #4 执行如下sql: update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('') where user = 'root'; flush privileges; #5 tskill mysqld #或taskkill -f /PID 7832 #6 重新启动mysql -----配置文件my.ini -统一字符编码 #mysql5.5以上:修改方式有所改动 [mysqld] character-set-server=utf8 collation-server=utf8_general_ci [client] default-character-set=utf8 [mysql] default-character-set=utf8
 权限管理
权限管理1 权限管理 2 1、创建账号 3 # 本地账号 4 create user 'egon1'@'localhost' identified by '123'; # mysql -uegon1 -p123 5 # 远程帐号 6 create user 'egon2'@'192.168.31.10' identified by '123'; # mysql -uegon2 -p123 -h 服务端ip 7 create user 'egon3'@'192.168.31.%' identified by '123'; # mysql -uegon3 -p123 -h 服务端ip 8 create user 'egon3'@'%' identified by '123'; # mysql -uegon3 -p123 -h 服务端ip 9 10 2、授权 11 user:*.* 12 db:db1.* 13 tables_priv:db1.t1 14 columns_priv:id,name 15 16 grant all on *.* to 'egon1'@'localhost'; 17 grant select on *.* to 'egon1'@'localhost'; 18 revoke select on *.* from 'egon1'@'localhost'; 19 20 grant select on db1.* to 'egon1'@'localhost'; 21 revoke select on db1.* from 'egon1'@'localhost'; 22 23 24 grant select on db1.t2 to 'egon1'@'localhost'; 25 revoke select on db1.t2 from 'egon1'@'localhost'; 26 27 grant select(id,name),update(age) on db1.t2 to 'egon1'@'localhost';
 1数据库相关概念
1数据库相关概念1、数据库服务器:运行数据库管理软件的计算机 2、数据库管理软件:mysql,oracle,db2,slqserver 3、库:文件夹 4、表:文件 5、记录:事物一系列典型的特征:egon,male,18,oldgirl 6、数据:描述事物特征的符号
 2 初识SQL语句
2 初识SQL语句1 SQL语句: 2 3 操作文件夹(库) 4 增 5 create database db1 charset utf8; 6 查 7 show create database db1; 8 show databases; 9 改 10 alter database db1 charset gbk; 11 删 12 drop database db1; 13 14 操作文件(表) 15 切换文件夹:use db1; 16 查看当前所在文件夹:select database(); 17 18 增 19 create table t1(id int,name char); 20 查 21 show create table t1; 22 show tables; 23 desc t1; 24 改 25 alter table t1 modify name char(6); 26 alter table t1 change name NAME char(7); 27 删 28 drop table t1; 29 30 操作文件内容(记录) 31 增 32 insert t1(id,name) values(1,'egon1'),(2,'egon2'),(3,'egon3'); 33 查 34 select id,name from db1.t1; 35 select * from db1.t1; 36 改 37 update db1.t1 set name='SB'; 38 update db1.t1 set name='ALEX' where id=2; 39 删 40 delete from t1 where id=2; 41 清空表: 42 delete from t1; 43 truncate table t1;(同时删除id)
 3 存储引擎介绍
3 存储引擎介绍1 1、什么是存储引擎? 2 存储引擎就是表的类型 3 4 2、查看MySQL支持的存储引擎 5 show engines; 6 7 8 3、指定表类型/存储引擎 9 create table t1(id int)engine=innodb; 10 create table t2(id int)engine=memory; 11 create table t3(id int)engine=blackhole; 12 create table t4(id int)engine=myisam; 13 14 15 insert into t1 values(1); 16 insert into t2 values(1); 17 insert into t3 values(1); 18 insert into t4 values(1);
 4 日期类型
4 日期类型1 create table student( 2 id int, 3 name char(6), 4 born_year year, 5 birth_date date, 6 class_time time, 7 reg_time datetime 8 ); 9 10 insert into student values 11 (1,'egon',now(),now(),now(),now()); 12 13 insert into student values 14 (2,'alex',"1997","1997-12-12","12:12:12","2017-12-12 12:12:12");
 5 字符类型
5 字符类型1 char:定长 2 varchar:变长 3 4 #宽度指的是字符的个数 5 create table t13(name char(5)); 6 create table t14(name varchar(5)); 7 8 insert into t13 values('李杰 '); #'李杰 ' 9 insert into t14 values('李杰 '); #'李杰 ' 10 11 12 select char_length(name) from t13; #5 13 select char_length(name) from t14; #3 14 15 16 select name from t13 where name='李杰'; 17 select name from t13 where name like '李杰'; 18 19 20 21 22 name char(5) 23 egon |alex |wxx | 24 25 26 name varchar(5) 27 1bytes+egon|1bytes+alex|1bytes+wxx| 28 4+egon|4+alex|3+wxx|
 6 枚举和集合类型
6 枚举和集合类型1 create table consumer( 2 id int, 3 name char(16), 4 sex enum('male','female','other'), 5 level enum('vip1','vip2','vip3'), 6 hobbies set('play','music','read','run') 7 ); 8 9 10 insert into consumer values 11 (1,'egon','male','vip2','music,read'); 12 13 insert into consumer values 14 (1,'egon','xxxxx','vip2','music,read');
 7.1 约束条件not null与default
7.1 约束条件not null与default1 create table t15( 2 id int(11) unsigned zerofill 3 ); 4 5 create table t16( 6 id int, 7 name char(6), 8 sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male' 9 ); 10 11 insert into t16(id,name) values(1,'egon');
 7.2 unique key
7.2 unique keyunique key 单列唯一 #方式一 create table department( id int unique, name char(10) unique ); #方式二: create table department( id int, name char(10), unique(id), unique(name) ); insert into department values (1,'IT'), (2,'Sale'); 联合唯一 create table services( id int, ip char(15), port int, unique(id), unique(ip,port) ); insert into services values (1,'192.168.11.10',80), (2,'192.168.11.10',81), (3,'192.168.11.13',80); insert into services values (4,'192.168.11.10',80);
 7.3 primary-key
7.3 primary-keyprimary key 约束:not null unique 存储引擎(innodb):对于innodb存储引擎来说,一张表内必须有一个主键 # 单列主键 create table t17( id int primary key, name char(16) ); insert into t17 values (1,'egon'), (2,'alex'); insert into t17 values (2,'wxx'); insert into t17(name) values ('wxx'); create table t18( id int not null unique, name char(16) ); # 复合主键 create table t19( ip char(15), port int, primary key(ip,port) ); insert into t19 values ('1.1.1.1',80), ('1.1.1.1',81);
 7.4 自增 &外键
7.4 自增 &外键1 auto_increment 2 3 create table t20( 4 id int primary key auto_increment, 5 name char(16) 6 ); 7 8 insert into t20(name) values 9 ('egon'), 10 ('alex'), 11 ('wxx'); 12 13 14 15 insert into t20(id,name) values 16 (7,'yuanhao'); 17 18 insert into t20(name) values 19 ('egon1'), 20 ('egon2'), 21 ('egon3'); 22 23 24 #了解 25 show variables like 'auto_inc%'; 26 27 #步长: 28 auto_increment_increment默认为1 29 #起始偏移量 30 auto_increment_offset默认1 31 32 #设置步长 33 set session auto_increment_increment=5; 34 set global auto_increment_increment=5; 35 36 #设置起始偏移量 37 set global auto_increment_offset=3; 38 强调:起始偏移量<=步长 39 40 create table t21( 41 id int primary key auto_increment, 42 name char(16) 43 ); 44 45 insert into t21(name) values 46 ('egon'), 47 ('alex'), 48 ('wxx'), 49 ('yxx'); 50 51 52 53 清空表: 54 delete from t20; 55 delete from t20 where id = 3; 56 insert into t20(name) values 57 ('xxx'); 58 59 truncate t20; #应该用它来清空表 60 61 62 63 foreign key:建立表之间的关系 64 65 #1、建立表关系: 66 #先建被关联的表,并且保证被关联的字段唯一 67 create table dep( 68 id int primary key, 69 name char(16), 70 comment char(50) 71 ); 72 73 74 #再建立关联的表 75 create table emp( 76 id int primary key, 77 name char(10), 78 sex enum('male','female'), 79 dep_id int, 80 foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id) 81 on delete cascade 82 on update cascade 83 ); 84 85 #2、插入数据 86 #先往被关联表插入记录 87 insert into dep values 88 (1,"IT","技术能力有限部门"), 89 (2,"销售","销售能力不足部门"), 90 (3,"财务","花钱特别多部门"); 91 92 #再往关联表插入记录 93 insert into emp values 94 (1,'egon','male',1); 95 96 insert into emp values 97 (2,'alex','male',1), 98 (3,'wupeiqi','female',2), 99 (4,'yuanhao','male',3), 100 (5,'jinximn','male',2); 101 102 103 104 105 delete from emp where dep_id=1; 106 delete from dep where id=1; 107 108 109 110 delete from dep where id=3;
 8 表关系
8 表关系1 两张表之间的关系: 2 1、多对一 3 出版社 书(foreign key(press_id) references press(id)) 4 2、多对多 5 作者 书 6 egon: 7 九阳神功 8 九阴真经 9 alex: 10 九阳神功 11 葵花宝典 12 yuanhao: 13 独孤九剑 14 降龙十巴掌 15 葵花宝典 16 wpq: 17 九阳神功 18 19 insert into author2book(author_id,book_id) values 20 (1,1), 21 (1,2), 22 (2,1), 23 (2,6); 24 25 26 3、一对一 27 customer表 student表 28
 8.1 单表查询
8.1 单表查询1 单表查询 2 3 select distinct 字段1,字段2,字段3 from 库.表 4 where 条件 5 group by 分组条件 6 having 过滤 7 order by 排序字段 8 limit n; 9 10 11 #where 12 select id,name,age from employee where id > 7; 13 14 select name,post,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary > 8000; 15 16 select name,salary from employee where salary >= 20000 and salary <= 30000; 17 select name,salary from employee where salary between 20000 and 30000; 18 19 select name,salary from employee where salary < 20000 or salary > 30000; 20 select name,salary from employee where salary not between 20000 and 30000; 21 22 23 select * from employee where age = 73 or age = 81 or age = 28; 24 select * from employee where age in (73,81,28); 25 26 select * from employee where post_comment is Null; 27 select * from employee where post_comment is not Null; 28 29 select * from employee where name like "jin%"; 30 select * from employee where name like "jin___"; 31 32 33 #group by 34 mysql> set global sql_mode="ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY"; 35 分组之后,只能取分组的字段,以及每个组聚合结果 36 37 select post from employee group by post; 38 39 #聚合函数 40 max 41 min 42 avg 43 sum 44 count 45 46 #每个职位有多少个员工 47 select post,count(id) as emp_count from employee group by post; 48 select post,max(salary) as emp_count from employee group by post; 49 select post,min(salary) as emp_count from employee group by post; 50 select post,avg(salary) as emp_count from employee group by post; 51 select post,sum(age) as emp_count from employee group by post; 52 53 #没有group by则默认整体算作一组 54 select max(salary) from employee; 55 56 #group_concat 57 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; 58 59 60 #练习: 61 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; 62 63 select post,count(id) from employee where age > 50 group by post; 64 65 select sex,count(id) from employee group by sex; 66 67 68 select sex,avg(salary) from employee group by sex 69 70 71 #having 72 select post,group_concat(name),count(id) from employee group by post; 73 74 select post,group_concat(name),count(id) from employee group by post having count(id) < 2; 75 76 77 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000; 78 79 80 #order by 81 select * from employee order by age asc; #升序 82 select * from employee order by age desc; #降序 83 84 select * from employee order by age asc,id desc; #先按照age升序排,如果age相同则按照id降序排 85 86 87 select distinct post,count(id) as emp_count from employee 88 where salary > 1000 89 group by post 90 having count(id) > 1 91 order by emp_count desc 92 ; 93 94 95 #limit 96 select * from employee limit 3; 97 select * from employee order by salary desc limit 1; 98 99 100 select * from employee limit 0,5; 101 select * from employee limit 5,5; 102 select * from employee limit 10,5; 103 select * from employee limit 15,5; 104 105 106 #总结: 107 语法顺序: 108 select distinct 字段1,字段2,字段3 from 库.表 109 where 条件 110 group by 分组条件 111 having 过滤 112 order by 排序字段 113 limit n; 114 115 执行顺序: 116 117 def from(db,table): 118 f=open(r'%s\%s' %(db,table)) 119 return f 120 121 def where(condition,f): 122 for line in f: 123 if condition: 124 yield line 125 126 def group(lines): 127 pass 128 129 def having(group_res): 130 pass 131 132 def distinct(having_res): 133 pass 134 135 def order(distinct_res): 136 pass 137 138 def limit(order_res) 139 pass 140 141 def select(): 142 f=from('db1','t1') 143 lines=where('id>3',f) 144 group_res=group(lines) 145 having_res=having(group_res) 146 distinct_res=distinct(having_res) 147 order_res=order(distinct_res) 148 res=limit(order_res) 149 print(res) 150 return res 151 152 #正则表达式 153 154 like 模糊查询: 155 select * from employee where name like 'jin%';(# %代表任意多个字符) 156 select * from employee where name like 'jin_' ( #'_' 表示任意单个字符) 157 158 regexp 正则匹配 159 select * from employee where name regexp '^jin'; 160 select * from employee where name regexp '^jin.*(g|n)$'; 161 162 163
 8.2 连表查询
8.2 连表查询1 内连接:只取两张表的共同部分 2 select * from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ; 3 4 左连接:在内连接的基础上保留左表的记录 5 select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ; 6 7 右连接:在内连接的基础上保留右表的记录 8 select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ; 9 10 全外连接:在内连接的基础上保留左右两表没有对应关系的记录 11 select * from employee full join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ; 12 13 14 select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id 15 union 16 select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ;
 存储过程
存储过程1 #1、无参存储过程 2 delimiter // 3 create procedure p1() 4 BEGIN 5 select * from db7.teacher; 6 END // 7 delimiter ; 8 9 10 # MySQL中调用 11 call p1(); 12 13 14 # Python中调用 15 cursor.callproc('p1') 16 17 18 #2、有参存储过程 19 delimiter // 20 create procedure p2(in n1 int,in n2 int,out res int) 21 BEGIN 22 select * from db7.teacher where tid > n1 and tid < n2; 23 set res = 1; 24 END // 25 delimiter ; 26 27 28 # MySQL中调用 29 set @x=0 30 call p2(2,4,@x); 31 select @x; 32 33 # Python中调用 34 cursor.callproc('p2',(2,4,0))# @_p2_0=2,@_p2_1=4,@_p2_2=0 35 cursor.execute('select @_p3_2') 36 cursor.fetchone() 37 38 39 40 41 应用程序与数据库结合使用 42 方式一: 43 Python:调用存储过程 44 MySQL:编写存储过程 45 46 47 方式二: 48 Python:编写纯生SQL 49 MySQL: 50 51 方式三: 52 Python:ORM->纯生SQL 53 MySQL: 54 55 56 57
 函数相关(如date_format)
函数相关(如date_format)1 CREATE TABLE blog ( 2 id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, 3 NAME CHAR (32), 4 sub_time datetime 5 ); 6 7 INSERT INTO blog (NAME, sub_time) 8 VALUES 9 ('第1篇','2015-03-01 11:31:21'), 10 ('第2篇','2015-03-11 16:31:21'), 11 ('第3篇','2016-07-01 10:21:31'), 12 ('第4篇','2016-07-22 09:23:21'), 13 ('第5篇','2016-07-23 10:11:11'), 14 ('第6篇','2016-07-25 11:21:31'), 15 ('第7篇','2017-03-01 15:33:21'), 16 ('第8篇','2017-03-01 17:32:21'), 17 ('第9篇','2017-03-01 18:31:21'); 18 19 20 21 select date_format(sub_time,'%Y-%m'),count(id) from blog group by date_format(sub_time,'%Y-%m')
 where约束查询(in,between,like等))
where约束查询(in,between,like等))1 where字句中可以使用: 2 3 1比较运算符:><>= <= <> != 4 2between 80 and 100 值在80到100之间 5 3in(80,90,100) 值是80或90或100 6 4 like 'egon%' 7 pattern可以是%或_, 8 %表示任意多字符 9 _表示一个字符 10 5逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not 11 12 #1:单条件查询 13 SELECT name FROM employee 14 WHERE post='sale'; 15 16 #2:多条件查询 17 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 18 WHERE post='teacher' AND salary>10000; 19 20 #3:关键字BETWEEN AND 21 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 22 WHERE salary BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; 23 24 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 25 WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; 26 27 #4:关键字IS NULL(判断某个字段是否为NULL不能用等号,需要用IS) 28 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee 29 WHERE post_comment IS NULL; 30 31 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee 32 WHERE post_comment IS NOT NULL; 33 34 SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee 35 WHERE post_comment=''; 注意''是空字符串,不是null 36 ps: 37 执行 38 update employee set post_comment='' where id=2; 39 再用上条查看,就会有结果了 40 41 #5:关键字IN集合查询 42 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 43 WHERE salary=3000 OR salary=3500 OR salary=4000 OR salary=9000 ; 44 45 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 46 WHERE salary IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; 47 48 SELECT name,salary FROM employee 49 WHERE salary NOT IN (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; 50 51 #6:关键字LIKE模糊查询 52 通配符’%’ 53 SELECT * FROM employee 54 WHERE name LIKE 'eg%'; 55 56 通配符’_’ 57 SELECT * FROM employee 58 WHERE name LIKE 'al__'; 59 1. 查看岗位是teacher的员工姓名、年龄 60 2. 查看岗位是teacher且年龄大于30岁的员工姓名、年龄 61 3. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资在9000-1000范围内的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 62 4. 查看岗位描述不为NULL的员工信息 63 5. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 64 6. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资不是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 65 7. 查看岗位是teacher且名字是jin开头的员工姓名、年薪 66 select name,age from employee where post = 'teacher'; 67 select name,age from employee where post='teacher' and age > 30; 68 select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary between 9000 and 10000; 69 select * from employee where post_comment is not null; 70 select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary in (10000,9000,30000); 71 select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary not in (10000,9000,30000); 72 select name,salary*12 from employee where post='teacher' and name like 'jin%';
- pymysql
 pymysql基本使用
pymysql基本使用1 #pip3 install pymysql 2 import pymysql 3 4 user=input('user>>: ').strip() 5 pwd=input('password>>: ').strip() 6 7 # 建立链接 8 conn=pymysql.connect( 9 host='192.168.10.15', 10 port=3306, 11 user='root', 12 password='123', 13 db='db9', 14 charset='utf8' 15 ) 16 17 # 拿到游标 18 cursor=conn.cursor() 19 20 # 执行sql语句 21 22 # sql='select * from userinfo where user = "%s" and pwd="%s"' %(user,pwd) 23 # print(sql) 24 25 sql='select * from userinfo where user = %s and pwd=%s' 26 rows=cursor.execute(sql,(user,pwd)) 27 28 cursor.close() 29 conn.close() 30 31 # 进行判断 32 if rows: 33 print('登录成功') 34 else: 35 print('登录失败')
 pymsql 增,删,改
pymsql 增,删,改1 #1、增删改 2 import pymysql 3 4 # 建立链接 5 conn=pymysql.connect( 6 host='127.0.0.1', 7 port=3306, 8 user='root', 9 password='', 10 db='text1', 11 charset='utf8' 12 ) 13 14 # 拿游标 15 cursor=conn.cursor() 16 17 # 执行sql 18 # 增、删、改 19 20 21 ################## 1 插入数据 ########### 22 # 单条插入 23 # sql='insert into t1(user,pwd) values(%s,%s)' 24 # # rows=cursor.execute(sql,('wxx','123')) # 25 # rows = cursor.execute('insert into t1(user,pwd) values(%(user)s, %(pwd)s)',{'user':'hah','pwd':'123'}) 26 # print(rows) 27 # 28 # # 批量插入 29 # rows=cursor.executemany(sql,[('egon3','123'),('egon4','111'),('egon5','2222')]) # 批量插入 30 # print(cursor.lastrowid) 31 32 ################## 2 修改数据 ########### 33 # sql='update t1 set user = %s where user ="wxx"' 34 # rows = cursor.execute(sql,("wh")) 35 # print(rows) 36 37 38 ################## 3 删除数据 ########### 39 # sql='delete from t1 where user like "%alin%"' 40 # rows = cursor.execute(sql) 41 # print(rows) 42 43 # conn.commit() 44 45 # # 关闭 46 # cursor.close() 47 # conn.close()
 pymsql 查询
pymsql 查询1 ################## 4 查询数据 ########### 2 3 4 # import pymysql 5 # 6 # # 建立链接 7 # conn=pymysql.connect( 8 # host='192.168.10.15', 9 # port=3306, 10 # user='root', 11 # password='123', 12 # db='db9', 13 # charset='utf8' 14 # ) 15 16 # 拿游标 17 # cursor=conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 18 19 # 执行sql 20 # 查询 21 # rows=cursor.execute('select * from t1;') 22 # print(rows) 23 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 24 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 25 26 27 28 # print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) 29 30 # print(cursor.fetchall()) 31 # print(cursor.fetchall()) 32 33 34 35 # cursor.scroll(3,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动 36 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 37 # cursor.scroll(2,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动 38 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 39 40 # 41 42 # 关闭 43 # cursor.close() 44 # conn.close()
 存储过程的执行
存储过程的执行#1、增删改 import pymysql # 建立链接 conn=pymysql.connect( host='192.168.10.15', port=3306, user='root', password='123', db='db7', charset='utf8' ) # 拿游标 cursor=conn.cursor() # 执行sql # cursor.callproc('p1') # print(cursor.fetchall()) cursor.callproc('p2',(2,4,0)) # print(cursor.fetchall()) cursor.execute('select @_p2_2') print(cursor.fetchone()) # 关闭 cursor.close() conn.close()
- 事务
 事务
事务import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8", db='userdb') cursor = conn.cursor() # 开启事务 conn.begin() try: cursor.execute("update users set amount=1 where id=1") int('asdf') cursor.execute("update tran set amount=2 where id=2") except Exception as e: # 回滚 print("回滚") conn.rollback() else: # 提交 print("提交") conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
- 排他锁
 应用场景:总共100件商品,每次购买一件需要让商品个数减1
应用场景:总共100件商品,每次购买一件需要让商品个数减1A: 访问页面查看商品剩余 100 B: 访问页面查看商品剩余 100 此时 A、B 同时下单,那么他们同时执行SQL: update goods set count=count-1 where id=3 由于Innodb引擎内部会加锁,所以他们两个即使同一时刻执行,内部也会排序逐步执行。 但是,当商品剩余 1个时,就需要注意了。 A: 访问页面查看商品剩余 1 B: 访问页面查看商品剩余 1 此时 A、B 同时下单,那么他们同时执行SQL: update goods set count=count-1 where id=3 这样剩余数量就会出现 -1,很显然这是不正确的,所以应该怎么办呢? 这种情况下,可以利用 排它锁,在更新之前先查询剩余数量,只有数量 >0 才可以购买,所以,下单时应该执行: begin; -- start transaction; select count from goods where id=3 for update; -- 获取个数进行判断 if 个数>0: update goods set count=count-1 where id=3; else: -- 已售罄 commit;
 排他锁(for update)
排他锁(for update)import pymysql import threading def task(): conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8", db='userdb') cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # cursor = conn.cursor() # 开启事务 conn.begin() cursor.execute("select id,age from tran where id=2 for update") # fetchall ( {"id":1,"age":10},{"id":2,"age":10}, ) ((1,10),(2,10)) # {"id":1,"age":10} (1,10) result = cursor.fetchone() current_age = result['age'] if current_age > 0: cursor.execute("update tran set age=age-1 where id=2") else: print("已售罄") conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close() def run(): for i in range(5): t = threading.Thread(target=task) t.start() if __name__ == '__main__': run()
- SQL工具类(数据库连接池)
1 单例与方法
 SQL操作类(基于数据库连接池)
SQL操作类(基于数据库连接池)# db.py # 单例与方法 import pymysql from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB class DBHelper(object): def __init__(self): # TODO 此处配置,可以去配置文件中读取。 self.pool = PooledDB( creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块 maxconnections=5, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数 mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建 maxcached=3, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制 blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错 setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set datestyle to ...", "set time zone ..."] ping=0, # ping MySQL服务端,检查是否服务可用。# 如:0 = None = never, 1 = default = whenever it is requested, 2 = when a cursor is created, 4 = when a query is executed, 7 = always host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='root123', database='userdb', charset='utf8' ) def get_conn_cursor(self): conn = self.pool.connection() cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) return conn, cursor def close_conn_cursor(self, *args): for item in args: item.close() def exec(self, sql, **kwargs): conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor() cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) conn.commit() self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor) def fetch_one(self, sql, **kwargs): conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor() cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) result = cursor.fetchone() self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor) return result def fetch_all(self, sql, **kwargs): conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor() cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) result = cursor.fetchall() self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor) return result db = DBHelper()
from db import db db.exec("insert into d1(name) values(%(name)s)", name="华王666") ret = db.fetch_one("select * from d1") print(ret) ret = db.fetch_one("select * from d1 where id=%(nid)s", nid=3) print(ret) ret = db.fetch_all("select * from d1") print(ret) ret = db.fetch_all("select * from d1 where id>%(nid)s", nid=2) print(ret)
2 基于上下文管理 db_context.py
db_context.py# db_context.py import threading import pymysql from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB POOL = PooledDB( creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块 maxconnections=5, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数 mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建 maxcached=3, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制 blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错 setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set datestyle to ...", "set time zone ..."] ping=0, host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='root123', database='userdb', charset='utf8' ) class Connect(object): def __init__(self): self.conn = conn = POOL.connection() self.cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) def __enter__(self): return self def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb): self.cursor.close() self.conn.close() def exec(self, sql, **kwargs): self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) self.conn.commit() def fetch_one(self, sql, **kwargs): self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) result = self.cursor.fetchone() return result def fetch_all(self, sql, **kwargs): self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs) result = self.cursor.fetchall() return result
from db_context import Connect with Connect() as obj: # print(obj.conn) # print(obj.cursor) ret = obj.fetch_one("select * from d1") print(ret) ret = obj.fetch_one("select * from d1 where id=%(id)s", id=3) print(ret)
-
操作表(utils)
 原生sql示例
原生sql示例#操作表 #1、自行创建测试数据; #班级表:class create table class( cid int primary key auto_increment, caption char(5), grade_id int ); insert into class values (1,'一年一班',1), (2,'二年一班',2), (3,'三年二班',3); #2、查询学生总人数; select count(sid) as total_sid from student; #3、查询“生物”课程和“物理”课程成绩都及格的学生id和姓名; #成绩表与课程表连表-一学生分组-找出条件 select sid,sname from student where sid in (select student_id from score inner join course #连表 on score.course_id=course.cid where score>=60 and cname ='生物' or cname ='物理' group by # 学生id分组 score.student_id having count(course_id)=2); #4、查询每个年级的班级数,取出班级数最多的前三个年级; select gname,count(gname) from class inner join class_grade on class.grade_id=class_grade.gid group by gname order by count(gname)desc limit(3); #5、查询平均成绩最高和最低的学生的id和姓名以及平均成绩; select sid, sname, t1.avg_score from student inner join( select student_id, avg(score)as avg_score from score group by student_id having avg(score) in( (select avg(score)as low_score from score group by student_id order by avg(score) limit 1), (select avg(score)as high_score from score group by student_id order by avg(score) desc limit 1)) )as t1 on student.sid=t1.student_id; #6、查询每个年级的学生人数; # 学生与班级连表-grade_id分组-统计人数 select grade_id,count(sid)as total_student from (select class.grade_id,student.sid from student inner join class on student.class_id=class.cid) as t1 group by t1.grade_id; #7、查询每位学生的学号,姓名,选课数,平均成绩; select sid, sname, t1.total_course, t1.avg_score from student left join( select student_id, count(course_id)as total_course, avg(score)as avg_score from score group by student_id )as t1 on student.sid=t1.student_id; #8、查询学生编号为“2”的学生的姓名、该学生成绩最高的课程名、成绩最低的课程名及分数; select sid, sname, t1.course_id, t1.score from student inner join( select student_id, course_id, score from score where score in( (select score from score where student_id=2 order by score desc limit 1), (select score from score where student_id=2 order by score limit 1 ) ) )as t1 on student.sid=t1.student_id; #9、查询姓“李”的老师的个数和所带班级数; select count(t1.tid)as total_li, count(teach2cls.cid)as total_class from teach2cls inner join( select tid from teacher where tname like "李%" )as t1 on teach2cls.tid=t1.tid #10、查询班级数小于5的年级id和年级名; select gid, gname from class_grade where gid in (select #年纪id与对应班级数的表 grade_id from class group by grade_id having count(cid)<5); #11、查询班级信息,包括班级id、班级名称、年级、年级级别(12为低年级,34为中年级,56为高年级) #班级id 班级名称 年级 年级级别 #1 一年一班 一年级 低 #班级表与年纪表连表--加入级别 select class.cid as '班级id', class.caption as '班级名称', class_grade.gname as '年级', case when class_grade.gid between 1 and 2 then '低' when class_grade.gid between 3 and 4 then '中' when class_grade.gid between 5 and 6 then '高' else 0 end as '年级级别' from class, class_grade where class.grade_id = class_grade.gid; #12、查询学过“张三”老师2门课以上的同学的学号、姓名; # 课程表与老师表连表--选出张三老师的课程-到成绩表以学生分类-统计符合条件学生 select student_id from score where course_id in (select course.cid from course inner join teacher on course.teacher_id=teacher.tid where teacher.tname='张三') group by student_id having count(course_id)>=2; #13、查询教授课程超过2门的老师的id和姓名; select tid, tname from teacher where tid in (select teacher_id from course group by teacher_id having count(cid)>2 ); #14、查询学过编号“1”课程和编号“2”课程的同学的学号、姓名; select sid,sname from student where sid in (select student_id from score where course_id in ('1','2') group by student_id having count(course_id)=2); #15、查询没有带过高年级的老师id和姓名; select tid, tname from teacher where tid in (select tid from teach2cls where cid in (select cid from class where grade_id<3)); #16、查询学过“张三”老师所教的所有课的同学的学号、姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid in ( select distinct student_id from score where course_id in ( select cid from course where teacher_id in( select tid from teacher where tname='张三' ) ) ); #17、查询带过超过2个班级的老师的id和姓名; select tid, tname from teacher where tid in ( select tid from teach2cls group by tid having count(cid)>2 ); #18、查询课程编号“2”的成绩比课程编号“1”课程低的所有同学的学号、姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid in ( select s1.student_id from score as s1 inner join score as s2 on s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.course_id = 1 and s2.course_id = 2 where s1.score < s2.score); #19、查询所带班级数最多的老师id和姓名; select tid, tname from teacher where tid in ( select tid from teach2cls group by tid having count(cid)=( select count(cid) from teach2cls group by tid order by count(cid) desc limit 1 ) ); #20、查询有课程成绩小于60分的同学的学号、姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid in ( select student_id from score where score<60 ); #21、查询没有学全所有课的同学的学号、姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid not in (select student_id from score group by student_id having count(course_id)=(select count(cid) from course) ); #22、查询至少有一门课与学号为“1”的同学所学相同的同学的学号和姓名; select sid,sname from student where sid in ( select distinct student_id from score where course_id in( select course_id from score where student_id =1 ) ) and sid !=1; #23、查询至少学过学号为“1”同学所选课程中任意一门课的其他同学学号和姓名; select sid,sname from student where sid in ( select distinct student_id from score where course_id in( select course_id from score where student_id =1 ) ) and sid !=1; #24、查询和“2”号同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学的学号和姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid in ( select student_id from score, (select course_id from score where student_id=2)as t1 where score.course_id = t1.course_id and score.student_id !=2 group by score.student_id having count(score.course_id)=(select count(course_id)from score where student_id=2) ); #25、删除学习“张三”老师课的score表记录; delete from score where course_id in ( select cid from course where teacher_id =( select tid from teacher where tname='张三') ); #26、向score表中插入一些记录,这些记录要求符合以下条件:①没有上过编号“2”课程的同学学号;②插入“2”号课程的平均成绩; insert score(student_id,course_id,score) select t1.sid,2,t2.avg_score from( (select sid from student where sid not in (select student_id from score where course_id = 2)) as t1, (select avg(score)as avg_score from score where course_id = 2) as t2); #27、按平均成绩从低到高显示所有学生的“语文”、“数学”、“英语”三门的课程成绩,按如下形式显示:学生ID,语文,数学,英语,课程数和平均分; select student_id, (select score from score where course_id =(select cid from course where cname='语文') and score.student_id =s1.student_id ) as '语文', (select score from score where course_id =(select cid from course where cname='数学') and score.student_id =s1.student_id ) as '数学', (select score from score where course_id =(select cid from course where cname='英语') and score.student_id =s1.student_id ) as '英语', count(course_id) as '有效课程数', avg(score) as '有效平均分' from score as s1 group by student_id order by avg(score); #28、查询各科成绩最高和最低的分:以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分; select course_id as id, max(score.score) as '最高分', min(score.score) as '最低分' from course left join score on score.course_id=course.cid group by course_id; #29、按各科平均成绩从低到高和及格率的百分数从高到低顺序; select course_id, avg(score) as avg_score, sum(case when score.score >= 60 then 1 else 0 end) / count(sid) * 100 as percent from score group by course_id order by avg(score) asc,percent desc; #30、课程平均分从高到低显示(现实任课老师); select t1.cid, t1.tname, t2.avg_score from( select teacher.tid as tid, teacher.tname as tname, course.cid as cid from teacher inner join course on teacher.tid = teacher_id )as t1 inner join (select course_id,avg(score)as avg_score from score group by course_id )as t2 on t1.cid=t2.course_id order by avg_score desc; #31、查询各科成绩前三名的记录(不考虑成绩并列情况) ; select student_id, score, course_id from score r1 where (SELECT count(1) from (select distinct score, course_id from score) r2 where r2.course_id = r1.course_id AND r2.score > r1.score) <= 2 order by course_id, score DESC; #32、查询每门课程被选修的学生数; select course_id, count(student_id) from score group by course_id; #33、查询选修了2门以上课程的全部学生的学号和姓名; elect sid, sname from student where sid in( select student_id from score group by student_id having count(course_id)>2); #34、查询男生、女生的人数,按倒序排列; select gender, count(sid) from student group by gender order by count(sid) desc; #35、查询姓“张”的学生名单; select * from student where sname like "张%"; #36、查询同名同姓学生名单,并统计同名人数; select sname, count(sid) from student group by sname having count(sid)>1; #37、查询每门课程的平均成绩,结果按平均成绩升序排列,平均成绩相同时,按课程号降序排列; select course_id, avg(score) from score group by course_id order by avg(score), course_id desc; #38、查询课程名称为“数学”,且分数低于60的学生姓名和分数; select student.sname, t1.score from student inner join ( select student_id, score from score where score.score<60 and course_id in ( select cid from course where cname='数学' ) )as t1 on t1.student_id=student.sid; #39、查询课程编号为“3”且课程成绩在80分以上的学生的学号和姓名; select sid, sname from student where sid in( select student_id from score where course_id=3 and score>80 ); #41、查询选修“王五”老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高和最低的学生姓名及其成绩; select s1.student_id, low_score, s2.student_id, high_score from( select tid, student_id, score as low_score from (select student_id,cid,cname,score,tid from score inner join (select tid,tname,cid,cname from teacher inner join course on teacher.tid=course.teacher_id where tname='王五')as t1 on score.course_id=t1.cid)as t2 order by score limit 1) as s1 inner join ( select tid,student_id,score as high_score from (select student_id,cid,cname,score,tid from score inner join (select tid,tname,cid,cname from teacher inner join course on teacher.tid=course.teacher_id where tname='王五')as t1 on score.course_id=t1.cid)as t2 order by score desc limit 1) as s2 on s1.tid=s2.tid; #42、查询各个课程及相应的选修人数; select course_id , count(student_id) from score group by course_id; #43、查询不同课程但成绩相同的学生的学号、课程号、学生成绩; select distinct s1.course_id, s1.student_id, s1.score, s2.course_id, s2.student_id, s2.score from score as s1, score as s2 where s1.score = s2.score and s1.course_id != s2.course_id; #44、查询每门课程成绩最好的前两名学生id和姓名; select student.sid,student.sname,course.cname, score.score from score inner join ( select course_id, score, ranking from ( select a.course_id, a.score, count(1) as ranking from (select course_id, score from score group by course_id, score order by course_id, score desc)as a inner join (select course_id, score from score group by course_id, score order by course_id, score desc)as b on a.course_id = b.course_id and a.score <= b.score group by course_id, score ) as t1 where ranking in (1, 2) order by course_id, ranking)as s1 on score.course_id = s1.course_id and score.score = s1.score inner join student on score.student_id = student.sid inner join course on score.course_id = course.cid; #45、检索至少选修两门课程的学生学号; select student_id from score group by student_id having count(course_id)>=2; #46、查询没有学生选修的课程的课程号和课程名; select course.cid, course.cname from course left join score on course.cid=score.course_id where score.student_id is null; #47、查询没带过任何班级的老师id和姓名; select teacher.tid, tname from teacher left join teach2cls on teacher.tid=teach2cls.tid where teach2cls.tcid is null; #48、查询有两门以上课程超过80分的学生id及其平均成绩; select student_id, avg(score) from score where score>80 group by student_id having count(course_id)>2; #49、检索“3”课程分数小于60,按分数降序排列的同学学号; select student_id, score from score where score<60 and course_id=3 order by score desc; #50、删除编号为“2”的同学的“1”课程的成绩; delete from score where student_id='2' and course_id='1'; #51、查询同时选修了物理课和生物课的学生id和姓名 select student.sid, student.sname from student where sid in ( select student_id from score where course_id IN ( select cid from course where cname = '物理' or cname = '生物' ) group by student_id having count(course_id) = 2 );
 SQLHelper
SQLHelper1 """ 2 3 使用 4 from mysql_utils.sql import SQLHelper 5 6 sql ="select * from 36kr" 7 print(SQLHelper.fetch_one(sql)) 8 print(SQLHelper.fetch_all(sql)) 9 10 # print(SQLHelper.fetchdic_one_dict(sql,{})) 11 # print(SQLHelper.fetch_all_list_dict(sql,{})) 12 """ 13 14 import pymysql 15 16 17 class SQLHelper(object): 18 19 @staticmethod 20 def open(cursor): 21 conn = pymysql.connect( 22 host='127.0.0.1', 23 port=3306, 24 user='root', 25 password='', 26 db='new_source', 27 charset='utf8' 28 ) 29 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=cursor) 30 return conn,cursor 31 32 @staticmethod 33 def close(conn,cursor): 34 conn.commit() 35 cursor.close() 36 conn.close() 37 38 @classmethod 39 def fetch_one(cls, sql, cursor=None): 40 """ 41 默认返回一个元组 42 :param sql: 43 :param args: 44 :param cursor: 45 :return: 46 """ 47 conn, cursor = cls.open(cursor) 48 cursor.execute(sql) 49 obj = cursor.fetchone() 50 cls.close(conn, cursor) 51 return obj 52 53 @classmethod 54 def fetch_all(cls, sql, cursor=None): 55 conn, cursor = cls.open(cursor) 56 cursor.execute(sql) 57 obj = cursor.fetchall() 58 cls.close(conn, cursor) 59 return obj 60 61 @classmethod 62 def fetchdic_one_dict(cls, sql, args, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor): 63 """ 64 默认返回一个字典 65 :param sql: 66 :param args: 67 :param cursor: 68 :return:{'id': 4, 'name': 'egon3', 'count': 123} 69 """ 70 conn, cursor = cls.open(cursor) 71 cursor.execute(sql, args) 72 obj = cursor.fetchone() 73 cls.close(conn, cursor) 74 return obj 75 @classmethod 76 def fetch_all_list_dict(cls,sql, args,cursor =pymysql.cursors.DictCursor): 77 """ 78 返回一个列表,列表元素为字典 79 :param sql: 80 :param args: 81 :param cursor: 82 :return: #[{'id': 4, 'name': 'egon3', 'count': 123}, {'id': 5, 'name': 'egon4', 'count': 111}] 83 """ 84 conn, cursor = cls.open(cursor) 85 cursor.execute(sql, args) 86 obj = cursor.fetchall() 87 cls.close(conn, cursor) 88 return obj
 mysql_utils
mysql_utils1 #coding:utf-8 2 import MySQLdb 3 import json 4 import time 5 6 7 db = "" 8 cursor = "" 9 def db_init(): 10 global db 11 global cursor 12 # db = MySQLdb.connect("", "c396313051","123456ok","news", charset="utf8mb4") 13 db = MySQLdb.connect("", "root","","news_crawl",port=22936,charset="utf8mb4") 14 cursor = db.cursor() 15 # 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标 16 # print("Connection is successful!") 17 18 def db_close(): 19 db.close() 20 21 def db_commit(): 22 db.commit() 23 24 def get_unupdate_count(): 25 db_init() 26 sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM news_detail WHERE flag_content_update = '0' " 27 try: 28 cursor.execute(sql) 29 result = cursor.fetchall() 30 # print("result", result) 31 print("result", result[0][0]) 32 return result 33 except Exception as e: 34 print("ERROR", e) 35 36 def get_unupdate_news(): 37 db_init() 38 sql = "SELECT * FROM news_detail WHERE flag_content_update = '0' AND web_source = 'techweb' ORDER BY release_time DESC LIMIT 5000" 39 try: 40 cursor.execute(sql) 41 result = cursor.fetchall() 42 # print("result", result) 43 news_list = [] 44 for row in result: 45 news_id = row[6] 46 news_url = row[1] 47 news_web_source = row[5] 48 news_list.append({ 49 "id": news_id, 50 "url": news_url, 51 "web_source": news_web_source 52 }) 53 print("news_list", news_list) 54 return news_list 55 except Exception as e: 56 print("ERROR", e) 57 58 def check_news(title, web_source): 59 db_init() 60 sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM news_detail WHERE title = '%s' AND web_source = '%s'" %(title, web_source) 61 try: 62 cursor.execute(sql) 63 result = cursor.fetchall() 64 # print("result", result) 65 print("result", result[0][0]) 66 return result[0][0] 67 except Exception as e: 68 print("ERROR", e) 69 70 def update_news_content(news_id, news_content): 71 if news_content != None: 72 db_init() 73 sql = "UPDATE news_detail SET content = '%s', flag_content_update = '1' WHERE id = '%s'" % (news_content, news_id) 74 try: 75 cursor.execute(sql) 76 db.commit() 77 print("content已更新!", news_id) 78 except Exception as e: 79 print("ERROR", e) 80 db.rollback() 81 82 def get_latest_data_50(web_source): 83 db_init() 84 sql = "SELECT * FROM news_detail WHERE web_source = '%s' ORDER BY release_time DESC LIMIT 50" % (web_source) 85 try: 86 cursor.execute(sql) 87 result = cursor.fetchall() 88 # print("result", result) 89 title_list = [] 90 for row in result: 91 title = row[0] 92 title_list.append(title) 93 # print("title_list", title_list) 94 return title_list 95 except Exception as e: 96 print("ERROR", e) 97 98 def get_latest_data(web_source): 99 db_init() 100 sql = "SELECT * FROM news_detail WHERE web_source = '%s' ORDER BY release_time DESC LIMIT 10" % (web_source) 101 try: 102 cursor.execute(sql) 103 result = cursor.fetchall() 104 # print("result", result) 105 title_list = [] 106 for row in result: 107 title = row[0] 108 title_list.append(title) 109 # print("title_list", title_list) 110 return title_list 111 except Exception as e: 112 print("ERROR", e) 113 114 def getData(source_name_val): 115 db_init() 116 # cursor = db.cursor() 117 sql = "SELECT * FROM source_info WHERE source_name = '%s'" % (source_name_val) 118 try: 119 cursor.execute(sql) 120 results = cursor.fetchall() 121 for row in results: 122 source_name = row[0] 123 update_time = row[1] 124 latest_news = row[2] 125 # print("source_name", source_name) 126 # print("update_time", update_time) 127 # print("latest_news", json.loads(latest_news)) 128 return latest_news 129 except Exception as e: 130 print("ERROR",e) 131 132 # 关闭数据库连接 133 db.close() 134 ''' 135 {"title": "寻电之路2:海外合资品牌的全面反攻", "url": "https://www.autotimes.com.cn/news/202012/1536909.html", "release_time": "2020-12-23 09:52", "source": "汽车之家", "content": "", "web_source": "qicheshidai", "source_type": "0", "polarity": 1} 136 ''' 137 def insertDataQuick(data_object): 138 # db_init() 139 sql = "INSERT INTO news_detail(title,url,release_time,source,content,web_source,source_type,polarity) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)" 140 # print(sql) 141 try: 142 cursor.execute(sql, (data_object["title"], data_object["url"], data_object["release_time"], data_object["source"], data_object["content"], data_object["web_source"],data_object["source_type"],data_object["polarity"])) 143 # db.commit() 144 except Exception as e: 145 print("ERROR", e) 146 db.rollback() 147 def insert_Data_many(news_list): 148 db_init() 149 news_values = [] 150 for news in news_list: 151 news_values.append((news["title"], news["url"], news["release_time"], news["web_source"], news["company"], news["source_type"])) 152 cursor.executemany('INSERT INTO news_detail(title,url, release_time, web_source, company, source_type) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)', news_values) 153 db.commit() 154 print("插入完成") 155 156 def insertData(data_object): 157 db_init() 158 sql = "INSERT INTO news_detail(title,url,release_time,source,content,web_source,source_type,polarity) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)" 159 # print(sql) 160 try: 161 cursor.execute(sql, (data_object["title"], data_object["url"], data_object["release_time"], data_object["source"], data_object["content"], data_object["web_source"], data_object["source_type"],data_object["polarity"])) 162 db.commit() 163 except Exception as e: 164 print("ERROR", e) 165 db.rollback() 166 167 # cursor.close() 168 # db.commit() 169 # 关闭数据库连接 170 db.close() 171 172 def updateData(latest_news_val, source_name_val): 173 db_init() 174 latest_news = json.dumps(latest_news_val, ensure_ascii=False) 175 sql = "UPDATE source_info SET latest_news = '%s' WHERE source_name = '%s'" % (latest_news, source_name_val) 176 try: 177 cursor.execute(sql) 178 db.commit() 179 except Exception as e: 180 print("ERROR", e) 181 db.rollback() 182 183 184 185 # latest_news_temp = ["新闻1","xxx"] 186 # db_init() 187 # data_ob = { 188 # "title": "x", 189 # "url": "http://sss", 190 # "release_time": "2020-11-11 10:30:00", 191 # "source": "sohu", 192 # "content": "c", 193 # "web_source": "sohu" 194 # } 195 # insertData(data_ob) 196 # insertData(data_ob) 197 # insertData(data_ob) 198 # getData('sohu') 199 # updateData(latest_news_temp, 'sohu') 200 # setData() 201 # get_latest_data("techweb") 202 # get_unupdate_news() 203 # get_unupdate_count() 204 # check_news("寻电之路2:海外合资品牌的全面反攻", "qicheshidai")
-
表结构设计 -demo
-
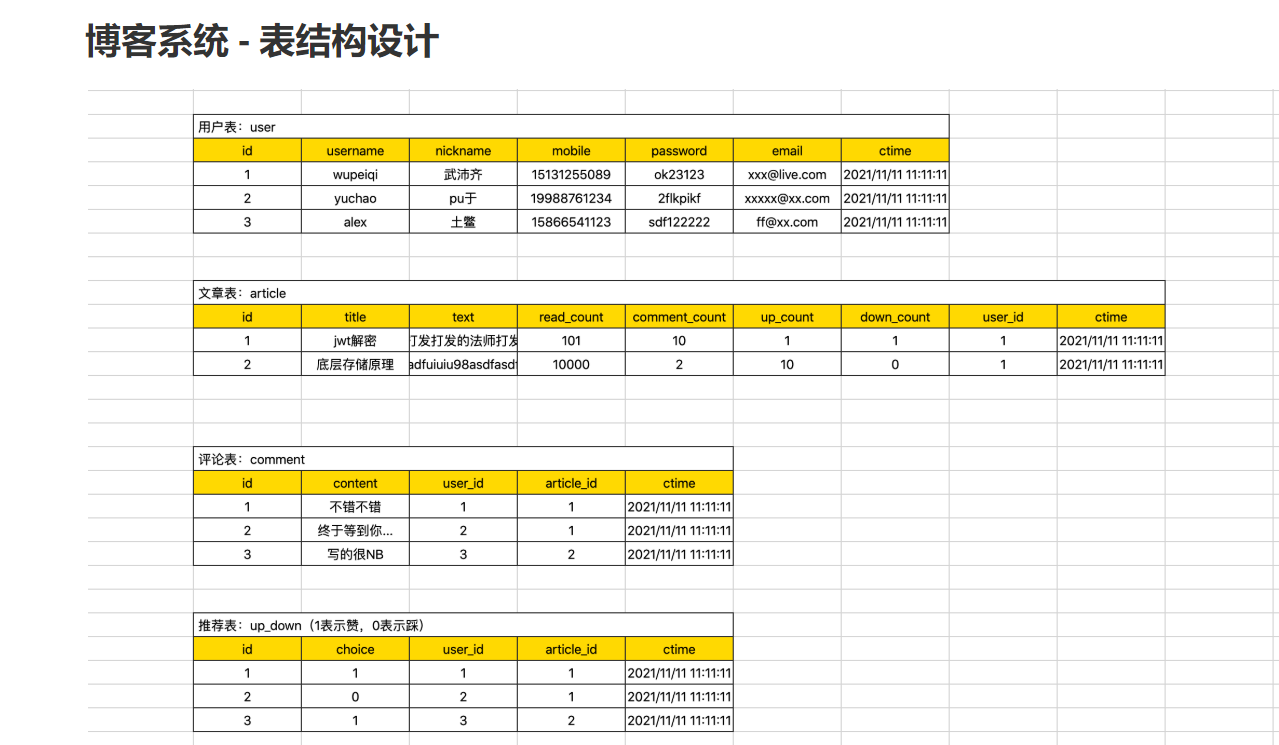
 博客系统-表结构设计
博客系统-表结构设计drop database blog; drop database IF EXISTS blog; create database blog default charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; use blog; create table user( id int not null auto_increment primary key, username varchar(16) not null, nickname varchar(16) not null, mobile char(11) not null, password varchar(64) not null, email varchar(64) not null, ctime datetime not null )default charset=utf8; create table article( id int not null auto_increment primary key, title varchar(255) not null, text text not null, read_count int default 0, comment_count int default 0, up_count int default 0, down_count int default 0, user_id int not null, ctime datetime not null, constraint fk_article_user foreign key (user_id) references user(id) )default charset=utf8; create table comment( id int not null auto_increment primary key, content varchar(255) not null, user_id int not null, article_id int not null, ctime datetime not null, constraint fk_comment_user foreign key (user_id) references user(id), constraint fk_comment_article foreign key (article_id) references article(id) )default charset=utf8; create table up_down( id int not null auto_increment primary key, choice tinyint not null, user_id int not null, article_id int not null, ctime datetime not null, constraint fk_up_down_user foreign key (user_id) references user(id), constraint fk_up_down_article foreign key (article_id) references article(id) )default charset=utf8;
作者:华王
博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/huahuawang/



