CSS中绝对定位与相对定位
在CSS中定位元素中,常用的就是相对定位(position:relative)和绝对定位(position:absolute),虽然都是用来定位,但是定位的机制却是相差甚远。
1、参照的位置
相对定位:对于相对定位来说,参照位置很简单就是元素在文档流中的初始位置。例如下面的这一段代码:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 <style> 7 #box1{ 8 background: #0000ff; 9 width: 50px; 10 height: 50px; 11 border: #0000ff solid; 12 } 13 #box2{ 14 background: fuchsia; 15 width: 50px; 16 height: 50px; 17 border: fuchsia solid; 18 } 19 #box3{ 20 position: relative; 21 top: 50px; 22 left: 50px; 23 background: chocolate; 24 width: 50px; 25 height: 50px; 26 border: chocolate solid; 27 } 28 </style> 29 </head> 30 <body> 31 <div id="box1">box1</div> 32 <div id="box2">box2</div> 33 <div id="box3">box3</div> 34 </body> 35 </html>
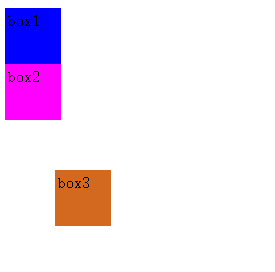
这段代码里面,第三块box3就是从原始的顺序位置处向右边和下面各偏移50px。
绝对定位:绝对定位的参考对象稍微复杂一点,它必须用已经定位的父级元素作为参照,并且是由近到远开始搜索,如果没有找到,就以最顶层的元素(body)最为参照。请看下面两个例子。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>相对定位与绝对定位</title> 6 <style> 7 #first{ 8 /*这个距离更远,不被选择*/ 9 position: relative; 10 width: 500px; 11 height: 500px; 12 border: #000000 solid; 13 } 14 #second{ 15 width: 200px; 16 height: 200px; 17 border: #ff0000 solid; 18 } 19 #three{ 20 /*这个已经定位了的元素距离目标元素最近,所以被选择为目标元素的参照*/ 21 position: relative; 22 width: 100px; 23 height: 100px; 24 border: #00ff00 solid; 25 } 26 #box1{ 27 background: #0000ff; 28 width: 50px; 29 height: 50px; 30 border: #0000ff solid; 31 } 32 #box2{ 33 background: fuchsia; 34 width: 50px; 35 height: 50px; 36 border: fuchsia solid; 37 } 38 #box3{ 39 position: absolute; 40 top: 50px; 41 left: 50px; 42 background: chocolate; 43 width: 50px; 44 height: 50px; 45 border: chocolate solid; 46 } 47 </style> 48 </head> 49 <body> 50 <div id="first"> 51 <div id="second"> 52 <div id="three"> 53 <div id="box1">box1</div> 54 <div id="box2">box2</div> 55 <div id="box3">box3</div> 56 </div> 57 </div> 58 </div> 59 </body> 60 </html>
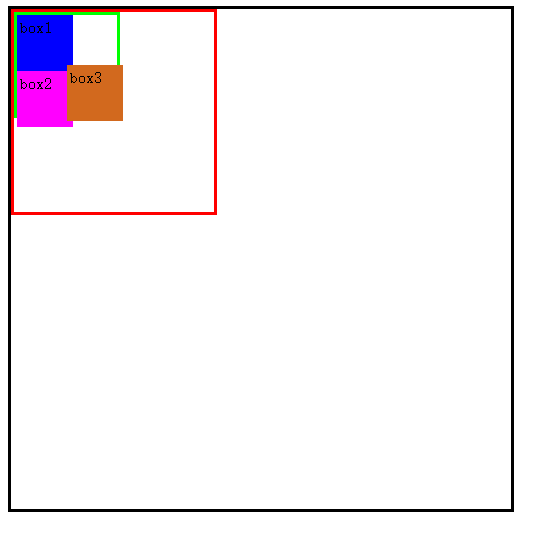
可以看到#three 块被选为了参照,二#two被抛弃。这就是绝对定位参照物选择的规律。
2、定位机制不一样
相对定位的在进行定位以后并不会从原始文档流中删除,依然占据原来的空间;而绝对定位却恰好相反,它会从原始的文档流中删除,重建一个块(无论之前元素是否为块元素)进行定位。继续看下面的例子。
绝对定位:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>绝对定位</title> 6 <style> 7 #wrapper{ 8 background: #ffffff; 9 width: 200px; 10 height: 200px; 11 border: #ff00ff solid; 12 } 13 #box1{ 14 background: #0000ff; 15 width: 50px; 16 height: 50px; 17 border: #0000ff solid; 18 } 19 #box2{ 20 position: absolute; 21 top: 50px; 22 left: 50px; 23 background: fuchsia; 24 width: 50px; 25 height: 50px; 26 border: fuchsia solid; 27 } 28 #box3{ 29 background: chocolate; 30 width: 50px; 31 height: 50px; 32 border: chocolate solid; 33 } 34 </style> 35 </head> 36 <body> 37 <div id="wrapper"> 38 <div id="box1">box1</div> 39 <div id="box2">box2</div> 40 <div id="box3">box3</div> 41 </div> 42 </body> 43 </html>
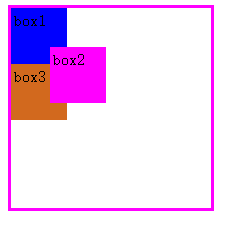
相对定位:

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>相对定位</title> 6 <style> 7 #wrapper{ 8 background: #ffffff; 9 width: 200px; 10 height: 200px; 11 border: #ff00ff solid; 12 } 13 #box1{ 14 background: #0000ff; 15 width: 50px; 16 height: 50px; 17 border: #0000ff solid; 18 } 19 #box2{ 20 position: relative; 21 top: 50px; 22 left: 50px; 23 background: fuchsia; 24 width: 50px; 25 height: 50px; 26 border: fuchsia solid; 27 } 28 #box3{ 29 background: chocolate; 30 width: 50px; 31 height: 50px; 32 border: chocolate solid; 33 } 34 </style> 35 </head> 36 <body> 37 <div id="wrapper"> 38 <div id="box1">box1</div> 39 <div id="box2">box2</div> 40 <div id="box3">box3</div> 41 </div> 42 </body> 43 </html>
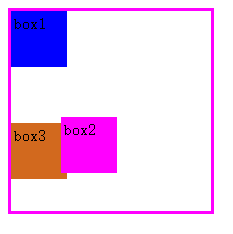
结果很明显,相对定位并没有删除原始文档流中的空间,而绝对定位缺删除了。
3、在第一部分中,绝对定位参考选择的问题中,已定位父级参考系的假设都是设置为position:relative,能不能设置为absolute呢?
答案:也是可以的,毕竟都是满足已经定位的父级元素。
4、上一个问题中,涉及到一个更深层的问题,关于position:absolute默认值的问题:可以继续参考下面这篇文章:
《绝对定位如果不设置top right bottom left 会怎么样?》链接地址:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000003109367


