函数题1-10 编程题 1-8
1 函数题
1,super.a 来明确访问父类的字段。super(a); 表示调用父类的构造函数,并传递参数 a
2,
抽象类继承需要写新的构造器,重写抽象方法
class Circle extends shape{
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
//构造器比较容易忘
//新的类型有新的变量所以要用构造器初始化
@Override
public double getArea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}// 求面积
public double getPerimeter(){
return 2*Math.PI*radius;
} // 求周长
}
3,比较类对象
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true; // 同一对象
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; // 空或不同类
Point point = (Point) o; // 类型转换
return this.xPos == point.xPos && this.yPos == point.yPos; // 属性比较
/*不能直接写this.id=id,这个不是传入的参数,不能直接调用,需要通过类*/
}
//而不是
public boolean equals(int x,int y)
{
if((this.xPos==x)&&(this.yPos==y))
return true;
else
return false;
}
//另一个
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true; // 同一对象
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; // 空或不同类
Student student = (Student) o; // 类型转换
return this.id==student.id; // 属性比较
}
4,接口
class Octagon implements Comparable<Octagon>,Cloneable{
private double side;
public Octagon(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
public double getSide() {
return side;
}
public void setSide(double side) {
this.side = side;
}
public double getPerimeter()
{
return side*8;
}
public double getArea()
{
return (2+4/Math.sqrt(2))*side*side;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Octagon o){
if(this.side>o.getSide())
return 1;
else if(this.side<o.getSide())
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
/*
在 Java 中,Comparable<T> 是一个泛型接口,
用于定义对象的自然顺序。这里的 <T> 表示一个类型参数,
允许您指定将要比较的对象的类型。
在 Comparable<Octagon> 中,<> 符号是用于指定泛型类型参数的
意味着在调用 compareTo 方法时,
参数必须是 Octagon 类型,确保类型安全。
*/
@Override
protected Object clone() {
return this;
}
}
5,类和子类
class Account{
private int id;
private int balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(int id, int balance) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public boolean withdraw(int money)
{
int tmp=balance-money;
if(tmp>=0)
setBalance(tmp);
return tmp>=0;
}
public void deposit(int money)
{
balance+=money;
}
public String toString()
{
return "The balance of account "+id+" is "+balance;
}
}
class CheckingAccount extends Account{
private int overdraft;
public CheckingAccount() {
}
public CheckingAccount(int id, int balance, int overdraft) {
super(id, balance);
this.overdraft = overdraft;
}
@Override
public boolean withdraw(int money) {
int tmp=getBalance()+overdraft-money;
if(tmp>=0)
setBalance(getBalance()-money);
return tmp>=0;
}
}
6,因为传入参数的不确定,我们要手动调用有参和无参方法。
public void pay(int hour)
{
pay();
}
public void pay()
{
System.out.println(40.0*rate);
}
7,继承
class Media{
String name;
public double getDailyRent(){
return 0.0;
}
}
class Book extends Media{
double price;
public Book(String name,double price)
{
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
//构造块
public double getDailyRent(){
return 0.01*price;
//重写
}
}
class DVD extends Media{
public DVD(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
public double getDailyRent(){
return 1;
}
}
class MediaShop{
public static double calculateRent(Media[] medias, int days){
double sum=0;
//静态方法全局方法,数组长度没有括号
for(int i=0;i<medias.length;i++)
{
sum+=medias[i].getDailyRent()*days;
}
return sum;
}
}
8,子类的继承
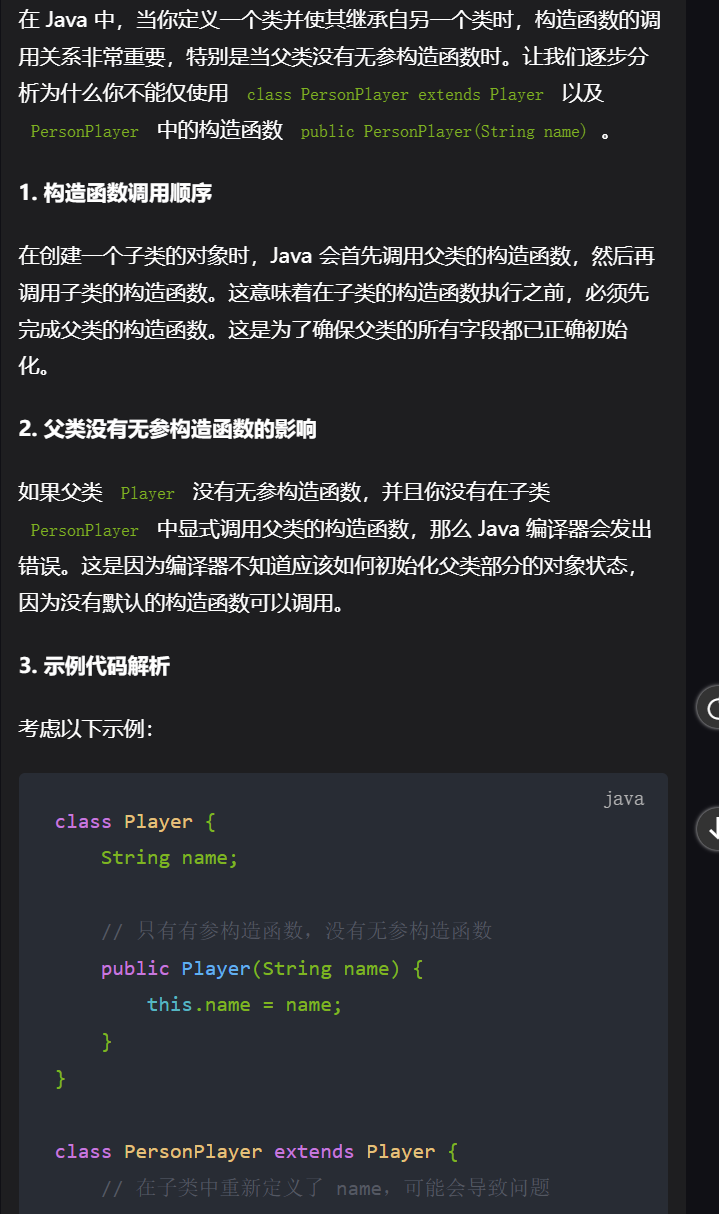
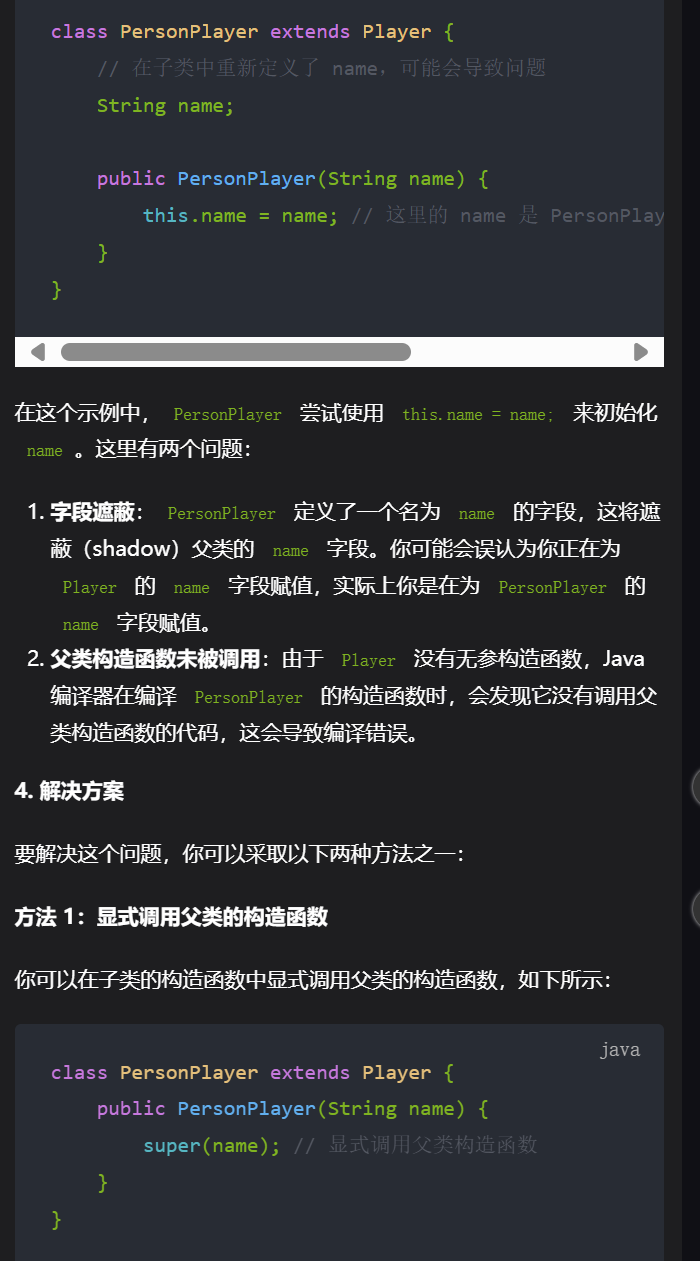
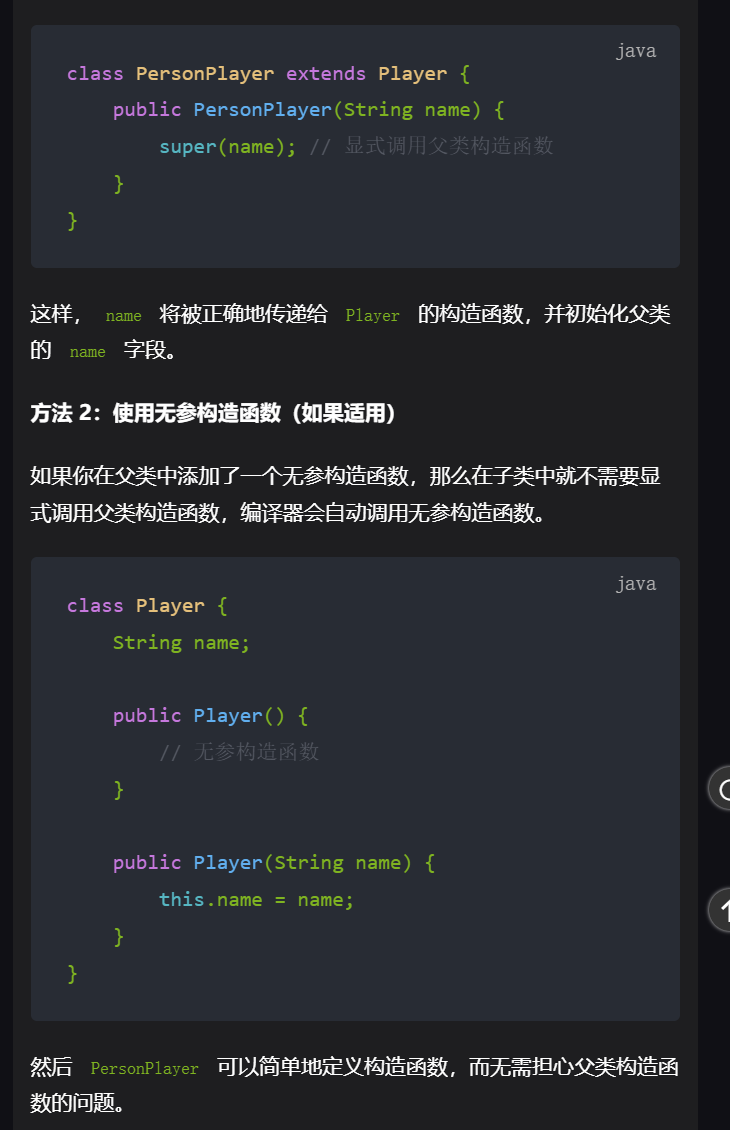
//样例2不通过
class ComputerPlayer extends Player {
String name;
public ComputerPlayer(String name) {
// this.name = name;这样写需要在父类定义无参构造器
super(name);
}
}
class PersonPlayer extends Player {
String name;
public PersonPlayer(String name) {
// this.name = name;
super(name);
}
int show() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int show = sc.nextInt();
return show;
}
}
class Game {
int A;
int B;
Game(Player A, Player B) {
this.A = A.show();
this.B = B.show();
}
public void start() {
if (A == B) {
System.out.println("A Draw.");
} else if ((A == 1 && B == 2) || (A == 2 && B == 3) || (A == 3 || B == 1)) {
System.out.println("Winner is personPlayer.");
} else {
System.out.println("Winner is computerPlayer.");
}
}
}
2 编程题
1,
//子类重写的方法中调用父类方法
return 2 * super.area() + length() * z;
// 调用的是父类 Rect 中定义的 area() 方法
//三个构造器
public Rect(double l, double h, double z) {
if (l > 0 && h > 0 && z > 0) {
this.l = l;
this.h = h;
this.z = z;
}
}
public Rect(int l) {
this(l, l, l);
}
public Rect() {
}
//格式化浮点数
//格式化数据
String area1=String.format("%.2f", cubic.area());
String volumn1=String.format("%.2f", cubic.volumn());
//输出数据
System.out.println(area1+" "+volumn1);
2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
ShapeTest shapeTest = new ShapeTest();
while (sc.hasNext()) {
Shape shape = null;
String strData = sc.nextLine();
// System.out.println(strData);
String[] arrayData = strData.split(" ");
/*strData 中的字符串分割成多个子字符串,
并将结果存储在一个字符串数组 arrayData 中。
*/
int count = arrayData.length;
if (count == 1) {
// 该行只有一个参数,构造圆形
double r = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[0]);
//字符串转化为double
shape = new Circle(r);
} else if (count == 2) {
// 该行有2个参数,构造长方形
double length = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[0]);
double width = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[1]);
shape = new Rectangle(length, width);
} else if (count == 3) {
// 该行有3个参数,构造三角形
double a = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[0]);
double b = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[1]);
double c = Double.parseDouble(arrayData[2]);
shape = new Triangle(a, b, c);
}
if (shape != null) {
double area = shapeTest.length(shape);
//调用 shapeTest 对象的 length 方法,计算形状的周长,并将结果存储在 area 中。
String strArea=String.format("%.2f", area);
System.out.println(strArea);
} else {
System.out.println("0.00");
}
}
}
}
interface Shape {
public double length();
}
class Triangle implements Shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
if (a < 0 || b < 0 || c < 0) {
a = 0;
b = 0;
c = 0;
}
if (a + b > c && a + c > b && b + c > a) {
// 能构成三角形就赋值
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
public double length() {
return a + b + c;
}
}
class Rectangle implements Shape {
private double l;
private double h;
public Rectangle(double l, double h) {
if (l > 0 && h > 0) {
// 二者均大于0,才能构成图形
this.l = l;
this.h = h;
}
}
public double length() {
return 2 * (l + h);
}
}
class Circle implements Shape {
double r;
public Circle(double r) {
if (r < 0) {
r = 0;
}
this.r = r;
}
public double length() {
return 3.14 * 2 * r;
}
}
class ShapeTest {
public double length(Shape shape) {
return shape.length();
}
}
3,接口和比较
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner r = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = r.nextInt();
PersonSortable2 s[] = new PersonSortable2[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String name = r.next();
int age = r.nextInt();
s[i] = new PersonSortable2(name,age);
}
Arrays.sort(s,new NameComparator());//对一个数组的所有元素进行排序,并且是按从小到大
//对数组 s 中的 PersonSortable2 对象按名字进行排序,使用 NameComparator 作为比较器。
System.out.println("NameComparator:sort");
for(PersonSortable2 i:s){
System.out.println(i);
}
Arrays.sort(s,new AgeComparator());
System.out.println("AgeComparator:sort");
for(PersonSortable2 i:s){
System.out.println(i.toString());
//用的是tostring(默认调用),重写了这个方法
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(NameComparator.class.getInterfaces()));//
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(AgeComparator.class.getInterfaces()));
//打印 NameComparator 类实现的接口。使用 getInterfaces() 方法获取实现的接口数组
// 并通过 Arrays.toString() 转换为字符串输出。
}
}
class PersonSortable2{
public String name;
public int age;
public PersonSortable2(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return name+"-"+age;
}
//重写tostring
}
class NameComparator implements Comparator<PersonSortable2>
//定义一个类 NameComparator,实现 Comparator 接口,用于按名字比较 PersonSortable2 对象。
{
public int compare(PersonSortable2 o1,PersonSortable2 o2){
if(o1.name.compareTo(o2.name)>0)return 1;
else if(o1.name.compareTo(o2.name)<0) return -1;
else return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);//return 0;
}
}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<PersonSortable2>{
public int compare(PersonSortable2 o1,PersonSortable2 o2){
if(o1.age<o2.age) return -1;
else return 1;
}
}
4,
interface USB{
void work(); //描述可以工作
void stop(); //描述停止工作
}
class Mouse implements USB{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("我点点点");
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
USB usb1=new Mouse();
usb1.work();
usb1.stop();
USB[] usbs=new USB[2];
usbs[0]=new UPan();
usbs[1]=new Mouse();
for(int i=0;i<usbs.length;i++)
{
usbs[i].work();
usbs[i].stop();
}
}
}
重点 答答租车系统
1,枚举实现
import java.util.Scanner;
class Car {
public int num;
public String model;
public int person;
public double ton;
public int money;
public Car() {
this.num = 0;
this.model = null;
this.person = 0;
this.ton = 0;
this.money = 0;
}
public Car(int num, String model, int person, double ton, int money) {
this.num = num;
this.model = model;
this.person = person;
this.ton = ton;
this.money = money;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public int getPerson() {
return person;
}
public void setPerson(int person) {
this.person = person;
}
public double getTon() {
return ton;
}
public void setTon(int ton) {
this.ton = ton;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getRant(int day) {
return day * money;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Car[] car = new Car[11];
car[1] = new Car(1, "A", 5, 0, 800);
car[2] = new Car(2, "B", 5, 0, 400);
car[3] = new Car(3, "C", 5, 0, 800);
car[4] = new Car(4, "D", 51, 0, 1300);
car[5] = new Car(5, "E", 55, 0, 1500);
car[6] = new Car(6, "F", 5, 0.45, 500);
car[7] = new Car(7, "G", 5, 2.0, 450);
car[8] = new Car(8, "H", 0, 3, 200);
car[9] = new Car(9, "I", 0, 25, 1500);
car[10] = new Car(10, "J", 0, 35, 2000);
int fg = scanner.nextInt();
if (fg == 1) {
int sumPer = 0, sumMon = 0;
double sumTon = 0;
int N = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int n = scanner.nextInt();
sumPer += (car[m].person * n);
sumTon += (car[m].ton * n);
sumMon += (car[m].money * n);
}
System.out.println(sumPer + " " + String.format("%.2f", sumTon) + " " + sumMon);
} else if (fg == 0) {
System.out.println("0 0.00 0");
}
}
}
//carsForRent[carsId[j] - 1] instanceof Trunk这个是啥意思
//判断是否输出trunk类
2,自己写的
import java.util.Scanner;
class Car {
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int id;
public int rent;
public String name;
public int getLoadr() {
return loadr;
}
public void setLoadr(int loadr) {
this.loadr = loadr;
}
public int getRent() {
return rent;
}
public void setRent(int rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getLoadh() {
return loadh;
}
public void setLoadh(double loadh) {
this.loadh = loadh;
}
public int loadr;
public double loadh;
public Car(int id, String name,int loadr, double loadh,int rent ) {
this.id=id;
this.name = name;
this.rent = rent;
this.loadr = loadr;
this.loadh = loadh;
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Car[] car = new Car[11];
car[1] = new Car(1, "A", 5, 0, 800);
car[2] = new Car(2, "B", 5, 0, 400);
car[3] = new Car(3, "C", 5, 0, 800);
car[4] = new Car(4, "D", 51, 0, 1300);
car[5] = new Car(5, "E", 55, 0, 1500);
car[6] = new Car(6, "F", 5, 0.45, 500);
car[7] = new Car(7, "G", 5, 2.0, 450);
car[8] = new Car(8, "H", 0, 3, 200);
car[9] = new Car(9, "I", 0, 25, 1500);
car[10] = new Car(10, "J", 0, 35, 2000);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
if(n==1)
{
int num=sc.nextInt();
int r=0;
double h=0.00;
int mon=0;
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
{
int idd=sc.nextInt();
int day= sc.nextInt();
r+=car[idd].getLoadr()*day;
h+=car[idd].getLoadh()*day;
mon+=car[idd].getRent()*day;
}
System.out.println(r+" "+String.format("%.2f",h)+" "+mon);
}
else
System.out.println("0 0.00 0");
}
}
3,
//1)字符串判断相等
S.equals("rect")
//2)是否属于xx类
A[i] instanceof Rectangle
3)吸收换行符
int radius = in.nextInt();
in.nextLine();
//4)数组存特定类
Shape A[] = new Shape[n];
A[i] = new Rectangle(wide, len);
A[i] = new Circle(radius);
4,
import java.util.*;
// 导入java.util包中的所有类
//可以替代
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Scanner;...
//创建动态数组
ArrayList<PersonOverride> ap=new ArrayList<PersonOverride>();
ap.add;ap.set;
//动态数组中是否存在a
aa.equals(a)
//去掉左右中括号
System.out.println(a.toString().replace("[", "").replace("]", ""));
5,动态数组

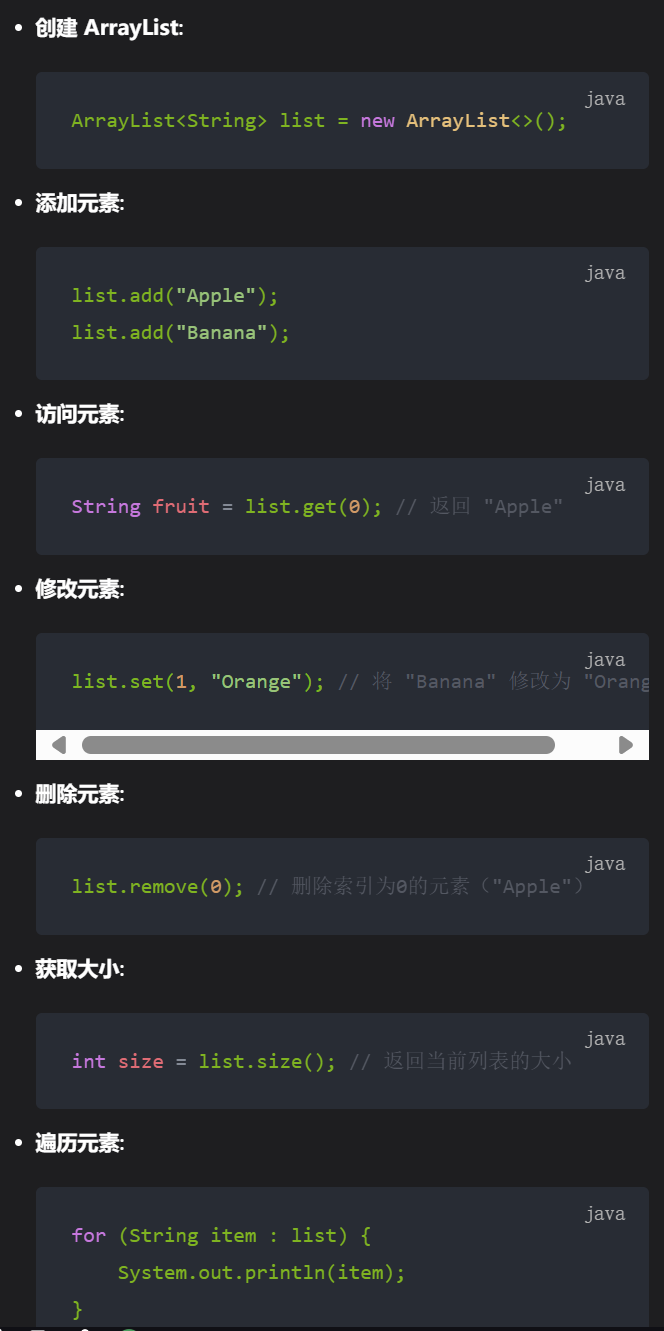
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Cherry");
// 访问元素
System.out.println("第一个水果是: " + fruits.get(0)); // 输出 "Apple"
// 修改元素
fruits.set(1, "Orange");
// 删除元素
fruits.remove("Cherry");
// 遍历列表
System.out.println("水果列表:");
for (String fruit : fruits) {
System.out.println(fruit);
}
// 获取大小
System.out.println("水果数量: " + fruits.size());
}
}
3 判断题
1,接口中的方法默认是public abstract方法
2,类在实现接口方法时必须给出方法体,并且一定要用public来修饰。
3,类在实现接口的方法时,必须显式地使用public修饰符。
4,一个类只能有一个父类,但一个接口可以有一个以上的父接口。
5,接口中的属性,都是静态常量。
//接口中的字段隐式地是 public、static 和 final 的。也就是说,即使没有显式地使用这些修饰符,接口中的字段也会被视为公共静态常量。
6,一般情况抽象类中不能有private的成员
7,覆盖只能在不同的类中完成。
8,子类不继承父类的构造方法。
虽然子类不能继承父类的构造方法,但子类可以通过 super 关键字显式调用父类的构造方法,以便在创建子类对象时初始化父类的部分。
9,使用上转型对象调用子类重写的方法时表现出多态性。
当你使用父类引用调用方法时,如果子类重写了该方法,运行时将调用子类的版本,而不是父类的版本。
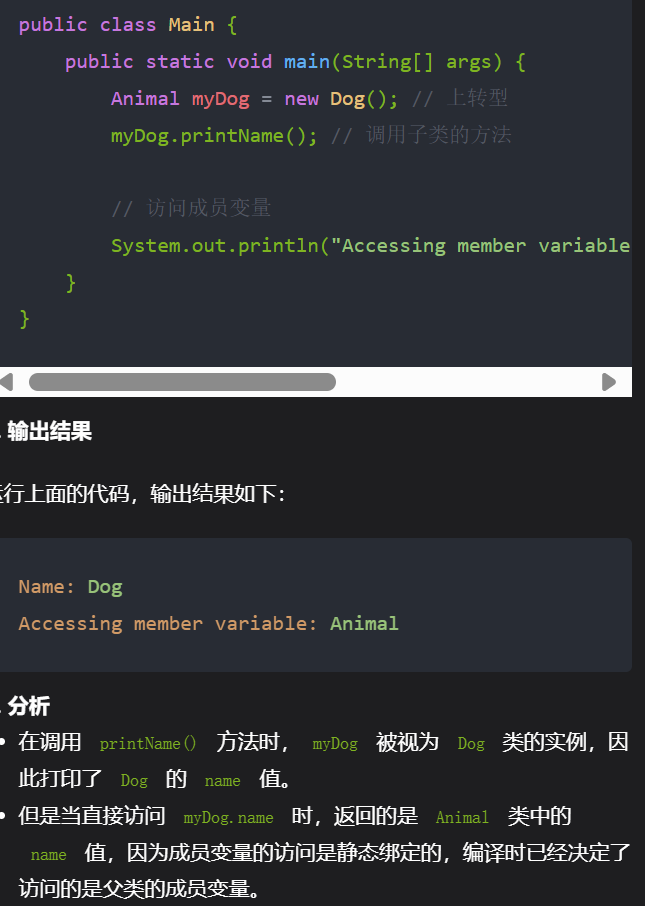
4 选择题
1,子类继承父类

2,接口的修饰符

3,执行子类构造方法时,会自动调用父类无参构造方法。
4,重写和重载


5,
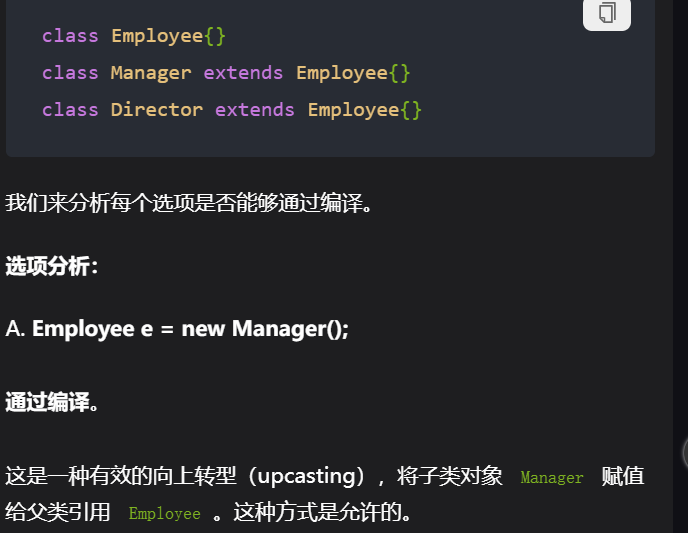

6,

7,
A obj = new B();
System.out.println(obj.f(4, 6));
/*
在 main 方法中,A obj = new B();
创建了一个 B 类的实例,并通过 A 类型的引用 obj 来引用它。
当调用 obj.f(4, 6); 时,
由于 obj 实际上是一个 B 类的对象,
Java 会调用 B 中重写的 f 方法,
而不是 A 中的 f 方法。
*/
8,上转型
方法调用: 使用的是对象的实际类型(B)。
属性访问: 使用的是引用的类型(A)。
class A {
int v1 = 10; // 类A中的实例变量v1
int v2 = 10; // 类A中的实例变量v2
public void m1() {
System.out.println("A m1"); // 方法m1的实现
}
public void m2() {
System.out.println("A m2"); // 方法m2的实现
}
}
class B extends A {
int v2 = 20; // 类B中的实例变量v2(遮蔽了类A中的v2)
int v3 = 20; // 类B中的实例变量v3
public void m2() {
System.out.println("B m2"); // 方法m2的实现,重写了类A中的m2
}
public void m3() {
System.out.println("B m3"); // 类B中的新方法m3
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B(); // 创建一个类B的对象,但将其引用赋给类A的变量
//上转型
/*
上转型是将子类的对象引用赋给父类类型的引用变量。
*/
a.m1(); // 调用m1(),将输出"A m1"
a.m2(); // 调用m2(),由于多态,将输出"B m2"
// a.m3(); // 这一行会导致编译错误,a的类型是A,不知道m3()
System.out.println(a.v1); // 输出类A中的v1,结果是10
System.out.println(a.v2); // 输出类A中的v2,因为v2在类B中是重定义的,结果是10
// System.out.println(a.v3); // 这一行会导致编译错误,因为v3在类A中不可见
}
}

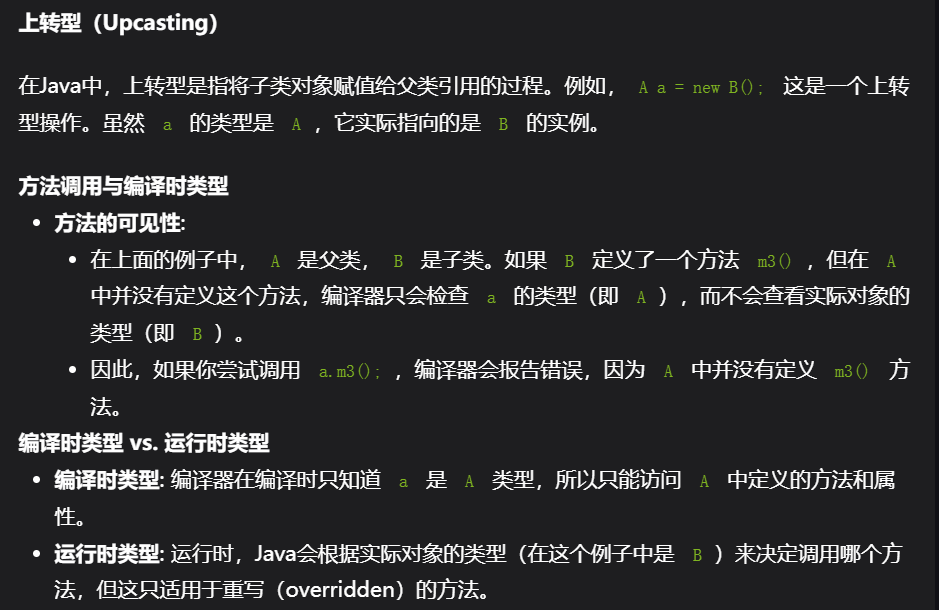
9,静态方法不能重写但可以隐藏
class Base {
static void test() {
System.out.println("Base.test()");
}
}
class Child extends Base {
static void test() {
System.out.println("Child.test()");
Base.test(); // Call the parent method
}
/*
隐藏(Hiding): 当子类定义一个与父类同名的静态方法时
,子类的静态方法会隐藏父类的静态方法,而不是重写它。
这意味着父类和子类各自都有自己的静态方法,
调用哪个方法取决于引用的类型,而不是对象的实际类型。
*/
class Father {
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
public void print() {
System.out.println(a + " " + b);
}
}
class Child extends Father {
int b = 300;
int c = 400;
public void print() {
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + c);
}
public void printExtend() {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] a) {
Father obj = new Child();
System.out.println(obj.a); / AA语句 100
System.out.println(obj.b); // BB语句 200
obj.print(); // CC语句 100 300 400,300不是200
obj.printExtend(); // DD语句 编译错误
//方法b重写的>a的,a中没有但b有会调用出错
//方法b,属性a。
}
}
class Father {
int a = 100;
static int b = 200;
void print() {
System.out.println(a);
}
static void printExtend() {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
class Child extends Father {
int a = 300; // 隐藏父类的字段 a
static int b = 400; // 隐藏父类的静态字段 b
void print() {
System.out.println(a); // 打印 Child 的 a
}
static void printExtend() {
System.out.println(b); // 打印 Child 的 b
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father obj = new Child();
System.out.println(obj.a); // 输出 100
System.out.println(obj.b); // 输出 200
obj.print(); // 输出 300
obj.printExtend(); // 输出 400
}
}
10,instacneof
//使用 instanceof 关键字时,它实际上判断的是实例对象的类型,而不是引用变量的类型。
class Father {
}
class Child extends Father {
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f1 = new Father();
Child c1 = new Child();
System.out.println(f1 instanceof Father); // true
System.out.println(f1 instanceof Child); // false
System.out.println(c1 instanceof Father); // true
System.out.println(c1 instanceof Child); // true
Father obj = new Child();
System.out.println(obj instanceof Father); // true
System.out.println(obj instanceof Child); // true
}
}
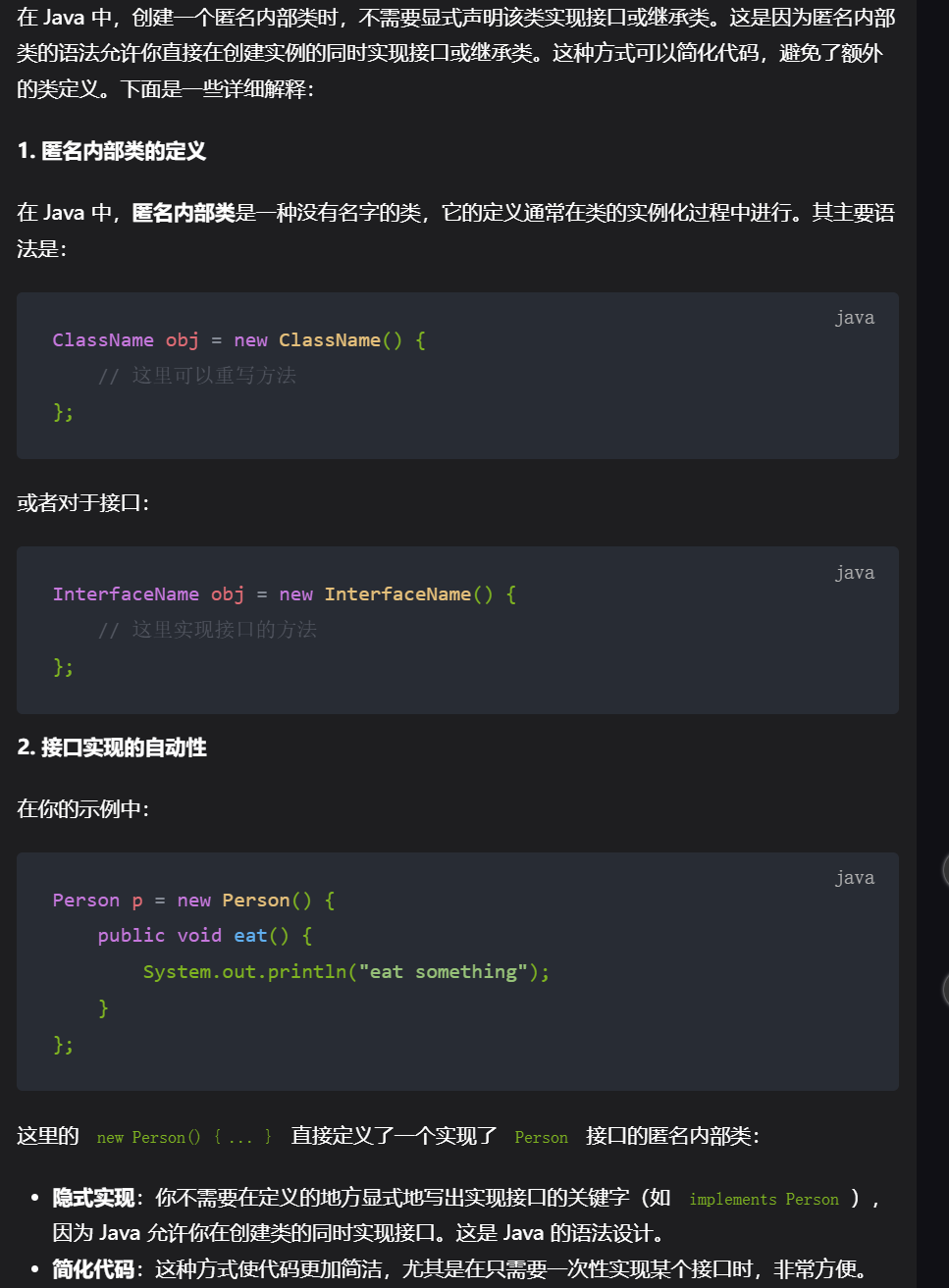
11,匿名内部类
interface Person {
public void eat();
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] a) {
// 创建一个 Person 接口的匿名内部类实例
Person p = new Person() {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat something");
}
};
// 调用 eat 方法
p.eat();
}
}