Taro的学习1
今天想通过地址管理这个界面学习下吧
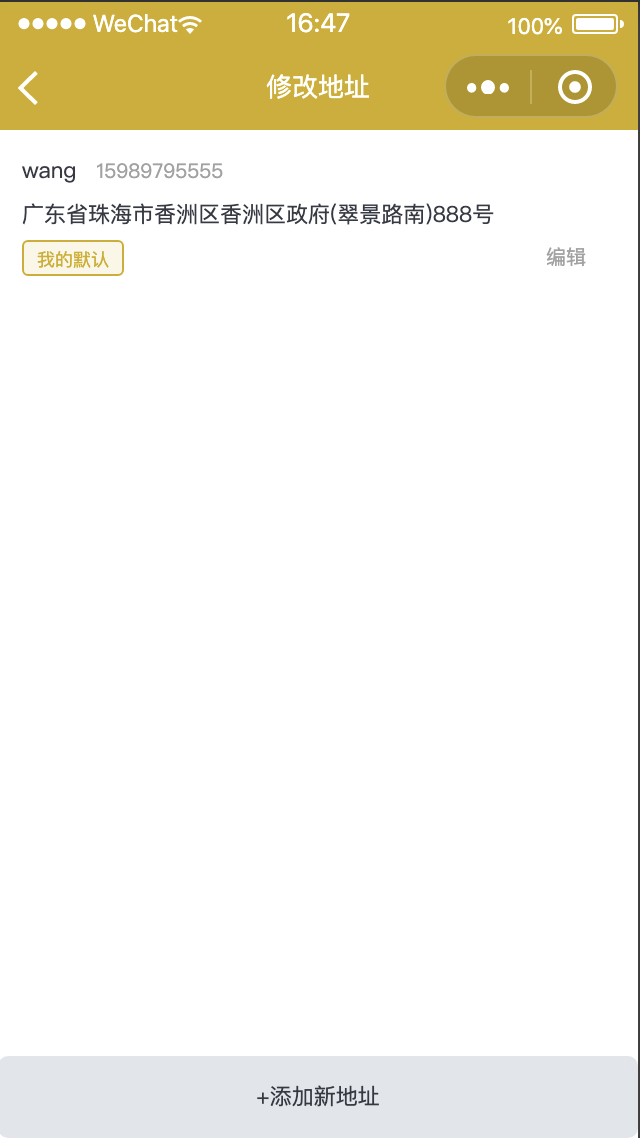
1.每个组件都用
static defaultProps = {
onChange: null,
};
3.然后设置下state:
state = {
userReady: false,
list: null,
error: false,
showEdit: false,
editItem: null,
tmpStyle: {},
};
4.界面部分,这是一个列表,对列表进行遍历:
render() {
const { showEdit, list, error, tmpStyle, editItem } = this.state;
return (
data-fixme='02 block to view. need more test' data-scoped='wk-cal-List' className='wk-cal-List'>
<View className='address-list' style={_safe_style_('display:' + (showEdit ? 'none' : ''))}>
{!!(list && !list.length) && <Empty></Empty>}
{!!error && <Error></Error>}
{!!list && (
<View className='address-list__list'>
{(list || []).map((item, index) => {
return (
<View
className='address-list__item'
key={index}
onClick={_fixme_with_dataset_(this.onSelected, { item: item })}
>
<View>
<Text className='address-list__item-name'>{item.consignee}</Text>
<Text className='address-list__item-mobile'>{item.mobile}</Text>
</View>
<View className='address-list__item-address'>
{(item.province || '') +
(item.city || '') +
(item.region || '') +
(item.address || '') +
(item.roomNumber || '')}
</View>
<View className='address-list__item-operator'>
{item.isDefault === 1 && (
<Text
className='address-list__item-default'
style={_safe_style_(
'color:' +
tmpStyle.btnColor +
';border-color:' +
tmpStyle.btnColor +
';background:' +
tmpStyle.bgColor
)}
>
我的默认
</Text>
)}
<Button className='address-list__item-edit' onClick={this.onEdit.bind(this, item)}>
编辑
</Button>
</View>
</View>
);
})}
</View>
)}
在这个列表的底部,有一个添加新地址的按钮:
{!error && (
<Button className='address-list__footer' onClick={this.onAdd}>
+添加新地址
</Button>
)}
5.在组件加载后,进行一些数据拉取是操作:
componentDidMount() {
this.getTemplateStyle();
this.fetchAddres();
}
这里面有两个方法,一个是获取模板style。一个是获取地址。
//获取模板配置
getTemplateStyle = () => {
const templateStyle = template.getTemplateStyle();
this.setState({
tmpStyle: templateStyle,
});
};
fetchAddres = () => {
wxApi
.request({
url: api.address.list,
loading: true,
})
.then((res) => {
this.setState({
list: res.data,
error: false,
});
})
.catch((error) => {
this.setState({
error: true,
});
});
};
这里通过微信的Api。获取到数据,然后将其setState,放到list中。
6.设置页面标题什么的
config = {
navigationBarTitleText: '地址管理',
component: true,
};
7.接下来看看,增加新地址的响应:
onAdd = () => {
this.setState({
showEdit: true,
editItem: null,
});
};
在这个onAdd方法中,把showEdit设为true.
8.在上面的界面代码中,可以看出地址列表有一个判断,即,如果showEdit为true就把地址列表隐藏。
在界面代码的下面有这样两行代码:
{!!showEdit && (
<Edit editItem={editItem} onSave={this.onSave.bind(this)} onDelete={this.onDelete.bind(this)}></Edit>
)}
这里以showEdit为条件判断。如果showEdit为true的话,就会隐藏增加地址的界面:
import Edit from '../edit/index';
因为上面的add方法中,用了
static defaultProps = {
editItem: null,
onSave: null,
onDelete: null,
};
10.接着设定每个输入框的验证规则:
const rules = {
consignee: [
{
required: true,
message: '请输入联系人',
},
{
reg: /^[0-9A-Za-z\u4e00-\u9fa5]+$/i,
message: '联系人姓名由字母、数字或汉字组成',
},
],
mobile: [
{
required: true,
message: '请输入手机号码',
},
{
reg: /^1[3|4|5|6|7|8|9][0-9]\d{8}$/,
message: '手机号码无效',
},
],
address: [
{
required: true,
message: '请选择收货地址',
},
],
roomNumber: [
{
required: true,
message: '请输入详细地址',
},
],
};
11.设定页面的初始数据:
/**
* 页面的初始数据
*/
state = {
region: [],
form: {
consignee: '',
mobile: '',
address: '',
source: 'manual',
status: 1,
roomNumber: '',
longitude: null,
latitude: null,
},
checked: false,
isEdit: false,
dialogShow: false,
cancelText: '',
tipMsg: '',
tmpStyle: {},
};
12.接下来我们从
componentDidMount() {
this.getTemplateStyle();
const { editItem: model } = this.props;
const { form } = this.state;
let title = '添加新地址';
if (model) {
form.consignee = model.consignee;
form.mobile = model.mobile;
form.address = model.address;
form.roomNumber = model.roomNumber;
form.longitude = model.longitude;
form.latitude = model.latitude;
this.setState({
form: { ...form },
isEdit: true,
region: [model.province, model.city, model.region],
checked: model.isDefault === 1 ? true : false,
});
this.model = model;
title = '修改地址';
}
wxApi.setNavigationBarTitle({
title: title,
});
}
可以看到,先是请求到模板style。然后从this.pros中拿到editItem。并重新命名为model.判断model不为空,即为编辑地址,这样的话,就进行赋值。接着,再对setState里的值进行赋值。
注意:要通过this.setState赋值刷新数据。form:{...form}这里的...是展开运算符,就是把每个属性都赋值上去。
我也不知道这里为什么不再需要connect什么的。我想是不是继承了taro的component。然后就直接写state就行了呢?
<View className='input-view'>
<Text className='input-view-text'>联系人:</Text>
<Input
className='form-input'
placeholderClass='placeholder'
maxlength='16'
value={form.consignee}
onBlur={this.nameInput}
placeholder='请输入联系人(最大16个字)'
></Input>
</View>
在这里,联系人输入框。注意onBlur事件是监听输入事件的:
//修改联系人
nameInput = (e) => {
const { form } = this.state;
form.consignee = e.detail.value.trim();
this.setState({
form,
});
};
注意这里,首先将this.state赋值给form.然后。通过e.detail.value.trim()获得输入的值。这个值就可以赋值给form.consignee。然后再通过this.setSate({form,});将值赋值给form。
最后是保存的按钮:
<Button
className='btn second'
onClick={this.addAddress}
style={_safe_style_('background:' + tmpStyle.btnColor)}
>
保存
</Button>
来看下响应代码:
//增加修改地址
addAddress = () => {
if (!this.validate()) {
return;
}
const { form, region, checked, isEdit } = this.state;
const params = { ...form };
params.isDefault = checked ? 1 : 0;
let url = api.address.add;
if (isEdit) {
params.id = this.model.id;
url = api.address.update;
}
wxApi
.request({
url: url,
loading: true,
data: params,
})
.then((res) => {
wxApi.showToast({
title: '保存成功。',
});
if (this.props.onSave) {
this.props.onSave();
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log('address setDefault error: ' + JSON.stringify(error));
});
};
我们来解读下代码:
1.首先,进行验证:
if (!this.validate()) {
return;
}
2.对一些变量进行赋值:
const { form, region, checked, isEdit } = this.state;
const params = { ...form };
params.isDefault = checked ? 1 : 0;
3.紧接着,进行保存的请求:
let url = api.address.add;
if (isEdit) {
params.id = this.model.id;
url = api.address.update;
}
wxApi
.request({
url: url,
loading: true,
data: params,
})
.then((res) => {
wxApi.showToast({
title: '保存成功。',
});
if (this.props.onSave) {
this.props.onSave();
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log('address setDefault error: ' + JSON.stringify(error));
});




