栈
1、栈的一个实际需求
2、栈的介绍
3、栈的应用场景
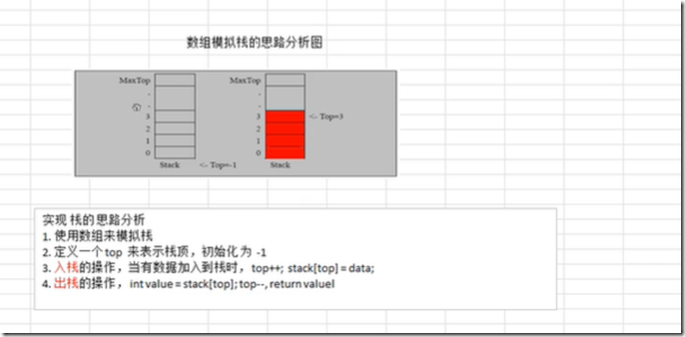
4、数组模拟栈
代码实现:
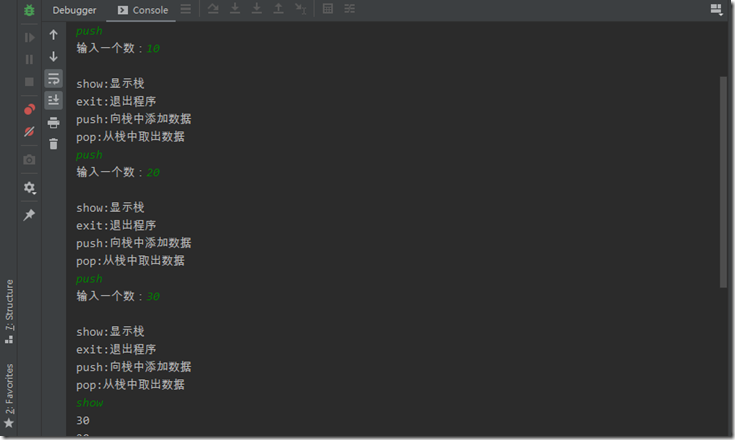
public class ArrayStackDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //测试ArrayStack是否正确 ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(3); String key = ""; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean loop =true; while(loop){ System.out.println("show:显示栈"); System.out.println("exit:退出程序"); System.out.println("push:向栈中添加数据"); System.out.println("pop:从栈中取出数据"); key=scanner.next(); switch (key){ case "show": stack.list(); break; case "push": System.out.print("输入一个数:"); int value = scanner.nextInt(); stack.push(value); break; case "pop": try { int pop = stack.pop(); System.out.printf("从队头取出的元素为:%d",pop); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.printf(e.getMessage()); } break; case "exit": scanner.close(); loop=false; break; } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("程序退出~~"); } } //定义一个ArrayStack表示栈 class ArrayStack{ private int maxSize; //栈的大小 private int[] stack; private int top =-1; //指向栈顶的指针 //构造器 public ArrayStack(int maxSize) { this.maxSize = maxSize; stack =new int[maxSize]; } //栈满 public boolean isFull(){ return top==maxSize-1; } //栈空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return top==-1; } //入栈 public void push(int elem){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈已满!不能添加元素"); } stack[++top]=elem; } //出栈 将栈顶的数据返回 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空!"); } return stack[top--]; } //遍历栈 public void list(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈为空!"); } for(int i=top;i>=0;i--){ System.out.println(stack[i]); } } }
5、栈实现综合计算器
使用栈完成表达式的计算思路
1、通过一个index(索引)来遍历我们的表达式
2、如果我们发现是一个数字,就直接入数栈
3、如果发现扫描到的是一个符号
3.1 如果当前的符号栈为空,则直接入栈
3.2 如果符号栈有操作符,就进行比较,如果当前操作符的优先级小于或者等于栈中
的操作符,则需要从数栈中pop出两个数,从符号栈中pop出一个符号,进行运算,将得到
的结果入数栈,将当前的操作符入符号栈;如果当前操作符的优先级大于符号栈中符号,就
直接写入符号栈
4、当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序的从数栈和符号栈中pop出相应的数和符号,并运行
5、最好在数栈中只有一个数字,就是我们的结果
/** * @author houChen * @date 2020/7/29 22:56 * @Description: 使用栈实现 计算器 */ public class Calculator { public static void main(String[] args) { String exp = "7-6-1-8"; ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10); ArrayStack2 operStack =new ArrayStack2(10); int index=0; int num1=0; int num2=0; int oper =0; int res=0; char ch=' '; while (true){ ch=exp.substring(index,index+1).charAt(0); if(operStack.isOper(ch)){ if(!operStack.isEmpty()){ if(operStack.priority(ch)<=operStack.priority(operStack.pick())){ num1= numStack.pop(); num2= numStack.pop(); oper = operStack.pop(); res= operStack.cal(num1,num2,oper); numStack.push(res); operStack.push(ch); }else { operStack.push(ch); } }else{ operStack.push(ch); } }else{ numStack.push(ch-48); } index++; if(index==exp.length()){ break; } } while (true){ if(operStack.isEmpty()){ break; } num1= numStack.pop(); num2= numStack.pop(); oper = operStack.pop(); res= operStack.cal(num1,num2,oper); numStack.push(res); } int res2= numStack.pop(); System.out.printf("表达式为 %s = %d\t",exp,res2); } } //定义一个ArrayStack表示栈 class ArrayStack2{ private int maxSize; //栈的大小 private int[] stack; private int top =-1; //指向栈顶的指针 //构造器 public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) { this.maxSize = maxSize; stack =new int[maxSize]; } //增加一个方法,返回当前栈顶的元素,但是不出栈 public int pick(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空!"); } return stack[top]; } //栈满 public boolean isFull(){ return top==maxSize-1; } //栈空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return top==-1; } //入栈 public void push(int elem){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈已满!不能添加元素"); } stack[++top]=elem; } //出栈 将栈顶的数据返回 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空!"); } return stack[top--]; } //遍历栈 public void list(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈为空!"); } for(int i=top;i>=0;i--){ System.out.println(stack[i]); } } //返回运算符的优先级 public int priority(int oper){ if(oper=='*'||oper=='/'){ return 1; }else if(oper=='+'||oper=='-'){ return 0; }else{ return -1; } } //判断是不是一个运算符 public boolean isOper(char val){ return val =='+'||val =='-'||val =='*'||val =='/'; } public int cal(int num1,int num2,int oper){ int res = 0; switch (oper){ case '+': res=num1+num2; break; case '-': res=num2-num1; break; case '*': res=num1*num2; break; case '/': res=num2/num1; break; default:break; } return res; } }
6、前缀表达式,中缀表达式,后缀表达式
1)前缀表达式(波兰表达式)
中缀表达式又称为波兰表达式,前缀表达式的运算符位于操作数之前
(3+4)*5-6 对应的前缀表达式为 - * + 3 4 5 6
2)中缀表达式
就是我们平时所写的表达式!
3)后缀表达式
后缀表达式又称为逆波兰表达式,运算符位于操作数之后
(3+4)*5-6 对应的后缀表达式为 3 4 + 5* 6 -
代码实现很简单,我就不写了!
7、中缀表达式转后缀表达式(未完成)







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号