基础算法复习 (上午)
双指针
一本书P页,第i页有知识点ai,同一个知识点可能多次提到,希望通过连续的一些页把所有知识点都覆盖到。求出连续的最少页数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=1e6+10;
int a[maxn];
int n;
set <int> s;
map <int,int> vis;
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
//cin.tie(0);
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
s.insert(a[i]);
}
int len=s.size();
int l=0,r=0,cnt=0;
int ans=n;
while (1){
while (r<n && cnt<len){
if (vis[a[r]]==0)
cnt++;
vis[a[r]]++;
r++;
}
if (cnt<len) break;
ans=min(ans,r-l);
vis[a[l]]--;
if (vis[a[l++]]==0)
cnt--;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
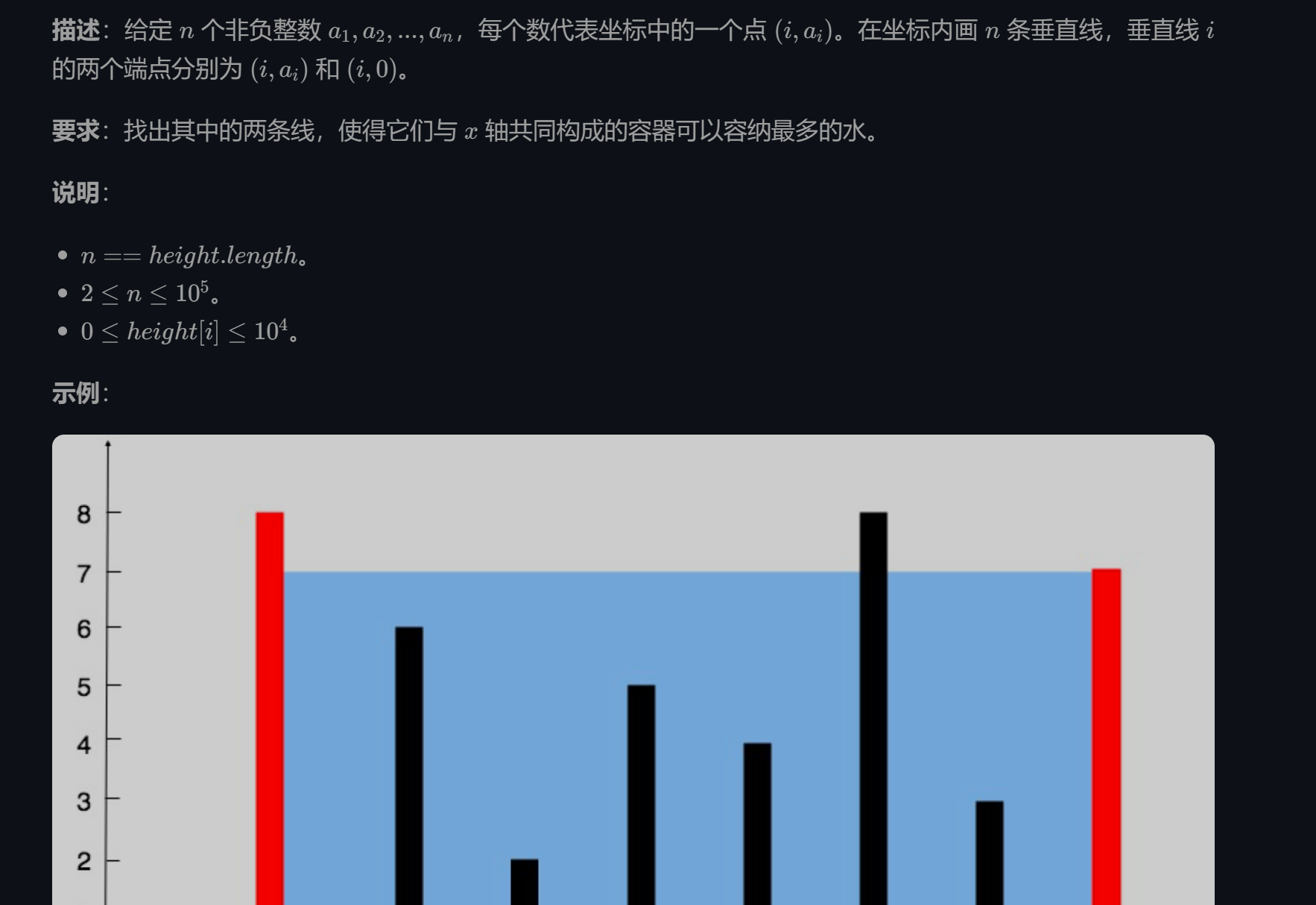
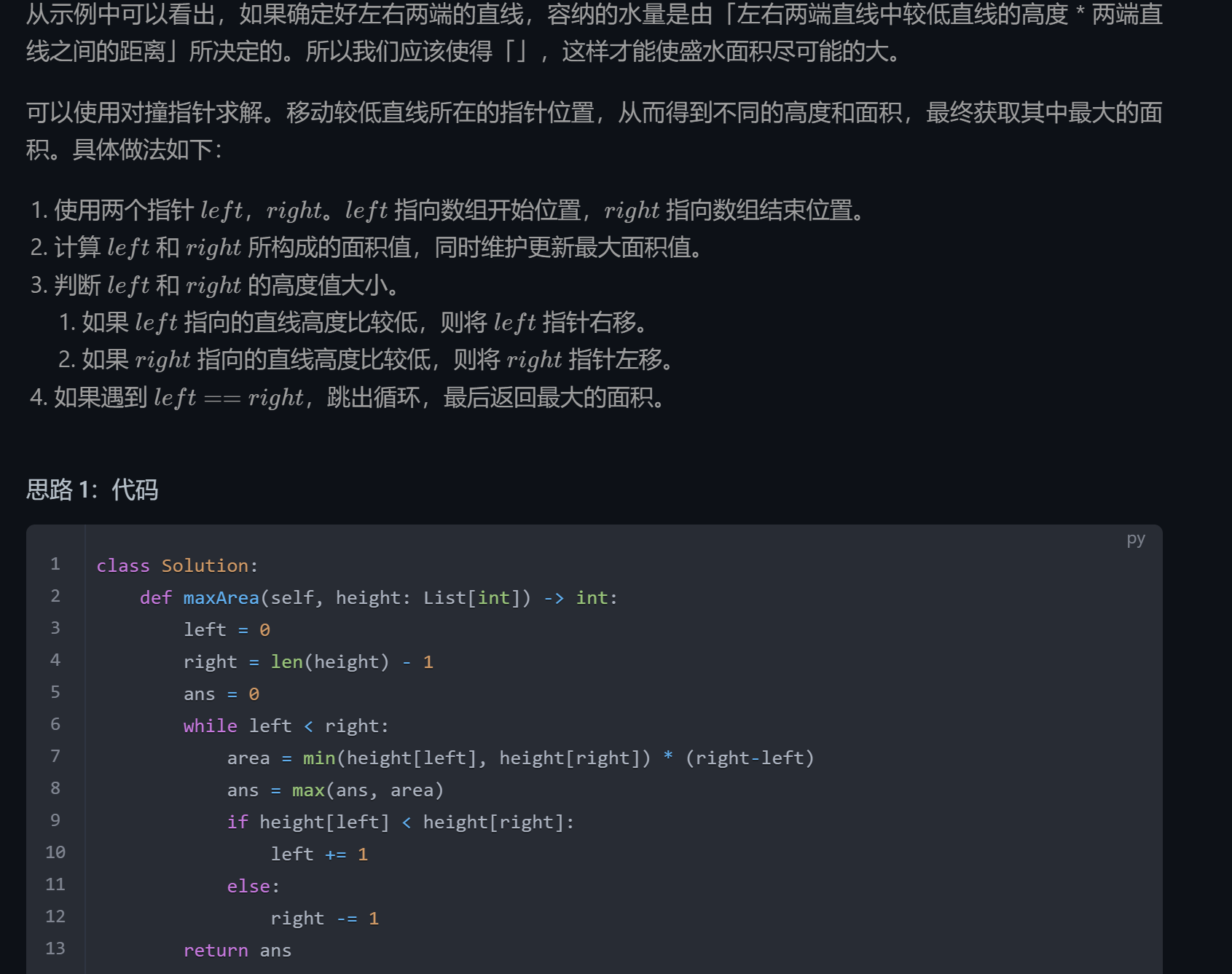
盛水问题
距离单调递减,所以我们保证长度较小的先去掉
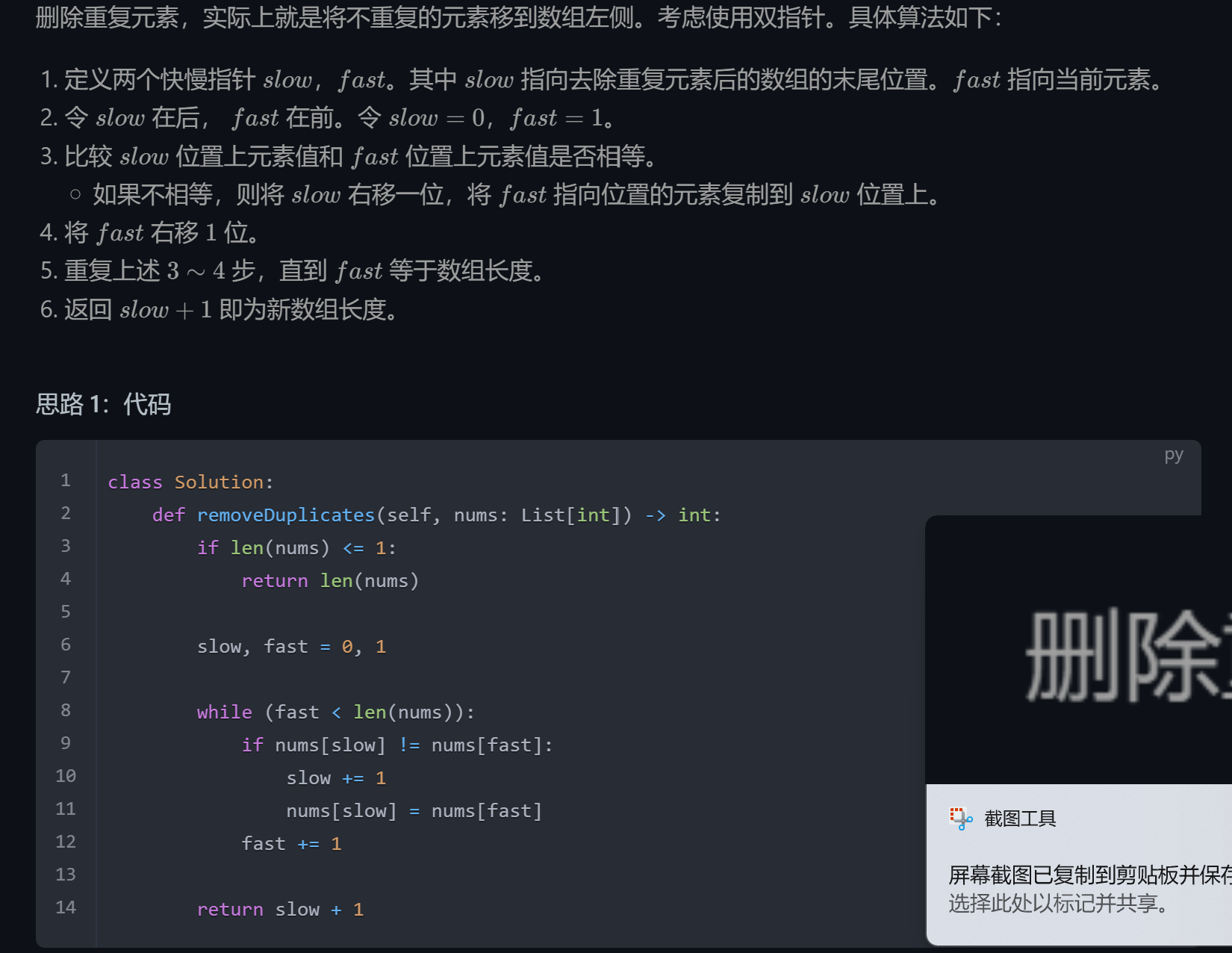
去重元素,空间o1
删除数组nums 中的重复元素,使每个元素只出现一次。并输出去除重复元素之后数组的长度。
题解:
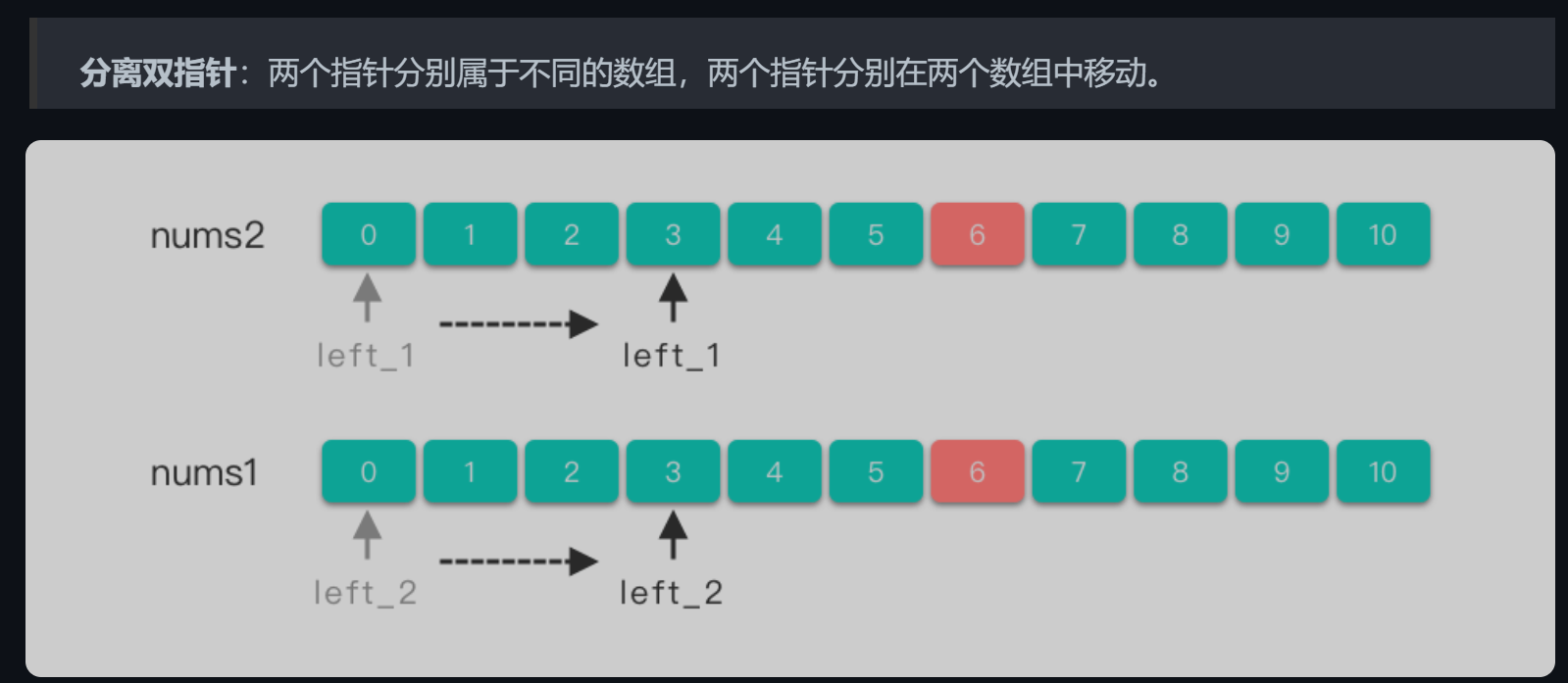
分离指针
分离双指针一般用于处理有序数组合并,求交集、并集问题。
三数之和
枚举i的位置,jz两个指针
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> res;
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
//当前项和前一项相同,则当前数字已经被刚才用过了,则直接跳过这个数字
if (i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1])
{
continue;
}
//第二重循环同时遍历 j 和 z
int z=n-1; //初始化z的位置,z从后往前
for (int j=i+1;j<n;j++) //j从前往后
{
//同理,跳过重复的数字
if (j>i+1 && nums[j]==nums[j-1])
{
continue;
}
//同时需要保证j<z:因为j作为左指针一定要在z右指针的左边
while (j<z && nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[z]>0)
{
//因为序列从小到大排序,当前的结果大于0,则减小z,寻找合适的位置
--z;
}
//如果j 和 z相遇,则表示无论j再往后,z再往前,他们都不可能再有结果了(和为0),因为j再往后遍历的数字一定和z之前的一个数字相同; z也是,一定和j之前的一个数字相同,我们已经遍历过了,所以这种情况直接退出
if (j==z)
{
break;
}
if (nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[z]==0)
{
res.push_back({nums[i],nums[j],nums[z]});
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
回文串问题
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiamian/p/11252214.html
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74922218/article/details/136886949
(动态规划版)

算法竞赛书 二分 (下午)
函数补充
**lower_bound **
lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 4)
upper_bound
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 4, 4, 5, 6};
int x = 4;
// 查找第一个不小于 x 的元素
auto lb = std::lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), x);
std::cout << "Index of the first element not less than " << x << ": " << (lb - vec.begin()) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Value at this index: " << *lb << std::endl;
// 查找第一个大于 x 的元素
auto ub = std::upper_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), x);
std::cout << "Index of the first element greater than " << x << ": " << (ub - vec.begin()) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Value at this index: " << (ub == vec.end() ? "end" : std::to_string(*ub)) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
//输出 4 2 4
4 4 5
equal_range
返回第一个不小于给定值的迭代器,又返回第一个大于给定值的迭代器
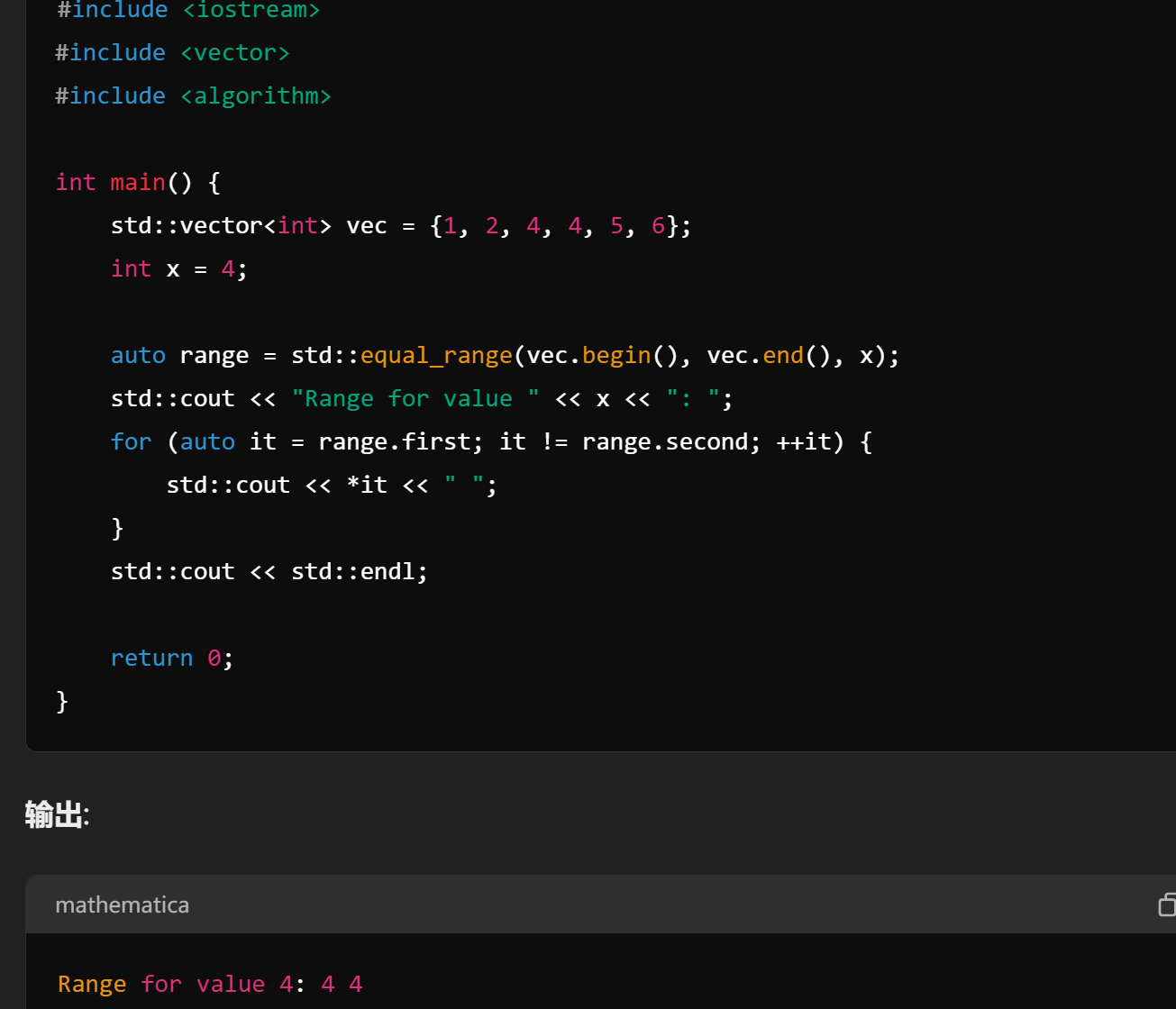
**find **
在容器中查找第一个等于给定值的元素,并返回指向该元素的迭代器。如果没有找到,返回指向容器末尾的迭代器。
**binary_search **
binary_search(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 4);找不到返回false
用于检查元素是否存在于排序数组中
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); // 排序
std::reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end()); // 逆序
find_if
#include <algorithm> // std::find_if
#include <vector>
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 4, 4, 5, 7};
auto it = std::find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int x) { return x > 4; });
// 查找第一个大于4的元素
二分
子数组最小值最大
(动态规划版)
动态规划
最大值最小化
有序列{2,2,3,4,5,1},划分为3个连续的子序列,子序列的和最大值最小
如(2,2,3),(4),(5,1)最大值最小为7
用二分法记录最大的值和在序列中最大的值3,而最大值最小一定在这里面。
(有点类似跳石头,跳石头枚举最小距离,最这个最小距离能否由拿走n块石头实现,这里枚举的使子序列和的最小值,看这样的最小值能不能在划分三次时成立)
类似的,划分数组为n个时,数组和的最大值(最小值最大)
csdn
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
int n, m;
int a[maxn];
int check(int x) {
int cnt = 1;
int s = a[1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (s + a[i] <= x) s += a[i];
else { s = a[i]; cnt++; }
}
return cnt;
}
int bin_search(int l, int r) {
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (check(mid) <= m) {
r = mid;
}
else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
int main() {
int t;
ll mx, sum;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
mx = 0, sum = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
sum += a[i];
if (mx < a[i])
mx = a[i];
}
int ans = bin_search(mx, sum);
cout << ans;
}
return 0;
}
琐碎(下午)
洛谷模拟例题

运用ASCII码
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int a[3];char s1,s2;
int main()
{
while (scanf("%c:=%c;",&s1,&s2)==2)//充分利用c++语言优势
a[s1-'a']=s2>='0' && s2<='9' ? s2-'0' : a[s2-'a']; //赋值语句简洁明了
printf("%d %d %d",a[0],a[1],a[2]);
}
运用map
#include<iostream>
#include<map>//Map头文件
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
map <char,int> num;//表示以char类型为下标,存储的是int
string st;
int main(){
cin>>st;//输入
int len=st.length();
num['a']=num['b']=num['c']='0';//注意初始化。。。。被坑了
for(int i=0;i<len;i+=5)
if(st[i+3]>='0'&&st[i+3]<='9')//注意判断是不是0~9
num[st[i]]=st[i+3];//直接取出数字赋值给对应变量
else num[st[i]]=num[st[i+3]];//变量之间相赋值
printf("%c %c %c",num['a'],num['b'],num['c']);
//输出三个变量
return 0;
}
技巧
为了防止多组测试,直接
while(cin>>n);
const long double pi=acosl(-1.0);//圆周率
sinl(),cosl()//三角函数的long double 版本
sinf//float版本
sin()//double
cout<<fixed<<serprecision(6);
头文件
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>//数学
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>//数学
#include<cctype>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<fstream>
vj团队赛2 (补题)
求最大公约数
有一个整数 n,1-n个数字分成两组,每一组至少有一个数,并且使得两组数字的和的最大公约数最大,请输出最大的最大公约数。

(即gcd a,b是sum的因子)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iomanip>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
int sum=n*(n+1)/2;
for(int i=2;i<=n/2;i++){
if(sum%i==0)
{
cout<<sum/i<<endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
七巧板
第一次6,第二次7...规律
int t=7+(6+n-1+6)*n/2;
圆内面积最大值

最小函数值
看不懂
https://blog.51cto.com/u_15357029/5098564
https://blog.csdn.net/u011815404/article/details/80657563
钟表问题
(暴力可过)
//还是要手动模拟一下,就知道怎么枚举了
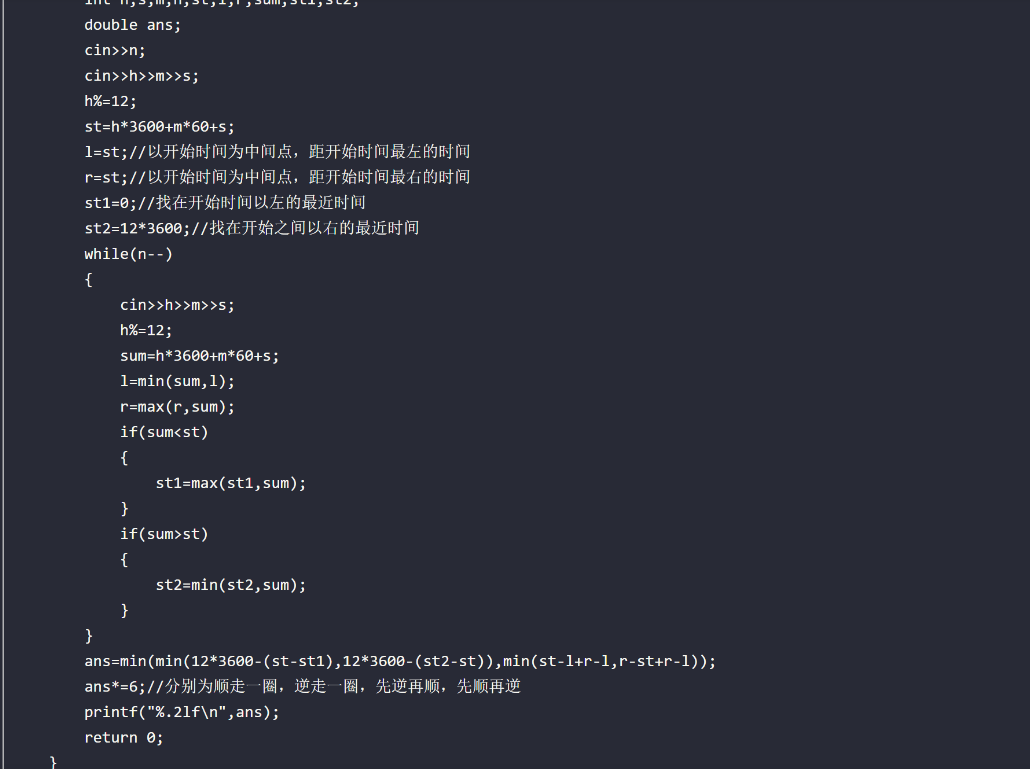
(暴力超时)(但是还是不懂怎么暴力
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double INF = 1e9;
// 将时间转换为秒
int time_to_seconds(int h, int m, int s) {
return h * 3600 + m * 60 + s;
}
// 计算从时间a到时间b的顺时针角度
double calculate_cw_angle(int a, int b) {
int diff = (b - a + 43200) % 43200; // 计算顺时针角度
return diff * 360.0 / 43200; // 计算角度
}
// 计算从时间a到时间b的逆时针角度
double calculate_ccw_angle(int a, int b) {
int diff = (a - b + 43200) % 43200; // 计算逆时针角度
return diff * 360.0 / 43200; // 计算角度
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> times(n + 1); // 用来存储时间的秒数,包含当前时间和所有目标时间
int h, m, s;
cin >> h >> m >> s;
int start_time = time_to_seconds(h % 12, m, s); // 将当前时间转化为秒
times[0] = start_time;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> h >> m >> s;
int time_point = time_to_seconds(h % 12, m, s); // 将目标时间转化为秒
times[i] = time_point;
}
double min_angle = INF;
// 枚举所有时间点的排列
vector<int> perm(n);
iota(perm.begin(), perm.end(), 1); // 排列从1到n的索引
do {
double total_angle = 0;
int current_time = start_time;
for (int i : perm) {
total_angle += calculate_cw_angle(current_time, times[i]);
current_time = times[i];
}
total_angle += calculate_cw_angle(current_time, start_time); // 返回到起点
min_angle = min(min_angle, total_angle);
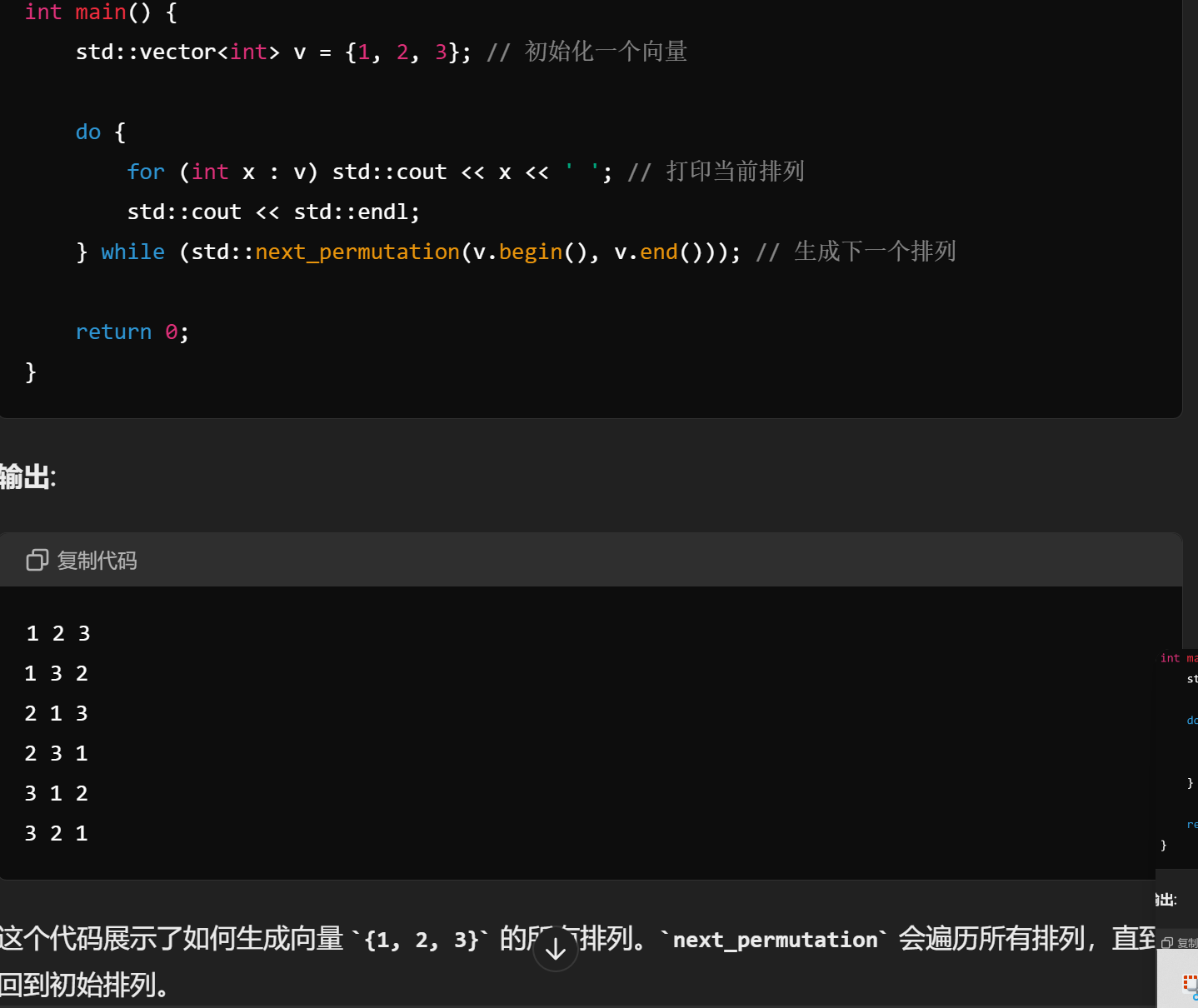
} while (next_permutation(perm.begin(), perm.end()));
// 输出结果,保留两位小数
printf("%.2f\n", min_angle);
return 0;
}
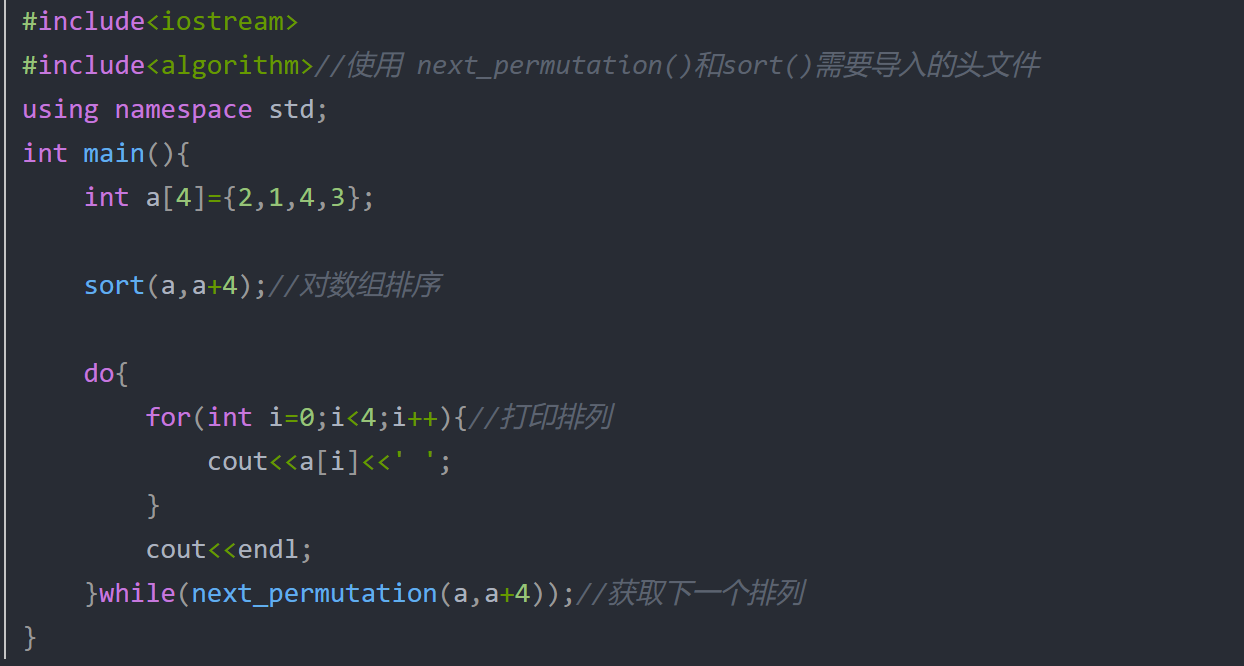
补充 next_permutation