Java练习20题
第一关:Welcome to Java
You must print two lines of output:
- Print
Hello, World.on the first line. - Print
Hello, Java.on the second line.
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World.");
System.out.println("Hello, Java.");
}
}
第二关:Java Stdin and Stdout I
用户输入三个整数,打印出来。
Sample Input
42
100
125
Sample Output
42
100
125
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
int c = scan.nextInt();
scanner.close();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
第三关:If-Else
任务:
输入一个整数n,如果是奇数,输出Weird;如果是[2,5]的偶数,输出Not Weird,[6,20]的偶数,输出Weird,大于20的偶数,输出Not Weird
解决方案:
public class Solution {
private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
if(N%2==1) {
System.out.println("Weird");
} else {
if((N>=2 && N<=5) || (N>20)) {
System.out.println("Not Weird");
} else {
System.out.println("Weird");
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
里面有句:
scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
以下解释来自stackoverflow:
- ? 匹配0或1个前面的字符
- | 选择
- [] 匹配其中的单个字符
- \u2028 行分隔符
- \u2029 段分隔符
- \u0085 下一行
总结一下就是跳过
\r\n(Windows 行结束)或\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085的其中一个。举例:对于代码
int a =scanner.nextInt(); String s = scanner.nextLine();用户输入:
4 This is next lines的结果是空串。
用户输入:
4 This is next lines的结果是
This is next line。所以通过skip跳过这些换行之类的操作,nextline的字符串就正确了。
第四关:Java Stdin and Stdout II
Sample Input
42
3.1415
Welcome to HackerRank's Java tutorials!
Sample Output
String: Welcome to HackerRank's Java tutorials!
Double: 3.1415
Int: 42
基本就是上面的如何跳过nextLine之前的换行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = scan.nextInt();
double d = scan.nextDouble();
scan.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
String s = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("String: " + s);
System.out.println("Double: " + d);
System.out.println("Int: " + i);
}
第五关:Java Output Formatting
输出排版,数字是第15个字符,不足三位补0
Sample Input
java 100
cpp 65
python 50
Sample Output
================================
java 100
cpp 065
python 050
================================
解决方案:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Formatter;
public class Solution {
static Formatter formatter = new Formatter(System.out);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("================================");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
String s1=sc.next();
int x=sc.nextInt();
formatter.format("%-14s %03d\n",s1,x);
}
System.out.println("================================");
sc.close();
}
}
第六关:Java Loops I
输入一个数,打印它和[1,10]的乘积表达式。
Sample Input
2
Sample Output
2 x 1 = 2
2 x 2 = 4
2 x 3 = 6
2 x 4 = 8
2 x 5 = 10
2 x 6 = 12
2 x 7 = 14
2 x 8 = 16
2 x 9 = 18
2 x 10 = 20
解决方案:
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// readLine()方法会返回用户在按下Enter键之前的所有字符输入,不包括最后按下的Enter返回字符
int N = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine().trim());
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
System.out.printf("%d x %d = %d\n",N,i,N*i);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
第七关:Java Loops II
第一行输入计算的次数,每次计算输入a, b, n,输出:
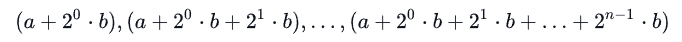
Sample Input
2
0 2 10
5 3 5
Sample Output
2 6 14 30 62 126 254 510 1022 2046
8 14 26 50 98
解决方案:
public static void main(String []argh){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int t=in.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){ int="" a="in.nextInt();" b="in.nextInt();" n="in.nextInt();" result="a;" pow="1;" for(int="" j="0;j<n-1;j++)" {="" +="pow*b;" system.out.printf("%d="" ",result);="" pow*="2;" }="" system.out.printf("%d\n",result+pow*b);="" in.close();="" ```="" ##="" 第八关:java="" int数据类型="" java整数类型:="" -="" bytes="" 8位有符号整型="" short="" 16位有符号整型="" 32位有符号整型="" long="" 64位有符号整型="" 输入一个数,判断能是什么类型。="" **sample="" input**="" ```shell="" 5-1501500001500000000213333333333333333333333333333333333-100000000000000="" output**="" -150="" can="" be="" fitted="" in:*="" short*="" int*="" long150000="" long1500000000="" long213333333333333333333333333333333333="" can't="" anywhere.-100000000000000="" **解决方案:**="" ```java="" public="" static="" void="" main(string="" []argh){="" scanner="" sc="new" scanner(system.in);="" t="sc.nextInt();" i="0;i<t;i++)" try="" x="sc.nextLong();" system.out.println(x+"="" in:");="" if(x="">=Byte.MIN_VALUE && x<=Byte.MAX_VALUE)System.out.println("* byte"); if(x>=Short.MIN_VALUE && x<=Short.MAX_VALUE)System.out.println("* short"); if(x>=Integer.MIN_VALUE && x<=Integer.MAX_VALUE)System.out.println("* int"); if(x>=Long.MIN_VALUE && x<=Long.MAX_VALUE)System.out.println("* long"); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(sc.next()+" can't be fitted anywhere."); } }}
用try catch判断是否能当做整数读入,能再继续判断。
第九关:Java End-of-file
统计读入EOF之前的行数。
Sample Input
Hello worldI am a fileRead me until end-of-file.
Sample Output
1 Hello world2 I am a file3 Read me until end-of-file.
解决方案:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String s; int n = 1; while((s=br.readLine())!=null) { System.out.println(n+" "+s); n+=1; } br.close();}
第十关:Java Static Initializer Block
输入长和宽,如果都为正,输出乘积,否则打印一个字符串。
public class Solution { static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); static int B = scanner.nextInt(); static int H = scanner.nextInt(); static boolean flag = false; static { if(B>0&&H>0) { flag = true; } else { System.out.println("java.lang.Exception: Breadth and height must be positive"); } } public static void main(String[] args){ if(flag){ int area=B*H; System.out.print(area); } }}
类方法的执行顺序:
public class Demo extends Base{ static { System.out.println("test static"); } public Demo(){ System.out.println("test constructor"); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Demo main func start"); new Demo(); System.out.println("Demo main func end"); }}class Base{ static{ System.out.println("base static"); } public Base(){ System.out.println("base constructor"); }}
输出
base statictest staticDemo main func startbase constructortest constructorDemo main func end
程序执行,先找到main方法,执行main前发现继承了Base类,就先执行Base的静态方法,然后是Demo的静态方法。之后开始执行main函数,创建了一个新对象Demo,先执行父类Base的构造函数,然后是Demo的构造函数,之后继续执行main方法。
第十一关:Java Int to String
一行:
String s = String.valueOf(n);
第十二关:Java Date and Time
输入年月日,输出星期几。
Sample Input
08 05 2015
Sample Output
WEDNESDAY
解决方案:
public static String findDay(int month, int day, int year) {
LocalDate dt = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
return dt.getDayOfWeek().toString();
}
LocalDate的使用:
Java8出的新的时间日期API都是线程安全的,并且性能更好,代码更简洁!
新时间日期API常用重要对象介绍:
- ZoneId: 时区ID,用来确定Instant和LocalDateTime互相转换的规则
- Instant: 用来表示时间线上的一个点(瞬时)
- LocalDate: 表示没有时区的日期, LocalDate是不可变并且线程安全的
- LocalTime: 表示没有时区的时间, LocalTime是不可变并且线程安全的
- LocalDateTime: 表示没有时区的日期时间, LocalDateTime是不可变并且线程安全的
- Clock: 用于访问当前时刻、日期、时间,用到时区
- Duration: 用秒和纳秒表示时间的数量(长短),用于计算两个日期的“时间”间隔
- Period: 用于计算两个日期间隔
应用示例:
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); // 年月日
System.out.println(localDate); // 2021-10-11
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); // 具体时间
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2021-10-11T21:20:28.455
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2021,10,11);
System.out.println(localDate1.getDayOfWeek()); // MONDAY
LocalDate localDate2 = localDate1.plusDays(5); // 加上5天
System.out.println(localDate2.getDayOfWeek()); // SATURDAY
System.out.println(localDate1.isLeapYear()); // 是否是闰年 false
// 格式化
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(formatter.format(localDateTime)); // 时间格式化 2021年10月11日 21:31:29
// Period 时间间隔
Period period = Period.between(localDate1,localDate2); //时间间隔应为5天
System.out.println(period.getDays()); // 5
第十三关:Java Currency Formatter
Sample Input
12324.134
Sample Output
US: $12,324.13
India: Rs.12,324.13
China: ¥12,324.13
France: 12 324,13 €
NumberFormat有一个专门处理货币的类。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double payment = scanner.nextDouble();
scanner.close();
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.US);
String us = numberFormat.format(payment);
numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(new Locale("en","IN"));
String india = numberFormat.format(payment);
numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.CHINA);
String china = numberFormat.format(payment);
numberFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.FRANCE);
String france = numberFormat.format(payment);
System.out.println("US: " + us);
System.out.println("India: " + india);
System.out.println("China: " + china);
System.out.println("France: " + france);
}
印度怎么和其它的不一样?
第十四关:Java Sort
ID NAME SCORE,先按SCORE逆序,再按名字正序。
Sample Input
533 Rumpa 3.6885 Ashis 3.8556 Samiha 3.7519 Samara 3.7522 Fahim 3.76
Sample Output
Ashis
Fahim
Samara
Samiha
Rumpa
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
class Student{
private int id;
private String fname;
private double cgpa;
public Student(int id, String fname, double cgpa) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.fname = fname;
this.cgpa = cgpa;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getFname() {
return fname;
}
public double getCgpa() {
return cgpa;
}
}
public class Solution
{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int testCases = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
List<student> studentList = new ArrayList<student>();
while(testCases>0){
int id = in.nextInt();
String fname = in.next();
double cgpa = in.nextDouble();
Student st = new Student(id, fname, cgpa);
studentList.add(st);
testCases--;
}
// ========== 排序代码
for(Student st: studentList){
System.out.println(st.getFname());
}
}
}
写法一:
Collections.sort(studentList, new Comparator<student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if (o1.getCgpa()==o2.getCgpa()) {
return o1.getFname().compareTo(o2.getFname());
}
return Double.compare(o2.getCgpa(),o1.getCgpa());
}
});
写法二:
Collections.sort(studentList, (o1, o2) -> {
if (o1.getCgpa()==o2.getCgpa()) {
return o1.getFname().compareTo(o2.getFname());
}
return Double.compare(o2.getCgpa(),o1.getCgpa());
});
写法三:
studentList.sort((o1, o2) -> {
if (o1.getCgpa() == o2.getCgpa()) {
return o1.getFname().compareTo(o2.getFname());
}
return Double.compare(o2.getCgpa(), o1.getCgpa());
});
第十五关:Java Dequeue
滑窗unique number的最大数,双端队列。
Sample Input
6 3 // 6是6个数,3是窗口大小为3
5 3 5 2 3 2
Sample Output
3
即5 3 2, 3 5 3, 5 2 3,2 3 2其中uniq number最多为3。
解决方案:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Deque<integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
Map<integer,integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int nn = in.nextInt();
int m = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int num = in.nextInt();
deque.addLast(num);
map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1);
}
int n = map.size(); // cur unique num length
int maxNum = n; // max uniq num len
int first;
for (int i = m; i < nn; i++) {
int num = in.nextInt();
first = deque.pollFirst();
map.put(first,map.get(first)-1);
if(map.get(first)==0) {
n -= 1;
}
deque.addLast(num);
map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1);
if(map.get(num)==1) {
n += 1;
}
maxNum = n>maxNum?n:maxNum;
}
System.out.println(maxNum);
}
第十六关:返回的类型
看看就好。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
//Complete the classes below
class Flower {
public String whatsYourName() {
return "I have many names and types.";
}
}
class Jasmine extends Flower {
@Override
public String whatsYourName() {
return "Jasmine";
}
}
class Lily extends Flower {
@Override
public String whatsYourName() {
return "Lily";
}
}
class Region {
public Flower yourNationalFlower() {
return new Flower();
}
}
class WestBengal extends Region{
@Override
public Flower yourNationalFlower() {
return new Jasmine();
}
}
class AndhraPradesh extends Region{
@Override
public Flower yourNationalFlower() {
return new Lily();
}
}
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = reader.readLine().trim();
Region region = null;
switch (s) {
case "WestBengal":
region = new WestBengal();
break;
case "AndhraPradesh":
region = new AndhraPradesh();
break;
}
Flower flower = region.yourNationalFlower();
System.out.println(flower.whatsYourName());
}
}
第十七关:Java Method Overriding
调用父类被重写的方法。输出:
Hello I am a motorcycle, I am a cycle with an engine.
My ancestor is a cycle who is a vehicle with pedals.
解决方案:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class BiCycle{
String define_me(){
return "a vehicle with pedals.";
}
}
class MotorCycle extends BiCycle{
String define_me(){
return "a cycle with an engine.";
}
MotorCycle(){
System.out.println("Hello I am a motorcycle, I am "+ define_me());
String temp=super.define_me(); //Fix this line
System.out.println("My ancestor is a cycle who is "+ temp );
}
}
class Solution{
public static void main(String []args){
MotorCycle M=new MotorCycle();
}
}
第十八关:Java Instanceof keyword
Object element=mylist.get(i);
if(element instanceof Student)
...
第十九关:Java Annotations
元注解:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 用到方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 运行时生效
@interface FamilyBudget {
String userRole() default "GUEST";
}
大致题意就是判断花费是否超预算(注解形式):
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface FamilyBudget {
String userRole() default "GUEST";
//~~Complete the interface~~
int budgetLimit() default 0;
}
class FamilyMember {
//~~Complete this line~~
@FamilyBudget(userRole = "SENIOR",budgetLimit=100)
public void seniorMember(int budget, int moneySpend) {
System.out.println("Senior Member");
System.out.println("Spend: " + moneySpend);
System.out.println("Budget Left: " + (budget - moneySpend));
}
//~~Complete this line~~
@FamilyBudget(userRole = "JUNIOR",budgetLimit=50)
public void juniorUser(int budget, int moneySpend) {
System.out.println("Junior Member");
System.out.println("Spend: " + moneySpend);
System.out.println("Budget Left: " + (budget - moneySpend));
}
}
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int testCases = Integer.parseInt(in.nextLine());
while (testCases > 0) {
String role = in.next();
int spend = in.nextInt();
try {
Class annotatedClass = FamilyMember.class;
Method[] methods = annotatedClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(FamilyBudget.class)) {
FamilyBudget family = method
.getAnnotation(FamilyBudget.class);
String userRole = family.userRole();
//int budgetLimit = ~~Complete this line~~;
int budgetLimit = family.budgetLimit();
if (userRole.equals(role)) {
//if(~~Complete this line~~){
if(budgetLimit>=spend) {
method.invoke(FamilyMember.class.newInstance(),
budgetLimit, spend);
}else{
System.out.println("Budget Limit Over");
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
testCases--;
}
}
}
第二十关:Java BigDecimal
大数逆序排序
Sample Input
9 //个数
-100
50
0
56.6
90
0.12
.12
02.34
000.000
Sample Output
90
56.6
50
02.34
0.12
.12
0
000.000
-100
解决方案:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Input
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
String []s=new String[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ s[i]="sc.next();" }="" sc.close();="" arrays.sort(s,="" collections.reverseorder((a1,="" a2)="" -=""> {
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(a1);
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(a2);
return a.compareTo(b);
}));
//Output
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
本文同步发布于orzlinux.cn


