【ACM】 计算几何
前言
因为没有拿到牌子,心情低迷,随缘更新..
计算几何
1、平面几何前置知识
///非科学计数法输出
cout.setf(ios::fixed);
///设置输出小数点
cout << setprecision(4) << x <<endl;
2、点
2.1、点的表示
在计算几何的题目中,基本上都是实数计算,所以我们一般都使用精度更高的 double 来进行计算。double 类型的数据在读入的时候要使用 %lf ,在输出的时候要使用 %f 。
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y):x(-x),y(_y){} /// 有参构造
}P[N];
2.2、两点之间的距离
两点距离公式: \(dis = \sqrt{(x_1-x_2)^2 + (y_1-y_2)^2}\)
double distance(Point P){
hypot(x-P.x,y-P.y); /// 库函数,求根号下,两数平方和
}
3、向量
3.1、计算机中的向量
我们一般表示一个向量也是直接用一个点来表示,方向是从原点指向(x,y)坐标
比如说 Point (4,2) 这个点就表示的是从原点指向 B 的一个向量,因为向量是可以平移的,所以为了方便计算,我们直接用一个点来表示一个向量。
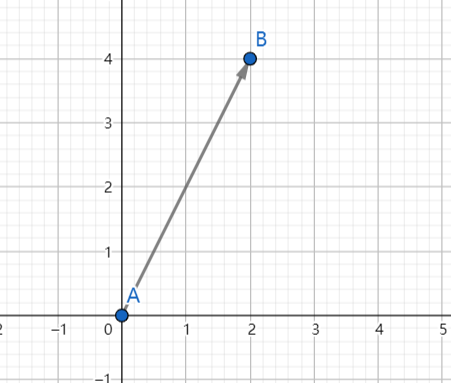
在计算中的,我们处理区间的运算,多数是在坐标原点处理的,可能他真实的情况是 \((A_1,C_1)\) ,\((A_2,B_2)\) 这样的情况,但是我们都将其平移到原点处理
3.1、点积(Dot Product)
向量的基本运算是 点积 和 叉积 ,计算几何的各种操作几乎都基于这两种运算。
已知两个 \(\vec{a},\vec{b}\) 向量 ,它们的夹角为 \(\theta\) ,那么:$ a \cdot b = |a||b|\cos \theta $
就是这两个向量的 数量积,也叫 点积 或 内积 。点积的几何意义为: \(\vec{a}\) 在 \(\vec{b}\) 上的投影乘以 \(\vec{b}\) 的模长
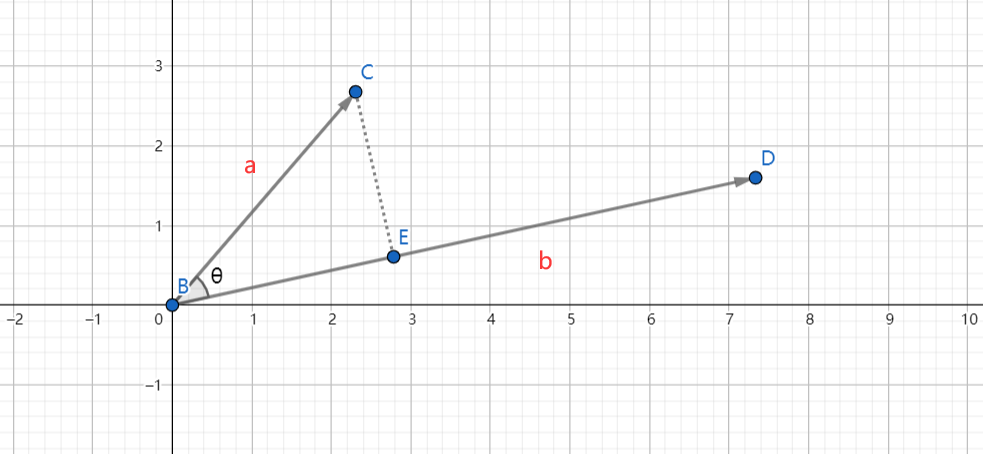
3.1.1、向量间的投影
由点积公式:$ a \cdot b = |a||b|\cos \theta $
double operator * (Point b){
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
我们可以发现 \(|a|\cos \theta\) ,\(|b|\cos \theta\) 都为一个向量到另一个向量的投影。
我们就可以通过点积来计算相互之间的投影:
\(|b|\cos \theta = \frac{ \vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}}{|\vec{a}|}\)
\(|a|\cos \theta = \frac{ \vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}}{|\vec{b}|}\)
3.1.2、点积与\(cos \theta\)
夹角 \(\theta\) 与点积大小的关系:
(补充cos的图)
- 若 \(\theta = 0°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = |\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\) ,同向共线
- 若 \(\theta = 180°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = -|\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\) ,反向向共线
- 若 \(\theta = 90°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = 0\) ,垂直
- 若 \(\theta < 90°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} > 0\) ,两向量的夹角为锐角
- 若 \(\theta > 90°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} < 0\) ,两向量的夹角为钝角
从上面我们可以发现,我们可以通过点积的结果来判断,共线的方向,以及垂直
3.2、叉积(Cross Product)
我们定义向量 \(\vec{a},\vec{b}\) 的向量积为一个向量,记为 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}\) ,其模与方向定义如下:
- \(|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}| = |\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\sin<a,b>\)
- \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}\) 与 \(\vec{a},\vec{b}\) 都垂直,且 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} ,\vec{a},\vec{b}\) 都符合右手法则。
我的右手和官方的不太一样,平摊(正面或者反面朝上)右手,大拇指和第一个向量方向相同,四指指向另一个(如果别扭就翻过来)。
手心向上,大于零,手心向下,小于零。我觉得这样方便点。
向量积也叫外积,也叫叉积。
double operator ^ (Point b){
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
3.2.1、求平行四边形面积
然而注意到向量积的模,联想到三角形面积计算公式 \(S = \frac{1}{2}ab\sin{C}\) ,我们可以发现向量积的几何意义是: \(|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|\) 是以为 $\vec{a},\vec{b} $ 为邻边的平行四边形的面积。
3.2.2、判断A,B向量方向关系
若 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} > 0\) ,\(\vec{b}\) 在 \(\vec{a}\) 的逆时针方向;
若 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} < 0\) ,\(\vec{b}\) 在 \(\vec{a}\) 的顺时针方向;
若 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 0\) , \(\vec{b}\) 与 \(\vec{a}\) 可能同向共线,也可能反向共线(刚才的点积就可以判断是同向共线还是反向共线),还可能平行。
3.4、向量的运算
3.4.1、向量模长
向量模长,就是原点到 (x,y) 坐标的距离(在我们的上述的建模方式下),对于向量 \(\vec{a}=(x,y)\) ,\(|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{(x-0)^2+(y-0)^2}\) ,所以我们用与求两点距离的方式来求向量的模长。
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
/// 长度的平方,便于之后的计算
double len2(){
return x*x + y*y;
}
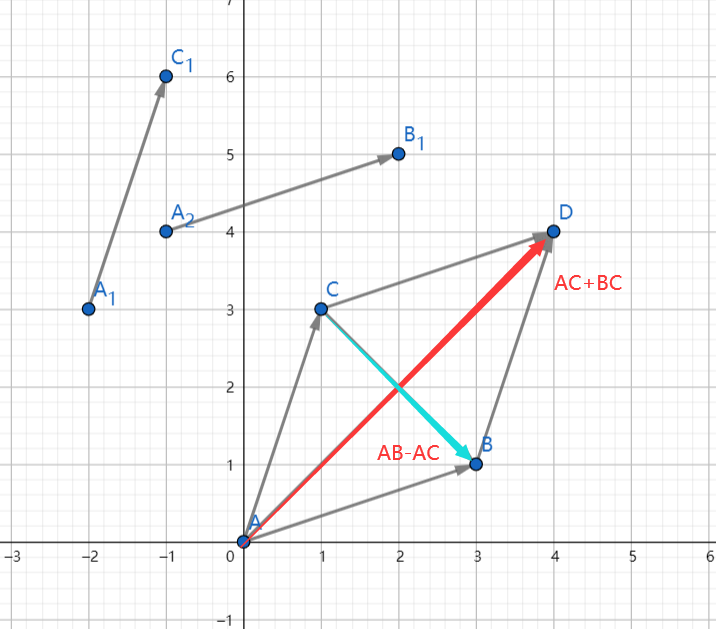
3.4.2、向量加、减
上图可以看到 \(\vec{AC}+\vec{AB}\) 的值就是坐标 \(D(C_x+B_x,C_y+B_y)\)
同时可以看到 \(\vec{AB}-\vec{AC}\) 的值就是坐标 \(\vec{CB}(B_x-C_x,B_y-C_y)\)
Point operator + (Point b){
return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );
}
Point operator - (Point b){
return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );
}
( 注:这些 operator 都是直接重载的结构体运算符,如果没有这方面的前置知识,请先学习如果重载结构体的运算符 )
3.4.3、向量数乘(放缩)
对于 \(\vec{a}=(x,y)\) ,\(\lambda \vec{a}=(\lambda x,\lambda y)\) ,除法的话等价于\(\frac{\vec{a}}{\lambda}=\frac{1}{\lambda}\vec{a}=(\frac{1}{\lambda} x,\frac{1}{\lambda} y)\)
Point operator * (double k){
return Point(k*x,k*y);
}
Point operator / (double k){
return Point(x/k , y/k);
}
对于数乘的具体应用是,把一个向量变为长度为 \(r\) 的向量,但是向量方向不变
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
r /= l;
return Point(x*r,y*r);
}
3.4.4、判断向量相等
因为计算机运行精度问题,所以我们不能直接用 == 来判断 double 类型的数据是否相等,这里引入,eps 来表示题目允许的误差范围,sgn 来代替比较运算符。
const double eps = 1e-8;
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
1e-8 表示的是\(1\times 10^{-8}\) 是判断两值相等所允许的误差范围,比如 \(1.000000002\) 与 \(1.000000005\) 被视为相等的两个数,均表示 \(1.00000000\) ,如果两数相减的值,小于 eps 那么我们就视为这是两个相等的数,基于此,我们可重载 < ,== 运算符。小于运算符的排序规则是,x 小的,y 小的在前,x作为第一标准,y作为第二标准。
bool operator == (Point b) {
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b){
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:b.x;
}
3.4.5、两向量夹角
前缀知识:
-
atan(x)表示求的是x的反正切,其返回值为\([-\frac{\pi}{2},+\frac{\pi}{2}]\)之间的一个数。 -
atan2(y,x)求的是y/x的反正切,其返回值为\([-\pi,+\pi]\)之间的一个数。
kuangbin用的方法是
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs( atan2( fabs( (a-p)^(b-p) ) , (a-p)*(b-p) ) );
}
我看了一眼没有理解,就直接推了一遍,并测试了在精度为 esp=1e-10的情况下,两则的答案相同
我自己的公式推导:
对于两个从原点出发的向量
由点积公式可得: $x_1 y_1+x_2y_2 = |A|\cdot |B|\cdot \cos \theta $ ,由模长公式和反三角函数可得 \(\theta = \acos({\frac{x_1 y_1+x_2y_2}{\sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2} \times \sqrt{x_2^2+y_2^2}} })\)
/// 求 a,b 向量对于原点的夹角
/// 如果是三个数的夹角的话,this 为中间的那个点,a,b为两端
/// return fabs( acos( ((a-tp)*(b-tp))/( (a-tp).len() * (b-tp).len() ) ) )
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point tp = *this;
return fabs(acos( (tp*b)/(tp.len() * b.len()) ));
}
哦哦哦,我明白了,kuangbin的是这样推的,还是推荐用kuangbin的因为代码更加简介,我的推导只用了点积(之后会讲解),或者也可以只用叉积,但是如果我们把叉积与点积 相除,就会得到 kuangbin 的式子,下面为推导。
\(叉积:x_1 y_2-x_2y_1 = |A|\cdot |B|\cdot \sin \theta\)
\(点积:x_1 y_1+x_2y_2 = |A|\cdot |B|\cdot \cos \theta\) ,相除可得
$\frac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } = \frac{x_1 y_2-x_2y_1}{x_1 y_1+x_2y_2} $,进一步推导 \(\tan \theta = \frac{\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} }{\vec{a} \times \vec{b} }\),然后求个反三角函数就好了,之后学习了点积和叉积的计算,同时我们重载了运算符之后,就会发现用这个方法来实现求夹角,代码就会比较精简。
kuangbin yyds!
3.4.6、向量旋转
设 \(\vec{a}=(x,y)\) ,倾角为 $\theta $ ,长度为 \(l = \sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) 。则 \(x=l\cos{\theta},y=l\sin{\theta}\) 。令其逆时针旋转 \(\alpha\) 度角,得到向量 \(\vec{b} = ( l\cos(\theta + \alpha),l\sin(\theta + \alpha) )\) 。
由三角恒等变换得,\(b = (l(\cos{\theta}\cos{\alpha}-\sin{\theta}\sin{\alpha}),(\sin{\theta}\sin{\alpha}+\cos{\theta}\sin{\alpha}))\)
将 \(x,y\) 的值带入式子得到,\(b=(x\cos{\alpha}-y\sin{\alpha},y\cos{\alpha}+x\sin{\alpha})\)
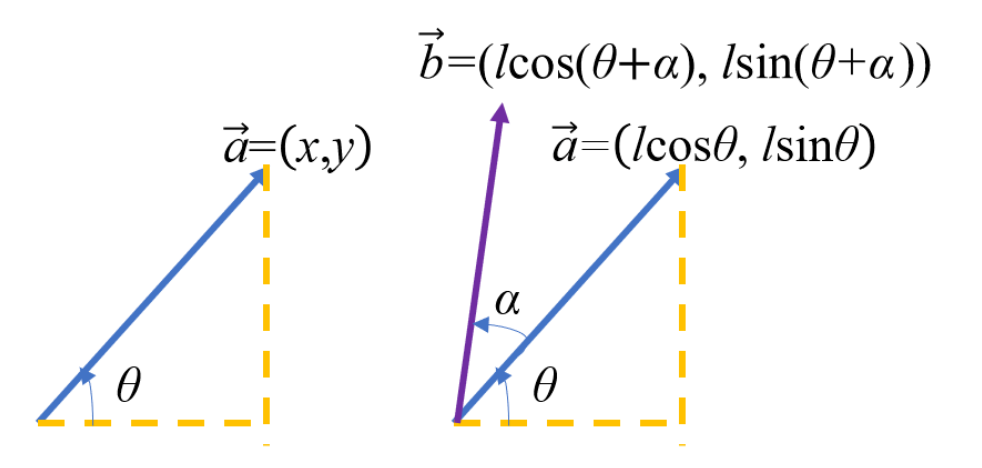
绕着 P 点旋转
Point rotata(Point p,double angle){
Point v = (*this) - p;
double c = cos(angle) , s = sin(angle);
return Point(p.x + v.x * c - v.y * s , p.y + v.x *s + v.y * c);
/// 绕原点旋转后,加上原来P点的偏移量
}
对于特殊的选择 90°,我们知道 \(\cos{90°}=0\) 所以就直接变成了
///逆时针旋转90度
Point rotleft(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
///顺时针旋转90度
Point rotright(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
3.5、向量板子
struct Point
{
double x,y;
double angle;
int id;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x; y = _y;
} /// 有参构造
/// 向量加法
Point operator + (const Point b) const{
return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );
}
/// 向量乘法
Point operator - (const Point b) const{
return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );
}
/// 向量数乘
Point operator * (const double k) const{
return Point(k*x,k*y);
}
/// 向量数除
Point operator / (const double k) const{
return Point(x/k , y/k);
}
bool operator == (const Point b) const{
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (const Point b) const {
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
/// 点积
double operator * (const Point b) const{
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
/// 叉积
double operator ^ (const Point b) const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
/// 两点之间的距离
double distance(const Point P) const {
return hypot(x-P.x,y-P.y); /// 库函数,求根号下,两数平方和
}
/// 向量长度
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
/// 长度的平方,便于之后的计算
double len2(){
return x*x + y*y;
}
/// 化为长度为 r 的向量
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
r /= l;
return Point(x*r,y*r);
}
/// 以 p 为中心点,pa,pb的夹角大小
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs( atan2( fabs( (a-p)^(b-p) ) , (a-p)*(b-p) ) );
}
/// 绕 p点 逆时针选择 angle 度
Point rotate(Point p,double angle){
Point v = (*this) - p;
double c = cos(angle) , s = sin(angle);
return Point(p.x + v.x * c - v.y * s , p.y + v.x *s + v.y * c);
/// 绕原点旋转后,加上原来P点的偏移量
}
///逆时针旋转90度
Point rotleft(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
///顺时针旋转90度
Point rotright(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
};
4、点与直线
4.1、直线,线段的表示
在计算几何中,直线,线段我们都用两个 Point 来表示,如果把 Point 视为点的话,那么所组成的就是线段,如果把 Point 视为向量的话,那么所组成的就是直线。
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e):s(_s),e(_e){}
};
4.1.1、由解析式来表示直线
- 斜截式式 \(y=kx+b\)
- 标准方程 \(ax + by + c = 0\)
通常,我们采用斜截式的时候是用直线与 \(x\) 轴的顺时针倾斜角与直线上一点来得到两点。
我们设直线的斜倾角为 \(\theta\) ,斜率为 \(k\) ,已知两点 \(P_1(x_1,y_1),P_2(x_2,y_2)\)
\(k = \frac{y1-y2}{x1-x2}\) ,\(\tan{\theta}= \frac{y1-y2}{x1-x2}=k\) ,那么\(\theta = atan(k)\)。
Line(Point p,double angle){
s = p;
if( sgn(angle - pi/2) == 0 ) e = (s + Point(0,1));
else e = (s + Point(1,tan(angle)));
}
///ax + by + c = 0;
Line(double a,double b,double c){
if( sgn(a) == 0 ) {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,-c/b);
}
else if(sgn(b) == 0) {
s = Point(-c/a,0);
e = Point(-c/a,1);
}
else {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,(-c-a)/b);
}
}
4.1.2、线段长度
就是两点之间的距离
double length(){
return s.distance(e);
}
4.1.3、直线基于 x 轴的斜倾角
就是用 4.1.1 中的公式来求
注:
const doubel pi = acos(-1);
double angle(){
double k = atan2(e.y-s.y , e.x-s.x);
if( sgn(k) < 0 ) k += pi;
if( sgn(k-pi) == 0 ) k -=pi;
return k;
}
4.2、点与直线
4.2.1、点与直线的位置关系
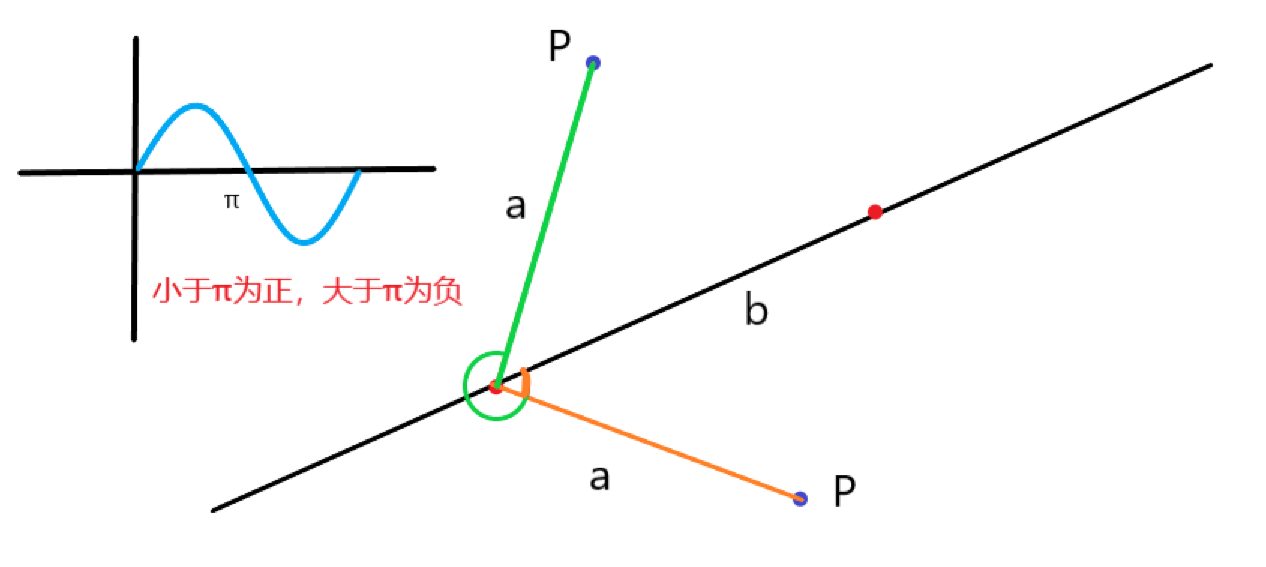
在二维平面上,点和直线有 3 种位置关系,点在直线左侧,点在直线右侧,点在直线上。记点为 \(P\),直线上的点为 \(P_1,P_2\) ,取 \(P_1P\),\(P_1P_2\) 构成向量用叉积就能得到位置关系。
///点与直线关系
///1在左侧
///2在右侧
///3在直线
int relation(Point p){
int c = sgn( (p-s) ^ (e -s) );
if(c < 0) return 1;
else if(c > 0) return 2;
else return 3;
}
4.2.2、点到直线的距离
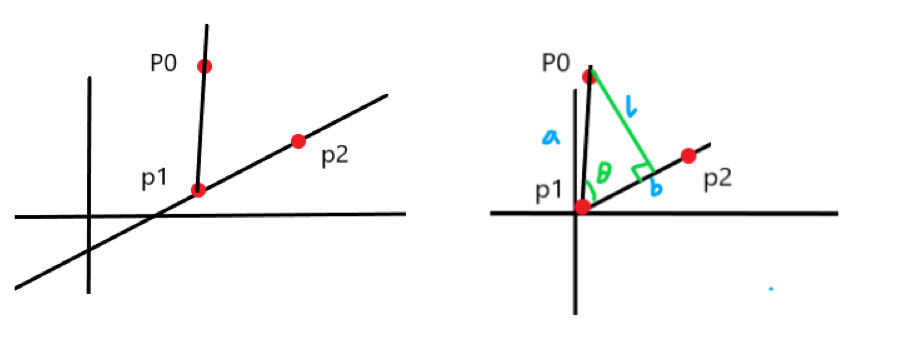
如图,我们设点 \(P_0\),取直线点 \(P_1,P_2\),我们用\(P_0-P_1,P_2-P_1\) 来将 \(P_1\) 点移动到原点,我们要求的点到直线的距离的长度设为 \(l\),\(P_0-P_1,P_2-P_1\) 两个向量的夹角设为 \(\theta\)。
通过叉积公式 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = |\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\sin{\theta}\)
我们可以得到 \(|\vec{b}|\sin{\theta}= \frac{\vec{a} \times \vec{b}}{|\vec{a}|}=l\),这样我们就得到了点到直线的距离的计算公式,因为叉积是有正负的,所以最后要取个绝对值。
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs( (p-s)^(e-s) ) / length();
}
4.2.3、点在直线上的投影(垂足)
还是上面哪个图,这次我们是要求 \(|\vec{b}|*\cos|\theta|\) , 我自己想的就是直接用点积来求,但是 kuangbin 和 黑书 都是用的成比例的方式,是因为求 cos 损失精度?需要 fabs ?
...
我去模拟了一下,才发现 lineProg 这个函数的返回值是 Point !!!所以这波是数学不过关。 我之前一直理解的是标量投影。但是这里我们求的是矢量投影,见百度百科。
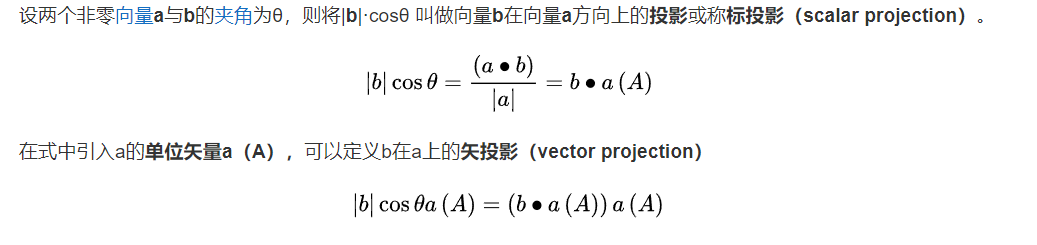
设 \(P_0\) 到 \(P_1P_2\) 的垂足为 \(P_3\) (均为向量),为了计算不用cos 所以我们要求一个 \(k = \frac{|P_3-P_1|}{|P_2-P_1|}\) ,长度比例嘛, \(P_3\) 就是我们要求的 矢投影。
由点积的公式:$ (P_0-P_1) \cdot (P_2-P_1) = |P_0-P_1||P_2-P_1|\cos \theta $ ,我们把 \(P_3\) 引入
公式变为 : \((P_0-P_1) \cdot (P_2-P_1) = |P_2-P_1| * |P3-P_1|\)
带入 k 的式子中: $ k = \frac{|P_3-P_1|}{|P_2-P_1|}=\frac{(P_0-P_1) \cdot (P_2-P_1)}{|P_2-P_1| * |P_2-P_1|} $
所以,$P_3 = P_1 + k*(P_2-P_1) $
/// 返回点p在直线上的投影
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ( (e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)) ) / ( (e-s).len2() ) );
}
这个也想相当于是,求点到直线的垂足向量。
4.2.4、点关于直线的对称点
求一个点对一条直线的对称点。先求点 \(P\) 在直线上的投影点 \(P_3\) (承接上一小节),再求对称点 。
就是把垂足的长度延长一倍就好了。
Point symmetrypoint(Point p){
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2*q.x-p.x,2*q.y-p.y);
}
一组测试数据
int main() { Point p = Point(4,5); Line l = Line( Point(0,0),Point(1,10) ); Point te = l.lineprog(p) ; printf("%.10f\n%.10f\n",te.x,te.y); Point t = l.symmetrypoint(p); printf("%.10f\n%.10f",t.x,t.y); return 0; } /* 输出 0.5346534653 5.3465346535 -2.9306930693 5.6930693069 */
4.3、点与线段
4.3.1、点与线段的位置关系
判断点 \(p\) 是否在线段上, 先用叉积判断是共线,再判断是否与端点组成的线段与原线段形成钝角。
在 3.1.2 节,我们知道:
若 \(\theta = 180°\) ,\(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = -|\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\) ,反向向共线
同时点 \(p\) 还有可能在端点上,所以最后为 \(\le 0\)
bool point_on_seg(Point p){
return sgn((p-s)^(e-s) ) == 0 && sgn( (p-s)*(p-e) ) <= 0 ;
}
4.3.2、点到线段的距离
点到线段的距离和点到直线的距离有所不同,设点为 \(P\) ,线段\(AB\) 。
在 P到AB的垂线长度,P到A的距离,P到B的距离,三者中取最小值。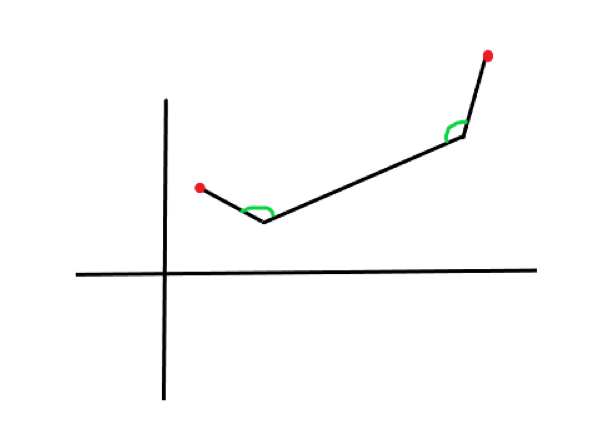
这是 if 判断的情况
double dispointtoseg(Point p){
if( sgn((p-s)*(e-s)) < 0 || sgn((p-e)*(s-e))<0 )
return min( p.distance(s),p.distance(e) );
return dispointtoline(p);
}
5、直线与线段
5.1、直线与直线的位置关系
5.1.1、判断直线与直线平行
在3.2.2小节,我们知道:
若 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 0\) , \(\vec{b}\) 与 \(\vec{a}\) 可能同向共线,也可能反向共线(刚才的点积就可以判断是同向共线还是反向共线),还可能平行。
bool parallel(Line v){
return sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-v.s) ) == 0 ;
}
5.1.2、两直线位置关系
思路就是,先判断平行,再判断是否共线,如果都不是的话那肯定是相交了。
这里共线我们直接用点与直线的共线来判断。
/// 判断两直线的位置关系
///0 平行
///1 共线
///2 相交
int linecrossline(Line v){
if( v.parallel(*this) ) return v.relation(s) == 3;
return 3;
}
5.2、直线与线段的位置关系
(-1)^(1) = 2
/// 直线与线段位置关系 -*this line -v seg
//2 规范相交
//1 非规范相交(顶点处相交)
//0 不相交
int linecrossseg(Line v){
int d1 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.s-s) );
int d2 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-s) );
if( (d1 ^ d2) == -2 ) return 2;
return (d1==0||d2==0);
}
5.3、线段与线段的位置关系
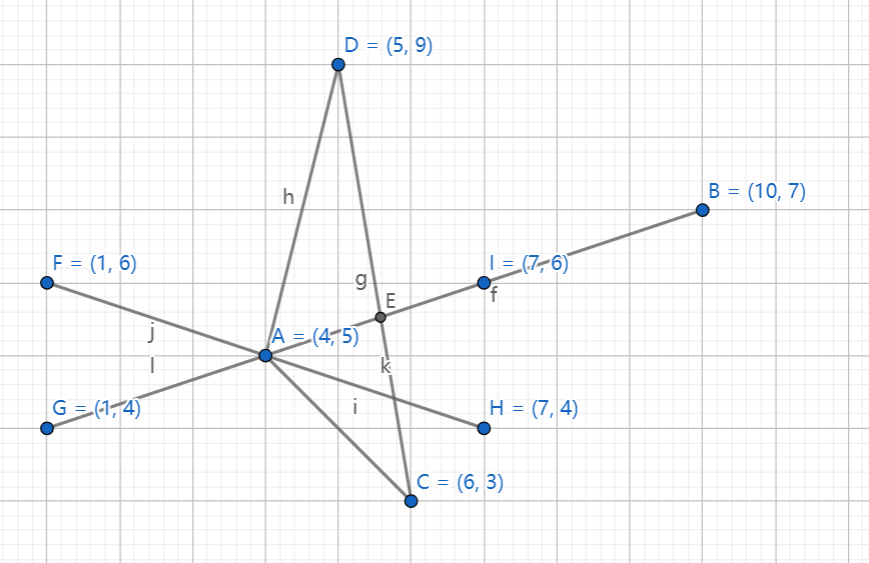
可用上图数据进行验证
///两线段相交判断
///2 规范相交
///1 非规范相交
///0 不想交
int segcrossseg(Line v) {
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e - s));
int d3 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (s - v.s));
int d4 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (e - v.s));
if ((d1 ^ d2) == -2 && (d3 ^ d4) == -2)return 2;
return (d1 == 0 && sgn((v.s - s) * (v.s - e)) <= 0) ||
(d2 == 0 && sgn((v.e - s) * (v.e - e)) <= 0) ||
(d3 == 0 && sgn((s - v.s) * (s - v.e)) <= 0) ||
(d4 == 0 && sgn((e - v.s) * (e - v.e)) <= 0);
}
5.4、线段到线段的距离
double disssegtoseg(Line v){
return min( { dispointtoseg(v.s),dispointtoseg(v.e) ,v.dispointtoseg(s), v.dispointtoseg(e) } );
}
直线到直线的距离,只有当两直线平行的时候才有意义,在两直线平行的情况下,我们直接随便取一个直线的 s,e 然后求点到直线的距离就可以了。
5.5、两条直线的交点
两直线,两线段的求交点是一样的,但是都要先判断是否相交,再求交点
Point crosspoint(Line v){
double a1 = (v.e-v.s)^(s-v.s);
double a2 = (v.e-v.s)^(e-v.s);
return Point( (s.x*a2-e.x*a1)/(a2-a1) , (s.y*a2-e.y*a1)/(a2-a1) );
}
6、线板子
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e){
s =_s; e= _e;
}
/// 点斜
Line(Point p,double angle){
s = p;
if( sgn(angle - pi/2) == 0 ) e = (s + Point(0,1));
else e = (s + Point(1,tan(angle)));
}
///ax + by + c = 0;
Line(double a,double b,double c){
if( sgn(a) == 0 ) {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,-c/b);
}
else if(sgn(b) == 0) {
s = Point(-c/a,0);
e = Point(-c/a,1);
}
else {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,(-c-a)/b);
}
}
/// 线段长度
double length(){
return s.distance(e);
}
/// 返回 0 <= angle <= pi 的基于 x轴 的斜倾角
double angle(){
double k = atan2(e.y-s.y , e.x-s.x);
if( sgn(k) < 0 ) k += pi;
if( sgn(k-pi) == 0 ) k -=pi;
return k;
}
///点与直线关系
//1 在左侧
//2 在右侧
//3 在直线
int relation(Point p){
int c = sgn( (p-s) ^ (e -s) );
if(c < 0) return 1;
else if(c > 0) return 2;
else return 3;
}
/// 点到直线的距离
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs( (p-s)^(e-s) ) /length();
}
/// 返回点p在直线上的投影点(垂足)
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ( (e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)) ) / ( (e-s).len2() ) );
}
/// 返回点p在直线上的对称点
Point symmetrypoint(Point p){
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2*q.x-p.x,2*q.y-p.y);
}
/// 点与线段的位置关系
bool point_on_seg(Point p){
return sgn((p-s)^(e-s) ) == 0 && sgn( (p-s)*(p-e) ) <= 0 ;
}
/// 点到线段的距离
double dispointtoseg(Point p){
if( sgn((p-s)*(e-s)) < 0 || sgn((p-e)*(s-e))<0 )
return min( p.distance(s),p.distance(e) );
return dispointtoline(p);
}
/// 判断平行
bool parallel(Line v){
return sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-v.s) ) == 0 ;
}
/// 判断两直线的位置关系
//0 平行
//1 共线
//2 相交
int linecrossline(Line v){
if( v.parallel(*this) ) return v.relation(s) == 3;
return 3;
}
/// 直线与线段位置关系 -*this line -v seg
//2 规范相交
//1 非规范相交(顶点处相交)
//0 不相交
int linecrossseg(Line v){
int d1 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.s-s) );
int d2 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-s) );
if( (d1 ^ d2) == -2 ) return 2;
return (d1==0||d2==0);
}
///两线段相交判断
///2 规范相交
///1 非规范相交
///0 不想交
int segcrossseg(Line v) {
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e - s));
int d3 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (s - v.s));
int d4 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (e - v.s));
if ((d1 ^ d2) == -2 && (d3 ^ d4) == -2)return 2;
return (d1 == 0 && sgn((v.s - s) * (v.s - e)) <= 0) ||
(d2 == 0 && sgn((v.e - s) * (v.e - e)) <= 0) ||
(d3 == 0 && sgn((s - v.s) * (s - v.e)) <= 0) ||
(d4 == 0 && sgn((e - v.s) * (e - v.e)) <= 0);
}
/// 线段到线段的距离
double disssegtoseg(Line v){
return min( min( dispointtoseg(v.s),dispointtoseg(v.e)) , min(v.dispointtoseg(s), v.dispointtoseg(e) ) );
}
/// 求两直线的交点
Point crosspoint(Line v){
double a1 = (v.e-v.s)^(s-v.s);
double a2 = (v.e-v.s)^(e-v.s);
return Point( (s.x*a2-e.x*a1)/(a2-a1) , (s.y*a2-e.y*a1)/(a2-a1) );
}
};
6、多边形
之前的多数来自于
kuangbin计算几何板子,黑书,之后的可能就是我自己想的很多方法了
6.1、多边形的表示
maxp 为点的数量,狂兵的把求凸包,求极角排序都写在 struct 里面了,但是我觉得这个应该是在 点集上进行的操作,所以我写在了外面。
const int maxp = 1e5+10;
struct Polygon
{
int n;
Point p[maxp];
Line l[maxp];
/// 在多边形中添加点
void add(Point q){
p[n++] = q;
}
/// 获取所有的线段
void getLine(){
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
l[i] = Line(p[i],p[(i+1)%n]);
}
}
};
6.2、多边形判定与求得
6.2.1、极角排序
对于一个二维平面上的点集,我们选择点集中,最左下角的点,做 J 点到 x轴 的平行线,为直线 JA,然后逆时针旋转 直线JA ,接触其他点的先后循序就是 极角排序 的结果。
如果有两个点与 JA 都相交,那么我们定义与 J 的距离短的优先级高。
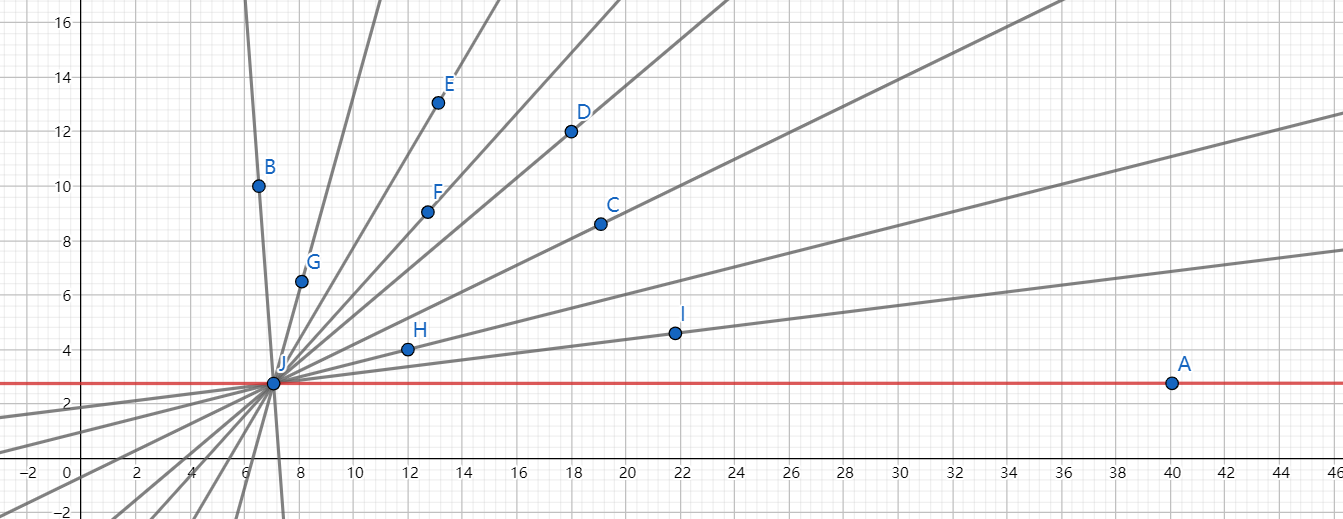
6.2.1.1、atan2得到极角排序
在 3.4.5 中我们知道了 atan 与 atan2 的区别,因为 atan2 的取值是在 \([-\pi,+\pi]\) 所以,我们用 atan2 来求,直线之间的夹角,因为极角排序其实就是夹角排序。
之前狂兵的板子中的
Point是没有angle属性的。我这里把极角排序从多边形中独立出来,多边形就只处理多边形那些关系,不管求凸包,极角排序这些,因为这些其实都是 点集 在干的事。
我调整了一下点的位置,把他们都变成了整数。
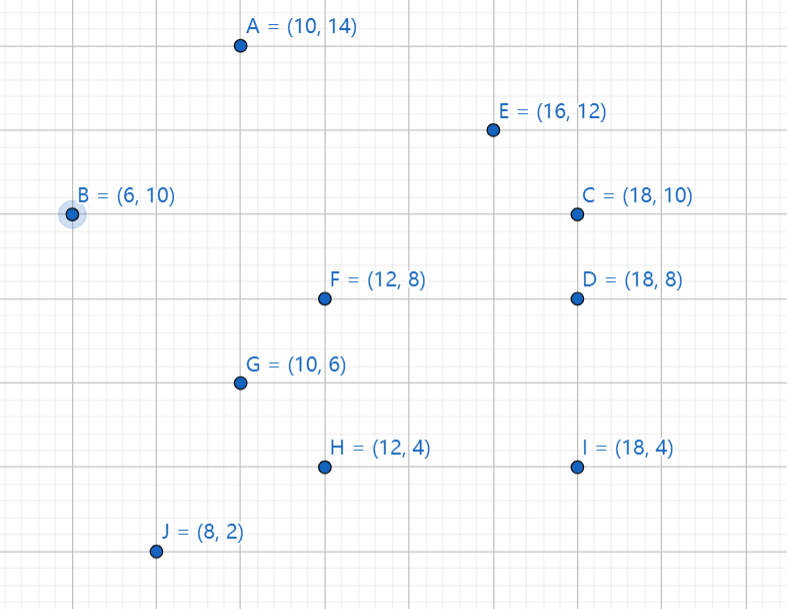
我先是这样写的 atan2 cmpAtan2Point 为最左下角的 J
te[i].angle = atan2( te[i].x - cmpAtan2Point.x,te[i].y - cmpAtan2Point.y );
然后我发现我是 x,y 写反了,最后他变成了 J与y轴平行,顺时针的过去!还有一个值得注意的问题:
\(atan2 \in [-\pi,+\pi]\) 所以,刚才的与
y轴平行的情况中B点的值为负,反而排到前面了,所以计算atan2的时候小于零的数都 \(+2π\) 。同时要注意,在
Point中,我们之前重载的<是x小就小x 的优先级比 y 高,这里我们需要提高 y 的优先级
修改的代码:
/// Point 的重载
bool operator < (Point b) const {
return sgn(y-b.y)==0?sgn(x-b.x)<0:y<b.y;
}
/// -------------------------------------------------///
/// 用来指定排序的极点
Point cmpAtan2Point = Point(inf,inf);
/// sort cmp
bool cmpAtan2(Point a,Point b)
{
if( sgn(a.angle - b.angle) == 0 ) return a.distance(cmpAtan2Point) < b.distance(cmpAtan2Point );
return a.angle < b.angle;
}
Point te[N];
int main()
{
te[0] = {6,10};
te[1] = {8,2};
te[2] = {10,6};
te[3] = {10,14};
te[4] = {12,4};
te[5] = {12,8};
te[6] = {16,12};
te[7] = {18,10};
te[8] = {18,8};
te[9] = {18,4};
te[10] = {6,8}; /// 我又加了一个,来验证负数的情况
/// 取到最小的数,所以需要重载运算符
for(int i = 0; i < 11 ; i++){
cmpAtan2Point = min(cmpAtan2Point,te[i]);
}
cout << cmpAtan2Point.x << ' ' << cmpAtan2Point.y << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 11 ; i++){
if( te[i] == cmpAtan2Point ){
te[i].angle = 0;
}
else{
te[i].angle = atan2( te[i].x - cmpAtan2Point.x,te[i].y - cmpAtan2Point.y );
if( sgn(te[i].angle) < 0 ) te[i].angle += 2*pi;
}
}
sort(te,te+11,cmpAtan2);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 11 ; i++){
cout << te[i].angle <<endl;
cout <<te[i].x << ' ' << te[i].y <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
最后的结果:(注意这是 做J垂直于Y顺时针的极角排序)
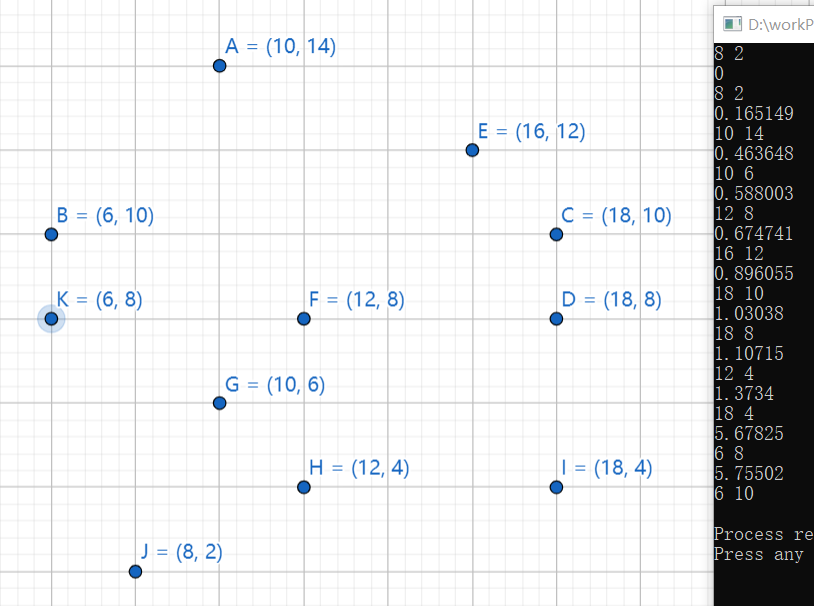
修改为 J平行于X轴,逆时针扫
te[i].angle = atan2( te[i].y - cmpAtan2Point.y , te[i].x - cmpAtan2Point.x); ///只用修改这里
6.2.1.2、叉积得到极角排序
这个比较老火,主要是用来排序,以左下角为极点的。
bool cmpCross(const Point a,const Point b)
{
double d = sgn((a-cmpPoint)^(b-cmpPoint)) ;
if( d == 0 ) return sgn( a.distance(cmpPoint) - b.distance(cmpPoint) ) < 0;
return d > 0;
}
6.2.2、得到凸包
Gradham 扫描法的变种,Andrew 算法
///--------------------- 凸包 --------------------///
/// 求之前的点集
Point convexP[N];
int Sizep; /// 点集大小
void getconvex(Polygon &convex)
{
/// 按照 x 从小到大排序,如果 x 相同,按 y 排序。
sort(convexP,convexP+Sizep);
convex.n = Sizep;
for(int i = 0 ; i < min(Sizep,2) ; i ++){
convex.p[i] = convexP[i];
}
/// 特判
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
if( Sizep <= 2 ) return ;
int &top = convex.n;
top = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < Sizep ; i++){
while( top && sgn( (convex.p[top] - convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i]) ) <= 0 ) top--;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
int temp = top;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[Sizep-2];
for(int i = Sizep-3 ; i >= 0 ; i--){
while( top != temp && sgn( (convex.p[top] -convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i])) <= 0 ) top --;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
/// 这样求出来的顺时针的凸包,如果要逆时针的话,来一次极角排序就好了。
/// 极角排序
cmpPoint = convex.p[0];
sort(convex.p,convex.p+convex.n,cmpCross);
}
6.2.3、判定多边形是否为凸多边形
如果直接用点集来判断的话,要先求一波极角排序
bool isconvex(){
bool s[2];
memset(s,0,sizeof s);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = (j+1)%n;
s[ sgn( (p[j]-p[i])^(p[k]-p[i]))+1 ] = true;
if( s[0] && s[2] ) return false;
}
return true;
}
6.3、多边形周长
double getcircumference(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
sum += p[i].distance(p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return sum;
}
6.4、多边形面积
如果是凹多边形,要按顺序排列才行。凸多边形,跑一边极角。
double getarea(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
sum += (p[i]^p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return fabs(sum)/2;
}
6.5、多边形的重心
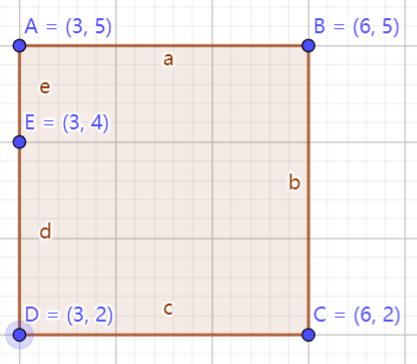
对于面积切割的加权平均。三角形的顶点重量都是分均的,但是多边形就不是了,所以要面积分均才是真正的重心。下图的这个5边形的重心要向上移,而不是在中间。
Point getbarycenter(){
Point ret(0,0);
double area = 0 ;
for(int i = 1; i < n-1 ; i++){
double tmp = (p[i]-p[0])^(p[i+1]-p[0]);
if( sgn(tmp) == 0 ) continue;
area += tmp;
ret.x += (p[0].x + p[i].x + p[i+1].x)/3*tmp;
ret.y += (p[0].y + p[i].y + p[i+1].y)/3*tmp;
}
if( sgn(area)) ret = ret/area;
return ret;
}
6.6、点与多边形
6.6.1、点与多边形的位置关系
//3 点上
//2 边上
//1 内部
//0 外部
int relationpoint(Point q){
/// 在点上
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if( p[i] == q ) return 3;
}
getLine(); /// 之前getline了的话,可以注释节约时间
/// 在边上
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if( l[i].point_on_seg(q) ) return 2;
}
/// 在内部
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = sgn( (q-p[j])^(p[i]-p[j]) );
int u = sgn( p[i].y - q.y );
int v = sgn( p[j].y - q.y );
if( k > 0 && u < 0 && v >= 0 ) cnt ++;
if( k < 0 && v < 0 && u >= 0 ) cnt--;
}
return cnt != 0;
}
6.7、直线与多边形
-
判断线段 \(AB\) 是否在任意多边形 \(Poly\) 以内:不相交且两端点 \(A,B\) 均在多边形以内。
-
判断线段 \(AB\) 是否在凸多边形 \(Poly\) 以内:两端点 \(A,B\) 均在多边形以内。
6.8、多边形与多边形
判断任意两个多边形是否相离:属于不同多边形的任意两边都不相交 且 一个多边形上的任意点都不被另一个多边形所包含。
int relationpolygon(Polygon Poly){
getLine();
Poly.getLine();
for(int i1 = 0 ; i1 < n ; i1++){
int j1 = (i1+1)%n;
for(int i2 = 0 ; i2 <= Poly.n ; i2++){
int j2 = (i2+1)%Poly.n;
Line l1 = Line(p[i1],p[j1]);
Line l2 = Line(Poly.p[i2],Poly.p[j2]);
if( l1.segcrossseg(l2) ) return 0;
if( Poly.relationpoint(p[i1]) || relationpoint(Poly.p[i2]) ) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
6.5、多边形与圆
6.6、多边形板子
struct Polygon
{
int n;
Point p[maxp];
Line l[maxp];
/// 在多边形中添加点
void add(Point q){
p[n++] = q;
}
/// 获取所有的线段
void getLine(){
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
l[i] = Line(p[i],p[(i+1)%n]);
}
}
/// 判断多边形是不是凸包
/// 如果是直接对点集效验的话,要先极角排序
bool isconvex(){
bool s[2];
memset(s,0,sizeof s);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = (j+1)%n;
s[ sgn( (p[j]-p[i])^(p[k]-p[i]))+1 ] = true;
if( s[0] && s[2] ) return false;
}
return true;
}
/// 多边形周长
double getcircumference(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
sum += p[i].distance(p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return sum;
}
/// 多边形面积
double getarea(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
sum += (p[i]^p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return fabs(sum)/2;
}
/// 重心
Point getbarycenter(){
Point ret(0,0);
double area = 0 ;
for(int i = 1; i < n-1 ; i++){
double tmp = (p[i]-p[0])^(p[i+1]-p[0]);
if( sgn(tmp) == 0 ) continue;
area += tmp;
ret.x += (p[0].x + p[i].x + p[i+1].x)/3*tmp;
ret.y += (p[0].y + p[i].y + p[i+1].y)/3*tmp;
}
if( sgn(area)) ret = ret/area;
return ret;
}
/// 判断点与任意多边形的关系
//3 点上
//2 边上
//1 内部
//0 外部
int relationpoint(Point q){
/// 在点上
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if( p[i] == q ) return 3;
}
// getLine(); /// 之前getline了的话,可以注释节约时间
/// 在边上
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if( l[i].point_on_seg(q) ) return 2;
}
/// 在内部
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = sgn( (q-p[j])^(p[i]-p[j]) );
int u = sgn( p[i].y - q.y );
int v = sgn( p[j].y - q.y );
if( k > 0 && u < 0 && v >= 0 ) cnt ++;
if( k < 0 && v < 0 && u >= 0 ) cnt--;
}
return cnt != 0;
}
/// 判断多边形是否与多边形相离
int relationpolygon(Polygon Poly){
getLine();
Poly.getLine();
for(int i1 = 0 ; i1 < n ; i1++){
int j1 = (i1+1)%n;
for(int i2 = 0 ; i2 <= Poly.n ; i2++){
int j2 = (i2+1)%Poly.n;
Line l1 = Line(p[i1],p[j1]);
Line l2 = Line(Poly.p[i2],Poly.p[j2]);
if( l1.segcrossseg(l2) ) return 0;
if( Poly.relationpoint(p[i1]) || relationpoint(Poly.p[i2]) ) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
};
/// 用来指定排序的极点
Point cmpPoint = Point(inf,inf);
/// 需重载 Point 的小于符号
bool cmpAtan2(Point a,Point b)
{
if( sgn(a.angle - b.angle) == 0 ) return a.distance(cmpPoint) < b.distance(cmpPoint );
return a.angle < b.angle;
}
/// 慎用,第一个基本上就够了
bool cmpCross(const Point a,const Point b)
{
double d = sgn((a-cmpPoint)^(b-cmpPoint)) ;
if( d == 0 ) return sgn( a.distance(cmpPoint) - b.distance(cmpPoint) ) < 0;
return d > 0;
}
///--------------------- 凸包 --------------------///
/// 求之前的点集
Point convexP[N];
int Sizep; /// 点集大小
void getconvex(Polygon &convex)
{
/// 按照 x 从小到大排序,如果 x 相同,按 y 排序。
sort(convexP,convexP+Sizep);
convex.n = Sizep;
for(int i = 0 ; i < min(Sizep,2) ; i ++){
convex.p[i] = convexP[i];
}
/// 特判
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
if( Sizep <= 2 ) return ;
int &top = convex.n;
top = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < Sizep ; i++){
while( top && sgn( (convex.p[top] - convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i]) ) <= 0 ) top--;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
int temp = top;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[Sizep-2];
for(int i = Sizep-3 ; i >= 0 ; i--){
while( top != temp && sgn( (convex.p[top] -convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i])) <= 0 ) top --;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
/// 这样求出来的顺时针的凸包,如果要逆时针的话,来一次极角排序就好了。
/// 极角排序
// cmpPoint = convex.p[0];
// sort(convex.p,convex.p+convex.n,cmpCross);
}
7、圆
7.1、圆的表示
struct Circle
{
Point c;
double r;
Circle(){}
Circle(Point _c,double _r):c(_c),r(_r){}
Circle(double x,double y,double _r){ /// 点的坐标,圆心
c = Point(x,y); r = _r;
}
bool operator == (Circle v){
return (p == v.p) && sgn(r-v.r) == 0;
} /// 以圆心为主排序,半径为副排序
bool operator < (Circle v) const{
return ( (p<v.p) || (p == v.p) && sgn(r-v.r)<0 );
}
/// 面积
double area(){
return pi*r*r;
}
/// 周长
double circumference(){
return 2*pi*r;
}
};
7.2、点和圆的关系
/// 点和圆的位置关系
//0 圆外
//1 圆上
//2 圆内
int relationPoint(Point b){
double dst = b.distance(p);
if( sgn(dst-r)<0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r)==0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
7.3、直线和圆的关系
7.3.1、直线和圆的位置关系
比较的是圆心到直线的距离和半径的关系
//0 圆外
//1 圆上
//2 园内
int relationLine(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoline(p);
if( sgn(dst-r) < 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r) == 1 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
7.3.2、直线和圆的交点
7.4、线段和圆的关系
比较的是圆心到线段的距离和半径的关系
int relationSeg(Line v){
double d = p.dispointtoSeg(p);
if( sgn(dst-r) < 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r) == 0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
7.5、圆与圆的关系
7.5.1、圆与圆的位置关系
//5 相离
//4 外切
//3 相交
//2 内切
//1 内含
int relationcircle(Circle v){
double d = p.distance(v.p);
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) > 0 ) return 5;
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) == 0 ) return 4;
double l = fabs(r-v.r);
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) < 0 && sgn(d-l) > 0 ) return 3;
if( sgn( d-l ) == 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn( d-l ) < 0 ) return 1;
}
7.5.2、圆与圆的交点个数
7.5.3、圆与圆的交点
7.5.4、两圆相交面积
7.6、直线和圆的交点
7.7、圆与三角形
7.7.1、三角形内接圆
7.7.2、三角形外接圆
7.7.3、圆与三角形相交面积
7.8、最小圆覆盖
8、专题
8.1、求凸包
6.2.2
8.2、最近点对
8.3、旋转卡壳
8.4、最远点对
8.4、半平面交
8.5、最小矩形覆盖
9、测试题
9.1、【LightOJ 1203】凸包+最小顶点夹角
9.2、【2020ICPC 昆明】线段与直线相交判断
这个题可以说是我计算几何的梦魇。今年上半年打昆明的时候,很快就发现了这个题是铜,但是到最后都没有过,今天知道原因了,没有排序的优先级有问题....
题意
给你一个点集,让你求任意一个点,与其他点所组成的直线与一条线段的第 k 个交点。保证没有3点共线。
题解
直接我们打个表,把所有的交点已经坐标都求出来,计算几何怎么搞都行,只要是基础的那些求交点,平行,都是\(O(1)\) 的世界复杂度。但是一定要对交点排序,排序的标准是距离线段第一个点的距离的长度!!。
还有就是,计算几何别用 cin !!! 计算几何别用 cin !!! 计算几何别用 cin !!!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
const int N = 1e3+10;
const int pi = acos(-1);
//square of a double
inline double sqr(double x){return x*x;}
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y):x(_x),y(_y){} /// 有参构造
/// 向量加法
Point operator + (Point b){
return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );
}
/// 向量乘法
Point operator - (Point b){
return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );
}
/// 向量数乘
Point operator * (double k){
return Point(k*x,k*y);
}
/// 向量数除
Point operator / (double k){
return Point(x/k , y/k);
}
bool operator == (Point b) {
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b){
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:b.x;
}
/// 点积
double operator * (Point b){
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
/// 叉积
double operator ^ (Point b){
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
/// 两点之间的距离
double distance(Point P){
return hypot(x-P.x,y-P.y); /// 库函数,求根号下,两数平方和
}
}P[N];
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e):s(_s),e(_e){}
/// 直线与线段位置关系 -*this line -v seg
//2 规范相交
//1 非规范相交(顶点处相交)
//0 不相交
int linecrossseg(Line v){
int d1 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.s-s) );
int d2 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-s) );
if( (d1 ^ d2) == -2 ) return 2;
return (d1==0||d2==0);
}
/// 求两直线的交点
Point crosspoint(Line v){
double a1 = (v.e-v.s)^(s-v.s);
double a2 = (v.e-v.s)^(e-v.s);
return Point( (s.x*a2-e.x*a1)/(a2-a1) , (s.y*a2-e.y*a1)/(a2-a1) );
}
};
double t1,t2,t3,t4;
vector<Point> ans[N];
bool cmp(Point a,Point b){
return a.distance(Point{t1,t2}) < b.distance(Point{t1,t2});
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&t1,&t2,&t3,&t4);
Line seg = Line(Point(t1,t2),Point(t3,t4));
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){
scanf("%lf%lf",&P[i].x,&P[i].y);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i ++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n ; j++){
if(i ==j)continue;
Line tel = Line(P[i],P[j]);
if( tel.linecrossseg(seg) ){
Point tep = tel.crosspoint(seg);
ans[i].push_back(tep);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){
sort(ans[i].begin(),ans[i].end(),cmp);
}
while(m--){
int te1,te2;
scanf("%d%d",&te1,&te2);
if( ans[te1].size() < te2 ){
puts("-1");
continue;
}
printf("%.6f %.6f\n",ans[te1][te2-1].x,ans[te1][te2-1].y);
}
return 0;
}
9.3、【POJ - 2007】极角排序
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double inf = 1e14;
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x,y;
double angle;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x; y = _y;
} /// 有参构造
/// 向量加法
Point operator + (Point b) const{
return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );
}
/// 向量乘法
Point operator - (Point b) const{
return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );
}
bool operator == (Point b) const{
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b) const {
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
/// 叉积
double operator ^ (Point b) const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
}P;
/// 用来指定排序的极点
Point cmpPoint = Point(inf,inf);
bool cmpCross(const Point &a,const Point &b)
{
double d = (a-cmpPoint)^(b-cmpPoint) ;
// if( sgn(d) == 0 ) return sgn( a.distance(cmpPoint) - b.distance(cmpPoint) ) < 0;
return d >= 0;
}
Point te[100];
int main()
{
int it = 0;
while(scanf("%lf%lf",&te[it].x,&te[it].y) != EOF) ++it;
cmpPoint = Point(0,0);
sort(te+1,te+it,cmpCross);
for(int i = 0 ; i < it ; i++){
printf("(%.0f,%.0f)\n",te[i].x,te[i].y);
}
return 0;
}
/*
80 20
50 -60
0 0
70 -50
60 30
-30 -50
90 -20
-30 -40
-10 -60
90 10
*/
9.4、【CF 598C】极角排序
9.5、【LightOj 1203】 凸包 + 边夹角
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-18;
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
const int N = 1e5+10;
const int maxp = 1e5+10;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const double inf = 1e14;
//square of a double
inline double sqr(double x){return x*x;}
/*
* Point ()
* distance(Point P) - distance from this to P
* len() - get the length from (0,0) to (x,y)
* trunc(double r) - transform to the vector which length is r
* rad(Point a)
*/
struct Point
{
double x,y;
double angle;
int id;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x; y = _y;
} /// 有参构造
Point operator + (const Point b) const{return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );}
Point operator - (const Point b) const{return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );}
/// 向量数乘
Point operator * (const double k) const{
return Point(k*x,k*y);
}
/// 向量数除
Point operator / (const double k) const{
return Point(x/k , y/k);
}
bool operator == (const Point b) const{
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (const Point b) const {
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
/// 点积
double operator * (const Point b) const{
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
/// 叉积
double operator ^ (const Point b) const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
/// 两点之间的距离
double distance(const Point P) const {
return hypot(x-P.x,y-P.y); /// 库函数,求根号下,两数平方和
}
/// 向量长度
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
/// 以 p 为中心点,pa,pb的夹角大小
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs( atan2( fabs( (a-p)^(b-p) ) , (a-p)*(b-p) ) );
}
};
struct Polygon
{
int n;
Point p[maxp];
};
/// 用来指定排序的极点
Point cmpPoint = Point(inf,inf);
/// 慎用,第一个基本上就够了
bool cmpCross(const Point a,const Point b)
{
double d = sgn((a-cmpPoint)^(b-cmpPoint)) ;
if( d == 0 ) return sgn( a.distance(cmpPoint) - b.distance(cmpPoint) ) < 0;
return d > 0;
}
///--------------------- 凸包 --------------------///
/// 求之前的点集
Point convexP[N];
int Sizep; /// 点集大小
void getconvex(Polygon &convex)
{
/// 按照 x 从小到大排序,如果 x 相同,按 y 排序。
sort(convexP,convexP+Sizep);
convex.n = Sizep;
for(int i = 0 ; i < min(Sizep,2) ; i ++){
convex.p[i] = convexP[i];
}
/// 特判
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
if( Sizep <= 2 ) return ;
int &top = convex.n;
top = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < Sizep ; i++){
while( top && sgn( (convex.p[top] - convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i]) ) <= 0 ) top--;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
int temp = top;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[Sizep-2];
for(int i = Sizep-3 ; i >= 0 ; i--){
while( top != temp && sgn( (convex.p[top] -convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i])) <= 0 ) top --;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
}
Polygon poly;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
Sizep = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
double tex,tey;
scanf("%lf%lf",&tex,&tey);
convexP[i] = Point(tex,tey);
}
if( n <= 2 ) {puts("0.000000");return ;}
getconvex(poly);
double ans_angle = 1e5;
for(int i = 0; i < poly.n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%poly.n;
int k = (j+1)%poly.n;
// printf("%.2f %.2f %.2f\n",poly.p[j].x,poly.p[i].x,poly.p[k].x);
double te_angle = poly.p[j].rad(poly.p[i],poly.p[k]);
ans_angle = min(te_angle,ans_angle);
}
printf("%.6f\n",((ans_angle)*180.0)/pi) ;
return ;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int i = 1; i <= t ; i++){
printf("Case %d: ",i);
solve();
}
}
/*
2
11
6 10
8 2
10 6
10 14
12 4
12 8
16 12
18 10
18 8
18 4
6 8
4
0 0
10 0
10 10
2 1
1
3
0 0
3 0
0 3
*/
10、kuangbin 计算几何板子
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double pi = acos( -1.0);
///Compares a double to zero
int sgn(double x)
{
if( fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
///square of a double
inline double sqr(double x) { return x * x; }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(){} ///no arguments constructor
Point(double _x,double _y) {
x = _x , y = _y; ///arguments constructor
}
/*void input(){
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
}
void output(){
printf("%.2f %.2f\n",x,y);
}*/
bool operator == (Point b) const{
return sgn(x - b.x) == 0 && sgn(y - b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b) const{
return sgn(x - b.x) == 0? sgn(y - b.y) < 0 : x < b.x;
}
///数量积
Point operator - (const Point &b) const{
return Point(x - b.x , y - b.y);
}
Point operator + (const Point &b) const{
return Point(x + b.x , y + b.y);
}
Point operator * (const double &k) const{
return Point(x * k , y * k );
}
Point operator / (const double &k) const{
return Point(x / k , y / k);
}
///叉积
double operator ^ (const Point &b) const{
return x * b.y - y * b.x;
}
///点积
double operator * (const Point &b) const{
return x * b.x + y * b.y;
}
///线段的长度
double len(){
return hypot(x,y); ///<cmath>
}
///长度的平方
double len2(){
return x * x + y * y;
}
///返回两点的距离
double distance(Point p){
return hypot( x - p.x , y - p.y );
}
///计算 pa 和 pb 的夹角
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs( atan2( fabs( (a-p)^(b-p) ) , (a-p)*(b-p) ) );
}
///化为长度为r的向量
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
if( !sgn(l) ) return *this;
r /= l;
return Point(-y,x);
}
///逆时针旋转90度
Point rotleft(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
///顺时针旋转90度
Point rotright(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
///绕着p点逆时针
Point rotata(Point p,double angle){
Point v = (*this) - p;
double c = cos(angle) , s = sin(angle);
return Point(p.x + v.x * c - v.y * s , p.y + v.x *s + v.y * c);
}
};
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line( Point _s, Point _e ){ s =_s ; e=_e; }
///由斜倾角angle与任意直线一点确定直线 y = kx + b;
void input( Point _s, Point _e ){ s =_s ; e=_e; }
Line(Point p,double angle){
s = p;
if( sgn(angle - pi/2) == 0 ) e = (s + Point(0,1));
else e = (s + Point(1,tan(angle)));
}
///ax + by + c = 0;
Line(double a,double b,double c){
if( sgn(a) == 0 )
{
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,-c/b);
}
else if(sgn(b) == 0)
{
s = Point(-c/a,0);
e = Point(-c/a,1);
}
else
{
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,(-c-a)/b);
}
}
double length(){ return s.distance(e);}
///直线与线段相交判断
///-*this line -v seg
///2规范相交,1非规范相交,0不相交
bool linecrossseg(Line v){
return sgn( (v.s - e) ^ (s - e) ) * sgn(( v.e-e ) ^ (s -e) ) <= 0;
}
///点与直线关系
///1在左侧
///2在右侧
///3在直线
int relation(Point p){
int c = sgn( (p-s) ^ (e -s) );
if(c < 0) return 1;
else if(c > 0) return 2;
else return 3;
}
///点在线段上的判断
bool point_on_seg(Point p){
return sgn((p-s)^(e-s) ) == 0 && sgn( (p-s)*(p-e) ) <= 0 ;
}
///两向量平行(对应直线平行或重合)
bool parallel(Line v){
return sgn( (e-s)^( v.e - v.s ) ) == 0;
}
///两直线关系 0-平行,1-重合,2-相交
int linecrossline(Line v){
if( (*this).parallel(v) )
return v.relation(s) == 3;
return 2;
}
///得到交点,需先判断直线是否相交
Point crosspoint(Line v){
double a1 = ( v.e - v.s ) ^ ( s - v.s );
double a2 = ( v.e - v.s ) ^ ( e - v.s );
return Point( (s.x * a2 - e.x * a1)/(a2 - a1) , (s.y *a2 - e.y *a1)/(a2 - a1));
}
///点到线段的距离
double dispointtoseg(Point p){
if( sgn( (p - s)*(e - s) < 0 ) || sgn( (p-e)*(s-e) ) < 0 )
return min( p.distance(s),p.distance(e) );
return dispointtoline(p);
}
/// 点到直线的距离
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs( (p-s)^(e-s) ) / length();
}
/// 返回点p在直线上的投影
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ( (e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)) ) / ( (e-s).len2() ) );
}
///两线段相交判断
///2 规范相交
///1 非规范相交
///0 不想交
int segcrossseg(Line v) {
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e - s));
int d3 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (s - v.s));
int d4 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (e - v.s));
if ((d1 ^ d2) == -2 && (d3 ^ d4) == -2)return 2;
return (d1 == 0 && sgn((v.s - s) * (v.s - e)) <= 0) ||
(d2 == 0 && sgn((v.e - s) * (v.e - e)) <= 0) ||
(d3 == 0 && sgn((s - v.s) * (s - v.e)) <= 0) ||
(d4 == 0 && sgn((e - v.s) * (e - v.e)) <= 0);
}
};
struct triangle
{
Point A,B,C;
Line a,b,c;
triangle(){}
triangle(Point _A,Point _B,Point _C){ A = _A ; B = _B ; C = _C;}
///求重心
Point incenter(){
return Point( ( A.x + B.x + C.x ) / 3, ( A.y + B.y + C.y ) / 3);
}
};
///已知三点求圆心与半径模板
void cal(int a,int b,int c)//求外心 ,外心为三角形三边的垂直平分线交点,
{
double a1 = p[b].x - p[a].x, b1 = p[b].y - p[a].y, c1 = (a1*a1 + b1*b1)/2;
double a2 = p[c].x - p[a].x, b2 = p[c].y - p[a].y, c2 = (a2*a2 + b2*b2)/2;
double d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1;
x = p[a].x + (c1*b2 - c2*b1)/d,y = p[a].y + (a1*c2 - a2*c1)/d;
r = dis2(a);
}
struct circle{
Point p; ///圆心
double r; ///半径
circle(){}
circle( Point _p,double _r ) { p = _p ; r = _r; }
bool operator == (circle v){
return (p == v.p) && sgn(r - v.r) == 0;
}
bool operator < (circle v) const{
return ( (p<v.p) || (p == v.p) && sgn( r - v.r ) < 0 );
}
double area(){
return pi*r*r;
}
double circumference(){
return 2*pi*r;
}
/// 点与圆的关系
///0 在圆外
///1 在圆上
///2 在圆内
int relation(Point b)
{
double dst = b.distance(p);
if( sgn(dst - r) < 0 ) return 2;
else if( sgn(dst-r) == 0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
///线段与园的关系
///比较的是圆心到线段的距离和半径的的关系
int relationseg(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoseg(p);
if( sgn(dst - r) < 0 ) return 2;
else if( sgn(dst - r) == 0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
/// 直线和圆的关系
/// 比较的是圆心到直线的距离和半径的关系
int relationline(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoline(p);
if( sgn(dst - r) == 0 ) return 2;
else if( sgn( dst - r) == 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
/// 求直线和圆的交点个数
int pointcrossline(Line v,Point &p1,Point &p2){
if( !(*this).relationline(v) ) return 0;
Point a = v.lineprog(p);
double d = v.dispointtoline(p);
d = sqrt(r*r - d*d);
if( sgn(d) == 0 ){
p1 = a,p2 = a;
return 1;
}
p1 = a + (v.e - v.s).trunc(d);
p2 = a - (v.e - v.s).trunc(d);
return 2;
}
/// 求圆和三角形 pab 的相交面积
double areatriangle( Point a,Point b ){
if( sgn((p-a)^(p-b)) == 0 ) return 0.0;
Point q[5];
int len =0;
q[len++] = a;
Line l(a,b);
Point p1,p2;
if( pointcrossline( l,q[1],q[2] ) == 2 ){
if( sgn( ( a - q[1] )*( b - q[1] ) ) < 0 ) q[len ++] = q[1];
if( sgn( ( a - q[2] )*( b - q[2] ) ) < 0 ) q[len ++] = q[2];
}
q[len ++] = b;
if( len == 4 && sgn( (q[0]-q[1])*(q[2]-q[1]) ) > 0 ) swap( q[1],q[2] );
double res = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len - 1; i++){
if( relation(q[i]) == 0 || relation( q[i + 1] ) == 0 ){
double arg = p.rad( q[i],q[i + 1] );
res += r*r*arg/2.0;
}
else{
res += fabs( (q[i] - p) ^ ( q[i+ 1] - p ) ) / 2.0;
}
}
return res;
}
};
const int maxp = 1100;
const int maxl = 2200;
struct polygon
{
int n; ///点的数量
Point p[maxp];
Line l[maxl];
struct cmp{
Point p;
cmp(const Point &p0){ p = p0;}
bool operator()( const Point &aa ,const Point &bb){
Point a = aa,b = bb;
int d = sgn( (a-p)^(b-p) );
if(d == 0) return sgn( a.distance(p) - b.distance(p)) < 0;
return d > 0;
}
};
///极角排序
///mi为最左下角的点
void norm(){
Point mi = p[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++) mi = min(mi,p[i]);
sort(p, p + n, cmp(mi) );
}
/// 判断任意点与多边形的关系
/// 3在顶点上
/// 2在边上
/// 1在内部
/// 0在外面
int relationpoint(Point tep)
{
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if( p[i] == tep ) return 3;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){
if( l[i].point_on_seg(tep) ) return 2;
}
int tecnt = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
int j = (i + 1) % n;
int c = sgn( (tep - p[j]) ^ (p[i] - p[j]) );
int u = sgn( p[i].y - tep.y );
int v = sgn( p[j].y - tep.y );
if( c > 0 && u < 0 && v >=0 ) tecnt ++;
if( c < 0 && u >= 0 && v < 0 ) tecnt --;
}
return tecnt != 0;
}
/// 得到凸包
/// 得到的凸包里的点编号是 0 ~ n-1 的
void getconvex(polygon &convex)
{
sort(p , p + n);
convex.n = n;
for(int i = 0 ; i < min(n,2) ; i++){
convex.p[i] = p[i];
}
///特判
if( convex.n == 2 && (convex.p[0] == convex.p[1]) ) convex.n--;
if( n <= 2) return;
int &top = convex.n;
top = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < n ; i++){
while(top && sgn( (convex.p[top] - p[i]) ^ (convex.p[top-1] - p[i])) <= 0 ) top --;
convex.p[++top] = p[i];
}
int temp = top;
convex.p[++top] = p[n-2];
for(int i = n - 3; i >=0 ; i--)
{
while( top!=temp && sgn( (convex.p[top] - p[i]) ^ (convex.p[top-1] - p[i]) ) <=0 ) top--;
convex.p[++top] = p[i];
}
if( convex.n == 2&& ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1]) ) convex.n --; ///特判
convex.norm();///得到的是顺时针的点,排序后逆时针
}
///判断是不是凸多边形,用点集,不是得到凸包之后的多边形
bool isconvex(){
bool s[2];
memset(s,false,sizeof(s));
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i + 1) % n;
int k = (j + 1) % n;
s[ sgn((p[j] - p[i]) ^ (p[k]-p[i]) ) + 1] =true;
if( s[0] && s[2]) return false;
}
return true;
}
///得到周长
double getcircumference(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
sum += p[i].distance( p[(i + 1)%n] );
}
return sum;
}
///得到面积
double getarea()
{
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
sum += ( p[i]^p[ (i+1)%n ] );
}
return fabs(sum)/2;
}
///得到重心
Point getbarycentre(){
Point ret(0,0);
double area = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; i ++){
double tmp = ( p[i] - p[0] ) ^ (p[i + 1] - p[0]);
if( sgn(tmp) == 0 ) continue;
area += tmp;
ret.x += ( p[0].x + p[i].x + p[i + 1].x ) / 3 * tmp;
ret.y += ( p[0].y + p[i].y + p[i + 1].y ) / 3 * tmp;
}
if( sgn(area) ) ret = ret / area;
return ret;
}
///多边形和园交的面积
double areacircle(circle c){
double ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
{
int j = (i + 1) %n;
if( sgn( (p[j] - c.p) ^ ( p[i] - c.p )) >= 0 )
ans += c.areatriangle( p[i],p[j] );
else ans -= c.areatriangle( p[i],p[j] );
}
return fabs(ans);
}
///多边形和圆的关系
/// 2圆完全在多边形内
/// 1圆在多边形里面,碰到了多边形边界
/// 0其他
int relationcircle(circle c){
int x = 2;
if( relationpoint(c.p) != 1 ) return 0; ///圆心不在内部
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if( c.relationseg(l[i] ) == 2 ) return 0;
if( c.relationseg(l[i] ) == 1 ) x = 1;
}
return x;
}
};
11、Hoppz 板子
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-18;
int sgn(double x)
{
if(fabs(x) < eps ) return 0;
if( x < 0 ) return -1;
else return 1;
}
const int N = 1e5+10;
const int maxp = 10;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const double inf = 1e14;
//square of a double
inline double sqr(double x){return x*x;}
/*
* Point ()
* distance(Point P) - distance from this to P
* len() - get the length from (0,0) to (x,y)
* trunc(double r) - transform to the vector which length is r
* rad(Point a)
*/
struct Point
{
double x,y;
double angle;
int id;
Point(){} /// 无参构造
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x; y = _y;
} /// 有参构造
/// 向量加法
Point operator + (const Point b) const{
return Point( x+b.x,y+b.y );
}
/// 向量乘法
Point operator - (const Point b) const{
return Point( x-b.x,y-b.y );
}
/// 向量数乘
Point operator * (const double k) const{
return Point(k*x,k*y);
}
/// 向量数除
Point operator / (const double k) const{
return Point(x/k , y/k);
}
bool operator == (const Point b) const{
return sgn(x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (const Point b) const {
return sgn(x-b.x)==0?sgn(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
/// 点积
double operator * (const Point b) const{
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
/// 叉积
double operator ^ (const Point b) const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
/// 两点之间的距离
double distance(const Point P) const {
return hypot(x-P.x,y-P.y); /// 库函数,求根号下,两数平方和
}
/// 向量长度
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
/// 长度的平方,便于之后的计算
double len2(){
return x*x + y*y;
}
/// 化为长度为 r 的向量
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
r /= l;
return Point(x*r,y*r);
}
/// 以 p 为中心点,pa,pb的夹角大小
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs( atan2( fabs( (a-p)^(b-p) ) , (a-p)*(b-p) ) );
}
/// 绕 p点 逆时针选择 angle 度
Point rotate(Point p,double angle){
Point v = (*this) - p;
double c = cos(angle) , s = sin(angle);
return Point(p.x + v.x * c - v.y * s , p.y + v.x *s + v.y * c);
/// 绕原点旋转后,加上原来P点的偏移量
}
///逆时针旋转90度
Point rotleft(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
///顺时针旋转90度
Point rotright(){
return Point(y,-x);
}
};
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e){
s =_s; e= _e;
}
/// 点斜
Line(Point p,double angle){
s = p;
if( sgn(angle - pi/2) == 0 ) e = (s + Point(0,1));
else e = (s + Point(1,tan(angle)));
}
///ax + by + c = 0;
Line(double a,double b,double c){
if( sgn(a) == 0 ) {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,-c/b);
}
else if(sgn(b) == 0) {
s = Point(-c/a,0);
e = Point(-c/a,1);
}
else {
s = Point(0,-c/b);
e = Point(1,(-c-a)/b);
}
}
/// 线段长度
double length(){
return s.distance(e);
}
/// 返回 0 <= angle <= pi 的基于 x轴 的斜倾角
double angle(){
double k = atan2(e.y-s.y , e.x-s.x);
if( sgn(k) < 0 ) k += pi;
if( sgn(k-pi) == 0 ) k -=pi;
return k;
}
///点与直线关系
//1 在左侧
//2 在右侧
//3 在直线
int relation(Point p){
int c = sgn( (p-s) ^ (e -s) );
if(c < 0) return 1;
else if(c > 0) return 2;
else return 3;
}
/// 点到直线的距离
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs( (p-s)^(e-s) ) /length();
}
/// 返回点p在直线上的投影点(垂足)
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ( (e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)) ) / ( (e-s).len2() ) );
}
/// 返回点p在直线上的对称点
Point symmetrypoint(Point p){
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2*q.x-p.x,2*q.y-p.y);
}
/// 点与线段的位置关系
bool point_on_seg(Point p){
return sgn((p-s)^(e-s) ) == 0 && sgn( (p-s)*(p-e) ) <= 0 ;
}
/// 点到线段的距离
double dispointtoseg(Point p){
if( sgn((p-s)*(e-s)) < 0 || sgn((p-e)*(s-e))<0 )
return min( p.distance(s),p.distance(e) );
return dispointtoline(p);
}
/// 判断平行
bool parallel(Line v){
return sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-v.s) ) == 0 ;
}
/// 判断两直线的位置关系
//0 平行
//1 共线
//2 相交
int linecrossline(Line v){
if( v.parallel(*this) ) return v.relation(s) == 3;
return 3;
}
/// 直线与线段位置关系 -*this line -v seg
//2 规范相交
//1 非规范相交(顶点处相交)
//0 不相交
int linecrossseg(Line v){
int d1 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.s-s) );
int d2 = sgn( (e-s)^(v.e-s) );
if( (d1 ^ d2) == -2 ) return 2;
return (d1==0||d2==0);
}
///两线段相交判断
///2 规范相交
///1 非规范相交
///0 不想交
int segcrossseg(Line v) {
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e - s));
int d3 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (s - v.s));
int d4 = sgn((v.e - v.s) ^ (e - v.s));
if ((d1 ^ d2) == -2 && (d3 ^ d4) == -2)return 2;
return (d1 == 0 && sgn((v.s - s) * (v.s - e)) <= 0) ||
(d2 == 0 && sgn((v.e - s) * (v.e - e)) <= 0) ||
(d3 == 0 && sgn((s - v.s) * (s - v.e)) <= 0) ||
(d4 == 0 && sgn((e - v.s) * (e - v.e)) <= 0);
}
/// 线段到线段的距离
double disssegtoseg(Line v){
return min( min( dispointtoseg(v.s),dispointtoseg(v.e)) , min(v.dispointtoseg(s), v.dispointtoseg(e) ) );
}
/// 求两直线的交点
Point crosspoint(Line v){
double a1 = (v.e-v.s)^(s-v.s);
double a2 = (v.e-v.s)^(e-v.s);
return Point( (s.x*a2-e.x*a1)/(a2-a1) , (s.y*a2-e.y*a1)/(a2-a1) );
}
};
struct Polygon
{
int n;
Point p[maxp];
Line l[maxp];
/// 在多边形中添加点
void add(Point q){
p[n++] = q;
}
/// 获取所有的线段
void getLine(){
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
l[i] = Line(p[i],p[(i+1)%n]);
}
}
/// 判断多边形是不是凸包
/// 如果是直接对点集效验的话,要先极角排序
bool isconvex(){
bool s[2];
memset(s,0,sizeof s);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = (j+1)%n;
s[ sgn( (p[j]-p[i])^(p[k]-p[i]))+1 ] = true;
if( s[0] && s[2] ) return false;
}
return true;
}
/// 多边形周长
double getcircumference(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
sum += p[i].distance(p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return sum;
}
/// 多边形面积
double getarea(){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
sum += (p[i]^p[(i+1)%n]);
}
return fabs(sum)/2;
}
/// 重心
Point getbarycenter(){
Point ret(0,0);
double area = 0 ;
for(int i = 1; i < n-1 ; i++){
double tmp = (p[i]-p[0])^(p[i+1]-p[0]);
if( sgn(tmp) == 0 ) continue;
area += tmp;
ret.x += (p[0].x + p[i].x + p[i+1].x)/3*tmp;
ret.y += (p[0].y + p[i].y + p[i+1].y)/3*tmp;
}
if( sgn(area)) ret = ret/area;
return ret;
}
/// 判断点与任意多边形的关系
//3 点上
//2 边上
//1 内部
//0 外部
int relationpoint(Point q){
/// 在点上
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if( p[i] == q ) return 3;
}
// getLine(); /// 之前getline了的话,可以注释节约时间
/// 在边上
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
if( l[i].point_on_seg(q) ) return 2;
}
/// 在内部
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
int j = (i+1)%n;
int k = sgn( (q-p[j])^(p[i]-p[j]) );
int u = sgn( p[i].y - q.y );
int v = sgn( p[j].y - q.y );
if( k > 0 && u < 0 && v >= 0 ) cnt ++;
if( k < 0 && v < 0 && u >= 0 ) cnt--;
}
return cnt != 0;
}
/// 判断多边形是否与多边形相离
int relationpolygon(Polygon Poly){
getLine();
Poly.getLine();
for(int i1 = 0 ; i1 < n ; i1++){
int j1 = (i1+1)%n;
for(int i2 = 0 ; i2 <= Poly.n ; i2++){
int j2 = (i2+1)%Poly.n;
Line l1 = Line(p[i1],p[j1]);
Line l2 = Line(Poly.p[i2],Poly.p[j2]);
if( l1.segcrossseg(l2) ) return 0;
if( Poly.relationpoint(p[i1]) || relationpoint(Poly.p[i2]) ) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
};
struct Circle
{
Point p;
double r;
Circle(){}
Circle(Point _p,double _r):p(_p),r(_r){}
Circle(double x,double y,double _r){ /// 点的坐标,圆心
p = Point(x,y); r = _r;
}
bool operator == (Circle v){
return (p == v.p) && sgn(r-v.r) == 0;
} /// 以圆心为主排序,半径为副排序
bool operator < (Circle v) const{
return ( (p<v.p) || (p == v.p) && sgn(r-v.r)<0 );
}
/// 面积
double area(){
return pi*r*r;
}
/// 周长
double circumference(){
return 2*pi*r;
}
/// 点和圆的位置关系
//0 圆外
//1 圆上
//2 圆内
int relationPoint(Point b){
double dst = b.distance(p);
if( sgn(dst-r)<0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r)==0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
/// 直线和圆的关系
//0 相离
//1 相切
//2 相交
int relationLine(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoline(p);
if( sgn(dst-r) < 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r) == 0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
/// 线段和圆的关系
int relationSeg(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoseg(p);
if( sgn(dst-r) < 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn(dst-r) == 0 ) return 1;
return 0;
}
/// 两圆的关系
//5 相离
//4 外切
//3 相交
//2 内切
//1 内含
int relationcircle(Circle v){
double d = p.distance(v.p);
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) > 0 ) return 5;
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) == 0 ) return 4;
double l = fabs(r-v.r);
if( sgn( d-r-v.r ) < 0 && sgn(d-l) > 0 ) return 3;
if( sgn( d-l ) == 0 ) return 2;
if( sgn( d-l ) < 0 ) return 1;
}
};
/// 用来指定排序的极点
Point cmpPoint = Point(inf,inf);
/// 需重载 Point 的小于符号
bool cmpAtan2(Point a,Point b)
{
if( sgn(a.angle - b.angle) == 0 ) return a.distance(cmpPoint) < b.distance(cmpPoint );
return a.angle < b.angle;
}
/// 慎用,第一个基本上就够了
bool cmpCross(const Point a,const Point b)
{
double d = sgn((a-cmpPoint)^(b-cmpPoint)) ;
if( d == 0 ) return sgn( a.distance(cmpPoint) - b.distance(cmpPoint) ) < 0;
return d > 0;
}
///--------------------- 凸包 --------------------///
/// 求之前的点集
Point convexP[N];
int Sizep; /// 点集大小
void getconvex(Polygon &convex)
{
/// 按照 x 从小到大排序,如果 x 相同,按 y 排序。
sort(convexP,convexP+Sizep);
convex.n = Sizep;
for(int i = 0 ; i < min(Sizep,2) ; i ++){
convex.p[i] = convexP[i];
}
/// 特判
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
if( Sizep <= 2 ) return ;
int &top = convex.n;
top = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < Sizep ; i++){
while( top && sgn( (convex.p[top] - convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i]) ) <= 0 ) top--;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
int temp = top;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[Sizep-2];
for(int i = Sizep-3 ; i >= 0 ; i--){
while( top != temp && sgn( (convex.p[top] -convexP[i])^(convex.p[top-1]-convexP[i])) <= 0 ) top --;
convex.p[++top] = convexP[i];
}
if( convex.n == 2 && ( convex.p[0] == convex.p[1] ) ) convex.n--;
/// 这样求出来的顺时针的凸包,如果要逆时针的话,来一次极角排序就好了。
/// 极角排序
// cmpPoint = convex.p[0];
// sort(convex.p,convex.p+convex.n,cmpCross);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号