Vue中为什么使用 + axios详解
1、Vue中选择什么网络模块?
Vuex中发送网络请求有非常多的方式
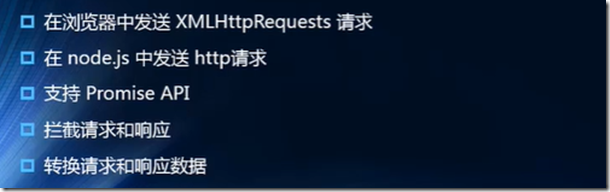
1)传统的Ajax是基于XMLHttpRequest(XHR)
为什么不使用?
配置和调用方式非常混乱,所以在开发中很少使用,而是使用 jquery-ajax
2)jquery-ajax
为什么不使用?
首先我们需要明确一点,在vue的整个开发中是不需要使用 jquery的,
那么意味着为了方便我们进行一个网络请求,特意引入一个重量级的框架jquery,得不偿失
3)axios
axios有非常多的优点,并且使用起来也非常的方便
2、axios框架的基本使用
axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/mutidata' //method: 'get'/'post' }).then(res => { console.log(res) }) //axios的get请求 //1) 参数直接跟在url上 axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/mutidata' }).then(res => { console.log(res) }) //2) 多个参数放在url中 axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data', params: { type: 'pop', page: 1 } }).then(res => { console.log(res) }) //3、使用axios.get - 参数写在url中 axios.get('http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/mutidata') .then(res=>{ console.log(res) }) //4、使用axios.get - 参数写在params中 axios.get('http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data', { params: { type: 'pop', page: 1 } }).then(res => { console.log(res) })
3、axios发送并发请求
//axios发送并发请求 //axios.all([axios(),axios()]).then(res => {}) // res是一个数组,包含每条请求的结果 axios.all([axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/mutidata' }),axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data', params: { type: 'pop', page: 1 } })]) .then(res => { console.log(res); console.log(res[0]); console.log(res[1]); })
解析结果,对结果进行一层处理:
axios.all([axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/mutidata' }),axios({ url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data', params: { type: 'pop', page: 1 } })]) .then(axios.spread((res1,res2) => { console.log(res1); console.log(res2); }))
4、axios的配置信息相关
事实上,在开发中很多参数是固定的,这个时候我们可以进行一些抽取,也可以利用axios的全局配置
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://123.207.32.32:8000' axios.defaults.timeout = 5000 axios.get('/home/data', { params: { type: 'pop', page: 1 } }).then(res => { console.log(res) })
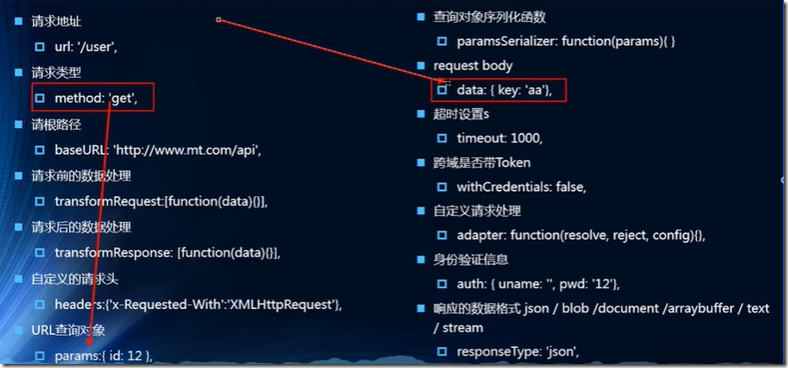
常见的配置选项:
5、axios的实例和模块封装
1)为什么要创建axios的实例?
当我们从axios模块中导入对象时,使用的实例是默认的实例
当给该实例设置一些默认的配置是,这些配置就被固定下来了
但是在后续的开发中,某些配置又可能不太一样,比如某些请求需要使用特定的baseURL,timeout或者content-Type 等
这个时候,我们可以创建新的实例,并且传入该实例的配置信息
2)如何创建axios的实例?
//创建对应的 axios 的实例 const instance1 = axios.create({ baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000', timeout: 5000 }) instance1({ url: '/home/multidata', }).then( res => { console.log(res); })
3)为什么要进行模块封装?
减少项目各个文件处对第三方框架的依赖,当需要替换框架时,只需要修改你自己封装的文件
,非常方便
4)如何封装 axios请求
第一种方式:传入成功和失败的回调函数
封装 request.js
import axios from "axios"; export function request(config,success,failure) { //1、创建axios的实例 const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000', timeout: 5000 }) //发送真正的网络请求 instance(config).then( res => { success(res); //成功的回调函数 } ).catch(err => { failure(err); //失败的回调函数 }) }
调用
//5、封装request模块 import {request} from "./network/request"; request({ url: "/home/mutidata" },res=>{ console.log(res); },err => { console.log(err); })
第二种方式:使用Promise
//使用 promise 进行封装 export function request(config,success,failure) { //1、创建axios的实例 return new Promise((resolve,reject) => { const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000', timeout: 5000 }) //发送真正的网络请求 instance(config).then( res => { resolve(res); //成功的回调函数 } ).catch(err => { reject(err); //失败的回调函数 }) }) }
第三种方式:直接返回 instance(config)
export function request(config,success,failure) { //1、创建axios的实例 const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000', timeout: 5000 }) return instance(config); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号