os.path.split()、os.path.realpath()和os.path.join()
有一个文件ReadConfigIni.py,这个文件的路径是 D:\SoftWare\autoTest\AutoRunTest\Public\Common\ReadConfigIni.py
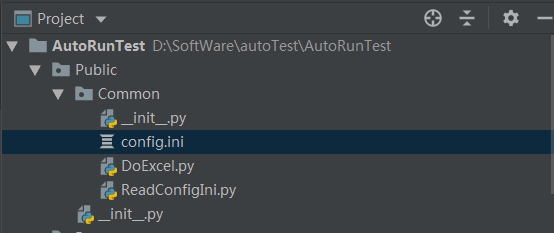
os.path.realpath(__file__)获取当前文件的绝对路径,__file__指当前文件,在ReadConfigIni.py文件中运行以下代码
# 当前文件路径 fp = os.path.realpath(__file__) print (fp) #输出结果 D:\SoftWare\autoTest\AutoRunTest\Public\Common\ReadConfigIni.py # 其他文件路径 fp = os.path.realpath("config.ini") print (fp) #输出结果 D:\SoftWare\autoTest\AutoRunTest\Public\Common\config.ini
os.path.realpath("PATH")
参数说明:
1. PATH指一个文件的全路径作为参数
2. 如果给出的是一个目录和文件名,则输出路径和文件名,输出为tuple
3. 如果给出的是一个目录名,则输出路径和空文件名,输出为tuple
实际上,该函数的分割并不智能,它仅仅是以"PATH"中的最后一个"/"作为分隔符,分隔后,将索引为0的视为目录(路径),
将索引为1的视为文件名
file_path = os.path.split("D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/ReadConfigIni.py") print (file_path) # 输出结果 # ('D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/', 'ReadConfigIni.py') file_path = os.path.split("D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/") print (file_path) # 输出结果 # ('D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/', '')
file_path = os.path.split("D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/ReadConfigIni.py")[0] print (file_path) # 输出结果 # D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/ file_path = os.path.split("D:/SoftWare/autoTest/AutoRunTest/Public/Common/ReadConfigIni.py")[1] print (file_path) # 输出结果 # ReadConfigIni.py

os.path.join()在路径后追加
os.path.join(file_path,"config.ini")
即:D:\SoftWare\autoTest\AutoRunTest\Public\Common\config.ini
分享促进成长



