ManualResetEvent 与 AutoResetEvent 区别
在多线程开发中,时常用到 ManualResetEvent 与 AutoResetEvent 。 它们如同道路交通中的信号灯。两者之间有什么区别呢?
共同点:
均继承 EventWaitHandle 接口,因此,均具有以下功能:
Reset() //红灯
Set() //绿灯
WaitOne() // 等待信号
不同点:
AutoResetEvent 收到 Set 后 , 一次只能执行一个线程,其它线程继续 WaitOne 。
ManualResetEvent 收到 Set 后,所有处理 WaitOne 状态线程均继续执行。
msdn 提到(如果没有线程 处于WaitOne() 状态,而调用 Set , AutoResetEvent 将保持Set 状态):
调用Set信号AutoResetEvent释放等待线程。 AutoResetEvent 将保持终止状态直到一个等待线程释放,并自动返回到非信号状态。 如果没有线程处于等待状态,状态将无限期地保持已发出信号。
因此通常WatiOne 之前,先 Reset() 一下,清除Set 信号
需要注意的是(两个 Set 调用之间时间较短,第二个 Set 信号可能会丢失,因此连续 Set 调用,中间需要 Sleep 一定时间):
不能保证的每个调用Set方法将释放一个线程。 如果两次调用太靠近在一起,以便第二次调用前释放线程发生,只有一个线程被释放。 就像第二次调用未发生。 此外,如果Set时没有等待的线程调用和AutoResetEvent已终止,则调用不起作用。
有网友说:
AutoResetEvent.Set() = ManualResetEvent.Set() + ManualResetEvent.Reset();
个人理解 ,这只是原理层面含义,实际使用过程中,有差别的,如下示例:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace testManualResetEvent { class Program { static object objManualResetEvent = new object(); static System.Threading.ManualResetEvent manu = new System.Threading.ManualResetEvent(false); //static System.Threading.AutoResetEvent manu = new System.Threading.AutoResetEvent(false); static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.Threading.Thread t = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart(() => { Product(); })); t.Start(); } manu.Set(); manu.Reset(); Console.ReadKey(); } static void Product() { manu.WaitOne(10000); Console.WriteLine(System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } } }
实际执行结果 , 在 执行 set 后 reset 前 ,有多少个线程唤起执行,无法预料:
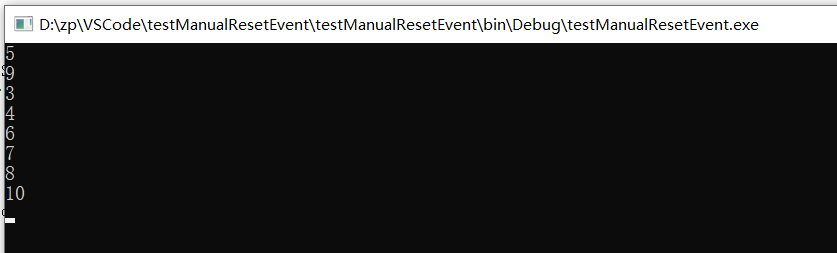
需要加锁 ,确保一次通过一个线程:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace testManualResetEvent { class Program { static object objManualResetEvent = new object(); static System.Threading.ManualResetEvent manu = new System.Threading.ManualResetEvent(false); //static System.Threading.AutoResetEvent manu = new System.Threading.AutoResetEvent(false); static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.Threading.Thread t = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart(() => { Product(); })); t.Start(); } manu.Set(); //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100); //连续 set 需要 sleep //manu.Set(); //manu.Reset(); //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100); //manu.Set(); //manu.Reset(); Console.ReadKey(); } static void Product() { lock (objManualResetEvent) { manu.WaitOne(10000);
manu.Reset(); Console.WriteLine(System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } } } }
执行结果:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号