EfficientNet网络
EfficientNet网络
目录
前言
在一些手工设计的网络中,我们常常将输入图像分辨率固定为224。为什么设置这个值,而网络的深度为什么这么设?如果要问的话,可能回复就四个字—工程经验。
而EfficientNet这篇文章就主要是使用了NAS(Neural Architecture Search)技术来搜索网络的图像分辨率$ r \(,网络的深度\) depth
\(以及\)chanel\(的宽度\) width
$这三个参数的合理化配置。在论文中提到,EfficientNet-B7模型在imagenet top-1上达到了当年最高准确率84.3%,与之前准确率最高的GPipe相比,参数数量仅为1/8.4,推理速度提升了6.1倍。下图是EfficientNet与其他网络的对比。
论文思想
在之前的一些论文中,有的会通过网络的width即增加卷积核的个数(增加特征矩阵的channels)来提升网络的性能,如图(b)所示;有的会通过增加网络的深度即使用更多的层结构来提升网络的性能,如图(c)所示;有的会通过增加输入网络的分辨率来提升网络的性能,如图(d)所示。而本论文中会同时增加网络的width、网络的深度以及输入网络的分辨率来提升网络的性能,如图(e)所示。
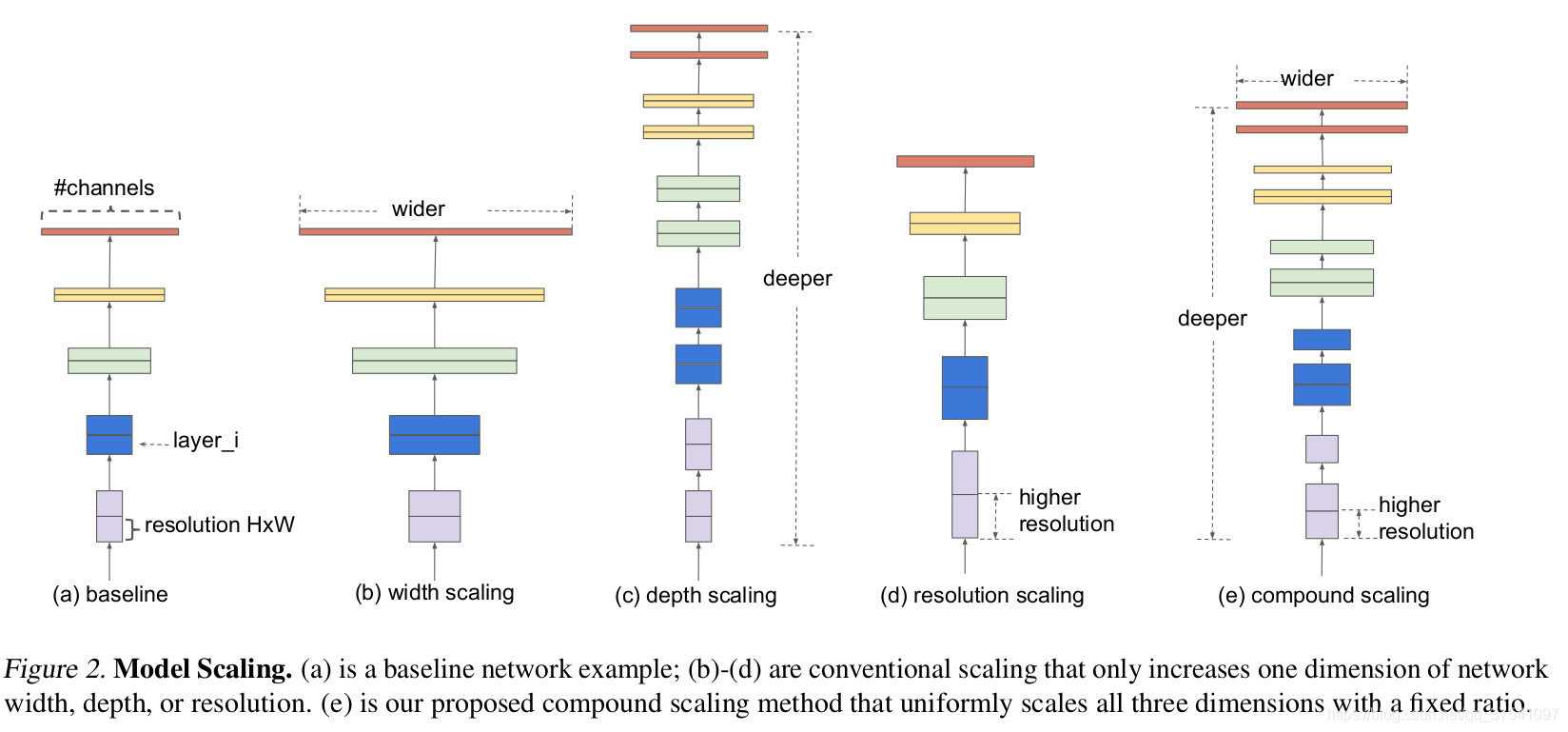
- 增加网络深度可以得到更丰富、复杂的特征并且能很好的应用到其它任务中。但网络的深度过深会面临梯度消失、训练困难的问题。
- 增加网络的宽度能够获得更高细粒度的特征并且也容易训练,但对于width很大而深度较浅的网络往往很难学到更深层次的特征。
- 增加输入的分辨率能够潜在获得更高细粒度的特征,但对于非常高的输入分辨率,准确率的增益也会减小。而且大分辨率图像会增加计算量。
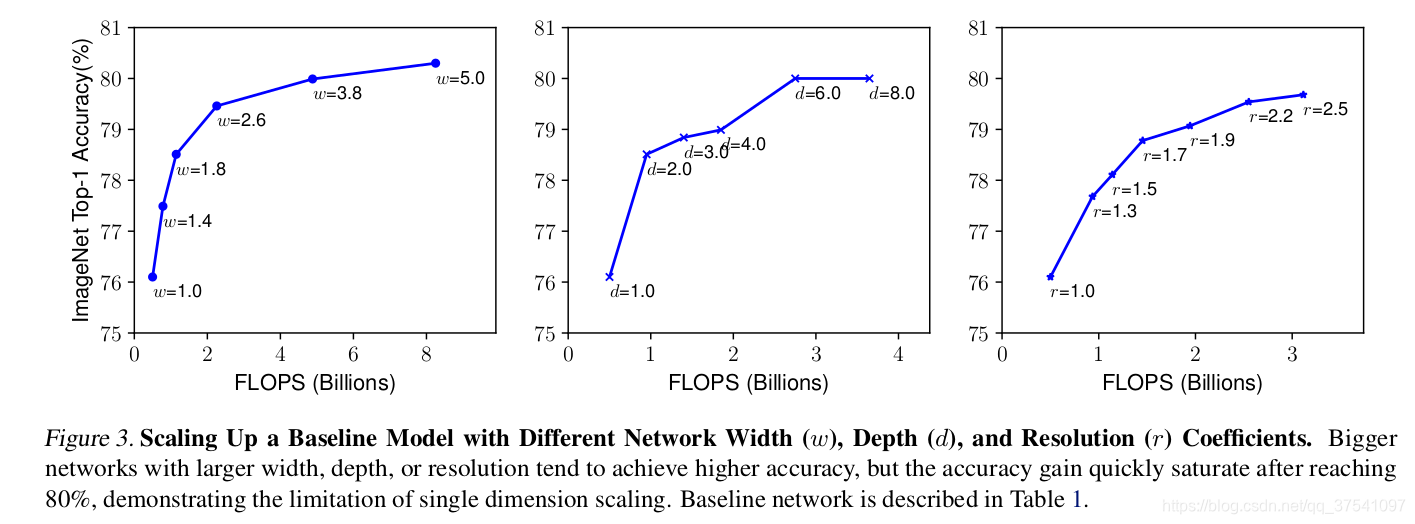
下图展示了在baseline B0上分别增加width、depth和resolution后得到的统计结果。
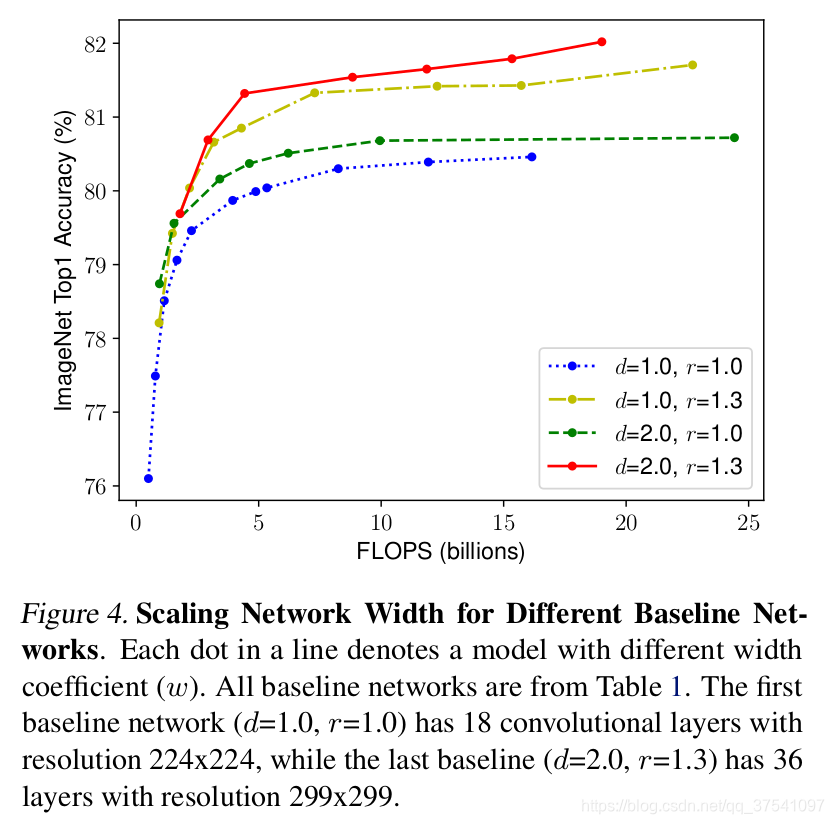
接着作者又做了一些实验,采用不同的\(d\),$ r $组合,然后不断改变网络的width得到了如下的曲线。
网络结构
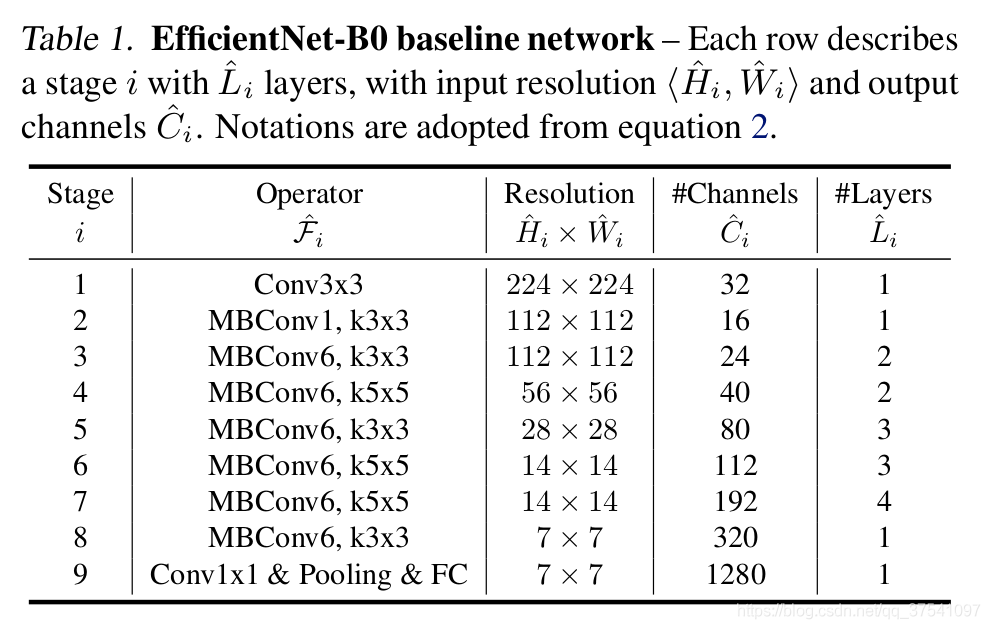
如下是EfficientNetB0的结构,它由一系列的stage组成,\(\widehat{F}_{i}\)表示对应stage的运算操作,\(\widehat{L}_{i}\)表示该stage中重复\(\widehat{F}_{i}\)的次数:
MBConv结构
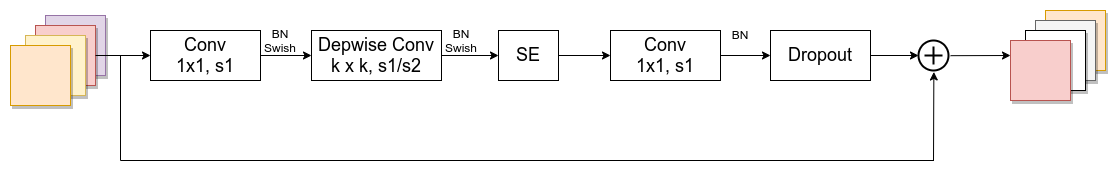
如图所示,MBConv结构主要由一个1 x 1的卷积,一个k x k的Depthwise Conv卷积(包含BN和Swish) ,k 的具体值在EfficientNet-B0的网络主要有3 x 3和5 x 5两种情况,一个SE模块,一个1 x 1的普通卷积(降维作用,包含BN),一个Dropout层构成。
- 第一个升维的1 x 1卷积层,它的卷积核个数是输入特征矩阵channel的/\(n\)倍,\(n∈\{{1},{6}\}\)
- 当\(n\)= 1时,则不要第一个升维的1 x 1 卷积层
- 关于shortcut连接,仅当输入MBConv结构的特征矩阵与输出的特征矩阵shape相同时才存在(代码中可以通过stride == 1 and inputc_channels == output_channels条件来判断)
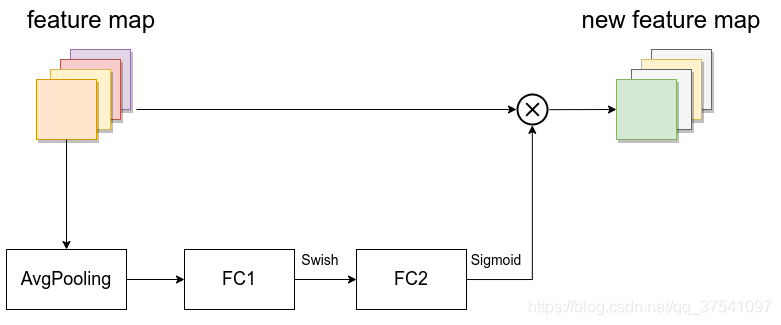
- SE模块如下所示,由一个全局池化、两个全连接层组成。第一个全连接层的节点个数是输入该MBConv特征矩阵channels的\(\frac{1}{4}\),且使用Swish激活函数。第二个全连接层的节点个数等于Depthwise Conv层输出的特征矩阵的channels,且使用Sigmoid激活函数
EfficientNet(B0-B7)参数
| Model | input_size | width_coefficient | depth_coefficient | drop_connect_rate | dropout_rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 224x224 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| B1 | 240x240 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| B2 | 260x260 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| B3 | 300x300 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| B4 | 380x380 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| B5 | 456x456 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| B6 | 528x528 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| B7 | 600x600 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
- input_size 代表训练网络时输入网络的图像大小
- width_coefficient代表channel维度上的倍率因子,如B0的stage1中3 x 3的卷积层所使用的卷积核个数是32,那么在B6中就是32 x 1.8 = 57.6,然后取整到最近的8的整数倍及56,其它stage同理
- depth_coefficient代表depth维度上的倍率因子(仅针对stage2到stage8),比如在EfficientNetB0中stage7的\(\widehat{L}_{i}=4\),那么在B6中就是4 x 2.6 = 10.4,然后向上取整11
- dropout_rate是最后一个全连接层前的dropout层(在stage9的Pooling与FC之间)的dropout_rate
代码
class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
width_coefficient: float,
depth_coefficient: float,
num_classes: int = 1000,
dropout_rate: float = 0.2,
drop_connect_rate: float = 0.2,
block: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None
):
super(EfficientNet, self).__init__()
# kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats
default_cnf = [[3, 32, 16, 1, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1],
[3, 16, 24, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2],
[5, 24, 40, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2],
[3, 40, 80, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 3],
[5, 80, 112, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 3],
[5, 112, 192, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 4],
[3, 192, 320, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1]]
def round_repeats(repeats):
"""Round number of repeats based on depth multiplier."""
return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats))
if block is None:
block = InvertedResidual
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.1)
adjust_channels = partial(InvertedResidualConfig.adjust_channels,
width_coefficient=width_coefficient)
# build inverted_residual_setting
bneck_conf = partial(InvertedResidualConfig,
width_coefficient=width_coefficient)
b = 0
num_blocks = float(sum(round_repeats(i[-1]) for i in default_cnf))
inverted_residual_setting = []
for stage, args in enumerate(default_cnf):
cnf = copy.copy(args)
for i in range(round_repeats(cnf.pop(-1))):
if i > 0:
# strides equal 1 except first cnf
cnf[-3] = 1 # strides
cnf[1] = cnf[2] # input_channel equal output_channel
cnf[-1] = args[-2] * b / num_blocks # update dropout ratio
index = str(stage + 1) + chr(i + 97) # 1a, 2a, 2b, ...
inverted_residual_setting.append(bneck_conf(*cnf, index))
b += 1
# create layers
layers = OrderedDict()
# first conv
layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3,
out_planes=adjust_channels(32),
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer)})
# building inverted residual blocks
for cnf in inverted_residual_setting:
layers.update({cnf.index: block(cnf, norm_layer)})
# build top
last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c
last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280)
layers.update({"top": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c,
out_planes=last_conv_output_c,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer)})
self.features = nn.Sequential(layers)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
classifier = []
if dropout_rate > 0:
classifier.append(nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate, inplace=True))
classifier.append(nn.Linear(last_conv_output_c, num_classes))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier)
# initial weights
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out")
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
def _forward_impl(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return self._forward_impl(x)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号