Java异常总结
一、异常的概述
异常定义:在程序中,发生“不正常”的事件,导致程序无法正常运行,并使JVM中断,称为异常
生活中的异常:早上起床上课,平时骑车20分钟可以到达教室,由于天气原因或闹钟响了自动关闭,不能按时到达教室上课,迟到了,此时就属于异常现象。
捕获异常:当程序在运行时,发生了异常,为了让程序正常执行,需要对异常捕获(catch),称之为捕获异常
Java是面向对象的语言,异常本身就是一个类(Exception),当发生异常时会创建异常对象,捕获的就是该对象。
System.out.println("请输入一个数字");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 对可能发生的异常 进行处理
int num = sc.nextInt();
if(num%2==0){
System.out.println("这个数是偶数");
}
以上代码可能发生异常,当用户输入非数字时,导致程序抛出一个异常对象:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Scanner.java:864)
二、异常捕获(异常关键字以及层次关系)
a、try:试一试,将可能发生的代码使用try包裹,try不能单独出现
b、catch:捕获异常,当发生指定的异常对象时,执行catch代码
System.out.println("请输入一个数字");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 对可能发生的异常 进行处理
try {
int num = sc.nextInt(); // 发生异常后,try里面的代码不再执行
if (num % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("这个数是偶数");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}catch(Exception ee){// 对应的异常类 来捕获对应的异常对象 ,不能确定异常类,可以使用父类Exception
System.out.println("你的输入不正确");
}
System.out.println("程序继续运行直到结束。。。。");
一个try+多个catch
// 抛出的异常 不能被catch捕获,会发生什么?
try {
int[] num = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(num[1]); // 没有捕获该异常对象,JVM依然终止运行
System.out.println(10/0);
}catch(NullPointerException ee){
System.out.println("这是空指针异常");
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ee){
System.out.println("数组下标越界异常");
}catch(Exception ee){
// 输出异常 堆栈消息 方便程序员排错(尽可能避免用户看见)
ee.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("系统繁忙!"+ee.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("程序结束");
c、finally:异常之后的最终处理(无论是否发生异常,程序都执行)
try......finally结构
try{
System.out.println("请输入两个数 ,计算两个数相除");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
double s = num1/num2; // 可能出错
System.out.println(" try里面结束,结果:"+s);
}finally{
System.out.println("无论是否发生异常,都会执行这个语句块,一般用于资源回收");
}
try...catch...finaally结构
try {
System.out.println("请输入两个数 ,计算两个数相除");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
double s = num1 / num2; // 可能出错
System.out.println(" try里面结束,结果:" + s);
}catch(ArithmeticException ee){
ee.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("除数不能为0 !!");
}catch(Exception ee){
ee.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("系统繁忙!!!");
}finally {
System.out.println("用于资源回收。");
}
三、抛出异常
/**
* 根据下标访问数组元素
* @param array
* @param index
* @return
*/
public static int getEleByIndex(int [] array , int index){
// 抛出异常: 可以在异常发生时 或发生之前 创建一个异常对象并抛出
// 手动抛出一个异常 throw new 异常类([异常消息]);
if(index <0 || index > array.length-1){
//抛出异常
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("你的下标越界了");
}
int n = array[index];
return n;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数组
int [] array = {2,1,4,5};
int index=4;
// 定义方法访问下标的元素 此时会产生异常 并抛出给方法的调用者
try {
int num = getEleByIndex(array, index);
System.out.println("访问的元素:" + num);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ee){
System.out.println(ee.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("结束。。。");
}
四、异常分类
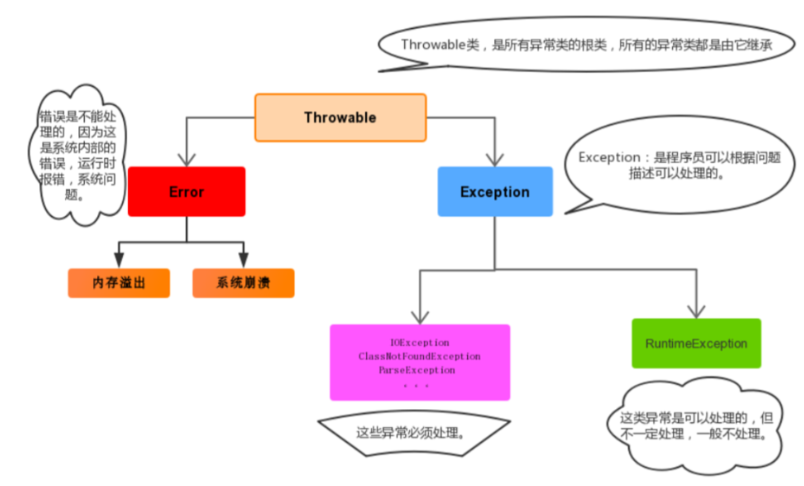
由于有些异常时不能直接抛出的,需要先声明才可以抛出,异常可以分为两大类:
1、编译期异常(check异常或者检查异常):在编译期间检查异常,如果没有处理异常,则编译出错。
//创建一个文件类的对象
File file = new File("d:/aaa.txt");
// 在写代码(编译之前)时 一定要处理的异常(try..catch 或者 throws),就是编译时异常
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
这里的IOException就是编译期异常,需要手动处理的
2、运行期异常(runtime异常或者运行异常):在运行期间检查异常,编译期可以不处理异常。
// 在运行期间抛出异常 不需要事先处理的 NullPointException是运行异常
String str=null;
System.out.println(str.length());
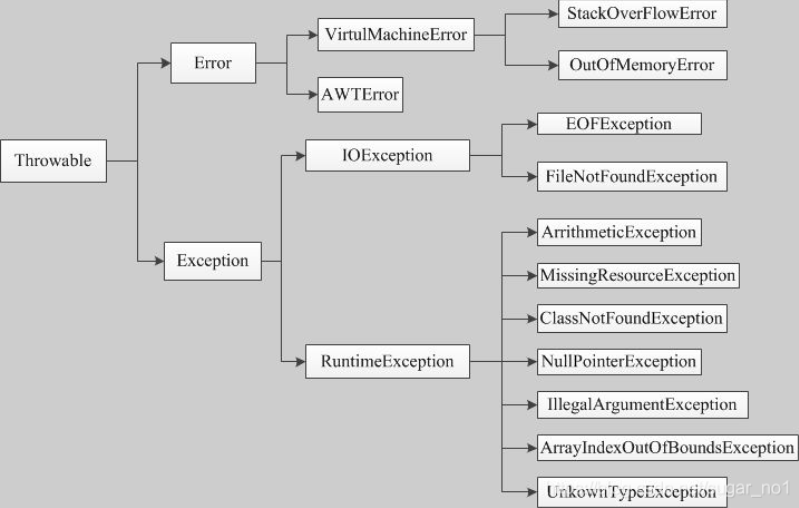
Exception中常用的异常类
- RuntimeException
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常
- NullPointerException:空指针异常
- ArithmeticException:算数异常
- NumberFormatException:数字格式化异常
- ClassNotFoundException:类没有找到异常
- ClassCastException:类转换异常
- 检查异常(check Exception)
- IOException:IO操作异常
- FileNotFoundException:文件未找到异常
- SQLException:数据库异常
- EOFEXception:读写文件尾异常
- ParseException:日期格式化异常
- SocketException:数据传输异常
注意:对于抛出检查异常,需要使用throws声明,对于抛出运行时异常,必须要使用throws声明
声明抛出异常语法:
声明抛出异常语法:
public ... 方法名([参数]) throws 异常类1,异常类2{
//通过throws抛出 或 处理 检查异常
}
/**
* 声明抛出异常语法:
* public ... 方法名([参数]) throws 异常类1,异常类2{
*
* }
*/
//创建文件
public static void createFile() throws FileNotFoundException ,IOException {
File file = new File("d:/hello.txt");
if(file.exists()){
// 不能创建 ,需要提示用户 该文件存在
throw new FileNotFoundException("这个文件已存在,不能创建");
}else{
//创建
file.createNewFile();
}
}
throws用于进行异常类的声明,若该方法可能有多种异常情况产生,那么在throws后面可以写多个异常类,用逗号隔开。
面试题:关于finally和return的执行顺序问题?
回答:当方法有返回值时,先执行finally,再return,但是finally的代码不会改变return结果
/**
* 方法有返回值 有 finally
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static int getNum(int n){
try{
if(n%2==0){
n++;
}else{
n--;
}
return n;
}catch(Exception ee){
System.out.println("catch--"+n);
return 0;
}finally {
// return 如果放在 try或catch中,不会受finally的改变
// 如果放在最下面,会受finally的改变
n++; // 5
System.out.println("fially----n:" + n); // 5
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m=getNum(5);
System.out.println(m);
}
结果返回
finally----n:5
4
当只有在try或者catch中调用退出JVM的相关方法,此时finally才不会执行,否则finally永远会执行。

异常注意事项
a、运行时异常被抛出可以不处理。即不捕获也不声明抛出。
b、如果finally有return语句,永远返回finally中的结果,避免该情况.
c、如果父类抛出了多个异常,子类重写父类方法时,抛出和父类相同的异常或者是父类异常的子类或者不抛出异
常。
d、父类方法没有抛出异常,子类重写父类该方法时也不可抛出异常。此时子类产生该异常,只能捕获处理,不
能声明抛出
五、自定义异常
5.1、为什么需要使用自定义异常
在Java中每一个异常类都表示特定的异常类型,例如NullPointerException表示空指针,ArithmeticException表示算数异常,但是sun公司提供的API中不可能将实际项目中的业务问题全部定义为已知的异常类,这时需要程序员根据业务需求来定制异常类,例如用户注册,可以定义用户注册异常(RegisterException),分数不可能为负数也可以定制异常(ScoreException)。
5.2、什么是自定义异常
在开发中根据自己的业务情况来定制异常类,灵活性较高,且方便易用。
5.3、如何实现自定义异常
a、定义编译期异常类,创建一个类继承java.lang.Exception;
b、定义运行期异常类,创建一个类继承java.lang.RuntimeException;
5.4、案例分析:自定义异常应用
要求:模拟用户注册操作,用户输入用户名,验证用户名是否存在,如果存在,则抛出一个异常消息“亲,该用户已存在,不能注册”,通过自定义异常提示消息
public class RegisterException extends Exception {
public RegisterException(){
}
public RegisterException(String message){
// 将message 赋值给父类的构造
super(message); // 将message赋值给父类的 属性,可通过getMessage()方法
}
}
public class TestRegister {
// 模拟已存在的用户
String [] users = {"张三","李四","王五"};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要注册的用户:");
String uname = sc.next();
TestRegister obj = new TestRegister();
try {
// 调用方法
obj.checkUserName(uname);
System.out.println("注册成功");
} catch (RegisterException e) {
System.out.println("注册失败");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 检查用户是否存在
* @param username
* @return true 表示通过
* 异常表示不通过
*/
public boolean checkUserName(String username) throws RegisterException{
// 使用foreach遍历
/**
* for(数据类型 变量名 : 数组名/集合名 ){
* 循环中的 变量名代表的就是数组的元素
* }
*/
for(String u : users){
// 判断u是否与 username相等 ,相等说明用户存在,需要抛出异常
if(u.equals(username)){
throw new RegisterException("亲,"+username+" 已存在,不能注册");
}
}
return true;
}
}



