centos7.9究极法-基础篇
@
前言
现在的三大主流的操作系统Windows、Mac、Linux
但windows啥都给你封装好了,这也做不了,那也不能干,那还有啥意思嘞,至于Mac(贵!!!)
linux多香,自由、开源、不要钱~,想用它做啥就做啥,完全听话,不像windows这个警告那个不准的,学计算机要是不会用linux,那岂不是很丢人
Linux发行版本
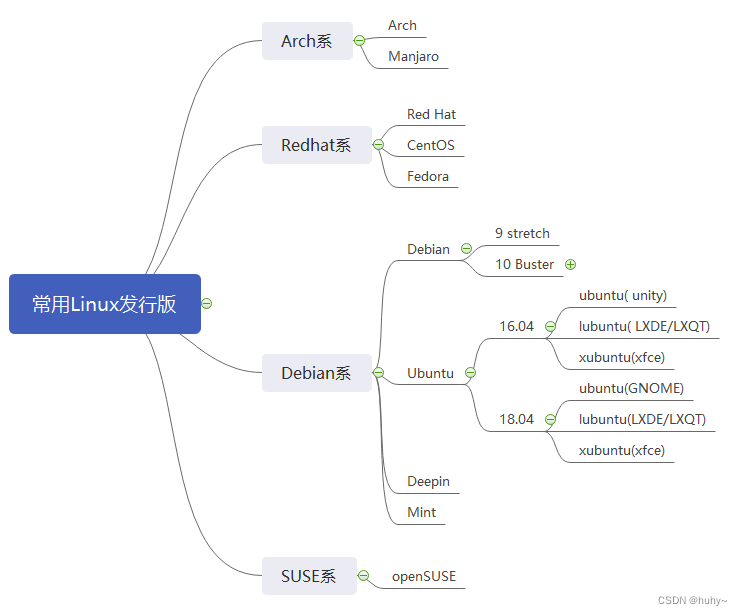
主流的体系和发行版本大致就是这些,各有各的好吧,要详细了解,自行百度了,本文主要介绍centos7.9
帮助命令
man命令
man(英文全拼:manual):帮助手册
man命令就相当于命令手册,可以用来查看命令的用法,帮助新手快速入门
命令格式:man [需查询的命令]
查看ls帮助手册为例,q退出,上下键查看手册详细信息
[root@huhy ~]# man ls
LS(1) User Commands LS(1)
NAME
ls - list directory contents
SYNOPSIS
ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
DESCRIPTION
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of
-cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all
do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all
do not list implied . and ..
--author
with -l, print the author of each file
-b, --escape
print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters
--block-size=SIZE
scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., '--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576
bytes; see SIZE format below
Manual page ls(1) line 1 (press h for help or q to quit)
help命令
help(英文:帮助):帮助手册
与man命令同样的功能,都是用于获取命令的帮助手册
命令格式:[需查询的命令] --help
查看ls帮助手册为例,会输出全部帮助手册,推荐使用man命令查询
[root@huhy ~]# ls --help
Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all do not list implied . and ..
--author with -l, print the author of each file
-b, --escape print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters
--block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,
'--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of
1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below
-B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last
modification of file status information);
with -l: show ctime and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'never', 'auto',
or 'always' (the default); more info below
-d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents
-D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type likewise, except do not append '*'
--format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l,
single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g like -l, but do not list owner
--group-directories-first
group directories before files;
can be augmented with a --sort option, but any
use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable with -l, print sizes in human readable format
(e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link
that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
(overridden by -a or -A)
--indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names:
none (default), slash (-p),
file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage
-l use a long listing format
-L, --dereference when showing file information for a symbolic
link, show information for the file the link
references rather than for the link itself
-m fill width with a comma separated list of entries
-n, --numeric-uid-gid like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs
-N, --literal print raw entry names (don't treat e.g. control
characters specially)
-o like -l, but do not list group information
-p, --indicator-style=slash
append / indicator to directories
-q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters
--show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default,
unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal)
-Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes
--quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names:
literal, locale, shell, shell-always, c, escape
-r, --reverse reverse order while sorting
-R, --recursive list subdirectories recursively
-s, --size print the allocated size of each file, in blocks
-S sort by file size
--sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S),
time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X)
--time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default
modification time: atime or access or use (-u)
ctime or status (-c); also use specified time
as sort key if --sort=time
--time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE:
full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT;
FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT
is FORMAT1<newline>FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies
to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files;
if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE
takes effect only outside the POSIX locale
-t sort by modification time, newest first
-T, --tabsize=COLS assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8
-u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time;
with -l: show access time and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by access time
-U do not sort; list entries in directory order
-v natural sort of (version) numbers within text
-w, --width=COLS assume screen width instead of current value
-x list entries by lines instead of by columns
-X sort alphabetically by entry extension
-1 list one file per line
SELinux options:
--lcontext Display security context. Enable -l. Lines
will probably be too wide for most displays.
-Z, --context Display security context so it fits on most
displays. Displays only mode, user, group,
security context and file name.
--scontext Display only security context and file name.
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units
are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000).
Using color to distinguish file types is disabled both by default and
with --color=never. With --color=auto, ls emits color codes only when
standard output is connected to a terminal. The LS_COLORS environment
variable can change the settings. Use the dircolors command to set it.
Exit status:
0 if OK,
1 if minor problems (e.g., cannot access subdirectory),
2 if serious trouble (e.g., cannot access command-line argument).
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'ls invocation'
文件目录管理命令
ls命令
ls(英文全拼:list files): 列出目录及文件名
用于查看目录和文件名,但不能查看文件的内容,常用ls命令参数如下
ls:查看当前目录下的文件或目录,不能查看隐藏的文件,可搭配路径进行查看
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]# ls /var/
adm crash empty gopher lib lock mail opt run tmp
cache db games kerberos local log nis preserve spool yp
[root@huhy ~]#
ls -a:查看当前目录下点开头的隐藏文件
[root@huhy ~]# ls -a
. .. anaconda-ks.cfg .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .cshrc .tcshrc
[root@huhy ~]#
ls -l(命令可缩写:ll):以长格式显示文件和目录的详细信息,包括文件权限、所有者、大小、修改日期等
[root@huhy ~]# ls -l
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]#
ls -R:递归地列出子目录的内容,包括子目录中的文件和目录(类型tree命令)
[root@huhy ~]# mkdir -p test/{test1,test2}
[root@huhy ~]# ls -R
.:
anaconda-ks.cfg test
./test:
test1 test2
./test/test1:
./test/test2:
[root@huhy ~]# ls test/
test1 test2
[root@huhy ~]#
ls -r:按照字母逆序(反向)列出文件和目录(感觉没啥用)
[root@huhy ~]# touch bbb
[root@huhy ~]# touch ccc
[root@huhy ~]# touch kkkk
[root@huhy ~]# touch zzzz
[root@huhy ~]# ls -r
zzzz kkkk ccc bbb anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]#
ls -t:按照修改时间排序,最近修改的文件和目录在前面(可以用来查看上一次修改的是哪个文件)
[root@huhy ~]# touch aaa
[root@huhy ~]# touch bbb
[root@huhy ~]# touch ccc
[root@huhy ~]# touch ddd
[root@huhy ~]# ls -t
ddd ccc bbb aaa anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]#
进阶用法可以组合搭配使用,例如ll -a等
[root@huhy ~]# ll -a
total 24
dr-xr-x---. 2 root root 158 Jul 28 21:38 .
dr-xr-xr-x. 17 root root 224 Jun 4 06:53 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 28 21:38 aaa
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18 Dec 28 2013 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 Dec 28 2013 .bash_profile
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 Dec 28 2013 .bashrc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 28 21:38 bbb
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 28 21:38 ccc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 100 Dec 28 2013 .cshrc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 28 21:38 ddd
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 129 Dec 28 2013 .tcshrc
pwd命令
pwd(英文全拼:print work directory):显示目前的目录路径
用于显示当前目录的路径,一般都直接使用
pwd:查看当前目录路径
[root@huhy ~]# cd /usr/local/bin/
[root@huhy bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
cd命令
cd(英文全拼:change directory):切换目录
用于切换进入到某个目录,通常情况下cd命令不需要参数
cd:用于切换到主目录通常是/root目录下
[root@huhy opt]# cd
[root@huhy ~]# pwd
/root
[root@huhy ~]#
cd 路径:用于切换到某个指定目录下
[root@huhy ~]# cd /opt/
[root@huhy opt]# pwd
/opt
[root@huhy opt]# cd /etc/
[root@huhy etc]# pwd
/etc
[root@huhy etc]# cd /usr/local/bin/
[root@huhy bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
[root@huhy bin]# cd
[root@huhy ~]# pwd
/root
[root@huhy ~]#
cd 两个点:表示切换到上一级目录
[root@huhy bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
[root@huhy bin]# cd ..
[root@huhy local]# pwd
/usr/local
[root@huhy local]#
cd 短杠:切换到上次所在的目录,如果不小心退出当前目录到其他目录,可用于返回到该目录
[root@huhy ~]# cd /usr/local/bin/
[root@huhy bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
[root@huhy bin]# cd
[root@huhy ~]# pwd
/root
[root@huhy ~]# cd -
/usr/local/bin
[root@huhy bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
[root@huhy bin]#
mkdir命令
mkdir(英文全拼:make directory):创建一个新的目录
创建目录命令
mkdir 目录名:用于创建一个目录
[root@huhy ~]# mkdir test
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:16 test
mkdir -p 目录名:用于递归创建多级目录结构,如果父目录不存在也会创建
[root@huhy ~]# mkdir -p demo/demo1/demo2
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R
.:
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 19 Jul 29 03:19 demo
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:16 test
./demo:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 19 Jul 29 03:19 demo1
./demo/demo1:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:19 demo2
./demo/demo1/demo2:
total 0
./test:
total 0
mkdir -m 目录名:用于创建目录的时候给目录赋予权限
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 19 Jul 29 03:19 demo
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:16 test
[root@huhy ~]# mkdir -m 777 huhy
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 19 Jul 29 03:19 demo
drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:22 huhy
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jul 29 03:16 test
[root@huhy ~]#
进阶方式:使用{}创建多个递归目录
[root@huhy ~]# mkdir -p test1/{test2,test3}/test4
[root@huhy ~]# ls test1/
test2 test3
[root@huhy ~]# ls test1/test2/
test4
[root@huhy ~]# ls test1/test3/
test4
[root@huhy ~]#
cp命令
cp(英文全拼:copy file): 复制文件或目录
用于复制文件或者目录
cp 源文件 目标文件:复制源文件为新的目标文件
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cp test.txt test2.txt
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test2.txt test.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
cp -r 源文件 目标文件:复制目录及其内容(递归复制)
[root@huhy ~]# ll demo/
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 03:41 test2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 03:36 test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cp -r demo/ /opt/
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R /opt/
/opt/:
total 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 39 Jul 29 03:51 demo
/opt/demo:
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 03:51 test2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 03:51 test.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
cp -v 源文件 目标文件:显示详细的复制过程,输出复制的文件名
[root@huhy ~]# cp -v test.txt /opt/
‘test.txt’ -> ‘/opt/test.txt’
[root@huhy ~]#
cp -b 源文件 目标文件:在复制时进行备份,保留原始文件的备份副本
[root@huhy ~]# cp -b test.txt test.txt.bak
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 12
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 12 Jul 29 04:00 test.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 12 Jul 29 04:06 test.txt.bak
[root@huhy ~]#
scp命令
scp(英文全拼:Secure Copy): 用于两台主机之间远程复制文件或目录
cp命令适用于主机内部,scp则用于两台之间的远程复制
scp 源文件 目标文件:可以把自己的文件复制到别人主机上,反之亦然,复制时需要输入密码确认,并且复制对方的服务器需要指定IP,我这里是以window和centos7.9为例
PS C:\Users\huhy> scp root@192.168.200.100:/root/test.txt C:\Users\huhy\Desktop\
root@192.168.200.100's password:
test.txt 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
PS C:\Users\huhy>
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -P | 指定远程主机的SSH端口号,默认是22 |
| -r | 递归复制目录,用于复制目录及其子目录和文件 |
| -v | 显示详细的操作信息,用于调试 |
| -p | 保持源文件的修改时间、权限和访问时间 |
| -C | 开启压缩,加快传输速度 |
| -q | 安静模式,不显示传输进度和错误信息 |
| -v | 显示详细的操作信息,用于调试 |
rm命令
rm(英文全拼:remove): 删除文件或目录
这个命令可以用来删除文件目录压缩包等,rm命令谨慎使用,删除后无法挽回
rm 文件或目录名:直接删除,并需要进行确认
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.txt test.txt.bak
[root@huhy ~]# rm test.txt
rm: remove regular file ‘test.txt’? y
[root@huhy ~]#
rm -r 目录名:递归删除啊!最常用在目录的删除
[root@huhy ~]# ll /opt/
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 06:39 aaaa.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jul 29 06:39 dddd.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 12 Jul 29 04:05 test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# rm -r /opt/*
rm: remove regular empty file ‘/opt/aaaa.txt’? y
rm: remove regular empty file ‘/opt/dddd.txt’? y
rm: remove regular file ‘/opt/test.txt’? y
[root@huhy ~]#
rm -f 目录名:就是 force 的意思,忽略不存在的文件,不会出现警告信息,直接删除
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.txt.bak
[root@huhy ~]# rm -f test.txt.bak
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
高阶用法
rm -rf * d *:批量删除除包括d字符的文件,用星号代替包含a的所有字符(慎用,我好像不小心删错东西了),还可以多个组合使用
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaaa.txt anaconda-ks.cfg dkcjd.txt dskdifj.txt kkkk.txt
[root@huhy ~]# rm -rf *d*
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaaa.txt kkkk.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaa bbb ccc ddd eee fff
[root@huhy ~]# rm -rf *b* *c* *d*
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaa eee fff
[root@huhy ~]#
rm -rf !(文件名1|文件名2):删除除了这个文件外的其他所有文件(慎用),需要开启extglob
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaaa.txt dddddd.txt kdickdk.txt kkkk.txt
[root@huhy ~]# shopt -s extglob
[root@huhy ~]# rm -rf !(aaaaa.txt)
[root@huhy ~]# ls
aaaaa.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
mv命令
mv(英文全拼:move file): 移动文件与目录,或修改文件与目录的名称
用来移动或者修改文件或者目录,此命令一般直接使用,不带参数
mv 文件或目录名:移动或命名
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg zzzz.txt
[root@huhy ~]# mv zzzz.txt /opt/
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@huhy ~]# ls /opt/
zzzz.txt
[root@huhy ~]# mv /opt/zzzz.txt /opt/bbb.txt
[root@huhy ~]# ls /opt/
bbb.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
chmod命令
chmod(英文全拼:Change Mode): 表示改变文件或目录的权限模式
本文针对使用数字权限的教学,不使用符号
| 数字 | 权限 |
|---|---|
| 4 | r (读权限) |
| 2 | w( 写权限) |
| 1 | x(执行权限) |
chmod 数字权限 文件或目录名:权限中分别代表(文件所有者、文件组、其他人),而每组分别用数字来表示其权限
注;-rw-r--r--(第一个短杠代表这是文件,目录用小写d表示,而后r开头的表示所有者、文件组、其他人的对应权限,分别有三组数字对应三个组别的权限)
[root@huhy ~]# touch huhy
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 10:41 huhy
[root@huhy ~]# chmod 777 huhy #7为(4读+3写+1执行)表示把该组别的读写执行的权限打开
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 10:41 huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
分别只打开所有者、用户组、其他人的读执行权限,不打开写权限
[root@huhy ~]# chmod 555 huhy #5(4读+1执行)
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
-r-xr-xr-x. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 10:41 huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
打开所有者的读写执行,用户组的读执行、其他人的写执行
[root@huhy ~]# chmod 753 huhy
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
-rwxr-x-wx. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 10:41 huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
chmod -R 数字 文件或目录名:递归地修改文件夹及其内容的权限
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R huhy/
huhy/:
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 11:02 zzz.txt
[root@huhy ~]# chmod -R 777 huhy/
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 21 Aug 6 11:02 huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R huhy/
huhy/:
total 0
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 11:02 zzz.txt
chown命令
chown(英文全拼:change owner):表示改变文件或目录的所有者
命令用于更改文件或目录的所有者(owner)和群组(group)
chown 新所有者:新群组 文件或目录名:改变文件或目录的所有者和群组
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 21 Aug 6 11:02 huhy
[root@huhy ~]# chown huhy:huhy huhy/
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 0
drwxrwxrwx. 2 huhy huhy 21 Aug 6 11:02 huhy #将root所有者和root组都改为huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
chown -R 新所有者:新群组 文件或目录名:递归改变文件或目录的所有者和群组
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R huhy/
huhy/:
total 0
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Aug 6 11:02 zzz.txt
[root@huhy ~]# chown -R huhy:huhy huhy/
[root@huhy ~]# ll -R huhy/
huhy/:
total 0
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 huhy huhy 0 Aug 6 11:02 zzz.txt
[root@huhy ~]#
文本内容管理命令
cat命令
cat(英文全拼:concatenate):主要是用于查看文件内容,但也有其它的高阶用法
cat命令很常用,除了查看文件外,还能复制文件,合并,创建等
cat 文件名:查看文件文件内容
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]#
cat 文件名1 文件名2:查看多个文件文件内容,并显示在同一屏幕
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]# cat test2.txt
vvvvvvvv
ddddd
gggggg
eeeeeeee
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt test2.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
vvvvvvvv
ddddd
gggggg
eeeeeeee
[root@huhy ~]#
cat -n 文件名:查看文件文件内容,并显示行号
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat -n test.txt
1 aaaaaaa
2 bbbbbbbbbb
3 cccccccccc
4 dddddddddddddd
5 eeeeeeeee
6 ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]#
cat -A 文件名:查看文件文件内容,并显示内容中结尾的空格,然后以美元符号结尾
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 8
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 89 Jul 29 21:42 test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat -A test.txt
aaaaaaa $
bbbbbbbbbb $
cccccccccc $
dddddddddddddd$
eeeeeeeee$
ffffffffffff$
[root@huhy ~]#
高阶用法
==cat > 文件名 <<eof ==:cat命令创建文件,回车后输入内容,然后eof结尾即可
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test2.txt test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat > test3.txt <<eof
> aaaaa
> bbbbb
> ccccc
> dddddddd
> eeeeeeeee
>
> ffffffffffff
> eof
[root@huhy ~]# cat test3.txt
aaaaa
bbbbb
ccccc
dddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]#
cat 源文件 > 目标文件:使用cat复制文件
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test2.txt test3.txt test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt > /opt/demo.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat /opt/demo.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]#
cat 文件名1 文件名2 > 新文件:使用cat合并文件为新的文件
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test2.txt test3.txt test.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
[root@huhy ~]# cat test2.txt
vvvvvvvv
ddddd
gggggg
eeeeeeee
[root@huhy ~]# cat test.txt test2.txt > demo.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat demo.txt
aaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbbb
cccccccccc
dddddddddddddd
eeeeeeeee
ffffffffffff
vvvvvvvv
ddddd
gggggg
eeeeeeee
[root@huhy ~]#
echo命令
echo(英文全拼:Ech-Oh):输出文件
主要是用于写入文件,和打印输出文件到屏幕
echo "字符":将字符输出到屏幕,建议是加引号,在一些复制的特殊字符情况下,不加引号可能会报错
[root@huhy ~]# echo "a b c d"
a b c d
[root@huhy ~]#
不加引号的区别
[root@huhy ~]# echo -e huhy\nhuhy
huhynhuhy
[root@huhy ~]# echo -e "huhy\nhuhy"
huhy
huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
echo "$字符":打印变量值
[root@huhy ~]# a=huhy
[root@huhy ~]# echo "$a"
huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
echo -e "字符\字符":将字符输出到屏幕并换行
[root@huhy ~]# echo -e "huhy\nhuhy"
huhy
huhy
echo "字符" > 文件:将字符内容重定向写入文件,文件不存在则自动创建
[root@huhy ~]# echo "huhy" > huhy.txt
[root@huhy ~]# cat huhy.txt
huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
less命令
less(英文全拼:Less is more):用于更方便的查看文件
它提供了比more命令更多的功能,可以向上或向下滚动浏览文件,搜索内容,跳转到指定行等
| 操作 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| 空格键 | 向下翻动一页 |
| [pagedown] | 向下翻动一页 |
| [pageup] | 向上翻动一页 |
| /字串 | 向下搜寻『字串』的功能 |
| n | 重复前一个搜寻 (与 / 或 ? 有关!) |
| N | 反向的重复前一个搜寻 (与 / 或 ? 有关!) |
| q | 离开 less 这个程序 |
tail命令
tail(英文全拼:Tail):用于实时查看文件内容
它的主要功能是输出文件的最后几行内容,可以帮助用户实时监视文件的更新或仅查看文件的末尾部分
tail -n 数字 文件名:不加参数默认显示10行,查看文件末尾多少行内容,查看后会退出
[root@huhy ~]# tail -n 5 /var/log/messages
Jul 29 21:54:02 huhy systemd: Started Cleanup of Temporary Directories.
Jul 29 22:01:02 huhy systemd: Started Session 2 of user root.
Jul 29 22:40:46 huhy systemd: Reloading.
Jul 29 22:40:46 huhy yum[1765]: Installed: vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64
Jul 29 23:01:01 huhy systemd: Started Session 3 of user root.
[root@huhy ~]#
tail -f 文件名:实时查看文件末尾内容,一般用于日志监控,一直实时查看日志内容
[root@huhy ~]# tail -f /var/log/messages
Jul 29 21:38:55 huhy systemd: Created slice User Slice of root.
Jul 29 21:38:55 huhy systemd-logind: New session 1 of user root.
Jul 29 21:38:55 huhy systemd: Started Session 1 of user root.
Jul 29 21:39:52 huhy chronyd[760]: Selected source 202.118.1.130
Jul 29 21:54:02 huhy systemd: Starting Cleanup of Temporary Directories...
Jul 29 21:54:02 huhy systemd: Started Cleanup of Temporary Directories.
Jul 29 22:01:02 huhy systemd: Started Session 2 of user root.
Jul 29 22:40:46 huhy systemd: Reloading.
Jul 29 22:40:46 huhy yum[1765]: Installed: vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64
Jul 29 23:01:01 huhy systemd: Started Session 3 of user root.
用户和组管理命令
useradd命令
useradd(英文全拼:User Add):在系统中添加新用户账户,并设置相关的用户信息和配置
在系统中添加用户,一般是搭配参数使用
| 常用参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -c | 指定用户的注释/描述信息 |
| -d | 指定用户的家目录路径 |
| -g | 指定用户所属的初始组(使用组名或组ID) |
| -m | 如果家目录不存在,则创建用户的家目录 |
| -s | 指定用户的默认Shell |
| -u | 为用户指定一个特定的用户ID |
| -e | 指定用户账户的过期日期 |
| -f | 设置用户账户的不活动时间,过了这个时间后账户将被锁定 |
useradd 参数 用户名:用全部参数作一个详细说明;创建用户hoyeong,工作目录opt下hoyeong,用户id9999,root用户组,描述信息”user_hoyeong“,过期时间2023-12-30,超过10天不用则用户锁定
[root@huhy ~]# useradd -m -d /opt/hoyeong -s /bin/bash -u 99999 -g root -c "user_hoyeong" -e 2023-12-30 -f 10 hoyeong
[root@huhy ~]# grep "hoyeong" /etc/passwd
hoyeong:x:99999:0:user_hoyeong:/opt/hoyeong:/bin/bash
[root@huhy ~]# id hoyeong
uid=99999(hoyeong) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
[root@huhy ~]# chage -l hoyeong
Last password change : Aug 07, 2023
Password expires : never
Password inactive : never
Account expires : Dec 30, 2023
Minimum number of days between password change : 0
Maximum number of days between password change : 99999
Number of days of warning before password expires : 7
userdel命令
useradd(英文全拼: User Delete):系统中删除用户账户
用于删除创建得用户
userdel 用户名:删除一个用户账户(不会删除家目录)
[root@huhy ~]# useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/test test
[root@huhy ~]# ll /home/
total 0
drwx------. 2 test test 62 Aug 7 01:08 test
[root@huhy ~]# userdel test
[root@huhy ~]# ll /home/
total 0
drwx------. 2 10000 10000 62 Aug 7 01:08 test
[root@huhy ~]#
userdel -r 用户名:删除一个用户账户(包括删除家目录和邮件箱)
[root@huhy ~]# useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/test3 test3
[root@huhy ~]# ll /home/
total 0
drwx------. 2 test2 test2 62 Aug 7 01:08 test
drwx------. 2 test3 test3 62 Aug 7 01:10 test3
[root@huhy ~]# userdel -r test3
[root@huhy ~]# ll /home/
total 0
drwx------. 2 test2 test2 62 Aug 7 01:08 test
[root@huhy ~]#
userdel -f 用户名:强制删除一个用户账户,即使用户当前已登录或有进程运行
[root@huhy ~]# userdel -f huhy #这个就不好展示了
[root@huhy ~]#
passwd命令
passwd(英文全拼:Password):在系统中更改用户密码
用于创建用户后给用户设置密码
passwd:用于给当前用户设置密码,需要输入两次
[root@huhy ~]# passwd
Changing password for user root.
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is a palindrome
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@huhy ~]#
passwd 用户名:用于给其他用户设置密码,需要管理员权限,且管理员可以免密登录普通用户,需要切换其他普通用户验证密码设置是否成功
[root@huhy ~]# useradd hwiung
[root@huhy ~]# passwd hwiung
Changing password for user hwiung.
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is a palindrome
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@huhy ~]# su huhy
[huhy@huhy root]$ su hwiung
Password:
[hwiung@huhy root]$
passwd -l 用户名:锁定用户,禁止登录
[root@huhy ~]# passwd -l hwiung
Locking password for user hwiung.
passwd: Success
[root@huhy ~]# su huhy
[huhy@huhy root]$ su hwiung
Password:
su: Authentication failure
[huhy@huhy root]$
passwd -u 用户名:解除锁定用户,允许登录
[root@huhy ~]# passwd -u hwiung
Unlocking password for user hwiung.
passwd: Success
[root@huhy ~]# su huhy
[huhy@huhy root]$ su hwiung
Password:
[hwiung@huhy root]$
passwd -d 用户名:删除用户密码,使其变成无密码状态
[root@huhy ~]# passwd -d hwiung
Removing password for user hwiung.
passwd: Success
[root@huhy ~]# su huhy
[huhy@huhy root]$ su hwiung
[hwiung@huhy root]$
passwd -e 用户名:将一个用户密码设置为过期,要求用户在下次登录时更改密码
[root@huhy ~]# passwd -e huhy
Expiring password for user huhy.
passwd: Success
[root@huhy ~]# su hwiung
[hwiung@huhy root]$ su huhy
Password:
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
Changing password for huhy.
(current) UNIX password:
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is the same as the old one
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password is the same as the old one
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password fails the dictionary check - it is based on a dictionary word
su: Have exhausted maximum number of retries for service
[hwiung@huhy root]$ su huhy
Password:
su: Authentication failure
[hwiung@huhy root]$
usermod命令
usermod(英文全拼:User Modify):用于修改已存在的用户账户的属性和设置
顾名思义,用来修改创建好的用户的信息,由于不经常用到,我就快速演示了
修改用户的注释/描述信息
usermod -c "New description" username
修改用户的家目录路径
usermod -d /new/home/directory username
修改用户的初始组
usermod -g newgroup username
将用户添加到附加组列表中
usermod -aG group1,group2 username
修改用户的登录名(用户名)
usermod -l newusername oldusername
修改用户的默认Shell
usermod -s /bin/bash username
groupadd命令
groupadd(英文全拼:Group Add):统中创建新的用户组
用户组可以管理一群用户的权限,由于不常用,就快速演示了
创建一个新的用户组
groupadd mygroup
创建一个新的用户组,并为其指定特定的组ID
groupadd -g 1001 mygroup
创建一个系统组
groupadd -r systemgroup
强制创建一个新的用户组,即使组名已存在,也不会报错
groupadd -f mygroup
groupdel命令
groupdel(英文全拼:Group Delete):删除系统中的用户组
删除用户组由于不常用,就快速演示了
删除一个用户组
groupdel mygroup
强制删除一个用户组,即使组内有用户或者文件拥有者
groupdel -f mygroup
su命令
su(英文全拼:Substitute User):用于切换用户身份
命令用于切换用户身份
su:默认切换到root超级用户
su -:切换到root超级用户,并刷新用户环境和权限(推荐使用)
su 用户名 -:切换到其他用户(普通用户切换需要输入密码)
[root@huhy ~]# su hwiung -
[hwiung@huhy root]$
su -c "命令" 用户:例如以超级用户身份执行特定命令
[root@huhy ~]# su -c "ls /opt" root -
hoyeong huhy
[root@huhy ~]#
网络管理命令
ip命令
ip(英文全拼:Internet Protocol):用于配置和管理网络的强大工具
本文主要简单使用,并未深入路由配置等信息
ip addr(ip a):查看网络接口信息
[root@huhy ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.100/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::2509:a1e6:bd33:cb1a/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:bc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.21/24 scope global ens34
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@huhy ~]#
ip link set 接口名 up/down:开启或关闭网络接口
[root@huhy ~]# ip link set ens34 down
[root@huhy ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.100/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::2509:a1e6:bd33:cb1a/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:bc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.21/24 scope global ens34
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@huhy ~]# ip link set ens34 up
[root@huhy ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.100/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::2509:a1e6:bd33:cb1a/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:bc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.21/24 scope global ens34
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@huhy ~]#
ip addr add IP地址 dev 接口名:添加临时IP地址,不同于修改配置文件,重启后就会失效
[root@huhy ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.100/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::2509:a1e6:bd33:cb1a/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:bc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.21/24 scope global ens34
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@huhy ~]#
ip addr del IP地址 dev 接口名:删除临时IP地址,不同于修改配置文件,重启后就会失效
[root@huhy ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.200.100/24 brd 192.168.200.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::2509:a1e6:bd33:cb1a/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens34: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:17:48:bc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
[root@huhy ~]#
ping命令
ping(英文全拼:Packet Internet Groper):用于网络诊断的工具,检测连通性
ping命令很常用,用法也很单一
ping ip地址:检测ip连通性,会持续发送,默认无限制,需要手动终止
[root@huhy ~]# ping 192.168.200.100
PING 192.168.200.100 (192.168.200.100) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.043 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.037 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.046 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.042 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.297 ms
^C
--- 192.168.200.100 ping statistics ---
7 packets transmitted, 7 received, 0% packet loss, time 5999ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.036/0.077/0.297/0.090 ms
[root@huhy ~]#
ping ip地址 -c 4:指定发送4次ping包
[root@huhy ~]# ping 192.168.200.100 -c 4
PING 192.168.200.100 (192.168.200.100) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.040 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.200.100: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms
--- 192.168.200.100 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.036/0.039/0.040/0.002 ms
[root@huhy ~]#
ss命令
ss(英文全拼:Socket Statistics):用于获取网络状态的工具
ss命令一般搭配参数使用
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -t | 显示 TCP 连接的统计信息 |
| -u | 显示 UDP 连接的统计信息 |
| -n | 以数字格式显示 IP 地址和端口号,而不进行 DNS 解析 |
| -l | 仅显示监听状态的连接 |
ss -tuln:显示当前系统上所有 TCP 和 UDP 监听连接的统计信息,包括端口号和 IP 地址
[root@huhy ~]# ss -tuln
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::1]:323 [::]:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
tcp LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:*
ssh命令
ssh(英文全拼:Secure Shell):一种加密的网络协议,用于在远程计算机之间进行安全的数据通信和远程登录
简而言之,就是用来远程登录主机的
ssh 用户名@地址:远程登录机器,并指定IP,需要输入机器密码
PS C:\Users\huhy> ssh root@192.168.200.100
root@192.168.200.100's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 7 23:14:40 2023 from 192.168.200.1
[root@huhy ~]#
ssh-keygen 参数:用于生成密钥,提供免密登录,一般默认不带参数,回车四下即可生成
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -t | 指定要生成的密钥类型(如rsa、dsa、ecdsa、ed25519等 |
| -b | 指定密钥的位数 |
| -C | 添加注释,通常是标识密钥的描述信息 |
| -f | 指定生成的密钥文件名 |
[root@huhy ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:ziTk9J8c7BcLclpdPmMDK/2VpR/Z/Vx9q+8hQ0chN7g root@huhy
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| ..+ |
| .o o|
| o . o..|
| + . . o E..B|
| o S B =.B=B|
| = O =.=.B*|
| + = oo.o+|
| . + .|
| .oo |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@huhy ~]#
ssh-copy-id 用户名@主机名:将生成的密钥文件发送给其他主机,以便其他主机可以免密登录
[root@huhy ~]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.200.100
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.200.100 (192.168.200.100)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:/LmYaZdcEvmXiTHfa5Kp7OwHmftooT5TsZxdN7Nid6c.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:51:4f:61:c7:6c:6e:84:ac:89:c6:df:cf:1c:b8:00:0c.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.200.100's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.200.100'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@huhy ~]# ssh 192.168.200.100
Last login: Tue Aug 8 12:19:08 2023 from 192.168.200.1
[root@huhy ~]#
wget命令
wget(英文全拼:Web Get):用于从网络上下载文件的命令行工具
很好用的一个工具,搭配参数使用,以下快速演示
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -r | 递归下载,下载指定URL页面上的所有链接指向的文件 |
| -N | 只下载比本地文件新的文件 |
| -P | 指定保存下载文件的目录路径 |
| -O | 将下载的文件保存为指定的文件名 |
| -c | 继续下载中断的文件 |
| -q | 静默模式,减少输出信息 |
| --limit-rate | 限制下载速率,以避免过大的网络流量 |
| --user | 设置HTTP用户名 |
| --password | 设置HTTP密码 |
| --ftp-user | 设置FTP用户名 |
| --ftp-password | 设置FTP密码 |
下载单个文件
wget http://example.com/file.txt
递归下载整个网站
wget -r http://example.com/
只下载比本地文件新的文件
wget -N http://example.com/file.txt
将下载的文件保存到指定目录
wget -P /path/to/save http://example.com/file.zip
将下载的文件保存为指定文件名
wget -O newfile.txt http://example.com/oldfile.txt
继续下载中断的文件
wget -c http://example.com/largefile.zip
静默模式,减少输出信息
wget -q http://example.com/file.txt
限制下载速率为100KB/s
wget --limit-rate=100k http://example.com/largefile.zip
使用用户名和密码进行下载(HTTP)
wget --user=myusername --password=mypassword http://example.com/securefile.txt
使用用户名和密码进行下载(FTP)
wget --ftp-user=myftpuser --ftp-password=myftppassword ftp://example.com/file.zip
curl命令
curl(英文全拼:Client URL):用于传输数据的命令行工具
一般用它下载网上文件比较多,以下快速演示
下载文件并保存到指定文件名
curl -o myfile.txt http://example.com/file.txt
下载文件并保存为远程文件名
curl -O http://example.com/file.zip
仅获取响应头信息,不下载文件数据
curl -I http://example.com/file.txt
软件包管理命令
yum命令
yum(英文全拼:Yellowdog Updater Modified):Yellowdog Updater Modified
用来管理软件包,包括安装、升级、删除和查询软件包信息
yum install -y 软件包名:-y表示自动回答yes,软件包名可以是多个
[root@huhy ~]# yum install -y vsftpd
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package vsftpd.x86_64 0:3.0.2-29.el7_9 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
========================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
========================================================================================================================
Installing:
vsftpd x86_64 3.0.2-29.el7_9 updates 173 k
Transaction Summary
========================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 173 k
Installed size: 353 k
Downloading packages:
vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64.rpm | 173 kB 00:00:00
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
vsftpd.x86_64 0:3.0.2-29.el7_9
Complete!
[root@huhy ~]#
更新软件包
yum update
升级系统
yum upgrade
删除软件:默认会连配置文件也删除
yum remove -y 软件包名
yum search 软件包名:搜索软件包
[root@huhy ~]# yum search mariadb
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
================================================= N/S matched: mariadb =================================================
mariadb-bench.x86_64 : MariaDB benchmark scripts and data
mariadb-devel.i686 : Files for development of MariaDB/MySQL applications
mariadb-devel.x86_64 : Files for development of MariaDB/MySQL applications
mariadb-embedded.i686 : MariaDB as an embeddable library
mariadb-embedded.x86_64 : MariaDB as an embeddable library
mariadb-embedded-devel.i686 : Development files for MariaDB as an embeddable library
mariadb-embedded-devel.x86_64 : Development files for MariaDB as an embeddable library
mariadb-libs.i686 : The shared libraries required for MariaDB/MySQL clients
mariadb-libs.x86_64 : The shared libraries required for MariaDB/MySQL clients
mariadb-server.x86_64 : The MariaDB server and related files
mariadb.x86_64 : A community developed branch of MySQL
mariadb-test.x86_64 : The test suite distributed with MariaD
Name and summary matches only, use "search all" for everything.
[root@huhy ~]#
yum info 软件包名:显示软件包信息
[root@huhy ~]# yum info vsftpd
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
Installed Packages
Name : vsftpd
Arch : x86_64
Version : 3.0.2
Release : 29.el7_9
Size : 353 k
Repo : installed
From repo : updates
Summary : Very Secure Ftp Daemon
URL : https://security.appspot.com/vsftpd.html
License : GPLv2 with exceptions
Description : vsftpd is a Very Secure FTP daemon. It was written completely from
: scratch.
[root@huhy ~]#
yum list | grep 软件包名:列出已安装软件包,一般搭配grep过滤
[root@huhy ~]# yum list|grep vsftpd
vsftpd.x86_64 3.0.2-29.el7_9 @updates
vsftpd-sysvinit.x86_64 3.0.2-29.el7_9 updates
[root@huhy ~]#
yum clean all:清理缓存
[root@huhy ~]# yum clean all
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Cleaning repos: base extras updates
Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors
[root@huhy ~]#
yum repolist:显示仓库列表
[root@huhy ~]# yum repolist
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Determining fastest mirrors
* base: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.cqu.edu.cn
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
(1/4): base/7/x86_64/group_gz | 153 kB 00:00:00
(2/4): extras/7/x86_64/primary_db | 250 kB 00:00:00
(3/4): base/7/x86_64/primary_db | 6.1 MB 00:00:01
(4/4): updates/7/x86_64/primary_db | 22 MB 00:00:03
repo id repo name status
base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base 10,072
extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras 518
updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates 5,130
repolist: 15,720
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl命令
systemctl(英文全拼:System Control):用于管理 Systemd 系统和服务
这个命令就厉害了,十分常用,常用的参数--now,可以在下面每个示例命令添加,立即生效
systemctl | grep 服务名:查找服务
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl | grep ftp
vsftpd.service loaded active running Vsftpd ftp daemon
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl start 服务名:启动服务
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl start vsftpd
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl stop 服务名:停止服务
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl stop vsftpd
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl restart 服务名:重启服务
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl restart vsftpd
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl status 服务名:查看服务状态
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl status vsftpd
● vsftpd.service - Vsftpd ftp daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-08-09 00:11:51 EDT; 29s ago
Process: 2465 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2466 (vsftpd)
CGroup: /system.slice/vsftpd.service
└─2466 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
Aug 09 00:11:51 huhy systemd[1]: Starting Vsftpd ftp daemon...
Aug 09 00:11:51 huhy systemd[1]: Started Vsftpd ftp daemon.
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl enable 服务名:启动开机自启动
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl enable vsftpd
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/vsftpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service.
[root@huhy ~]#
systemctl disable 服务名:禁用开机自启动
[root@huhy ~]# systemctl disable vsftpd
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/vsftpd.service.
[root@huhy ~]#
journalctl命令
journalctl(英文全拼:Journal Control):用于在 Systemd 系统中查看和管理系统日志
查看日志排错等
查看所有日志
journalctl
查看引导时的日志
journalctl -b
查看内核消息
journalctl -k
仅显示错误和警告消息
journalctl -p err..warning
输出详细信息
journalctl -xe
进程和系统状态命令
ps命令
ps(英文全拼:Process Status):查看正在运行的进程列表
查看进程列表,快速演示
显示当前终端下的进程
[root@huhy ~]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
2137 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
2186 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
2951 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
显示所有正在运行的进程:通常要过滤
ps aux
显示当前用户的进程
ps -u username
显示指定进程的详细信息
ps -p PID
free命令
free(英文全拼:Free - Display Amount of Free and Used System Memory):显示系统内存的使用情况
查看系统内存情况,快速演示
free:显示内存信息
[root@huhy ~]# free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3861288 309148 3108272 20068 443868 3309736
Swap: 4063228 0 4063228
[root@huhy ~]#
free -h:以人类可读的格式显示内存信息
[root@huhy ~]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3.7G 302M 3.0G 19M 433M 3.2G
Swap: 3.9G 0B 3.9G
[root@huhy ~]#
free -m:只显示物理内存信息
[root@huhy ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3770 302 3035 19 433 3231
Swap: 3967 0 3967
[root@huhy ~]#
free -s 秒数:持续显示内存信息,如秒数2,则以2miao显示一次
[root@huhy ~]# free -s 2
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3861288 309028 3108388 20068 443872 3309856
Swap: 4063228 0 4063228
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3861288 309028 3108388 20068 443872 3309856
Swap: 4063228 0 4063228
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3861288 309028 3108388 20068 443872 3309856
Swap: 4063228 0 4063228
^C
[root@huhy ~]#
搭配h参数可视化使用
[root@huhy ~]# free -h -s 2
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3.7G 301M 3.0G 19M 433M 3.2G
Swap: 3.9G 0B 3.9G
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3.7G 302M 3.0G 19M 433M 3.2G
Swap: 3.9G 0B 3.9G
^C
[root@huhy ~]#
uptime命令
uptime(英文全拼:Uptime - Show How Long the System Has Been Running):显示系统的运行时间以及平均负载信息
主要查看系统运行的时间和负载
uptime:显示系统运行时间、平均负载和登录用户数
[root@huhy ~]# uptime
04:54:17 up 6:39, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
[root@huhy ~]#
uptime -p:以可读格式显示系统运行时间
[root@huhy ~]# uptime -p
up 6 hours, 40 minutes
[root@huhy ~]#
who命令
who(英文全拼:Who - Display Who is on the System):显示当前登录到系统上的用户信息
它可以显示登录用户的用户名、登录时间、终端等信息
who:显示登录用户信息
[root@huhy ~]# who
root tty1 2023-06-03 23:54
root pts/0 2023-08-08 22:36 (192.168.200.1)
[root@huhy ~]#
who -a:显示详细登录信息
[root@huhy ~]# who -a
system boot 2023-06-03 23:54
root + tty1 2023-06-03 23:54 old 788
run-level 3 2023-06-03 23:54
root + pts/0 2023-08-08 22:36 . 2137 (192.168.200.1)
who -q: 显示登录用户数量
[root@huhy ~]# who -q
root root
# users=2
kill命令
kill(英文全拼:Kill - Terminate Processes):用于终止或发送信号给正在运行的进程
用于停止运行中的进程,更改进程的状态,或者与进程进行通信
终止进程:PID就要搭配ps命令进行查看
kill PID
使用终止信号终止进程
kill -15 PID
使用强制终止信号终止进程
kill -9 PID
列出可用的信号
kill -l
通过进程名称终止进程
pkill process_name
系统和硬件管理命令
uname命令
uname(英文全拼:Unix Name):显示关于操作系统的信息,例如内核版本、主机名、操作系统类型
查看系统信息
uname:显示操作系统名称
[root@huhy ~]# uname
Linux
[root@huhy ~]#
uname -r:显示内核版本
[root@huhy ~]# uname -r
3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
[root@huhy ~]#
uname -n:显示操作系统主机名
[root@huhy ~]# uname -n
huhy
uname -m:显示处理器架构
[root@huhy ~]# uname -m
x86_64
[root@huhy ~]#
hostnamectl命令
hostnamectl(英文全拼:Hostname Control):用于在 Systemd 系统中管理主机名以及相关的系统信息
主要是用于设置主机名
hostnamectl:显示主机名信息
[root@huhy ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: huhy
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 52ba7d9d368a447b9f94ead0a5fd3496
Boot ID: 436facd4f55546f48d81270168498f67
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:7
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
[root@huhy ~]#
hostnamectl set-hostname 新主机名:设置主机名
[root@huhy ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname huhy-test
[root@huhy ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: huhy-test
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 52ba7d9d368a447b9f94ead0a5fd3496
Boot ID: 436facd4f55546f48d81270168498f67
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:7
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
[root@huhy ~]#
lshw命令
lshw(英文全拼:List Hardware):用于列出系统中的硬件信息
包括处理器、内存、硬盘、显卡、网络接口等
显示所有硬件信息,内容较长
lshw
只显示 CPU 信息
lshw -C cpu
只显示内存信息
lshw -C memory
只显示网络接口信息
lshw -C network
lscpu命令
lscpu(英文全拼:List CPU):用于显示有关系统中的 CPU(中央处理器)信息
关于处理器架构、核心数、线程数、CPU频率等信息
lscpu:显示 CPU 信息
[root@huhy ~]# lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 6
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-5
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 3
Socket(s): 2
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 154
Model name: 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-12500H
Stepping: 3
CPU MHz: 3110.402
BogoMIPS: 6220.80
Virtualization: VT-x
Hypervisor vendor: VMware
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 48K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 1280K
L3 cache: 18432K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-5
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon rep_good nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ssbd ibrs ibpb stibp ibrs_enhanced tpr_shadow vnmi ept vpid fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rdseed adx smap clflushopt clwb sha_ni xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 arat umip pku ospke gfni vaes vpclmulqdq movdiri movdir64b md_clear spec_ctrl intel_stibp flush_l1d arch_capabilities
[root@huhy ~]#
lscpu -e:以可读格式显示 CPU 信息
[root@huhy ~]# lscpu -e
CPU NODE SOCKET CORE L1d:L1i:L2:L3 ONLINE
0 0 0 0 0:0:0:0 yes
1 0 0 1 1:1:1:0 yes
2 0 0 2 2:2:2:0 yes
3 0 1 3 3:3:3:1 yes
4 0 1 4 4:4:4:1 yes
5 0 1 5 5:5:5:1 yes
[root@huhy ~]#
lsblk命令
lsblk(英文全拼:List Block Devices):用于列出系统中的块设备信息,包括硬盘、磁盘分区、磁盘挂载点等
能够提供有关存储设备和文件系统的详细信息
lsblk:能够提供有关存储设备和文件系统的详细信息
[root@huhy ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 100G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 99G 0 part
├─centos-root 253:0 0 50G 0 lvm /
├─centos-swap 253:1 0 3.9G 0 lvm [SWAP]
└─centos-home 253:2 0 45.1G 0 lvm /home
sr0 11:0 1 4.4G 0 rom
[root@huhy ~]#
lsblk -t:以树状结构显示块设备信息
[root@huhy ~]# lsblk -t
NAME ALIGNMENT MIN-IO OPT-IO PHY-SEC LOG-SEC ROTA SCHED RQ-SIZE RA WSAME
sda 0 512 0 512 512 1 deadline 128 4096 32M
├─sda1 0 512 0 512 512 1 deadline 128 4096 32M
└─sda2 0 512 0 512 512 1 deadline 128 4096 32M
├─centos-root 0 512 0 512 512 1 128 4096 32M
├─centos-swap 0 512 0 512 512 1 128 4096 32M
└─centos-home 0 512 0 512 512 1 128 4096 32M
sr0 0 2048 0 2048 2048 1 deadline 128 128 0B
[root@huhy ~]#
lspci命令
lspci(英文全拼:List Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)):用于列出系统中连接到 PCI 总线的设备信息
包括网络适配器、显卡、声卡、USB 控制器等。它能够提供有关系统硬件的详细信息
lspci:显示 PCI 设备信息
[root@huhy ~]# lspci
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 440BX/ZX/DX - 82443BX/ZX/DX Host bridge (rev 01)
00:01.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 440BX/ZX/DX - 82443BX/ZX/DX AGP bridge (rev 01)
00:07.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ISA (rev 08)
00:07.1 IDE interface: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 IDE (rev 01)
00:07.3 Bridge: Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI (rev 08)
00:07.7 System peripheral: VMware Virtual Machine Communication Interface (rev 10)
00:0f.0 VGA compatible controller: VMware SVGA II Adapter
00:10.0 SCSI storage controller: Broadcom / LSI 53c1030 PCI-X Fusion-MPT Dual Ultra320 SCSI (rev 01)
00:11.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI bridge (rev 02)
00:15.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.1 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.2 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.3 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.4 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.5 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.6 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:15.7 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.1 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.2 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.3 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.4 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.5 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.6 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:16.7 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.1 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.2 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.3 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.4 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.5 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.6 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:17.7 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.1 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.2 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.3 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.4 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.5 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.6 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
00:18.7 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01)
02:00.0 USB controller: VMware USB1.1 UHCI Controller
02:01.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82545EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (Copper) (rev 01)
02:02.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82545EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (Copper) (rev 01)
02:03.0 Multimedia audio controller: Ensoniq ES1371/ES1373 / Creative Labs CT2518 (rev 02)
02:04.0 USB controller: VMware USB2 EHCI Controller
[root@huhy ~]#
lspci -t:以树状结构显示设备信息
[root@huhy ~]# lspci -t
-[0000:00]-+-00.0
+-01.0-[01]--
+-07.0
+-07.1
+-07.3
+-07.7
+-0f.0
+-10.0
+-11.0-[02]--+-00.0
| +-01.0
| +-02.0
| +-03.0
| \-04.0
+-15.0-[03]--
+-15.1-[04]--
+-15.2-[05]--
+-15.3-[06]--
+-15.4-[07]--
+-15.5-[08]--
+-15.6-[09]--
+-15.7-[0a]--
+-16.0-[0b]--
+-16.1-[0c]--
+-16.2-[0d]--
+-16.3-[0e]--
+-16.4-[0f]--
+-16.5-[10]--
+-16.6-[11]--
+-16.7-[12]--
+-17.0-[13]--
+-17.1-[14]--
+-17.2-[15]--
+-17.3-[16]--
+-17.4-[17]--
+-17.5-[18]--
+-17.6-[19]--
+-17.7-[1a]--
+-18.0-[1b]--
+-18.1-[1c]--
+-18.2-[1d]--
+-18.3-[1e]--
+-18.4-[1f]--
+-18.5-[20]--
+-18.6-[21]--
\-18.7-[22]--
[root@huhy ~]#
显示详细信息(包括驱动程序)
lspci -v
文件压缩解压命令
tar命令
tar(英文全拼:Tape Archive):用于创建和提取归档文件
通常用于在 Unix 和类 Unix 系统中对文件和目录进行打包、压缩和解压缩操作
从归档文件中提取文件和目录:v参数会显示提前内容
tar -xvf archive.tar
== 将文件添加到已存在的归档文件中==
tar -rvf archive.tar new_files
仅将比归档文件中相应文件更新的文件添加到归档中
tar -uvf archive.tar updated_files
使用 gzip 压缩
tar -zcvf archive.tar.gz files
切换到指定目录并在那里执行操作
tar -cvf archive.tar -C /path/to/directory files
gzip命令
gzip(英文全拼:GNU Zip):对文件进行压缩和解压缩操作
它使用 GNU 压缩算法进行压缩,生成以 .gz 扩展名结尾的压缩文件(缺点只能压缩一个文件,结果tar命令使用)
gzip 文件名:压缩文件,原始文件将被删除
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test
[root@huhy ~]# gzip test
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 8
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 25 Aug 9 07:48 test.gz
[root@huhy ~]#
gzip -d 文件名.gz / gunzip 文件名.gz:两个命令都有用于解压缩
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test.gz
[root@huhy ~]# gunzip test.gz
[root@huhy ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1326 Jun 4 06:54 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 9 07:50 test
[root@huhy ~]#
gzip -c 文件名 > 文件名.gz:压缩文件,并保留原始文件
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test
[root@huhy ~]# gzip -c test > test.gz
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test test.gz
[root@huhy ~]#
gzip -r 目录名:这将递归压缩 目录中的所有文件
[root@huhy ~]# gzip -r test/
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test
[root@huhy ~]# cd test/
[root@huhy test]# ls
c.gz d.gz g.gz t.gz
[root@huhy test]#
zip命令
zip(英文全拼:Zip):用于创建和提取 ZIP 格式的压缩文件
常见的跨平台压缩格式。zip 命令可以在终端中创建和管理 ZIP 压缩文件或目录
zip 压缩名 文件名:压缩文件,此命令需要下载,文件名可以多个
[root@huhy ~]# zip test.zip test
adding: test/ (stored 0%)
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test test.zip
unzip -l 压缩包:查看压缩包里面的内容,unzip需要下载
[root@huhy ~]# zip test.zip test test2
adding: test (stored 0%)
adding: test2 (stored 0%)
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test test2 test.zip
[root@huhy ~]# unzip -l test.zip
Archive: test.zip
Length Date Time Name
--------- ---------- ----- ----
0 08-09-2023 08:05 test
0 08-09-2023 08:05 test2
--------- -------
0 2 files
[root@huhy ~]#
unzip 压缩包 -d /opt/:解压zip压缩包并指定解压后路径
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test test2 test.zip
[root@huhy ~]# unzip test.zip -d /opt/
Archive: test.zip
extracting: /opt/test
extracting: /opt/test2
[root@huhy ~]# ls /opt/
test test2
[root@huhy ~]#
zip -r 压缩包 添加的文件:将新文件添加到压缩包里面
[root@huhy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg test test2 test.zip
[root@huhy ~]# touch test3
[root@huhy ~]# zip -r test.zip test3
adding: test3 (stored 0%)
[root@huhy ~]# unzip -l test.zip
Archive: test.zip
Length Date Time Name
--------- ---------- ----- ----
0 08-09-2023 08:05 test
0 08-09-2023 08:05 test2
0 08-09-2023 08:08 test3
--------- -------
0 3 files
[root@huhy ~]#
df命令
df(英文全拼:Disk Free):用于显示文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况
可以告诉您各个挂载点、分区或文件系统的磁盘使用情况,包括可用空间、已用空间、总空间等信息
df:显示所有文件系统的磁盘使用情况
[root@huhy ~]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 1918640 0 1918640 0% /dev
tmpfs 1930644 0 1930644 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 1930644 20068 1910576 2% /run
tmpfs 1930644 0 1930644 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 52403200 1488664 50914536 3% /
/dev/sda1 1038336 153664 884672 15% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home 47285700 32992 47252708 1% /home
tmpfs 386132 0 386132 0% /run/user/0
df -Th:可视化显示文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况
[root@huhy ~]# df -Th
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs devtmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 1.9G 20M 1.9G 2% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 50G 1.5G 49G 3% /
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 151M 864M 15% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home xfs 46G 33M 46G 1% /home
tmpfs tmpfs 378M 0 378M 0% /run/user/0
[root@huhy ~]#
mount命令
mount(英文全拼:Mount):用于将文件系统挂载到指定的挂载点
通过挂载,您可以访问存储设备、网络共享等,并在文件系统中使用它们
显示当前已挂载的文件系统列表
mount
挂载指定设备到指定目录
mount /dev/device_name /mount_point
以只读方式挂载文件系统
mount -o ro /dev/device_name /mount_point
以读写方式挂载文件系统
mount -o rw /dev/device_name /mount_point
卸载(解除挂载)指定目录的文件系统
umount /mount_point
挂载指定设备并指定文件系统类型
mount -t filesystem_type /dev/device_name /mount_point
#例如
mount -t ntfs /dev/sdb1 /mnt/windows
其他命令
date命令
date(英文全拼:Display Date and Time):用于显示系统的日期和时间,以及对日期和时间进行格式化
还可以用于设置系统的日期和时间
date:显示当前日期和时间
[root@huhy ~]# date
Wed Aug 9 08:11:09 EDT 2023
[root@huhy ~]#
date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S:指定格式显示时间日期
[root@huhy ~]# date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
2023-08-09 08:12:00
[root@huhy ~]#
date -s "yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS":设置系统的时间和日期
[root@huhy ~]# date -s "2020-08-22 12:04:22"
Sat Aug 22 12:04:22 EDT 2020
[root@huhy ~]# date
Sat Aug 22 12:04:24 EDT 2020
[root@huhy ~]#
history命令
history(英文全拼:Command Historye):用于显示当前用户在终端中执行过的命令历史记录
以帮助您回顾以前执行过的命令,以及重新执行这些命令
history:显示最近执行的命令历史记录
history N:显示指定数量的最近命令历史记录
[root@huhy ~]# history 5
199 date -u
200 date -s "2020-08-22 12:04:22"
201 date
202 history
203 history 5
[root@huhy ~]#
!N:使用 !N 重新执行历史记录中的第 N 条命令
[root@huhy ~]# history 5
201 date
202 history
203 history 5
204 ! 201
205 history 5
[root@huhy ~]# !201
date
Sat Aug 22 12:09:29 EDT 2020
[root@huhy ~]#
!!:使用 !! 重新执行最近一条命令
[root@huhy ~]# !201
date
Sat Aug 22 12:09:29 EDT 2020
[root@huhy ~]# !!
date
Sat Aug 22 12:10:10 EDT 2020
[root@huhy ~]#
history | grep 关键字:搜索命令历史记录中包含指定关键字的命令
[root@huhy ~]# history | grep da
102 lsblk /dev/sda
195 date
196 date +format
197 date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
198 date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
199 date -u
200 date -s "2020-08-22 12:04:22"
201 date
206 date
207 history | grep da
[root@huhy ~]#
history -c:清除历史命令
[root@huhy ~]# history -c
[root@huhy ~]# history
1 history
[root@huhy ~]#
基础篇暂时到此,后续有新命令会调整添加
 centos7.9基础语法篇
centos7.9基础语法篇

