FutureMask
Java Future Task
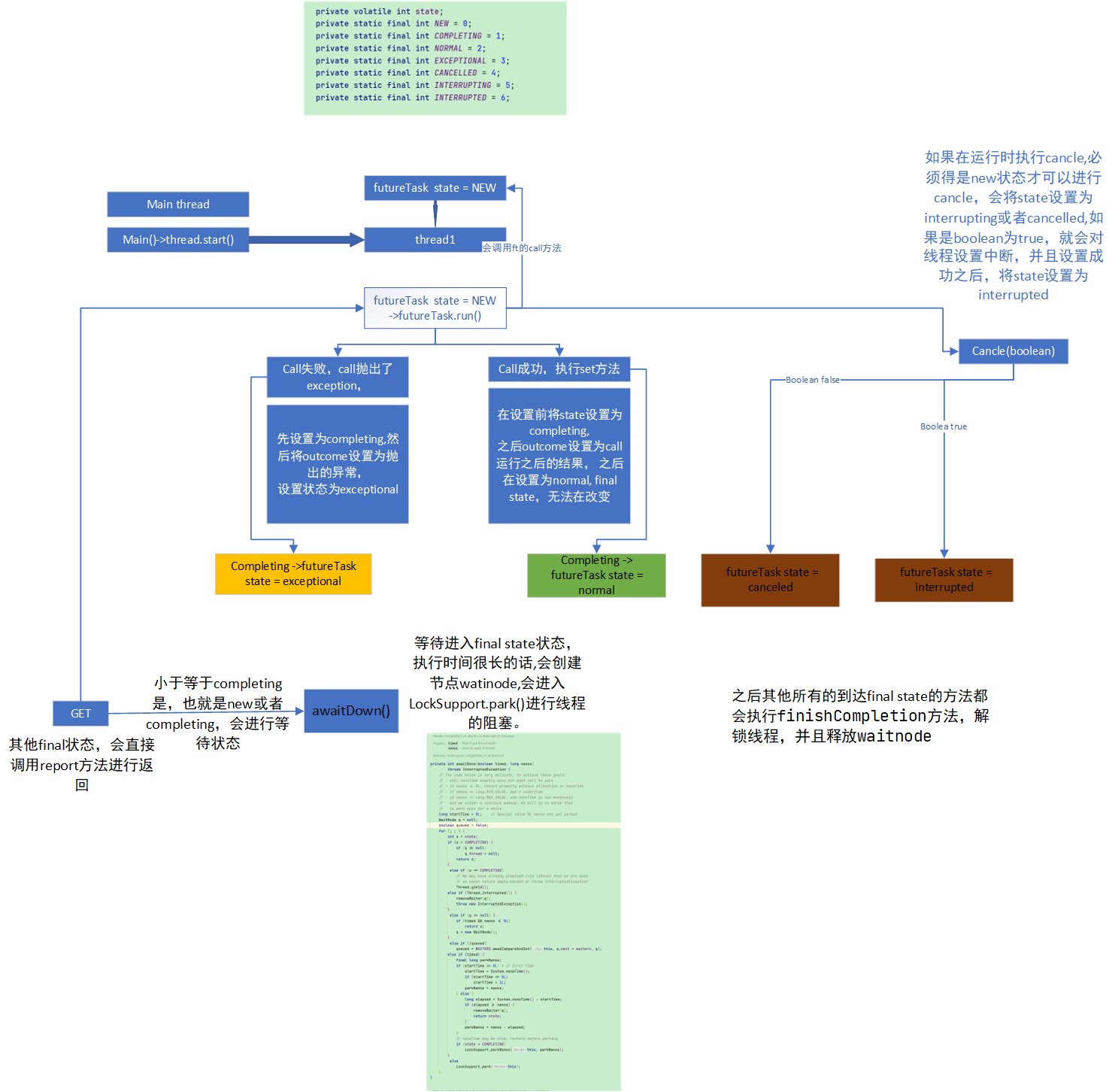
Java FutureTask通过继承Future和Runnable实现了将Callable封装到Runnable中,便于Thread直接调用,也可以使用线程池调用,并且,可以通过FutureTask对象获取任务执行的结果,是抛出异常了还是其他问题。FutureTask通过内部volatile变量int state进行状态的封装,能够通过state状态变量得知认为执行的结果。并且,使用了CAS进行状态的更新,保证了线程安全。(不会出现ABA,因为从低等级状态到高等级状态不会变回低等级状态,并且final state也无法再变)
Pipeline
State
/**
* The run state of this task, initially NEW. The run state
* transitions to a terminal state only in methods set,
* setException, and cancel. During completion, state may take on
* transient values of COMPLETING (while outcome is being set) or
* INTERRUPTING (only while interrupting the runner to satisfy a
* cancel(true)). Transitions from these intermediate to final
* states use cheaper ordered/lazy writes because values are unique
* and cannot be further modified.
*
* Possible state transitions:
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
* NEW -> CANCELLED
* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
*/
private volatile int state;
// 创建的状态
private static final int NEW = 0;
// 表示正在处理
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
// final state 无法再次更改的变化
private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 正常完成任务
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 任务抛出异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 任务取消,但是不中断正在执行的线程
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 任务取消,并且正在中断线程
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 已经对线程进行打断
封装Runnable和Callable
通过两个有参构造器直接进行封装,会将FutureTask里面的callable设置为送入的任务,和state变为new
运行
public void run() {
if (state != NEW || // 当前状态不为new,
!RUNNER.compareAndSet(this, null, Thread.currentThread())) // 将当前对象的RUNNER设置为当前的线程
return; // 如果不为new或者设置失败,直接返回
try {
Callable<V> c = callable; // job
if (c != null && state == NEW) { // 再次判断
V result; // 用来接受返回的结果
boolean ran; // 表示是否正确完成
try {
result = c.call(); // 执行
ran = true; // 正确执行,
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null; // 失败执行
ran = false; //
setException(ex); // 设置execption,将result设置为抛出的异常,将this的outcome设置为抛出的异常,并且将状态设置为 exceptional
}
if (ran) // 成功运行,设置为normal,此时result就是运行结果,将outcome设置为运行的结果
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); // 如果还未设置为interrupted,会一直等待直到设置成功
}
}
Cancel
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { // mayInterruptIfRunning 在cancel时,如果为true,那么会对运行job的线程进行interrupt,如果不是,那么只进行futuretask state的cancel
if (!(state == NEW && STATE.compareAndSet
(this, NEW, mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED))) // 只有在new状态才进行改变,通过CAS进行设置,ture -> interrupting false -> cancelled
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception ture 对线程进行打断
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
STATE.setRelease(this, INTERRUPTED); // 设置为interrupted
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion(); //
}
return true;
}
GET
得到当前的运行结果,成功运行,返回结果,失败,直接抛出异常(只有没时间的get,有时间get超过了时间会进行timeouterror)
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
// The code below is very delicate, to achieve these goals:
// - call nanoTime exactly once for each call to park
// - if nanos <= 0L, return promptly without allocation or nanoTime
// - if nanos == Long.MIN_VALUE, don't underflow
// - if nanos == Long.MAX_VALUE, and nanoTime is non-monotonic
// and we suffer a spurious wakeup, we will do no worse than
// to park-spin for a while
long startTime = 0L; // Special value 0L means not yet parked
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) { //
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING)
// We may have already promised (via isDone) that we are done
// so never return empty-handed or throw InterruptedException
Thread.yield();
else if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
else if (q == null) {
if (timed && nanos <= 0L)
return s;
q = new WaitNode();
}
else if (!queued)
queued = WAITERS.weakCompareAndSet(this, q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
final long parkNanos;
if (startTime == 0L) { // first time
startTime = System.nanoTime();
if (startTime == 0L)
startTime = 1L;
parkNanos = nanos;
} else {
long elapsed = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
if (elapsed >= nanos) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
parkNanos = nanos - elapsed;
}
// nanoTime may be slow; recheck before parking
if (state < COMPLETING)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, parkNanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
简单来说,就是等待状态到达final state,处在completing状态,就让出时间片,进行等待,一直查找。任务进入completing的futuretask马上就要进入final state,就直接进行等待。
大于completing,表示进入了final state,就返回状态并退出,(并且处理waitnode)
并且如果当前执行get方法的线程被interrupted,那么就直接抛出异常。也就是说,该方法对线程中断敏感。
当前是new,并且线程没有打断,那么创建一个新的waitnode,waitnode会将运行get方法的线程进行记录,记录到node的thread中。
之后,入队,头插法进行入队。
在这两步之间如果完成或者打断了,直接退出。并且释放掉waitnode。(出队列表在set和setExecption中执行)
入了对之后,还没有结束,那么调用LockSupprot.park(this)进行阻塞。
finishCompletion
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (WAITERS.weakCompareAndSet(this, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
在set、cancel和setException中调用,进行waitnode的出队和线程的unpark,针对get中调用locksupprot的park的阻塞。


