hdu 4651 Partition (利用五边形定理求解切割数)
下面内容摘自维基百科:
五边形数定理[编辑]
五边形数定理是一个由欧拉发现的数学定理,描写叙述欧拉函数展开式的特性[1] [2]。欧拉函数的展开式例如以下:
亦即
欧拉函数展开后,有些次方项被消去,仅仅留下次方项为1, 2, 5, 7, 12, ...的项次,留下来的次方恰为广义五边形数。
当中符号为- - + + - - + + .....
若将上式视为幂级数,其收敛半径为1,只是若仅仅是当作形式幂级数(formal power series)来考虑,就不会考虑其收敛半径。
和切割函数的关系
当中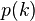 为k的切割函数。
为k的切割函数。
上式配合五边形数定理,能够得到
考虑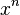 项的系数,在
n>0 时,等式右側的系数均为0,比較等式二側的系数,可得
项的系数,在
n>0 时,等式右側的系数均为0,比較等式二側的系数,可得
因此可得到切割函数p(n)的递归式
以n=10为例
-
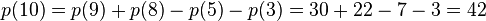
- 知道这个定理的话,hdu 4651就能够直接套模板了
-
#include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<map> #include<set> #define MP make_pair #define LL long long #define CLR(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a)) using namespace std; const int maxn = 100100; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const LL MOD = 1000000007; int fiv[maxn]; LL p[maxn]; void init() { int tot = 1; for(int i = 1; fiv[tot - 1] < maxn; i ++)///五边形数 { fiv[tot ++] = i*(3*i-1)/2; fiv[tot ++] = i*(3*i+1)/2; } p[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i < maxn; i ++)///i的切割数p(i) { p[i] = 0;int flag = 1; for(int j = 1; ; j ++) { if(fiv[j] <= i) { p[i] += flag * p[i - fiv[j]]; p[i] = (p[i] % MOD + MOD) % MOD; } else break; if(j % 2 == 0) flag = -flag; } } } int main() { int T, n; init(); scanf("%d", &T); while(T --) { scanf("%d", &n); printf("%lld\n", p[n]); } }



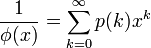
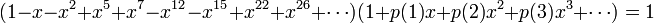
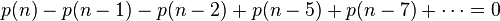


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号