(二)shell脚本基础
read 内置命令
-p #设置提示信息
-t #等待用户输入超时,timeout
[root@shell opt]# read -t 15 -p "please enter name,age:" you_name you_age
please enter name,age:gm 18
[root@shell opt]# echo $you_name $you_age
gm 18
字符串条件测试
test 命令
test 评估表达式,结果为真echo $? 为0,反之为其它数。
1.文件测试
示例命令 test -e filename
-e :该文件是否存在
-f :该文件是否存在且是file类型
-d :该文件是否存在且为目录
-b :该文件是否存在且为block device装置
-c :该文件是否存在且为character device装置
-S :该文件是否存在且为Socket文件
-p :该文件是否存在且为pipe文件
-L :该文件是否存在且为连接档
2.文件权限测试
示例命令 test -r filename
-r:该文件是存在且具有可读属性
-w:该文件是否存在且具有可写属性
-x:该文件是否存在且具有可执行权限
-u:该文件是否存在且具有SUID
-g:该文件是否存在且具有SGID
-k:该文件是否存在且Sticky bit属性
-s:该文件是否存在且为非空白文件
3.俩文件之间的比较
示例命令 test file1 -nt file2
-nt:(newer than)file1是否比file2新
-ot: (older than)file1是否比file2旧
-ef:判断file1与file2是否为同一文件
4.判断字符串
示例命令 test -z string
-z:判断字符串是否为0.若为空字符串,返回true,否则返回false
-n:判断字符串是否非为0。若为空字符串,则返回false,否则返回false
另外 判断两个字符串是否相等或不等,还可以用 == 或 != 判断,和其他语言一样
5.两整数之间的判断
示例命令 test n1 -eq n2
-eq :两整数是否相等 equal
-ne: 两整数不相等 not equal
-gt: n1是否比n2大 great than
-lt: n1是否比n小 less than
-ge:n1是否大于等于n2 greater than or equal
-le:n1是否小于等于n2 less than or equal
6.多重条件判断
-a 作用就是and 如 test -r file -a -x file 只有当file有读,可执行权限才返回true
-o 作用就是or 如 test -r file -o -x file 当file有读,可执行权限,只要有一个满足就返回true
!反状态 如 test ! -r file 当file没有可读权限时返回true
[] 条件测试
脚本中[]用到比较多,跟text命令一样(参数也一样)。
注意:1.中括号,前后的空格 必须有。
2.变量需要带引号""。
使用括号的注意事项
if语句
#单分支
if <条件表达式>
then
运行的代码...
fi
#双分支
if <条件表达式>
then
代码...
if <条件表达式>
then
代码...
fi
fi
#if-else
if <条件表达式>
then
成立就运行的代码...
else
否则就.....
fi
#if-elif多分支 //不得超过3层
if <条件表达式>
then
成立就运行的代码...
elif
then
否则就.....
else
以上都不成立在执行这个代码....
fi
测试内存
1.检测linux剩余内存,当前可以用内存小于100m就发邮件
2.每三分钟检查一次
思路:
1.获取当前内存
2.配置邮件警告策略
3.开发脚本,内存下与100m
4.加入crontab,写规则
#!/bin/bash
FREE_M=`free -m | awk -F"[ /]+" 'NR==2 {print $7}'`
CHARS="run out of memory surplus $FREE_M"
if [ "$FREE_M" -lt "300" ]
then
echo $CHARS | tee /opt/text.txt
#mail -s "主题" 收件人 <
#mail -s "`date +%F-$T`$CHARS" 11111@163.com < /opt/text.txt
echo "内存不足"
fi
#将脚本写入crontab 每3分钟跑一次
[root@shell opt]# crontab -e
#显示crontab写人的代码
[root@shell opt]# crontab -l
*/3 * * * * /bin/bash /opt/free.sh $>/dev/null
监控脚本
函数开发
-
执行shell命令组合起来的,组合成的一个
函数体 -
还得给函数体起一个名字,称
函数名 -
函数名+函数体=函数
shell函数语法
-
先定义函数,最后再调用函数,否则函数无效
-
函数体内部变量是局部变量
-
必须加入return语句(return只能写在函数中,exit是shell的内置命令,用于退出shell环境)
-
函数写入单独文件中,需要使用source读取(用于加载)
#三种方法定义函数的方法
1.function 函数名(){
函数体
想执行linux命令...
return 返回值
}
2.function 函数名{
函数体
想执行linux命令...
return 返回值
}
3.函数名{
函数体
想执行linux命令...
return 返回值
}
alias 别名
[root@shell ~]# alias catip="ip a" #添加别名
[root@shell ~]# catip
......
[root@shell ~]# unalias catip #删除别名
写脚本思路
-
这个脚本写来是干什么用的
-
为后期的维护减轻负担
-
简介有备注
##脚本美化
# Use LSB init script functions for printing messages, if possible
#
lsb_functions="/lib/lsb/init-functions"
if test -f $lsb_functions ; then
. $lsb_functions
else
log_success_msg()
{
echo " SUCCESS! $@"
}
log_failure_msg()
{
echo " ERROR! $@"
}
fi
脚本
linux 初始化操作
背景
公司新购十台linux操作系统,需要初始化
要求:
-
设置时区并同步
-
禁用 selinux
-
清空防火墙默认策略
-
历史命令显示时间
-
禁止 root 远程登录
-
禁止定时任务发送邮件
-
减少 Swap 使用
-
系统内核参数优化
-
设置最大打开文件数
-
安装系统性能分析工作及其他工作常用工具
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
#yum
yum install -y ntpdate vim net-tools gcc make sysstat autoconf
#rm -rf
rm -rf /etc/localtime
#date
ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
if ! crontab -l|grep ntpdate &>/dev/null
then
(echo "* 1 * * * ntpdata time.windows.com >/dev/null 2>&1";crontab -l)|crontab
fi
#stop selinux
sed -i '/SELINUX/{s#enforcing#disabled#}' /etc/selinux/config
#stop firewalld
if egrep "7.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null
then
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
elif egrep "6.[0-9]" /etc/redhat-release &>/dev/null
then
service iptables stop
chkconfig iptables off
fi
#显示操作命令时间
if ! grep HISTTIMEFORMAT /etc/bashrc
then
echo 'export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F%T`whoami`"' >> /etc/bashrc
fi
#ssh 超时时间
if ! grep "TMOUT=600" /etc/profile &>/dev/null
then
echo "export TMOUT=600" >> /etc/profile
fi
#stop ssh root
sed -i 's/#PermitRootLogin yes/PermitRootLogin no' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#定时发送邮件
sed -i 's/^MAILTO=root/MAILTO=""/'/etc/crpmtab
#文件打开数
if ! grep "* soft nofile 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf &>/dev/null
then
cat >> /etc/security/limits.conf << EOF
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
EOF
fi
#系统内核
cat >>/etc/sysctl.conf << EOF
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 20480
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 20480
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 20
EOF
#减少 SWAP 使用
echo "0" > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
批量创建用户并设置不同密码
背景:
公司来一批新员工,要创建以实习生为名的账号
需求:
-
公司新生一百位实习生,手动创建用户名太麻烦
-
每个人的名字都不一样,所以用户名不规律
-
密码不能一致,需要使用随机密码
-
判断要创建的用户是否存在
脚本:
先批量创建10有规律用户
#!/bin/bash
# 创建一个变量在当前目录下创建一个名为user_password的文件
USER_FILE=./user_password
# USER 系统创建的用户都会在这个USER里,user 递增十次
for USER in user{1..10}
do
# id 是linux下的一个命令
if ! id $USER &>/dev/null
then
# $RANDOM 随机升成有些密码,md5sum 是md5加密,cut -c 1-8 是截取前八个随机密码作为密码
PASS=$(echo $RANDOM |md5sum |cut -c 1-8)
useradd $USER
# --stdin 密码不能使用交互式
echo $PASS |passwd --stdin $USER
#把升成的用户名和密码写入USER_FILE文件里
echo "$USER $PASS" >> USER_FILE
echo "$user user create cuccessful"
else
echo "USER user already exists!"
fi
done
创建没有规律的用户
#!/bin/bash
USER_FILE=./user_password
# 接手脚本后面参数
USER_LIST=$@
for USER in $USER_LIST
do
if ! id $USER &>/dev/null
then
PASS=$(echo $RANDOM |md5sum |cut -c 1-8)
useradd $USER
echo $PASS |passwd --stdin $USER
echo "$USER $PASS" >> USER_FILE
echo "$user user create cuccessful"
else
echo "USER user already exists!"
fi
done
批量删除用户
#!/bin/bash
userName=`ls -l /home | grep '4月' | awk {'print$9'}`
for file in $userName
do
id $file >& /dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "*********用户$file 不存在*********"
if [ -d "$file" ]; then
echo "检测到用户$file 的文件夹还存在"
rm -rf "$file"
echo “用户$file 的文件夹已经删除”
fi
else
userdel -rf $file
echo "*********用户$file 已删除*********"
fi
done
一键查看服务器利用率
背景:
在没有监控的情况下,如何查看服务器网络和服务器利用率
需求:
-
CPU 60%
-
内存 利用率
-
硬盘 利用率
-
TCP 链接状态 netstat -atnp a:显示所以的socker,t:显示所以的 tcp 链接 n:不解析名字 p:显示 socker 的PID/程序名
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
function cpu(){
NUM=1
while [ $NUM -le 3 ]
do
util=`vmstat |awk '{if(NR==3)print 100-$15"%"}'`
user=`vmstat |awk '{if(NR==3)print $13}'`
sys=`vmstat |awk '{if(NR==3)print $14}'`
iowait=`vmstat |awk '{if(NR==3)print $16}'`
echo "CPU的使用率:$uitl,等待磁盘的IO响应使用率:$iowait"
let NUM++
sleep 1
done
}
function memory(){
total=`free -m |awk '{if(NR==2)printf "%.f",$2/1024}'`
used=`free -m |awk '{if(NR==2)printf "%.f",($2-$NF)/1024}'`
available=`free -m |awk '{if(NR==2)printf "%.f",$NF/1024}'`
echo "内存 - 总内存:${total}G,使用${used}G,剩余:${available}G"
}
function disk(){
fs=$(df -h |awk '/^\/dev/{print $1}')
for p in $fs
do
mounted=$(df -h |awk '$1=="'$p'"{print $NF}')
size=$(df -h |awk '$1=="'$p'" {pirnt $2}')
used=$(df -h |awk '$1=="'$p'"{print $3}')
used_percent=$(df -h|awk '$1=="'$p'"{print $5}')
echo "硬盘 - 挂载点:$mounted、总大小:$size、使用:$used、使用率:$used_percent"
done
}
function tcp_status() {
summary=$(ss -antp |awk '{status[$1]++}END{for(i in status) printf i":"status[i]" "}')
echo "TCP连接状态 - $summary"
}
cpu
memory
disk
tcp_status
Nginx 访问日志分析
背景:
分析公司网站访问情况
需求:
1、 日志格式: $remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"
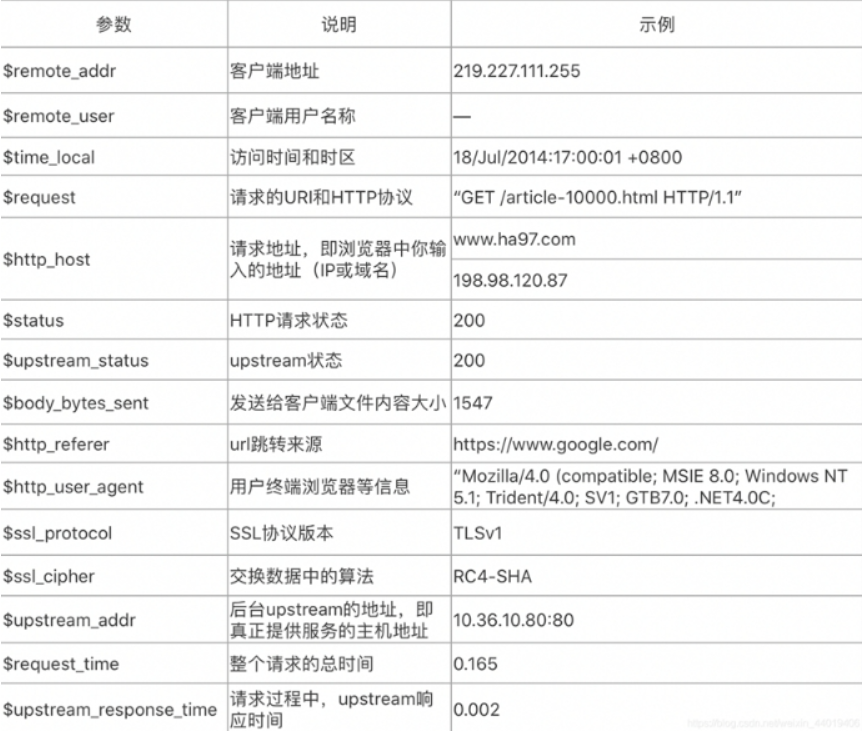
2、 统计访问最多的IP
3、 统计指定时间段访问最多的IP
4、 统计被访问最多的页面
5、 统计访问页面状态码数量
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
LOG_FILE=$1
echo "统计访问最多的10个IP"
awk '{a[$1]++}END{print "UV:",length(a);for(v in a)print v,a[v]}' $LOG_FILE |sort -k2 -nr |head -10
echo "----------------------"
echo "统计时间段访问最多的IP"
awk '$4>="[01/Dec/2018:13:20:25" && $4<="[27/Nov/2018:16:20:49"{a[$1]++}END{for(v in a)print v,a[v]}' $LOG_FILE |sort -k2 -nr|head -1
echo "----------------------"
echo "统计访问最多的10个页面"
awk '{a[$7]++}END{print "PV:",length(a);for(v in a){if(a[v]>10)print v,a[v]}}' $LOG_FILE |sort -k2 -nr |head -10
echo "----------------------"
echo "统计访问页面状态码数量"
awk '{a[$7" "$9]++}END{for(v in a){if(a[v]>5)print v,a[v]}}' $LOG_FILE |sort -k3 -nr





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)