编程题 1-7
1,大数
import java.math.BigInteger;
BigInteger num1, num2, num3;
num1 = new BigInteger(sc.next());
//这是类,不是基本数据类型
//用sc.next读入而不是nextbiginteger
num3=num1.add(num2);
num3=num1.subtract(num2);
.multiply
.divide
.mod
2, System.out.printf("%.6f\n",a);
保留六位小数
3,
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
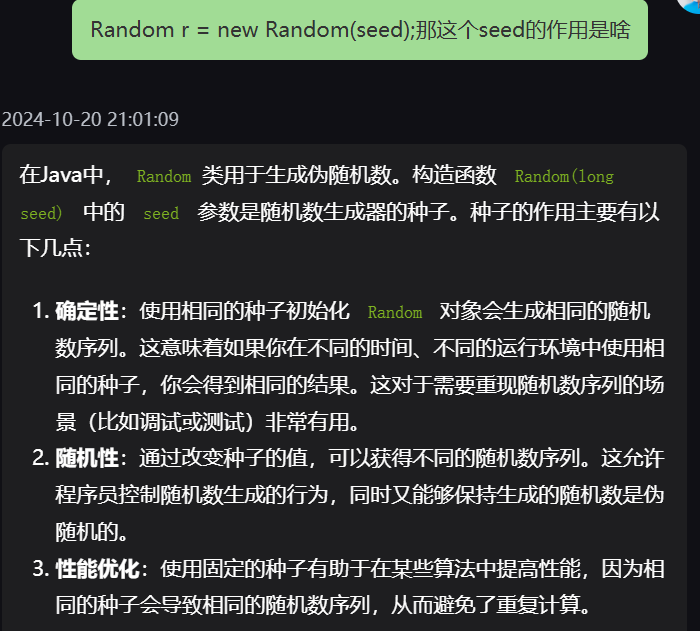
long seed=sc.nextLong();
int n=sc.nextInt();
Random r = new Random(seed);
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
double x =r.nextDouble()*2-1;
double y =r.nextDouble()*2-1;
/*
使用 for 循环生成 n 次随机点,r.nextDouble() 生成一个在 区间 [0.0, 1.0) 之间 区间的随机数,
通过 * 2 - 1 将其转换为在 [-1, 1) 区间的随机数。
这两个随机数 x 和 y 分别代表平面上的点的 x 和 y 坐标。
*/
if ( Math.pow(x, 2) + Math.pow(y, 2)<=1)
{
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(4*(double)count/n);
}
}
4,随机数种子
5,
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
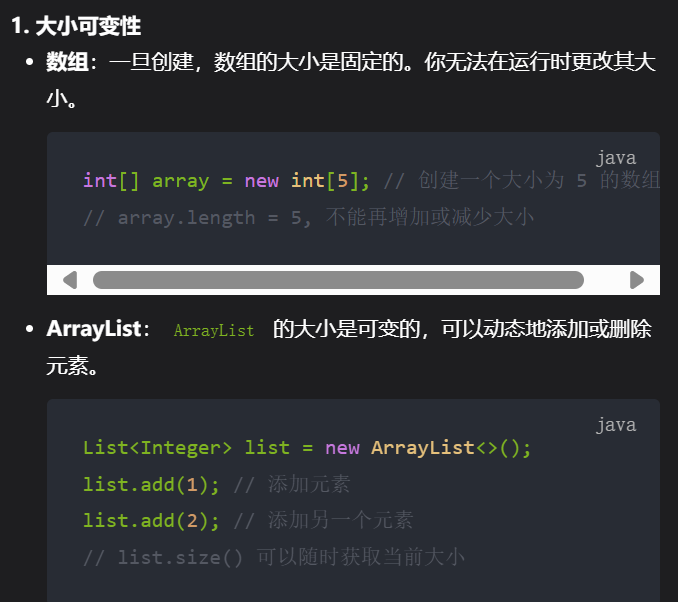
List<Integer> ss = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//List 是一个接口,ArrayList 是实现这个接口的具体类
//声明一个 ArrayList 类型的整数列表 ss,用于存储生成的随机整数。
//Set<Integer> ss = new HashSet<Integer>();
Random rand = new Random(k);
//并用种子 k 进行初始化。这个种子用于生成可复现的随机数序列。
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
// ss.add(rand.nextInt(m));
// //于 0 和 m-1 之间的随机整数,并将其添加到 ss 列表中。
if(i==n-1)
System.out.println(ss.get(i));
//仅打印最后一次生成的种子,不使用列表直接打印最后一个也可以
}
}
}
6,进制转化
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = scanner.nextInt();//输入
String[] number = new String[T]; for(int i=0;i<T;i++){//输入
number[i] = bin(scanner.nextInt());
//bin 方法将其转换为二进制字符串,然后存储在 number 数组
}
for(String i:number){//输出
System.out.println(count(i));
}
}
public static String bin(int num1){//递归实现,将十进制转为二进制
if(num1/2==0){//商为0时
return num1%2 + "";//返回转换为String类型的余数
}else{
return bin(num1/2) + num1%2 + " ";//下一层递归的结果放左侧
}
}
public static int count(String str){//计算字符串中1的个数
int num = 0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){//遍历字符串
if(str.charAt(i)=='1'){
num ++;
}
}
return num;
}
}
7,日历
import java.util.Calendar; // 导入 Calendar 类,用于处理日期和时间
import java.util.Scanner; // 导入 Scanner 类,用于获取用户输入
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 创建 Scanner 对象,用于读取用户输入
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); // 获取一个 Calendar 实例,表示当前时间
int a = sc.nextInt(); // 读取用户输入的年份
int count = 0; // 初始化计数器,统计星期六的次数
// 如果输入的年份大于或等于1998
if (a >= 1998) {
// 遍历从1月到11月
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
cal.set(Calendar.YEAR, a); // 设置年份为用户输入的年份
cal.set(Calendar.MONTH, i); // 设置月份(0表示一月,11表示十二月)
cal.set(Calendar.DATE, 13); // 设置日期为13号
int t = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); // 获取当前设置的日期是星期几
// 如果星期几为星期六(6)
if (t == 6) {
count++; // 计数器加1
}
}
}
System.out.println(count); // 输出13号是星期六的次数
}
}
2 判断题
1,由Date到String的转换需要用到SimpleDateFormat类对象的format方法。
由String到Date的转换需要用到SimpleDateFormat类对象的parse方法。
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateToStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 Date 对象,表示当前时间
Date currentDate = new Date();
// 创建 SimpleDateFormat 对象,定义日期格式
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 使用 format 方法将 Date 转换为 String
String dateString = dateFormat.format(currentDate);
// 输出结果
System.out.println("Date to String: " + dateString);
}
}
2String到Date
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class StringToDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个日期字符串
String dateString = "2024-10-20 14:30:45";
// 创建 SimpleDateFormat 对象,定义日期格式
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
try {
// 使用 parse 方法将 String 转换为 Date
Date parsedDate = dateFormat.parse(dateString);
// 输出结果
System.out.println("String to Date: " + parsedDate);
} catch (ParseException e) {
// 处理解析异常
System.out.println("Date format is incorrect: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
3 单选题
1,
Math.abs 方法会根据输入参数的类型返回相同类型的结果。
2,
floor向下取整
ceil向上取整
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
double x = 6.5;
System.out.println(Math.floor(x + 1)); // 7.0不是7!!!
System.out.println(Math.ceil(x)); // 7.0不是7!!!
System.out.println(Math.round(x)); // 四舍五入7!!!
}
}
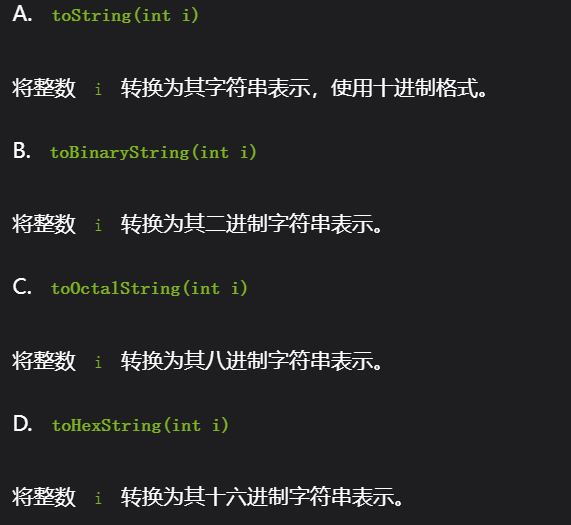
3,数字字符串转化
4,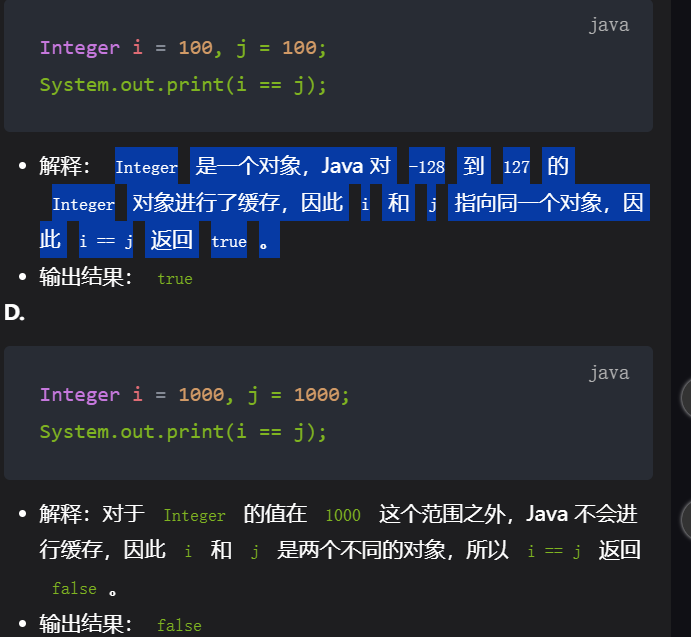
5,
利用java.util.Date类创建对象,欲得到系统当前时间的语句为
new Date();
6,exp(x) 返回 e^x
7,
int i1=(int)Math.random()*10;
一直是0,因为Math.r返回0.0-1.0(不含)然后强制转化变成0
Random r=new Random();
int i3 = r.nextInt(10);
[0,10)





