插槽
1、为什么要使用插槽
组件的插槽
组件的插槽是为了让我们封装的组件更加具有扩展性
让使用者可以决定组件内部的一些内容到底是什么
2、如何封装这类组件呢? slot
最好的方式就是将共性抽取到组件中,将不同暴露为插槽
一旦我们预留了插槽,就可以让使用者根据自己的需求,决定插槽中插入什么内容
是搜索框,还是文字,还是菜单,由调用者自己来决定
3、插槽的基本使用
<!--1、插槽的基本使用 <slot></slot>
2、插槽的默认值 <slot><button>按钮</button></slot>
3、插槽中可以放多个元素
-->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>我是组件</h2>
<p>我是组件,哈哈哈哈</p>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<div id="app">
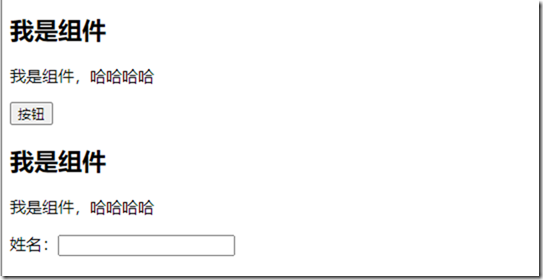
<cpn><button>按钮</button></cpn>
<cpn>姓名:<input type="text"></cpn>
</div>4、具名插槽的使用
当一个组件中有多个插槽时,可以使用具名插槽,利用插槽名来替换具体的插槽
<div id="app">
<cpn>
<span slot="mid">替换的呀</span>
</cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>我是组件</h2>
<slot name="left"><span>我是左边的</span></slot>
<slot name="mid"><span>我是中间的</span></slot>
<slot name="right"><span>我是右边的</span></slot>
</div>
</template>5、作用域插槽
作用域插槽是slot一个比较难理解的点,而且官方文档说的又有点不清晰。
这里,我们用一句话对其做一个总结,然后我们在后续的案例中来体会:
父组件替换插槽的标签,但是内容由子组件来提供
<div id="app">
<cpn>
<!--目的是获取子组件中的pLanguage-->
<template slot-scope="slot"> <!--slot-scope="slot" 引用这个插槽对象-->
<span v-for="item in slot.data">{{item}} —— </span>
</template>
</cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<slot :data="pLanguages">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in pLanguages">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app", //用于挂载要管理的元素
data: { //定义数据
message: 'hello',
},
components: {
cpn: {
template: "#cpn",
data(){
return {
pLanguages: ['javaScript','c++','java',"c#","python","go"]
}
}
}
}
})
</script>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号