Spring Jdbc 框架整合的第一天
Spring Jdbc的概述
它是Spring框架的持久层子框架。用于对数据库的操作
什么是数据库的操作?
答:对数据库的增删改查
在使用Spring Jdbc框架,要用到一个类---->JdbcTemplate,他是spring jdbc 子框架中提供的一个操作类,用于对原始jabc API的简单封装
那么如何创建Template呢?
首先看一下它的源码:
public JdbcTemplate() { } /** * Construct a new JdbcTemplate, given a DataSource to obtain connections from. * <p>Note: This will not trigger initialization of the exception translator. * @param dataSource the JDBC DataSource to obtain connections from */ public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) { setDataSource(dataSource); afterPropertiesSet(); } /** * Construct a new JdbcTemplate, given a DataSource to obtain connections from. * <p>Note: Depending on the "lazyInit" flag, initialization of the exception translator * will be triggered. * @param dataSource the JDBC DataSource to obtain connections from * @param lazyInit whether to lazily initialize the SQLExceptionTranslator */ public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource, boolean lazyInit) { setDataSource(dataSource); setLazyInit(lazyInit); afterPropertiesSet(); }
在此段代码中我们可以看出要创建一个jdbcTemplate 对象,需要获得一个数据库连接的数据源
如何获得一个数据库连接的数据源呢?

org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource,这个路径位于jdbc驱动包中
再配置springjdbc的四要素:
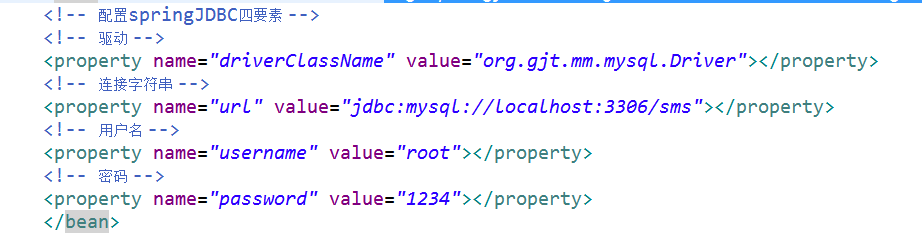
实现代码:
配置文件代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <!--配置一个数据源 由于jjabc模块提供的DriverManagerDataSource数据源,是一个直连数据源, 所以每次访问数据库,都要去打开连接才能访问,效率不高! 所以引入了连接池的概念。。。 连接池中的四个重要属性 1.最大超时毫秒数 2.最大连接数 3.最小连接数 4.最大空闲时间 destroy-method:在连接池对象注销之前,先关闭数据库(关闭连接池) --> <!-- 数据源的作用:获得数据库的链接,从而引出springJDBC的四要素 --> <bean name="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <!-- 配置springJDBC四要素 --> <!-- 驱动 --> <property name="driverClassName" value="org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver"></property> <!-- 连接字符串 --> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sms"></property> <!-- 用户名 --> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <!-- 密码 --> <property name="password" value="1234"></property> <!-- 最大超时毫秒数 --> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="30000"></property> <!-- 最大连接数 --> <property name="maxTotal" value="100"></property> <!-- 最小连接数 --> <property name="initialSize" value="50"></property> <!-- 最大空闲连接 --> <property name="maxIdle" value="55"></property> </bean> <!-- 获得JDBCTemplate操作对象 --> <bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!-- 设置 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置dao --> <bean name="studentDAO" class="cn.gzsxt.dao.StudentDAO"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> </bean> </beans>
dao层:
package cn.gzsxt.dao; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import cn.gzsxt.pojo.Student; public class StudentDAO implements DAO<Student>{ private JdbcTemplate JdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { JdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } @Override public int insert(Student entity) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //事物的操作(增删改)都可以是update方法 Object [] objects = {entity.getStuName(),entity.getStuPwd()}; int update = JdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO t_student(stuName,stuPwd) VALUES(?,?)", objects); return update; } }
pojo层
package cn.gzsxt.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable{ /**什么是序列化? * 将对象通过流的形式写出去 * 反序列化 * 读取流形式的数据 * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 114525114257637298L; private int stuId; private String stuName; private String stuPwd; public int getStuId() { return stuId; } public void setStuId(int stuId) { this.stuId = stuId; } public String getStuName() { return stuName; } public void setStuName(String stuName) { this.stuName = stuName; } public String getStuPwd() { return stuPwd; } public void setStuPwd(String stuPwd) { this.stuPwd = stuPwd; } public Student(int stuId, String stuName, String stuPwd) { super(); this.stuId = stuId; this.stuName = stuName; this.stuPwd = stuPwd; } public Student() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } }
测试代码:
package cn.gzsxt.test; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.gzsxt.dao.StudentDAO; import cn.gzsxt.pojo.Student; public class ApplicationContextTest { private StudentDAO studentDAO; private ClassPathXmlApplicationContext conn; @Before public void Before(){ conn = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); //获得数据源对象 studentDAO = conn.getBean(StudentDAO.class); } @After public void after(){ conn.close(); } /** * junit代替main方法,使得类能同时有多个main方法的功能 * 使用时要注意,返回值必须为空,为void */ // @Test // public void dataSource(){ // //通过配置文件创建容器 // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext conn = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); // // //获取数据源对象 // DataSource dataSource = conn.getBean(DataSource.class); // // try { // //打印数据库链接地址,测试连接是否成功 // System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); // } catch (SQLException e) { // // TODO Auto-generated catch block // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // } @Test public void insert(){ Student entity = new Student(); entity.setStuName("王八"); studentDAO.insert(entity); } }
spring jdbc 的优化!
由于jdbc模块提供的DriverManagerDataSource数据源,是一个直连数据源,所以每次访问数据库,都要去打开连接才能访问,效率不高,所以引入了连接池的概念,连接池的四个重要属性:
1.最大超时毫秒数
2.最大连接数
3.最小连接数
4.最大空闲时间

如何关闭连接池呢?
destroy-method:在连接池对象注销之前,先关闭数据库(关闭连接池)

