1.2. HASH POINTERS AND DATA STRUCTURES
《BITCOIN AND CRYPTOCURRENCY TECHNOLOGIES》Chapter 1系列
1.2. HASH POINTERS AND DATA STRUCTURES哈希指针及数据结构
一、Hash pointer 哈希指针
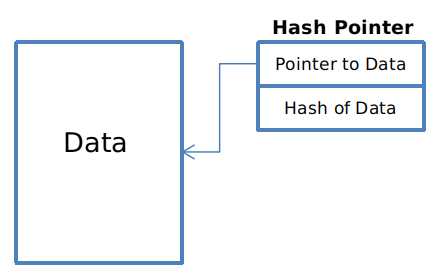
书中原话:A hash pointer is a pointer to where data is stored together with a cryptographic hash of the value of this data at some fixed point in time.
我的理解:哈希指针指向某个特定时刻下,数据及数据的加密后哈希值一起存储的位置。常规指针提供了一种检索数据的方法,而哈希指针还可以验证数据是否未更改。(如果Data改变,那么Hash of Data就会变)
二、Block Chain 区块链
下图所示为一个Block Chain。
在一般性的链表中,每个块(block)都包含自己的数据(data)和一个指向前一个块(block)的指针(pointer)。
而在区块链中,前一个块的指针被哈希指针替代。
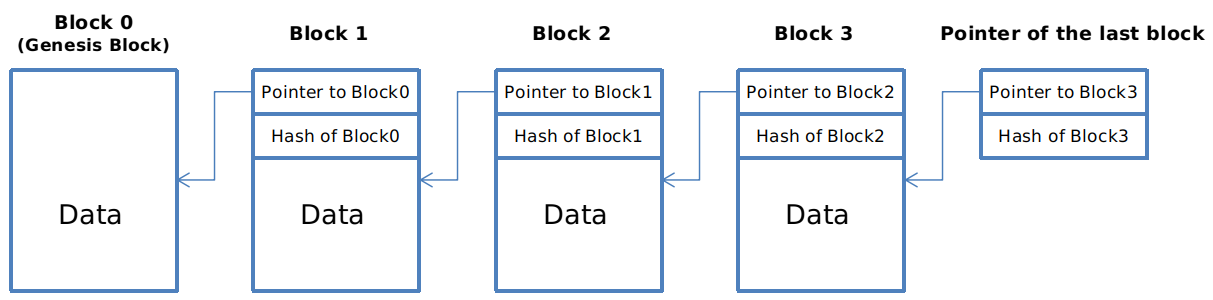
FIGURE 1.5. Block chain. A block chain is a linked list that is built with hash pointers instead of pointers.
哈希链表能防篡改:如果Block1中的data改变,那么Block2中的Hash of Block1就会改变,以此类推,后面的所有块的哈希值就会变,篡改很容易被发现。
三、Merkle Trees 梅克尔树(或默克尔树)
用哈希指针组成的二叉树就是Merkle Tree。
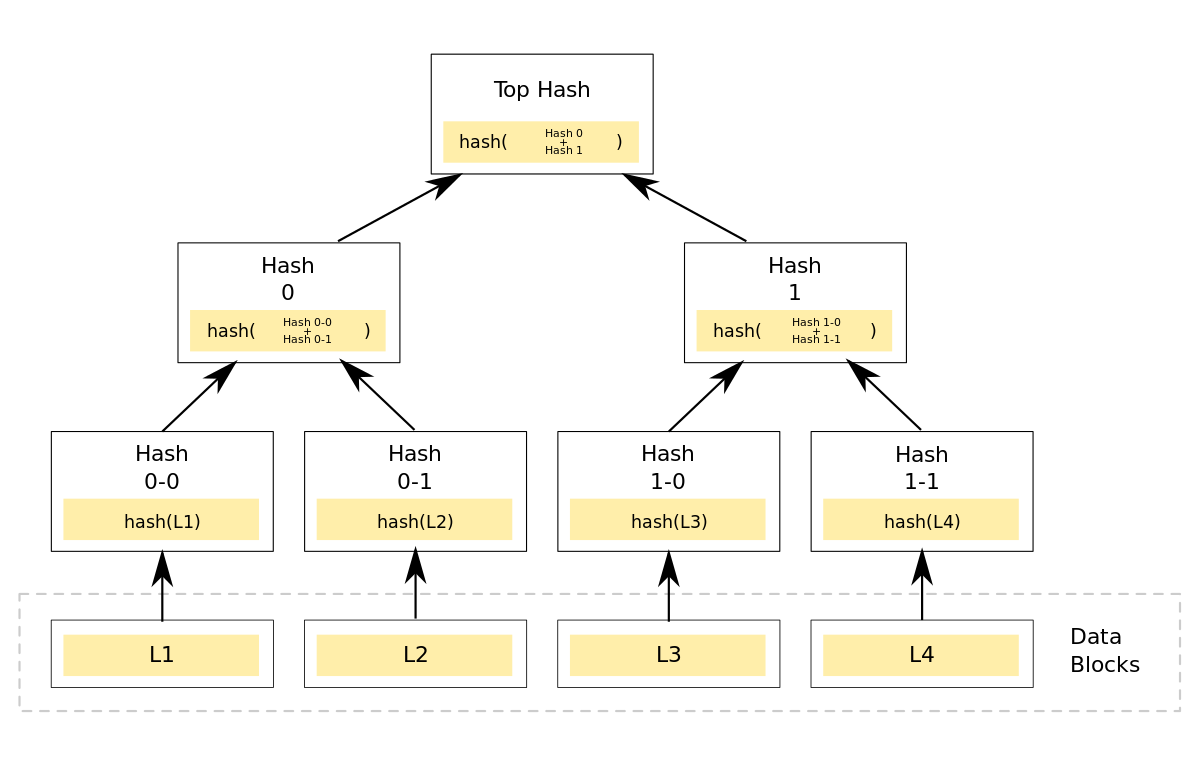
FIGURE 1.7. Merkle tree. In a Merkle tree, data blocks are grouped in pairs, and the hash of each of these blocks is stored in a parent node. The parent nodes are in turn grouped in pairs, and their hashes stored one level up the tree. This pattern continues up the tree until we reach the root node.
-
Tamper evident
就像区块链一样,我们只需要记住根节点(顶级节点)中的哈希指针,然后我们可以向下遍历任何叶数据块,检查节点是否在树中或是否被篡改。
-
Proof of Membership
默尔科夫树能快速验证某个数据块,即便于轻节点查询某个交易(tx)是否已经被写入到区块链中(即对比存储的根哈希值和计算出来的根哈希值是否相等),如下图所示。时间复杂度是log(n)
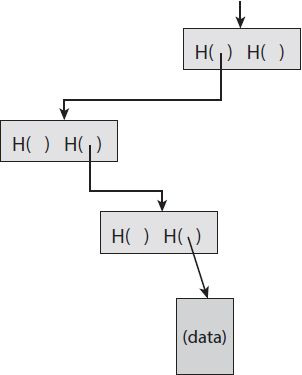
FIGURE 1.8. Proof of membership. To prove that a data block is included in the tree only requires showing the blocks in the path from that data block to the root.
-
proof of non-membership
即证明某个交易不在区块中。如果交易列表是不排序的,那么只能是轻结点只能向全结点请求交易列表的所有内容,然后遍历,证明某个交易不在其中,计算复杂度为O(n)。
如果交易列表是排序的(sorted Merkle tree),比如按照交易的哈希值排序,那么只需要请求相邻两个交易(或者四个,分奇偶)以及其路径上的H(),计算出根哈希值对比本地的根哈希值,如果相同,则说明这几个交易之间没有其他交易,证明此交易的不存在,计算复杂度O(log(n))。
比特币中没有使用sorted Merkle tree,因为比特币不需要这种不存在证明。
参考:
《BITCOIN AND CRYPTOCURRENCY TECHNOLOGIES》
Hash Pointers and Data Structures https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2063525区块链学习笔记与思考-3-比特币中的数据结构 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44083899/article/details/110316342


