HihoCoder 1033交错和(数位DP第三题)
(写挂了,有空再补)
时间限制:10000ms
单点时限:1000ms
内存限制:256MB
描述
给定一个数 x,设它十进制展从高位到低位上的数位依次是 a0, a1, ..., an - 1,定义交错和函数:
f(x) = a0 - a1 + a2 - ... + ( - 1)n - 1an - 1
例如:
f(3214567) = 3 - 2 + 1 - 4 + 5 - 6 + 7 = 4
给定
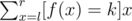
输入
输入数据仅一行包含三个整数,l, r, k(0 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ 1018, |k| ≤ 100)。
输出
输出一行一个整数表示结果,考虑到答案可能很大,输出结果模 109 + 7。
提示
对于样例 ,满足条件的数有 110 和 121,所以结果是 231 = 110 + 121。
更多样例:
| Input |
| 4344 3214567 3 |
| Output |
| 611668829 |
| Input |
| 404491953 1587197241 1 |
| Output |
| 323937411 |
| Input |
| 60296763086567224 193422344885593844 10 |
| Output |
| 608746132 |
| Input |
| 100 121 -1 |
| Output |
| 120 |
- 样例输入
-
100 121 0 - 样例输出
-
231

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long int //需要用long long 来进行存放
const int mod = 1000000007;//结果的最大值,用于取模
struct node{
ll s, n;//s: 各数位交错和 n:满足条件的个数
};
node dp[21][20][400];//[长度][以哪个数作为开头][该数的数位交错和]
int bits[21];//存放一个数的各位,低到高存放在0到20
ll base[21];//每一数位的基准 比如十位数=base[2]=10
//len数位长度, dig是首个数字, begin_zero表示从最高位到当前位是否全部为0, limit表示下一位枚举是否有限制(bit[len-2]或9), sum是要求的数字和
node dfs(int len, int dig, bool begin_zero, bool limit, int sum){
node t;//存放长度为 len的结果
t.s = 0, t.n = 0;
//超过边界值
if (len <= 0 || len >= 20 || dig < 0 || dig > 9 || sum < -200 || sum >= 200)
return t;
//返回已有的DP结果,即记忆化搜索
if (!limit && dp[len][dig + (begin_zero ? 0 : 10)][sum + 200].n != -1)
return dp[len][dig + (begin_zero ? 0 : 10)][sum + 200];
//长度只有一位,就不需要枚举下一位了,直接讨论返回即可
if (len == 1){
if (dig != sum)
return t;
t.n = 1, t.s = sum;
return t;
}
//开始枚举下一位的数字
int end = limit ? bits[len - 2] : 9;//下一位数字的最大值
int newsum = dig - sum;
node tmp;
for (int j = 0; j < end + 1; j++)
{
if (begin_zero){//前面都是0,接下来的就由当前位决定 j是否为0
tmp = dfs(len - 1, j, j == 0, limit && (j == end), sum);
}
else{//前面不是全为0
tmp = dfs(len - 1, j, false, limit && (j == end), newsum);
}
//将tmp的值累加到t上
t.n += tmp.n;//满足条件的个数
//计算满足条件的长度为 len 的data[len]所有数的和, tmp 是长度为 i-1的data[len-1]所有数的和
//每一个: data[len] = dig * base[len] + data[len-1] 且共有n个
//t.s = t.s + tmp.n * (dig * base[len]) + tmp.s 增加 %mod 就得到下面的结果
t.s = ((t.s + tmp.s) % mod + ((tmp.n * dig) % mod * base[len]) % mod) % mod;
}
//当长度为len,且以dig开头的,数位和为sum 的所有结果都计算完成,才将其进行存储
if (!limit)
dp[len][dig + (begin_zero ? 0 : 10)][sum + 200] = t;
//dig + (begin_zero ? 0 : 10) 用来区分两种状态,(1. 前导都为0;2. 前导包含其它数)
return t;
}
int solve(ll n, int s){
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
int l = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 21; i++)
bits[i] = 0;
//将n的每一位从低到高放到 bits[0]到bits[l] 中
while (n){
bits[l++] = n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
//从l+1开始,比n的长度大1,并且第l+1位数置为0
return dfs(l + 1, 0, true, true, s).s;
}
int main(){
ll l, r, s;
node t;
t.n = -1;
t.s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 21; i++)//长度
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++)//第i位的取值
for (int k = 0; k < 400; k++)// i到0 所有位上的交错和 + 200
dp[i][j][k] = t;
base[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < 21; i++)//base 是作为基准数 比如两位数需要 *10, 三位数需要*100
base[i] = base[i - 1] * 10 % mod;
cin >> l >> r >> s;
cout << (solve(r, s) - solve(l - 1, s) + mod) % mod << endl;
return 0;
}

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<memory>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const LL Mod=1000000007;
LL a[20],cnt,L,R,S;
LL ans,dp[20][400][2][2][2];
LL dfs(LL pos,LL sum,LL limit,LL sign,LL fir,LL sub)
{
if(pos==0) return sum==S?sub:0;
if(!limit&&sign&&dp[pos][S-sum+200][1][1][1]) {
for(int i=1;i<=pos;i++) sub=sub*10%Mod;
sub=(sub+dp[pos][S-sum+200][1][1][1])%Mod;
return sub;
}
LL Up=limit?a[pos]:9;
LL tmp=0;
for(LL i=0;i<=Up;i++){
if(fir&&i==0) continue;
tmp=(tmp%Mod+dfs(pos-1,sum+(sign?1:-1)*i,limit&&i==Up,1-sign,0,sub*10%Mod+i))%Mod;
}
dp[pos][sum][limit][sign][fir]=tmp;
return tmp;
}
LL cal(int v)
{
cnt=0;ans=0;
while(v){
a[++cnt]=v%10;
v/=10;
}
for(LL i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
LL tmp=dfs(i,200,i==cnt,1,1,0);//枚举第一位 ,避开前导0
ans+=tmp;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&L,&R,&S);
S+=200;
printf("%lld",(cal(R)-cal(L-1)+Mod)%Mod);
return 0;
}
It is your time to fight!






