\w 匹配字母数字及下划线
\W 匹配f非字母数字下划线
\s 匹配任意空白字符,等价于[\t\n\r\f]
\S 匹配任意非空字符
\d 匹配任意数字
\D 匹配任意非数字
\A 匹配字符串开始
\Z 匹配字符串结束,如果存在换行,只匹配换行前的结束字符串
\z 匹配字符串结束
\G 匹配最后匹配完成的位置
\n 匹配一个换行符
\t 匹配一个制表符
^ 匹配字符串的开头
$ 匹配字符串的末尾
. 匹配任意字符,除了换行符,re.DOTALL标记被指定时,则可以匹配包括换行符的任意字符
[....] 用来表示一组字符,单独列出:[amk]匹配a,m或k
[^...] 不在[]中的字符:[^abc]匹配除了a,b,c之外的字符
* 匹配0个或多个的表达式
+ 匹配1个或者多个的表达式
? 匹配0个或1个由前面的正则表达式定义的片段,非贪婪方式
{n} 精确匹配n前面的表示
{m,m} 匹配n到m次由前面的正则表达式定义片段,贪婪模式
a|b 匹配a或者b
() 匹配括号内的表达式,也表示一个组
1.re.match():从字符串起始位置匹配,如果不是起始位置匹配返回none.
语法格式:
re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
result.group()获取匹配的结果
result.span()获去匹配字符串的长度范围
尽量使用泛匹配,使用括号得到匹配目标,尽量使用非贪婪模式,有换行符就用re.S
常规匹配和范匹配
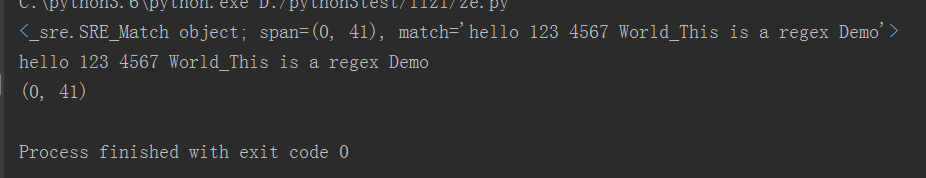
import re content="hello 123 4567 World_This is a regex Demo" #常规匹配 #result=re.match('^hello\s\d\d\d\s\d{4}\s\w{10}.*Demo$',content) #范匹配 result=re.match("^hello.*Demo$",content) print(result) print(result.group()) print(result.span())
贪婪匹配
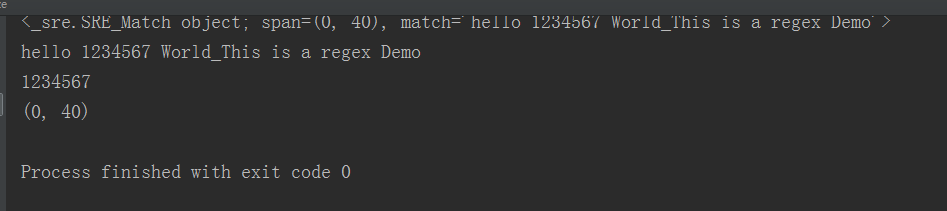
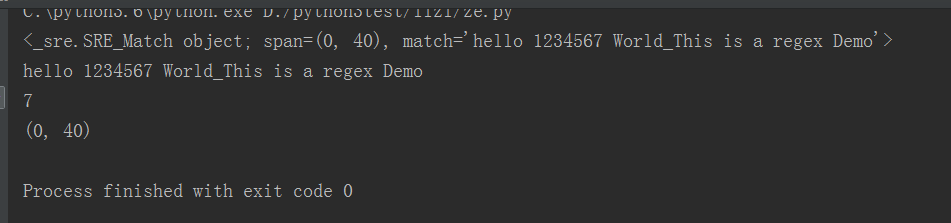
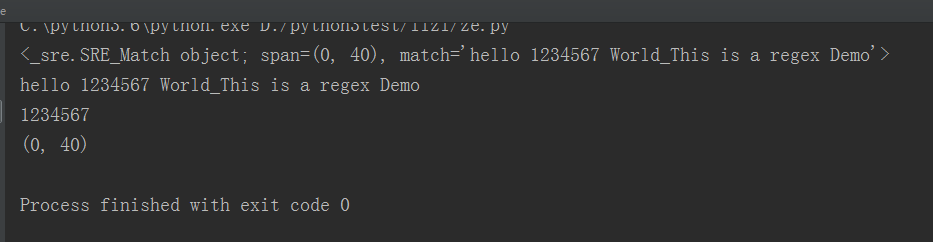
import re content= "hello 1234567 World_This is a regex Demo" #目标匹配,为了匹配字符串中具体的目标,则需要通过()括起来 #result = re.match('^hello\s(\d+)\sWorld.*Demo$',content) #贪婪匹配 #result=re.match('^hello.*(\d+).*Demo',content) #用贪婪匹配到1234567 result= re.match('^he.*?(\d+).*Demo',content) print(result) print(result.group()) print(result.group(1)) print(result.span())
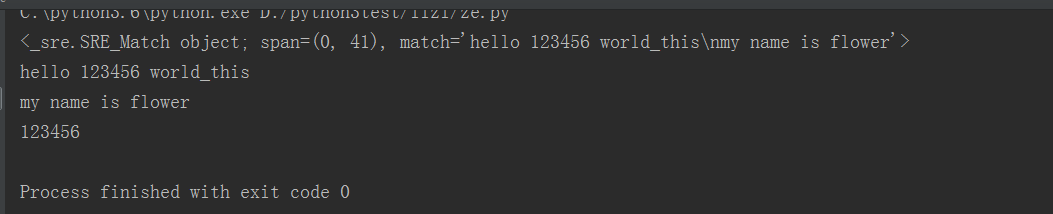
#换行匹配
import re content = """hello 123456 world_this my name is flower """ result=re.match('^he.*?(\d+).*?flower$',content,re.S) print(result) print(result.group()) print(result.group(1))
转义
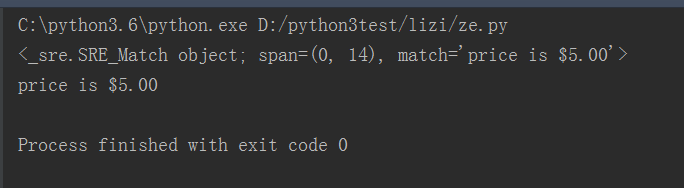
#转义,匹配的内容中存在特殊字符的时候,就需要用到转移符号\.
import re content= "price is $5.00" result = re.match('price is \$5\.00',content) print(result) print(result.group())
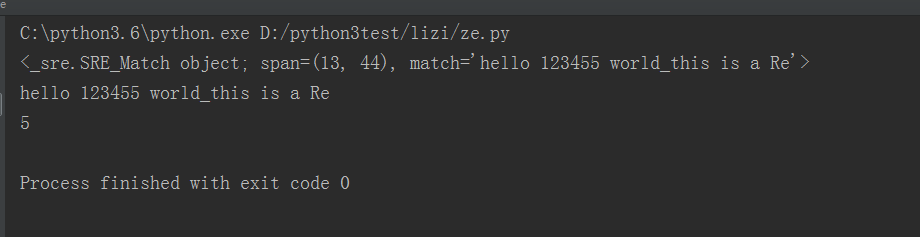
2.re.search扫描整个字符串返回第一个成功匹配的结果
#不需要在写^以及$,因为search是扫描整个字符串
import re content = "extra things hello 123455 world_this is a Re Extra things" result=re.search("hello.*(\d+).*?Re",content) print(result) print(result.group()) print(result.group(1))
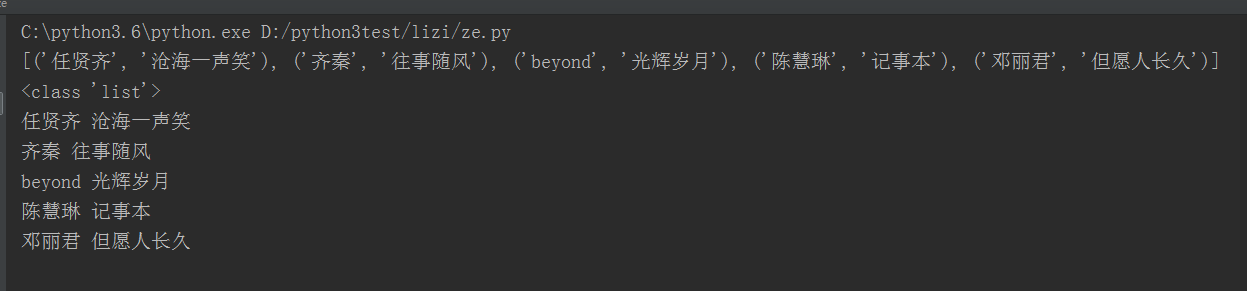
3.re.findall搜索字符串,以列表的形式返回全部能匹配的子串。
import re html = '''<div id="songs-list"> <h2 class="title">经典老歌</h2> <p class="introduction"> 经典老歌列表 </p> <ul id="list" class="list-group"> <li data-view="2">一路上有你</li> <li data-view="7"> <a href="/2.mp3" singer="任贤齐">沧海一声笑</a> </li> <li data-view="4" class="active"> <a href="/3.mp3" singer="齐秦">往事随风</a> </li> <li data-view="6"><a href="/4.mp3" singer="beyond">光辉岁月</a></li> <li data-view="5"><a href="/5.mp3" singer="陈慧琳">记事本</a></li> <li data-view="5"> <a href="/6.mp3" singer="邓丽君">但愿人长久</a> </li> </ul> </div>''' #result = re.search('<li.*?active.*?singer="(.*?)">(.*?)</a>',html,re.S) #results=re.findall('<li.*?href="(.*?)".*?singer="(.*?)">(.*?)</a>',html,re.S) results=re.findall('<li.*?singer="(.*?)">(.*?)</a>',html,re.S) print(results) print(type(results)) for result in results: #print(result) print(result[0],result[1])
5.re.sub替换字符串中每一个匹配的子串后返回替换后的字符串
import re content = "Extra things hello 123455 World_this is a regex Demo extra things" #将数字替换成空字符串 #result=re.sub('\d+','',content) #获取我们匹配的字符串,后面添加一些内容 result=re.sub('(\d+)',r'\1 7890',content) print(result)
6.re.compile将正则表达式编译成正则表达式对象,方便复用该正则表达式
import re content= """hello 12345 world_this 123 flower """ pattern =re.compile("hello.*flower",re.S) result = re.match(pattern,content) print(result) print(result.group())

7.正则综合练习
#获取豆瓣网书籍的页面的书籍信息 import requests import re content = requests.get('https://book.douban.com/').text #print(content) #pattern = re.compile('<li.*?cover.*?href="(.*?)".*?title="(.*?)".*?more-meta.*?author">(.*?)</span>.*?year">(.*?)</span>.*?</li>', re.S ) results = re.findall(pattern,content) #print(results) for result in results: url,name,author,date=result author = re.sub('\s','',author) date = re.sub('\s','',date) print(url,name,author,date)


