Book of the Dead 死者之书Demo学习

1.前言
一转眼离Book of the Dead Environment Demo开放下载已过去多年,当时因为技术力有限,以及对HDRP理解尚浅,
所以这篇文章一直搁浅到了现在;如今也对HDRP有了一些理解,因此回顾一下该Demo。
Book of the Dead——死者之书,是Unity2018年展示的Demo作品。
其主要展现HDRP的运用、源码修改展示、音频处理方案等。
该Demo已传百度网盘:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UBY0EcAGLwRJEW1VaDyUgQ
提取码:f47c
打开使用版本:unity2018.2.21f1(新建一个Build-in管线工程,然后导入包)
2.Feature
下面直接对Demo中Feature文件夹中的技术内容进行展开。
2.1 PropertyMaster
该模块链接了Volume数值与具体组件对象,贯穿整个项目,
因此提前讲解。
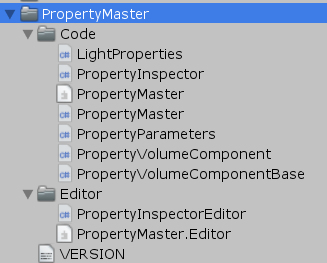
脚本中的PropertyVolumeComponentBase、PropertyVolumeComponent继承自VolumeComponent
继承了VolumeComponent也就是说可以在Volume中被加载,因此项目里继承了PropertyVolumeComponent
的那些组件也就可以挂载于Volume中:
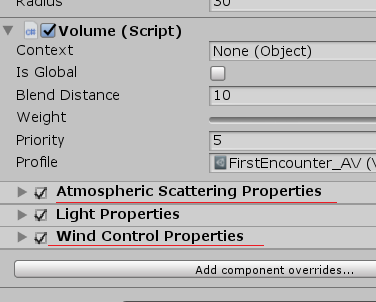
而Volume绑定的是通用组件,无法和场景中的具体对象绑定或是数值同步。这时候
扩展的PropertyVolumeComponent就出现作用了:
public abstract class PropertyVolumeComponent<X> : PropertyVolumeComponentBase where X : PropertyVolumeComponent<X> { static PropertyVolumeComponent() { PropertyMaster.componentTypes.Add(typeof(X)); } }
PropertyMaster.componentTypes会记录需要和场景中具体对象绑定的所有类型,然后做这一步操作:
public void UpdateProperties() {//在PropertyMaster类里 var manager = VolumeManager.instance; var stack = manager.stack;//拿到当前Volume if (updateVolumes && volumeTrigger && volumeLayerMask != 0) manager.Update(volumeTrigger, volumeLayerMask); foreach (var type in componentTypes) {//刚刚缓存的类型 var component = (PropertyVolumeComponentBase) stack.GetComponent(type); if (component.active) component.OverrideProperties(this); } }
PropertyMaster实现了IExposedPropertyTable接口,在上述代码的OverrideProperties处,
将自己传进去,再通过ExposedReference和名称的Guid匹配,拿到对应场景对象。
关于ExposedRenference具体可以看这篇测试:https://www.cnblogs.com/hont/p/15815344.html
PropertyInspector则提供Volume信息的Debug,在编辑器下获取到属于当前Layer的Volume,以方便查看:
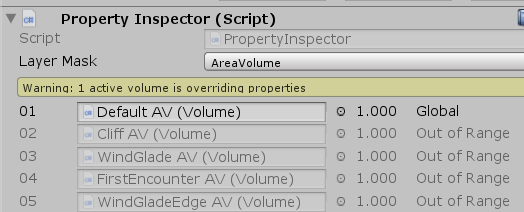
最后会在每次HDRenderPipeline.OnBeforeCameraCull处更新一次绑定信息,保证每帧的数值都是最新的。
总结来说,PropertyMaster的做法适合如URP RenderFeature、HDRP Custom Volume之类组件的场景对象解耦。
2.2 AxelF
AxelF是项目里对声音部分进行处理的一个模块,查看项目中的音频环境配置;需打开场景文件AudioZones:
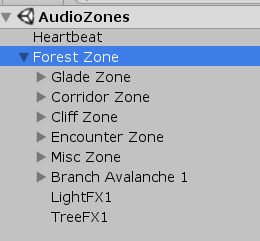
该模块分为如下部分:
-
- Patch 不同音频对象的最小单位,ScriptableObject对象。可内嵌多个音源,设置是否随机播放,序列播放等
- Zone 不同音频区域的空间标记,内部存放所有Zone的静态List,在Heartbeat类的
Update中统一更新。并且存放了AudioEmitter的引用,当角色进入Zone后触发AudioEmitter - AudioEmitter 音频播放组件,
OnEnable时调用Sequencer播放Patch - Heartbeat 音频统一更新组件,负责其他几个部分的
Update统一更新,绑定玩家位置等
通过场景中摆放不同Zone,来控制角色到达不同位置时声音的播放逻辑。
该模块的SceneGUI处理较为有趣:
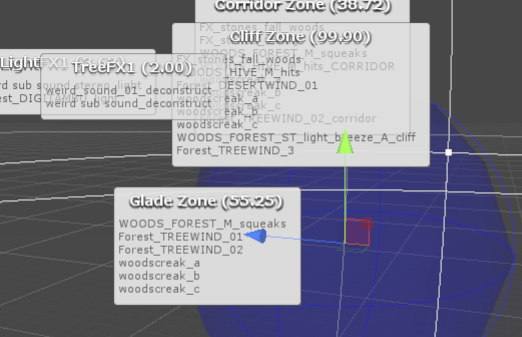
其使用对象位置信息在SceneGUI部分绘制HelpBox风格GUI,具体可查看DrawZoneLabelStatic方法。
部分逻辑:
m.y = l.y + 1f; EditorGUI.HelpBox(m, y.text, MessageType.None); EditorGUI.DropShadowLabel(l, x); GUI.color = c; Handles.EndGUI();
2.3 DepthOfFieldAutoFocus自动对焦

(自动对焦——镜头转向树后,焦距切换,背景被自动虚化)
该模块有如下特点:
-
- Compute Shader写入RWStructuredBuffer,再传入屏幕Shader的无缝链接
- Compute Shader传入RWStructuredBuffer后,数据不取回放在GPU端自动更新
- 增加
IDepthOfFieldAutoFocus接口,对原先景深功能的修改
2.3.1 Compute Shader部分
在C#端对自动对焦需要的参数做ComputeShader部分传入(ComputeShader的线程数是1,一会会讲):
void Init(float initialFocusDistance) { if (m_AutoFocusParamsCB == null) { m_AutoFocusParamsCB = new ComputeBuffer(1, 12); m_ResetHistory = true; } if (m_AutoFocusOutputCB == null) m_AutoFocusOutputCB = new ComputeBuffer(1, 8); ...
CS端通过比对对角线四个点深度,得到最新焦距并插值更新(Depth方法也在这个CS里):
float3 duv = float3(1.0, 1.0, -1.0) * 0.01; float focusDistance = Depth(0); focusDistance = min(focusDistance, Depth( duv.xy));//1,1 focusDistance = min(focusDistance, Depth( duv.zy));//-1,1 focusDistance = min(focusDistance, Depth(-duv.zy));//1,-1 focusDistance = min(focusDistance, Depth(-duv.xy));//-1,-1 focusDistance = max(focusDistance, _FocalLength);
然后更新params的RWStructuredBuffer,该结构是放在GPU端一直更新的:
AutoFocusParams params = _AutoFocusParams[0]; params.currentFocusDistance = SmoothDamp(params.currentFocusDistance, focusDistance, params.currentVelocity); _AutoFocusParams[0] = params;
最后输出:
Output(params.currentFocusDistance);
接着,到了后处理阶段,shader DepthOfField.hlsl,直接拿到刚刚处理过的_AutoFocusOutput获取数据:
//custom-begin: autofocus #if AUTO_FOCUS struct AutoFocusOutput { float focusDistance; float lensCoeff; }; StructuredBuffer<AutoFocusOutput> _AutoFocusOutput : register(t3); float2 GetFocusDistanceAndLensCoeff() { return float2(_AutoFocusOutput[0].focusDistance, _AutoFocusOutput[0].lensCoeff); } #else
到这里,完成了焦距信息的传入。
之前第一次打开Book of the Dead,看见这种做法不理解,为什么一个线程的信息也要用Compute Shader去做,后来
接触到Compute Shader处理完StructuredBuffer直接丢VF Shader这种做法,发现还可以这么用,
另外由于自动对焦涉及到屏幕信息读取,还是属于GPU部分擅长的操作,因此Demo中才用Compute Shader来做这个。
2.3.2 对后处理景深组件的修改
虽然自己扩展也可以,但不如直接改后处理中的Depth of View,与渲染管线的修改关键字不同,
查看修改处,需要搜索该关键字:
//custom-begin: autofocus
其修改部分位于_LocalPackages中:

首先,在PostProcessLayer.cs中定义了字段:
//custom-begin: autofocus public Object depthOfFieldAutoFocus; //custom-end
方便直接把自动对焦组件链接到PostProcessLayer中:
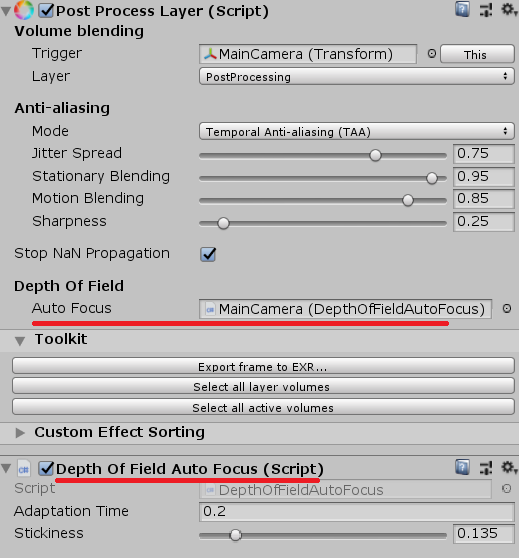
然后定义了一个接口:
//custom-begin: autofocus public interface IDepthOfFieldAutoFocus { void SetUpAutoFocusParams(CommandBuffer cmd, float focalLength /*in meters*/, float filmHeight, Camera cam, bool resetHistory); } //custom-end
在上下文中也存放了自动对焦组件的引用,在每帧后处理渲染时,调用接口方法,更新自动对焦逻辑:
public override void Render(PostProcessRenderContext context) { ... //custom-begin: autofocus if (context.depthOfFieldAutoFocus != null) context.depthOfFieldAutoFocus.SetUpAutoFocusParams(cmd, f, k_FilmHeight, context.camera, m_ResetHistory); //custom-end ...
在自动对焦逻辑中,每帧会调用Dispatch更新ComputeShader:
cmd.DispatchCompute(m_Compute, 0, 1, 1, 1);
2.4 GrassOcclusion植被AO遮蔽
GrassOcclusion通过烘焙植被AO,增强植被部分在画面中的表现。
文件目录结构如下:
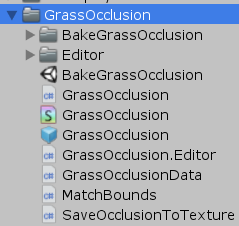
该模块分为如下部分:
-
- 单个植被通过OcclusionProbes烘焙出单个植被顶视图AO Texture,一般64x64
- 整个场景植被通过地形拿到数据,拼接这些单个植被AO图,生成一张2048x2048的大AO图,然后再在shader里整合
关于单个植被的AO烘焙,可以打开BakeGrassOcclusion场景查看,它通过OcclusionProbes烘焙,通过脚本SaveOcclusionToTexture储存。
接下来讲解整个场景的大AO图烘焙。
2.4.1 整个场景的大AO图烘焙
参数配置可以看prefab GrassOcclusion:
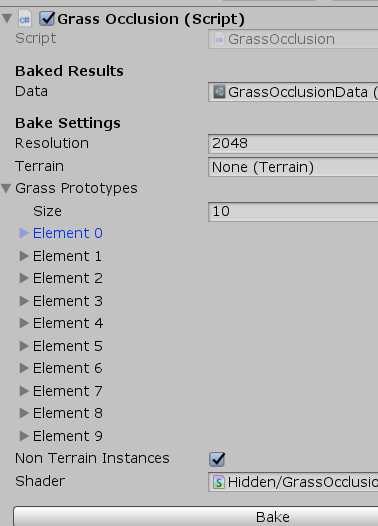
Grass Prototypes 存放所有烘焙好的单个植被引用。Terrain链接的是场景地形文件。
当点击Bake烘焙时,会进入GrassOcclusion.Editor.cs的Bake函数。
先进行一些变量准备工作,通过地形拿到所有植被:
TreeInstance[] instances = m_Terrain.terrainData.treeInstances;
TreePrototype[] prototypes = m_Terrain.terrainData.treePrototypes;
此处有一个地形缩放的魔数:
float magicalScaleConstant = 41.5f; //yea, I know float terrainScale = magicalScaleConstant / m_Terrain.terrainData.size.x;
然后创建一张RT:
RenderTexture rt = RenderTexture.GetTemporary(m_Resolution, m_Resolution, 0, RenderTextureFormat.ARGB32, RenderTextureReadWrite.Linear); Graphics.SetRenderTarget(rt);
遍历所有单个植被,具体会根据植被的旋转等信息进行匹配操作,这里不深入:
foreach(GrassPrototype p in m_GrassPrototypes) SplatOcclusion(p, instances, prototypes, m_Material, terrainScale, m_NonTerrainInstances, worldToLocal);
不过SplatOcclusion函数中DrawProcedural稍微说下:
Graphics.DrawProcedural(MeshTopology.Triangles, vertCount, instanceCount);
这里就是有多少个实例就是多少个绘制pass(烘焙阶段的),以每次画一个四边面进行绘制。
最后会顺便存下高度图,然后统一存入GrassOcclusionData(ScriptableObject)中。
具体应用到场景中的数据可以在Scenes/Forest_EnvironmentSample下查看。
2.4.2 渲染管线中的运用
GrassOcclusion这一步的操作是通过改渲染管线实现的,可在修改后的HDRP中查找关键字:
//forest-begin
当获取Grass部分AO时,借助GrassOcclusion传入的全局信息会进行计算,在HDRP Shader中逻辑代码如下:
float SampleGrassOcclusion(float3 positionWS) { float3 pos = mul(_GrassOcclusionWorldToLocal, float4(positionWS, 1)).xyz; float terrainHeight = tex2D(_GrassOcclusionHeightmap, pos.xz).a; float height = pos.y - terrainHeight * _GrassOcclusionHeightRange; UNITY_BRANCH if(height < _GrassOcclusionCullHeight) { float xz = lerp(1.0, tex2D(_GrassOcclusion, pos.xz).a, _GrassOcclusionAmountGrass); return saturate(xz + smoothstep(_GrassOcclusionHeightFadeBottom, _GrassOcclusionHeightFadeTop, height)); // alternatively: // float amount = saturate(smoothstep(_GrassOcclusionHeightFade, 0, pos.y) * _GrassOcclusionAmount); // return lerp(1.0, tex2D(_GrassOcclusion, pos.xz).a, amount); } else return 1; }
最后会根据相对高度进行一次渐变混合,部分OcclusionProbes的逻辑将在下面讲解。
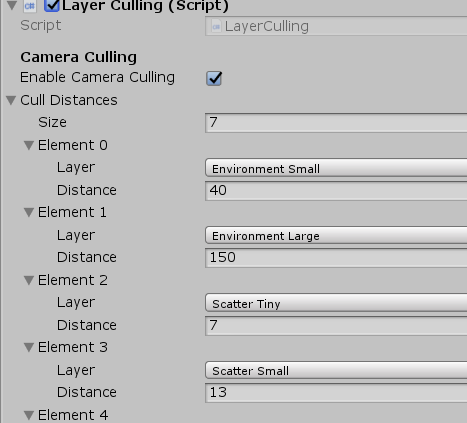
2.5 LayerCulling
LayerCulling主要是对Unity不同层显示距离控制接口的封装。
Unity在很早的版本就有提供针对不同Layer的剔除接口:
Layer视距剔除:
var distances = Enumerable .Repeat(Camera.main.farClipPlane, 32) .ToArray(); distances[12] = 3f;//Layer12的剔除距离为3 testCamera.layerCullDistances = distances;//!一定要以数组赋值,否则无效 testCamera.layerCullSpherical = true;//是否以球形为基准剔除
Layer平行光阴影剔除:
testLight.layerShadowCullDistances = distances;
在项目场景Forest_EnvironmentSample中,搜索LayerCulling,即可找到对应的剔除配置:
2.6 OcclusionProbes环境AO遮蔽探针
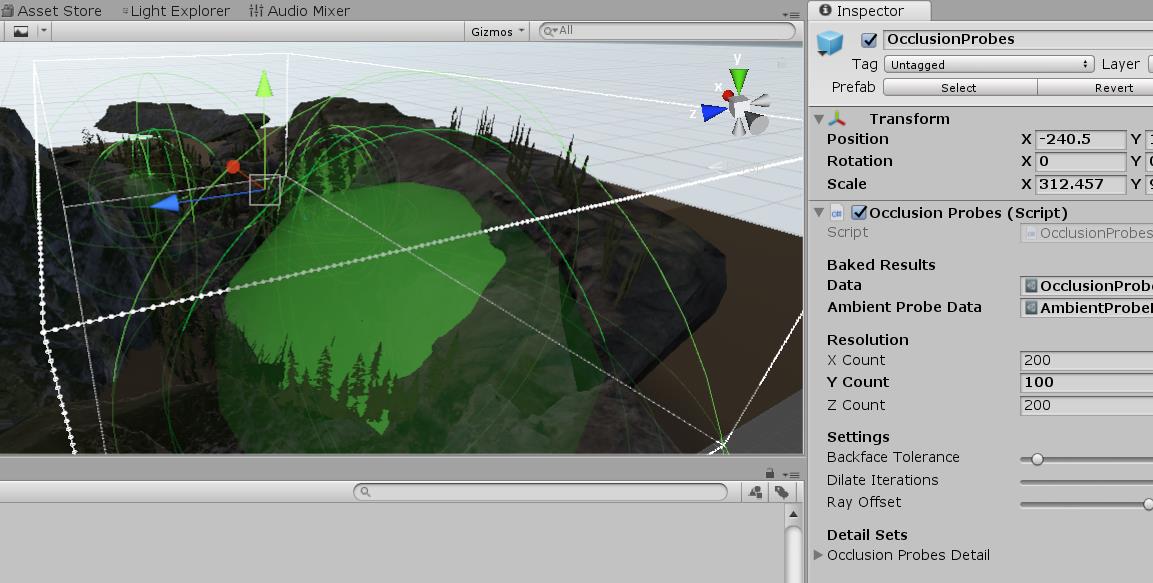
之前的GrassOcclusion用了OcclusionProbes烘焙单个植被的AO,这里OcclusionProbes覆盖整个场景,
将较低频的场景体积AO信息储存进ScriptableObject。
这部分主要讲述
-
- 调用内部接口烘焙遮蔽探针,存入Texture3D
- 解包Unity环境SH(球谐探针),一起丢入Shader
- Shader部分整合计算得到AO值
首先,我们可以从场景中挂载的OcclusionProbes处开始,它会绑定Lightmapping烘焙接口:
void AddLightmapperCallbacks() { Lightmapping.started += Started; Lightmapping.completed += Completed; }
当烘焙开始时将调用到Started函数,函数中会去设置探针位置等初始化操作。
烘焙结束后,调用Completed函数。
在函数里可以直接拿到烘焙好的遮蔽信息:
Vector4[] results = new Vector4[count]; if (!UnityEditor.Experimental.Lightmapping.GetCustomBakeResults(results))
然后Data和DataDetail会分别转换成3DTexture进行储存(项目里没有用Detail数据):
Color32[] colorData = new Color32[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { byte occ = (byte)Mathf.Clamp((int)(data[i].x * 255), 0, 255); colorData[i] = new Color32(occ, occ, occ, occ); } tex.SetPixels32(colorData);
除了遮蔽的3DTexture信息,OcclusionProbes还会存一份环境SH(球谐探针),用于后期参与计算:
public AmbientProbeData m_AmbientProbeData;
这个SH是从RenderSettings.ambientProbe获取的,并且做了修正操作,
修正操作指:
Unity存的SH(指SphericalHarmonicsL2部分)有一部分计算放在了CPU端进行了化简,
可能是把sh[6](l2,r0)的部分项合并到了sh[0](l0,r0)上,通过SphericalHarmonicsL2走Unity内部传入shader的球谐,
走的都是压缩的球谐系数(这部分资料比较少,不保证正确,欢迎斧正)。
OcclusionProbes.cs中恢复常规球谐的代码:

private static void GetShaderConstantsFromNormalizedSH(ref SphericalHarmonicsL2 ambientProbe, Vector4[] outCoefficients) { for (int channelIdx = 0; channelIdx < 3; ++channelIdx) { // Constant + Linear // In the shader we multiply the normal is not swizzled, so it's normal.xyz. // Swizzle the coefficients to be in { x, y, z, DC } order. outCoefficients[channelIdx].x = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 3]; outCoefficients[channelIdx].y = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 1]; outCoefficients[channelIdx].z = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 2]; outCoefficients[channelIdx].w = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 0] - ambientProbe[channelIdx, 6]; // Quadratic polynomials outCoefficients[channelIdx + 3].x = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 4]; outCoefficients[channelIdx + 3].y = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 5]; outCoefficients[channelIdx + 3].z = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 6] * 3.0f; outCoefficients[channelIdx + 3].w = ambientProbe[channelIdx, 7]; } // Final quadratic polynomial outCoefficients[6].x = ambientProbe[0, 8]; outCoefficients[6].y = ambientProbe[1, 8]; outCoefficients[6].z = ambientProbe[2, 8]; outCoefficients[6].w = 1.0f; }
不过理论上不恢复也不影响计算。
然后回到调用处:
var ambientProbe = RenderSettings.ambientProbe; m_AmbientProbeData.sh = new Vector4[7]; // LightProbes.GetShaderConstantsFromNormalizedSH(ref ambientProbe, m_AmbientProbeData.sh); GetShaderConstantsFromNormalizedSH(ref ambientProbe, m_AmbientProbeData.sh); EditorUtility.SetDirty(m_AmbientProbeData);
这样,有了SH(_AmbientProbeSH)和3DTexture遮蔽信息(_OcclusionProbes),下一步可以看下Shader里如何进行整合的。
准备和数据传入就到这里,下面是HDRP shader整合部分。
在MaterialUtilities.hlsl,SampleOcclusionProbes中,有获取环境3DTexture AO值的操作:
float SampleOcclusionProbes(float3 positionWS) { // TODO: no full matrix mul needed, just scale and offset the pos (don't really need to support rotation) float occlusionProbes = 1; float3 pos = mul(_OcclusionProbesWorldToLocalDetail, float4(positionWS, 1)).xyz; UNITY_BRANCH if(all(pos > 0) && all(pos < 1)) { occlusionProbes = tex3D(_OcclusionProbesDetail, pos).a; } else { pos = mul(_OcclusionProbesWorldToLocal, float4(positionWS, 1)).xyz; occlusionProbes = tex3D(_OcclusionProbes, pos).a; } return occlusionProbes; }
这里用_OcclusionProbesWorldToLocalDetail,将位置转换为本地位置,因为外面场景OcclusionProbes对象设置了Transform缩放
通过这个缩放转回本地坐标之后,就是0-1范围内的值了。算是一个技巧。
拿到存在3DTexture中的环境AO后,再乘上之前计算的GrassOcclusion,得到skyOcclusion:
float SampleSkyOcclusion(float3 positionRWS, float2 terrainUV, out float grassOcclusion) { float3 positionWS = GetAbsolutePositionWS(positionRWS); grassOcclusion = SampleGrassOcclusion(terrainUV); return grassOcclusion * SampleOcclusionProbes(positionWS); }
并且skyOcclusion存放在surfaceData里:
surfaceData.skyOcclusion = SampleSkyOcclusion(input.positionRWS, grassOcclusion);
刚刚说还存了环境SH(_AmbientProbeSH),在SampleBakedGI里,刚好拿计算好的skyOcclusion乘上_AmbientProbeSH,
再加在环境GI的SH上,也就是将天光信息加在当前场景位置采样到的光照探针上:
//forest-begin: sky occlusion #if SKY_OCCLUSION SHCoefficients[0] += _AmbientProbeSH[0] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[1] += _AmbientProbeSH[1] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[2] += _AmbientProbeSH[2] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[3] += _AmbientProbeSH[3] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[4] += _AmbientProbeSH[4] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[5] += _AmbientProbeSH[5] * skyOcclusion; SHCoefficients[6] += _AmbientProbeSH[6] * skyOcclusion; #endif //forest-end
对于OcclusionProbes的做法,可以看下育碧在GDC16上发表的《Global Illumination in Tom Clancy's The Division》,
包括天光的处理,有一定共通之处。
2.7 StaggeredCascade
交错阴影主要指CSM(级联阴影)的后面几级级联拆分到不同帧,分开更新。
这部分不做展开,感兴趣可以搜索一些资料,也是比较多的。
2.8 TerrainFoley
Foley是术语'拟音'的意思,指通过传统方法手工制作的音效(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42927286),这里的Foley主要指角色经过草丛,
或角色周围所听到的音效,和控制这些音效的逻辑。
TerrainFoley部分主要通过地形API,拿到地形不同部分对应的音效信息。通过PlayerFoley类,去进行实时监听和更新。
例如获得当前所踩位置,脚步音效的部分:
var terrainFoley = TerrainFoleyManager.current; footstepIndex = _foleyMap.GetFoleyIndexAtPosition(position, terrainFoley.splatMap); footstep = foley.footsteps[footstepIndex];
这部分具体可参考TerrainFoleyManager.cs
3.其他关注点
3.1 HDRP修改
当时的版本还不算完善,整体流程也不是像新版本走RenderGraph驱动的。
关于项目中的修改处,具体可搜索关键字:
//forest-begin
例如当时增加了VelocityBuffer到GBuffer,去实现运动模糊,
而现在HDRP已经支持了运动模糊:
//forest-begin: G-Buffer motion vectors if(hdCamera.frameSettings.enableGBufferMotionVectors) cmd.EnableShaderKeyword("GBUFFER_MOTION_VECTORS"); else cmd.DisableShaderKeyword("GBUFFER_MOTION_VECTORS"); var gBuffers = m_GbufferManager.GetBuffersRTI(enableShadowMask); if(hdCamera.frameSettings.enableGBufferMotionVectors) { m_GBuffersWithVelocity[0] = gBuffers[0]; m_GBuffersWithVelocity[1] = gBuffers[1]; m_GBuffersWithVelocity[2] = gBuffers[2]; m_GBuffersWithVelocity[3] = gBuffers[3]; m_GBuffersWithVelocity[4] = m_VelocityBuffer.nameID; gBuffers = m_GBuffersWithVelocity; } HDUtils.SetRenderTarget(cmd, hdCamera, gBuffers, m_CameraDepthStencilBuffer); //forest-end:
更多改动更像是为了弥补当时HDRP未完成的功能而临时增加的。
3.2 性能统计
在MiniProfiler.cs中,运用到一个Unity当时新提供的API,可以直接在IMGUI中输出Profile项:
RecorderEntry[] recordersList = { new RecorderEntry() { name="RenderLoop.Draw" }, new RecorderEntry() { name="Shadows.Draw" }, new RecorderEntry() { name="RenderLoopNewBatcher.Draw" }, new RecorderEntry() { name="ShadowLoopNewBatcher.Draw" }, new RecorderEntry() { name="RenderLoopDevice.Idle" }, };
void Awake() { for(int i = 0; i < recordersList.Length; i++) { var sampler = Sampler.Get(recordersList[i].name); if(sampler != null) { recordersList[i].recorder = sampler.GetRecorder(); } } }
具体可搜索sampler.GetRecorder()进行了解学习。
3.3 Object Space法线的运用
项目中的植被为了防止LOD跳变,使用了Object Space Normal Map(OSNM),而现在最新的HDRP
版本直接提供了法线空间模式切换的选项:
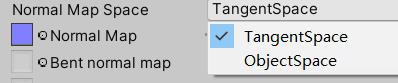
可以想象模型有一个面,法线贴图让其法线向上偏移45度。
此时增加一个lod级别,该面片与另外一个面合并,变成一个向上倾斜的新面,
若用切线空间则法线在原偏移上又向上偏移了45度;而对象空间则依然不变。
相关阅读
Siggraph2018 - The Road toward Unified Rendering with Unitys High Definition Render Pipeline
http://advances.realtimerendering.com/s2018/index.htm
《Book of the Dead》死者之书的场景制作流程


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号