springboot国际化与@valid国际化支持
springboot国际化
springboot对国际化的支持还是很好的,要实现国际化还简单。主要流程是通过配置springboot的LocaleResolver解析器,当请求打到springboot的时候对请求的所需要的语言进解析,并保存在LocaleContextHolder中。之后就是根据当前的locale获取message。
springboot中关于国际化消息处理的顶层接口是MessageSource,它有两个开箱即可用的实现
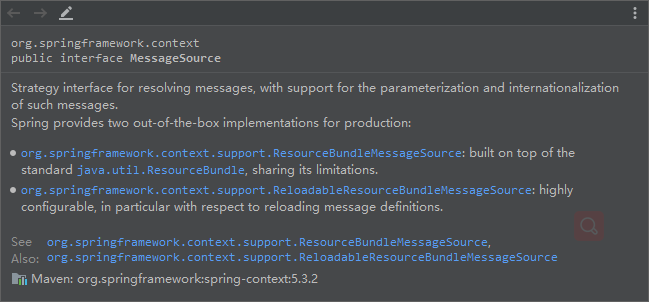
1。新建国际化文件
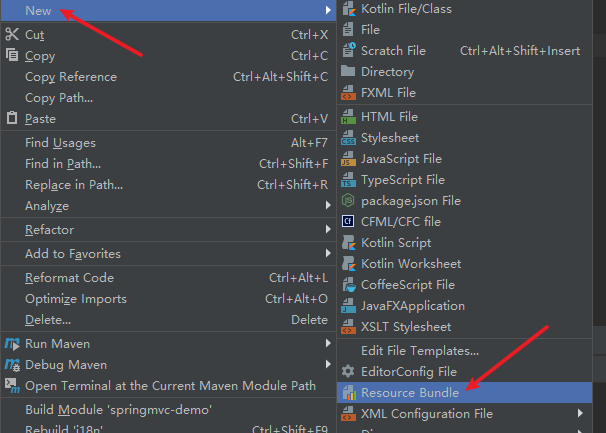
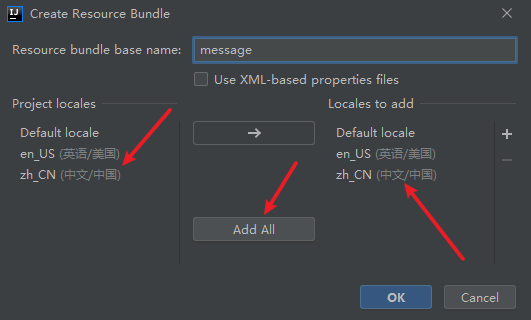
这里只是中英文,右键可加入其它的语种

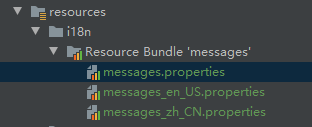
多语种情况下,不用打开每个语种的文件一个一个去修改。直接在message.properties编辑即可
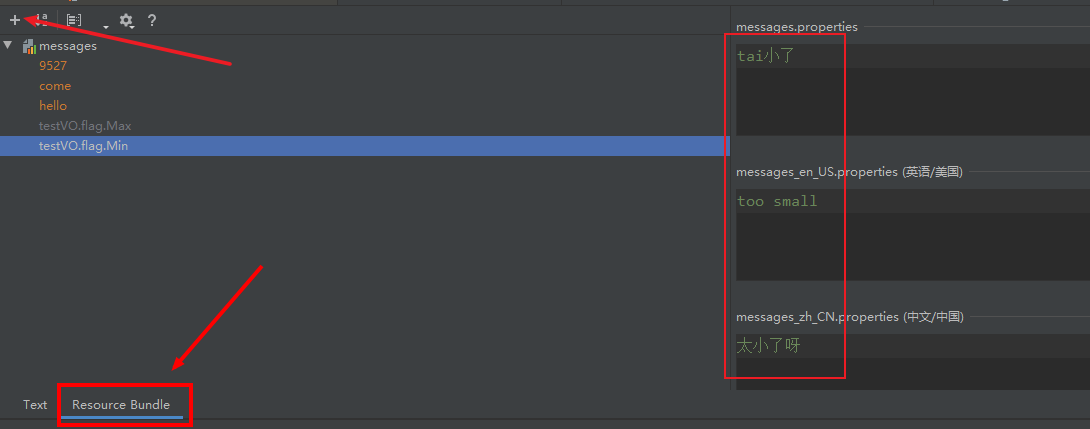
messages.properties
9527=bojack
come=来吧
hello=你好
testVO.flag.Max=tai大了呀
testVO.flag.Min=tai小了messages_en_US.properties
9527=jack
come=come
hello=hello
testVO.flag.Max=too big
testVO.flag.Min=too smallmessages_zh_CN.properties
9527=杰克
come=来吧
hello=你好
testVO.flag.Max=太多了呀
testVO.flag.Min=太小了呀2。配置国际化文件的位置
application.yml
spring:
messages:
basename: i18n/messages # 多个文件用逗号分隔3。配置localeResolver,解析当前请求的locale,LocaleResolver是个接口,它也有多种实现,这个也可以根据自己的实际情况自已去实现,我这里用的是默认的解析器 AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver,他是通过获取请求头accept-language来获取当前的locale。
/**
* 设置默认语言
* @return
*/
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver acceptHeaderLocaleResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
acceptHeaderLocaleResolver.setDefaultLocale(Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE);
return acceptHeaderLocaleResolver;
}注意:这里是zh-CN,如果写成zh_CN是解析不了的。这里还可以配置权重,具体参考https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/section/1189889
test.http
### 简体中文
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: zh-CN
### 美国英语
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: en-US4。如何使用
package com.springmvc.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("i18n")
public class I18nController {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@GetMapping("test")
public Object test() {
Locale locale = LocaleContextHolder.getLocale();
String displayName = locale.getDisplayName();
System.out.println("displayName = " + displayName);
String hello = messageSource.getMessage("hello", null, locale);
System.out.println("hello = " + hello);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("hello", hello);
map.put("displayName", displayName);
map.put("locale", locale);
String come= messageSource.getMessage("come", null, locale);
map.put("come", come);
String c9527= messageSource.getMessage("9527", null, locale);
map.put("9527", c9527);
return map ;
}
}@valid 参数校验与国际化
@valid默认其实是支持国际化的,只是它感觉支持的不是很好,如果在 userId上加个@Notnull注解,当userId为空的时候,只会提示 `不能为空`,如果有多个@notnull注解,不会提示具体是哪个不能为空。这个倒还好,可以解决。但是一般给用户的提示,不可能提示 `userId 不能为空` 而是要提示成 `账号不能为空`。所以默认的validationMessage用起来还有点麻烦,还不如直接用在国际化文件里写好的message
抽象类:org.hibernate.validator.messageinterpolation.AbstractMessageInterpolator
参数校验不通过时抛出 MethodArgumentNotValidException 异常
/**
* The name of the default message bundle.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_VALIDATION_MESSAGES = "org.hibernate.validator.ValidationMessages";国际化文件:
实体类
package com.springmvc.demo.vo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;//MethodArgumentNotValidException
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
@Data
public class TestVO {
@Min(value = 3)//这里不用写messages了,因为要支持国际化
@Max(value = 10)
private Integer flag;
@NotNull
private Integer age;
}国际化文件中写成这样
testVO.flag.Max=too big
testVO.flag.Min=too small注解名可以写在前也可以写在后面,可以在文件中配置,注意默认是写在前面的
spring:
messages:
basename: i18n/messages
mvc:
message-codes-resolver-format: postfix_error_code参数校验不能过时会抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException 异常,因些可以在全局异常处理器中,捕获异常,根据locale获取相应的message
String message = messageSource.getMessage(fieldError, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
package com.springmvc.demo.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.api.R;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class GlobalExceptionHandlerResolver {
@Autowired
MessageSource messageSource;
@ExceptionHandler({MethodArgumentNotValidException.class, BindException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public R handleBodyValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException exception) {
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<String, String>();
//得到所有的属性错误
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = exception.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
//将其组成键值对的形式存入map
for (FieldError fieldError : fieldErrors) {
String[] str= fieldError.getField().split("\\.");
if(str.length>1){
errors.put(str[1], fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}else {
errors.put(fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
String message = messageSource.getMessage(fieldError, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
return R.failed(message);
}
log.error("参数绑定异常,ex = {}", errors);
return R.failed("haha");
}
}测试:test.http
###
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: zh
###
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: en-US
###
POST localhost:8080/test
Content-Type: application/json
{
"flag": 2,
"age": 22
}
###
POST localhost:8080/test
Content-Type: application/json
Accept-Language: en-US
{
"flag": 5
}源码解析
从请求头accept-language中取locale
org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#parseLocales
/**
* Parse request locales.
*/
protected void parseLocales() {
localesParsed = true;
// Store the accumulated languages that have been requested in
// a local collection, sorted by the quality value (so we can
// add Locales in descending order). The values will be ArrayLists
// containing the corresponding Locales to be added
TreeMap<Double, ArrayList<Locale>> locales = new TreeMap<>();
Enumeration<String> values = getHeaders("accept-language");
while (values.hasMoreElements()) {
String value = values.nextElement();
parseLocalesHeader(value, locales);
}
// Process the quality values in highest->lowest order (due to
// negating the Double value when creating the key)
for (ArrayList<Locale> list : locales.values()) {
for (Locale locale : list) {
addLocale(locale);
}
}
}org.springframework.context.support.AbstractMessageSource#getMessage(org.springframework.context.MessageSourceResolvable, java.util.Locale)
@Override
public final String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException {
String[] codes = resolvable.getCodes();
if (codes != null) {
for (String code : codes) {
String message = getMessageInternal(code, resolvable.getArguments(), locale);
if (message != null) {
return message;
}
}
}
String defaultMessage = getDefaultMessage(resolvable, locale);
if (defaultMessage != null) {
return defaultMessage;
}
throw new NoSuchMessageException(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(codes) ? codes[codes.length - 1] : "", locale);
}org.hibernate.validator.messageinterpolation.AbstractMessageInterpolator#resolveMessage
private String resolveMessage(String message, Locale locale) {
String resolvedMessage = message;
ResourceBundle userResourceBundle = userResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
ResourceBundle constraintContributorResourceBundle = contributorResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
ResourceBundle defaultResourceBundle = defaultResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
String userBundleResolvedMessage;
boolean evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce = false;
do {
// search the user bundle recursive (step 1.1)
userBundleResolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
resolvedMessage, userResourceBundle, locale, true
);
// search the constraint contributor bundle recursive (only if the user did not define a message)
if ( !hasReplacementTakenPlace( userBundleResolvedMessage, resolvedMessage ) ) {
userBundleResolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
resolvedMessage, constraintContributorResourceBundle, locale, true
);
}
// exit condition - we have at least tried to validate against the default bundle and there was no
// further replacements
if ( evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce && !hasReplacementTakenPlace( userBundleResolvedMessage, resolvedMessage ) ) {
break;
}
// search the default bundle non recursive (step 1.2)
resolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
userBundleResolvedMessage,
defaultResourceBundle,
locale,
false
);
evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce = true;
} while ( true );
return resolvedMessage;
}

