红黑树原理 新增,删除,打印
模板图
二叉查找树
由于红黑树本质上就是一棵二叉查找树,所以在了解红黑树之前,咱们先来看下二叉查找树。
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),也称有序二叉树(ordered binary tree),排序二叉树(sorted binary tree),是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若任意结点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若任意结点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 任意结点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
- 没有键值相等的结点(no duplicate nodes)。
因为,一棵由n个结点,随机构造的二叉查找树的高度为,所以顺理成章,一般操作的执行时间为
但二叉树若退化成了一棵具有n个结点的线性链后,则此些操作最坏情况运行时间为O(n)。后面我们会看到一种基于二叉查找树-红黑树,它通过一些性质使得树相对平衡,使得最终查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏情况下依然为。
红黑树
前面我们已经说过,红黑树,本质上来说就是一棵二叉查找树,但它在二叉查找树的基础上增加了着色和相关的性质使得红黑树相对平衡,从而保证了红黑树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏为,理论上,极端的情况下可以出现RBTree的高度达到,但实际上很难遇到
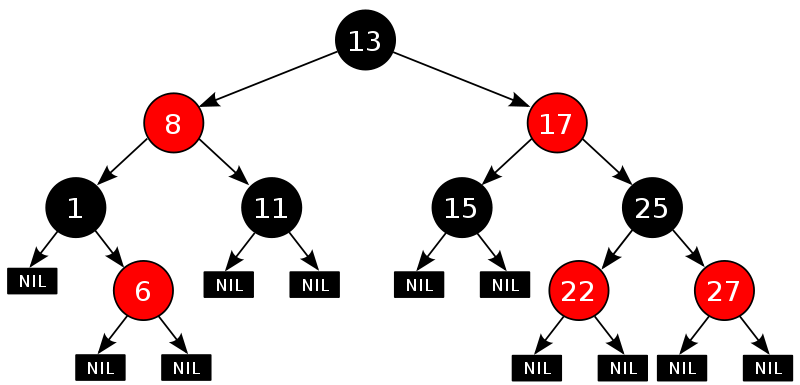
但它是如何保证一棵n个结点的红黑树的高度始终保持在h =的呢?这就引出了红黑树的5条性质:
1)每个结点要么是红的,要么是黑的。
2)根结点是黑的。
3)每个叶结点(叶结点即指树尾端NIL指针或NULL结点)是黑的。
4)如果一个结点是红的,那么它的两个子节点都是黑的。
5)对于任一结点而言,其到叶结点树尾端NIL指针的每一条路径都包含相同数目的黑结点。
性质5保证了红色节点要么有两个黑色子节点,要么就是由两个NIL子节点,不能一个黑色节点,一个NIL节点
性质4和性质5可保证任意节点到其每个叶子节点路径最长不会超过最短路径的2倍
正是红黑树的这5条性质,使得一棵n个结点是红黑树始终保持了的高度,从而也就解释了上面我们所说的“红黑树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏为这一结论的原因。
如下图所示,即是一颗红黑树(下图引自wikipedia:http://t.cn/hgvH1l):
上文中我们所说的 "叶结点" 或"NULL结点",它不包含数据而只充当树在此结束的指示,这些结点以及它们的父结点,在绘图中都会经常被省略。
红黑树保证了最坏情形下在 时间复杂度内完成查找、插入及删除操作;因此红黑树可用于很多场景,比如在 Java 的集合框架 (HashMap、TreeMap、TreeSet)、Nginx 的 Timer 管理、Linux 虚拟内存管理以及 C++ 的 STL 等等都能看到它的应用。
为什么还要红黑树?
二叉查找树并非平衡树,它只限制了左右子树与根点之间的大小关系,只有在平衡二叉查找树时,其时间复杂度才能达到 ** **,并且在极端情况下它甚至会退化成链表;
如下所示在新创建的二叉查找树上依次添加数据 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10 节点,此二叉查找树就退化成了链表,增删查性能也退化到了O(n),所以为了避免这种情况,就出现了 AVL 及红黑树这种能自平衡的二叉查找树;
AVL 树是严格的平衡二叉树,必须满足所有节点的左右子树高度差不超过 1;而红黑树是相对黑色节点平衡的二叉树,
AVL树结构比红黑树更加平衡,这也表示其增删节点时也更容易失衡,失衡就需要纠正,增删节点时开销会比红黑树大。但不可否认的是AVL树搜索的效率是非常稳定的。
因此在大量数据需要插入或者删除时,AVL需要平衡调整的频率会更高。因此,红黑树在需要大量插入和删除节点的场景下,效率更高。自然,由于AVL高度平衡,因此AVL的Search效率略高。
红黑树不是高度平衡树,但平衡的效果已经很好了。所以,可以认为红黑树是一种折中的选择,其综合性能较好。
平衡性的修正
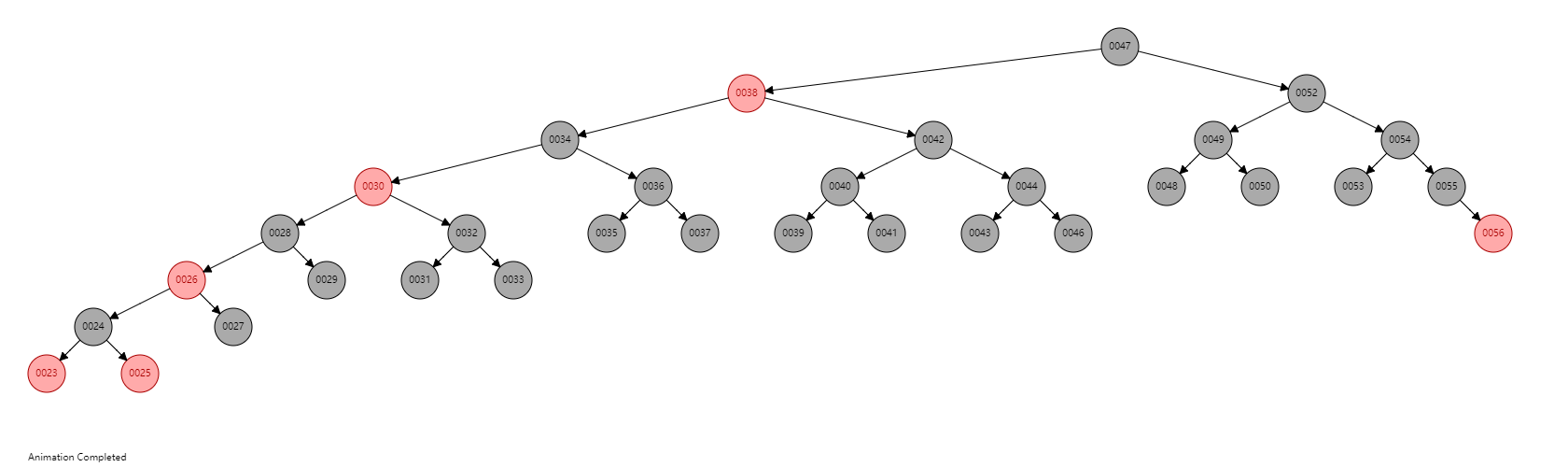
我们把正在处理(遍历)的结点叫做当前结点,如图2中的D,它的父亲叫做父结点,它的父亲的另外一个子结点叫做兄弟结点,父亲的父亲叫做祖父结点。
前面讲到红黑树能自平衡,它靠的是什么?三种操作:左旋、右旋和变色。
-
左旋:以某个结点作为支点(旋转结点),其右子结点变为旋转结点的父结点,右子结点的左子结点变为旋转结点的右子结点,左子结点保持不变。
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋): * px px * / / * x y * / \ --(左旋)-. / \ * lx y x ry * / \ / \ * ly ry lx ly -
右旋:以某个结点作为支点(旋转结点),其左子结点变为旋转结点的父结点,左子结点的右子结点变为旋转结点的左子结点,右子结点保持不变。
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋): * py py * / / * y x * / \ --(右旋)-. / \ * x ry lx y * / \ / \ * lx rx rx ry -
变色:结点的颜色由红变黑或由黑变红。
假设规定
新增节点用
设根节点为R节点
设祖父节点为G节点
设父节点为P节点
设叔叔节点为S节点 (sibling)
设插入节点为A节点
父子左左关系为:P节点为G节点的左孩子,A节点为P节点左孩子
父子左右关系为:P节点为G节点的左孩子,A节点为P节点右孩子
父子右右关系为:P节点为G节点的右孩子,A节点为P节点右孩子
父子右左关系为:P节点为G节点的右孩子,A节点为P节点左孩子
删除节点用
设删除节点为D节点
设删除节点D的后继节点为Y节点
设真正被删除的节点为G节点(如果被删除节点D有子节点,那么G为D的后继节点Y,反之就为D本身)
设真正被删除节点的父节点为R节点
设真正被删除节点的相邻节点(叔叔节点)为S节点
设真正被删除节点的右子节点(如果存在的话)为X节点
插入操作
红黑树的插入过程和二叉查找树插入过程基本类似,不同的地方在于,红黑树插入新节点后,需要进行平衡调整,以满足红黑树的性质。
默认插入节点的颜色
性质1规定红黑树节点的颜色要么是红色要么是黑色,那么在插入新节点时,这个节点应该是红色还是黑色呢?答案是红色,
因为红黑树是完美平衡黑色树,如果插入节点默认为黑色,那么调整起来比较麻烦。
平衡修正流程
- 判断P节点是否为红色,如果为黑色,只要设置根节点为黑色即可,A节点默认为红色。
- 如果P节点为红色S节点
- 判断P节点为G节点的左孩子,还是右孩子,找出对应的S节点
- 找出对应的S节点,判断S节点是否为红色,如果是 ,那么仅需变色(S,P变黑,G变红),并以G节点为A节点递归循环
- 将父子关系为左右,右左的全部旋转为左左,右右父子关系。 (旋转是以P节点旋转,并且旋转以后以新的子节点为插入节点)
- P节点黑色,G节点红色,并以G节点旋转(左左关系右旋转,右右关系左旋转)
- 记住每次都要设置根节点为黑色
删除操作
二叉树删除节点
将红黑树当成一颗二叉树,将节点删除
- 被删除节点没有子节点,直接删除
- 被删除节点只有一个子节点,这个子节点直接替换其父节点
- 被删除节点有两个子节点,查找被删除节点的后继节点(后继节点只能有一个右子节点,或者没有任何子节点),后继节点替换被删除的节点,链接关系以及颜色都采用被删除节点的。(相当于只换了值,但是如果后继节点有子节点,需要交给后继节点的替换前的父节点,就替换原先后继节点的位置,并且不变色)
平衡修正流程
后继节点就是实际上删除的节点
- 判断真正被删除节点G的颜色,如果为红色,直接跳过,不需要修复平衡
- 如果真正被删除节点G为黑色
- 相邻节点S为红色
- 相邻节点S为黑色(Case1)
- S节点的两个子节点为黑色 (Case2)
- S节点的右节点为黑色,左节点为红色 (Case3)
- S节点的右节点为红色,左节点不管 (Case4)
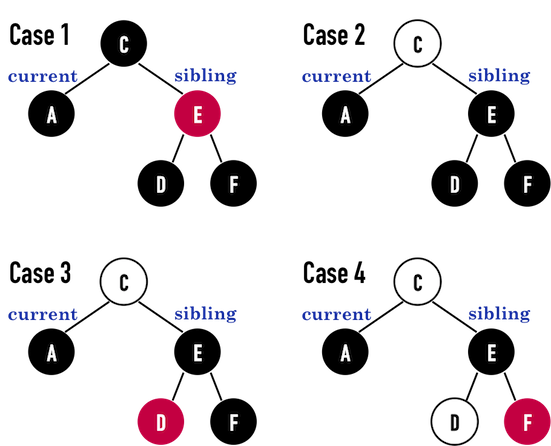
Case1
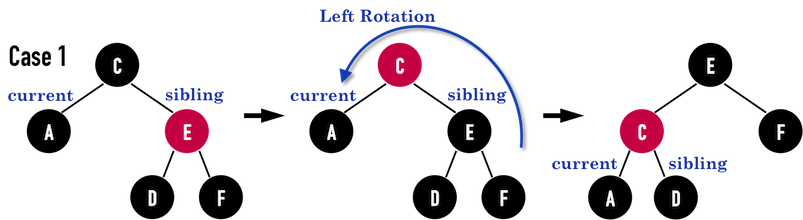
在上述步骤中,并没有更改current之内存位置和颜色,current仍为黑色。不过其sibling必定会变成黑色,因此将进入Case2、Case3或Case4。
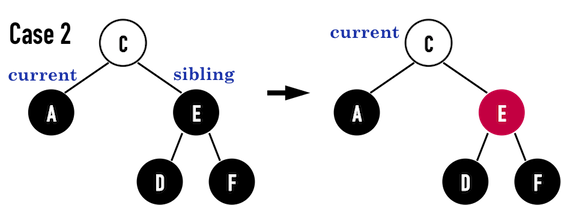
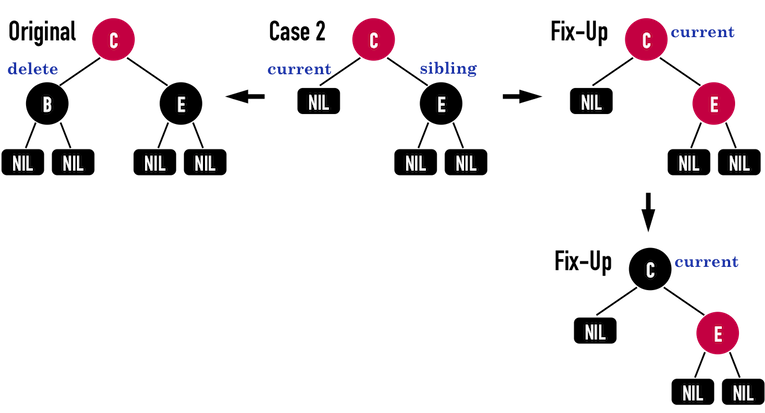
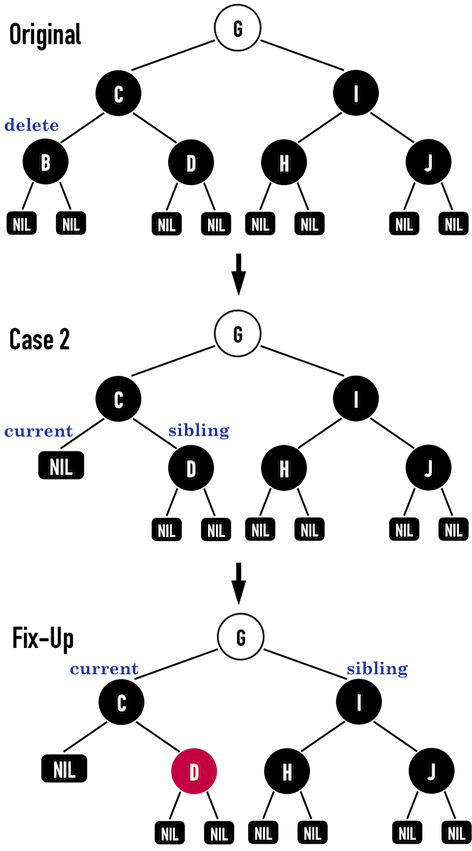
Case2
Case3
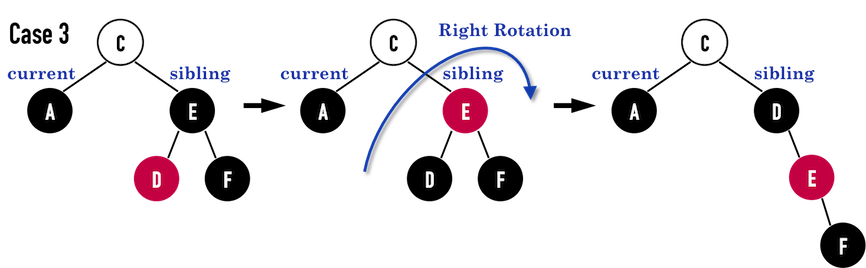
经过以上修正步骤,sibling之rightchild成为红色,便进入Case4。
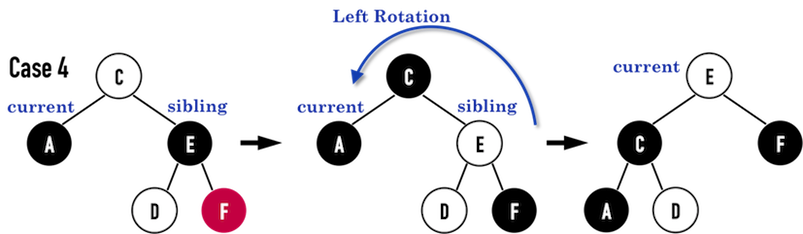
Case4
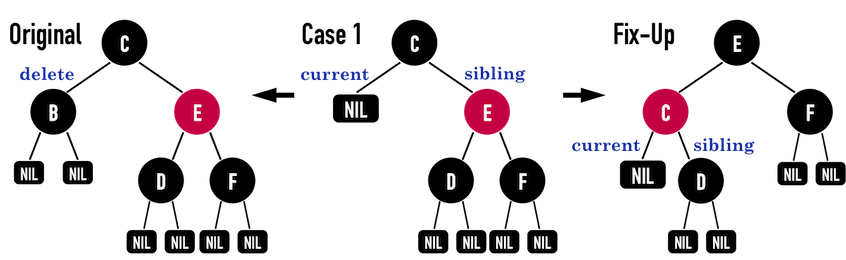
若sibling为黑色,并且sibling之rightchild为红色,修正的方法如下
- 将sibling涂成current之parent的颜色:
- 若node(C)是红色,则将node(E)涂成红色;
- 若node(C)是黑色,则将node(E)涂成黑色;
- 将parent涂成黑色:node(C)涂成黑色;
- 将sibling之rightchild涂成黑色:node(F)涂成黑色;
- 对parent进行Left Rotation:对node(C)做Left Rotation;
- 将current移至root,把root涂黑。
(注意:图五(d)之node(E)未必是RBT之root。)
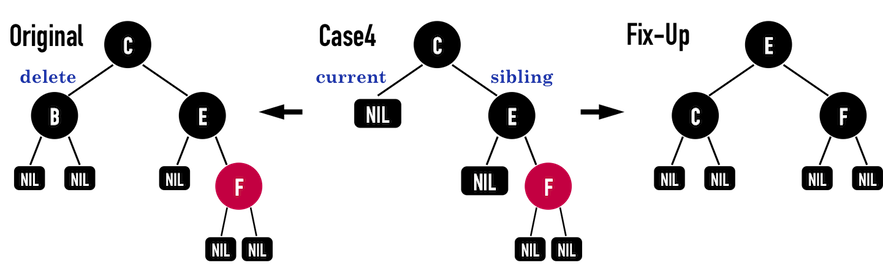
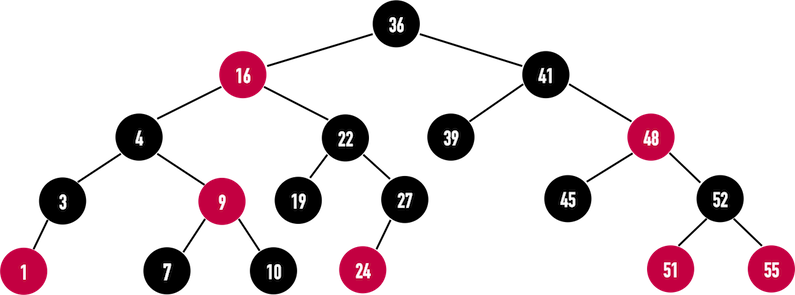
完整范例
接着以一个简单的范例操作上述四种Case的修正方法。
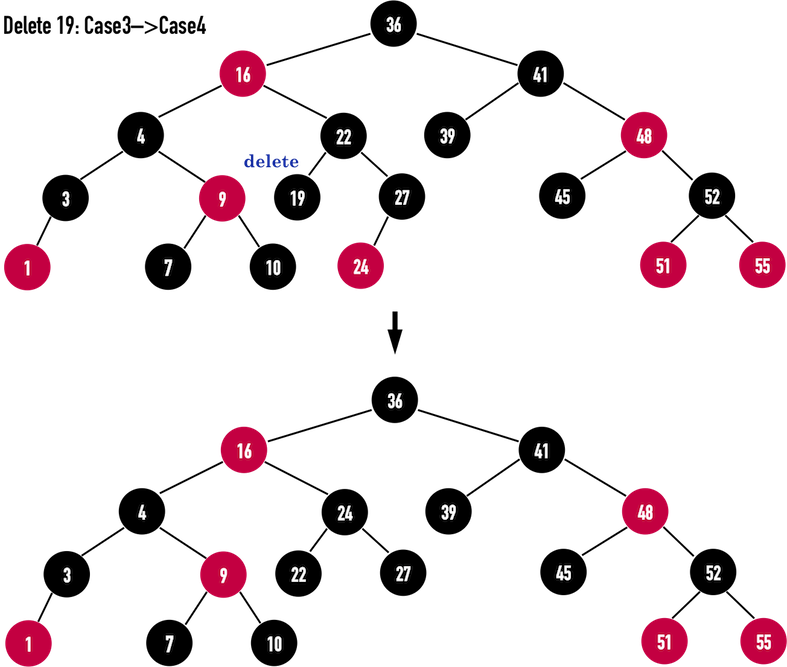
Case3->Case4
若考虑删除node(19),由于node(19)是黑色,需要修正。
接着判断,node(19)的child(为黑色的NIL)之sibling:node(27)为黑色,且sibling之rightchild为黑色,符合Case3的描述,因此利用Case3之修正方法
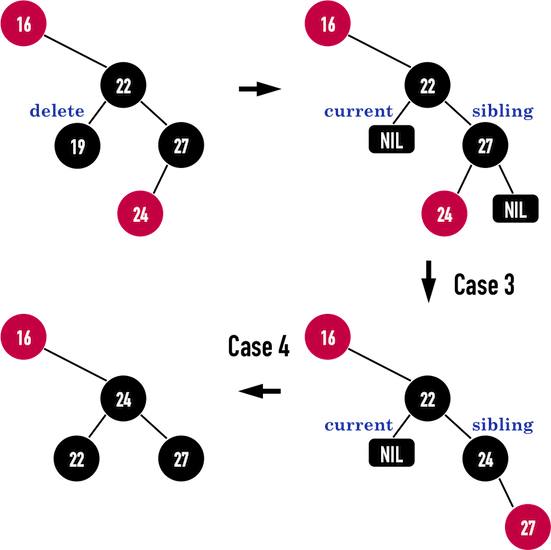

- 将
sibling之leftchild涂成黑色:node(24)涂成黑色; - 将
sibling涂成红色:node(27)涂成红色; - 对
sibling进行Right Rotation:对node(27)进行Right Rotation; - 将
sibling移至current->parent的rightchild:将sibling移至node(24);
接着进入Case4:subling为黑色,而且sibling之rightchild为红色,进行修正:
- 将
sibling涂成current之parent的颜色:node(22)是黑色,则将node(24)涂成黑色; - 将
parent涂成黑色:node(22)涂成黑色; - 将
sibling之rightchild涂成黑色:node(27)涂成黑色; - 对
parent进行Left Rotation:对node(22)做Left Rotation; - 将
current移至root,把root涂黑。
如此一来便再次满足RBT之特征限制
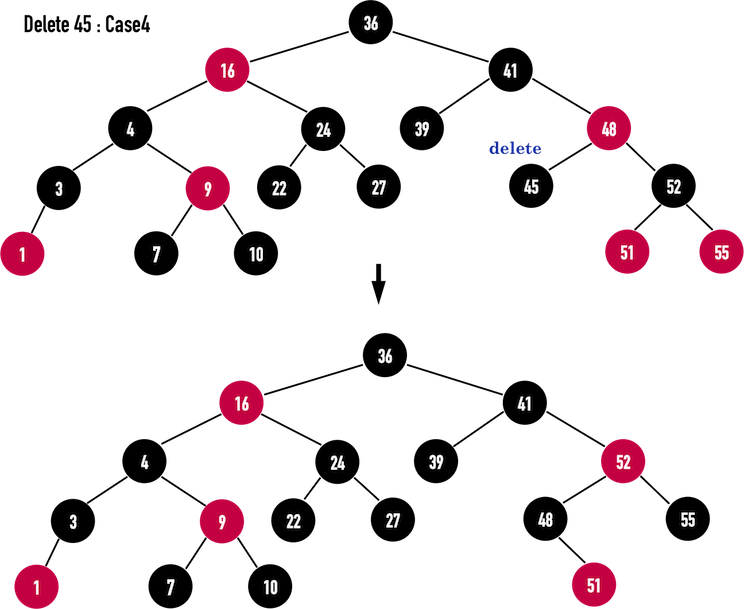
Case4
再考虑删除黑色的node(45),判断:node(45)的child(为黑色的NIL)之sibling:node(52)为黑色,且sibling之rightchild:node(55)为红色,符合Case4的描述,并利用Case4方法修正

- 将
sibling涂成current之parent的颜色:node(48)是红色,则将node(52)涂成红色; - 将
parent涂成黑色:node(48)涂成黑色; - 将
sibling之rightchild涂成黑色:node(55)涂成黑色; - 对
parent进行Left Rotation:对node(48)做Left Rotation; - 将
current移至root,把root涂黑。
如此一来便再次满足RBT之特征限制,
Case1->Case4
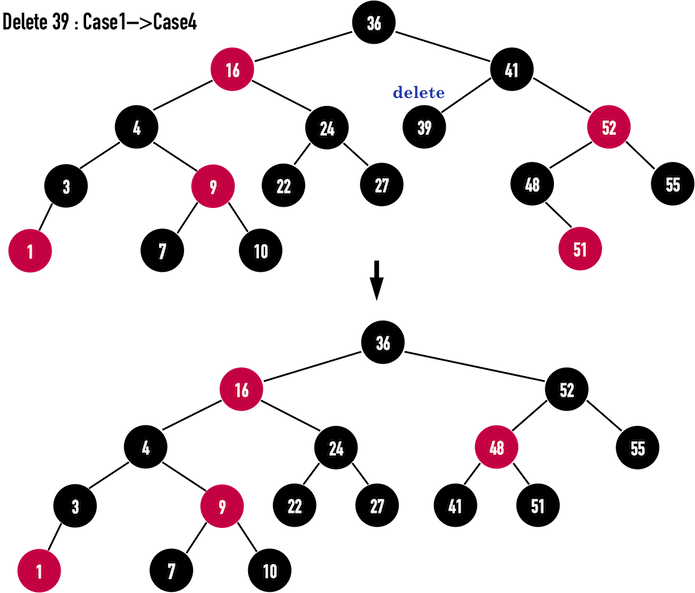
接着考虑删除黑色的node(39),判断:node(39)的child(为黑色的NIL)之sibling:node(52)为红色,符合Case1之描述,便利用Case1之方法,调整成Case4
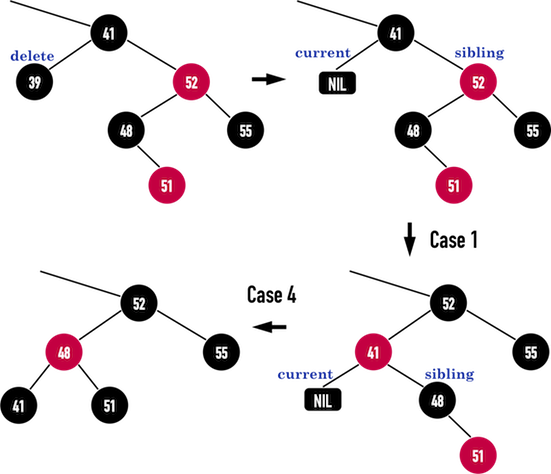
Case1调整:
- 将
sibling涂成黑色:node(52)涂成黑色; - 将
current之parent涂成红色:node(41)涂成红色; - 对
current之parent做Left Rotation:对node(41)做Left Rotation; - 将
sibling移动到current->parent的rightchild:将sibling移动至node(48);
再利用Case4的方法修正,便能满足RBT之特征,
Case2
若要删除黑色的node(7),由于node(7)的child之sibling:node(10)为黑色,且具有两个黑色的child(都是NIL),符合Case2的情况,便修正如下
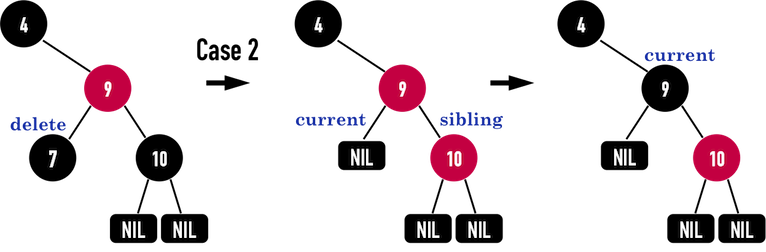
- 将
sibling涂成红色:node(10)涂成红色; - 将
current移至currnet的parent:current移至node(9); - 若新的
current:node(9)为红色,即跳出回圈,并将current涂黑。
经修正后,便符合RBT之特征
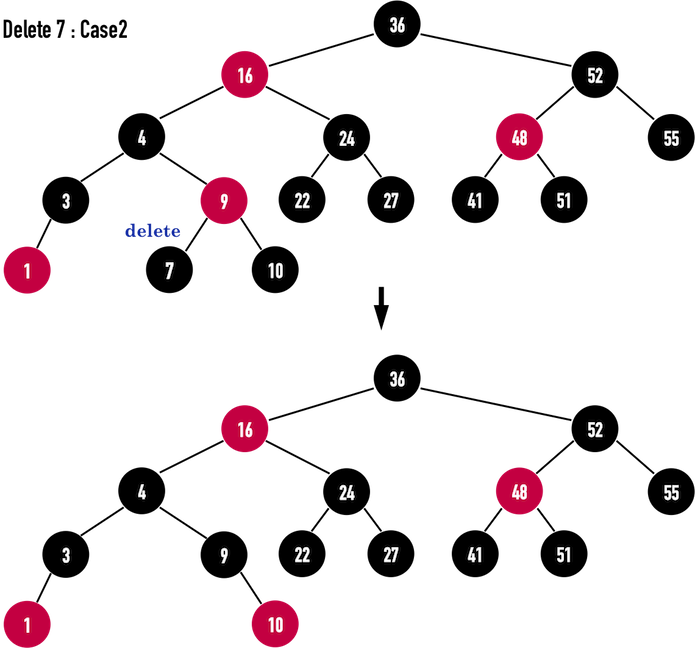
情况0:当前为红色或当前为根
最后,若要删除黑色的node(3)呢?由于node(3)的child:node(1)为红色,并不需要考虑到Case1( sibling为红色,两个child为黑色),只要将node(1)涂黑即可
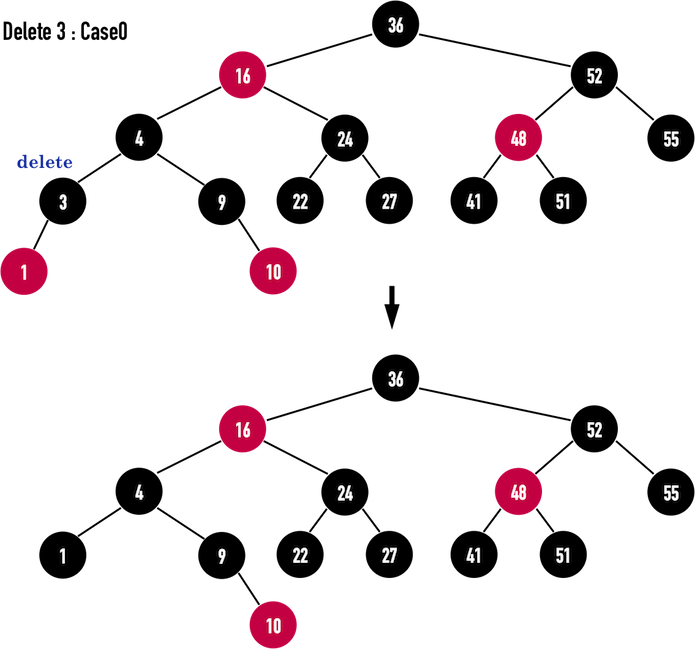
双黑问题
双黑是指删除操作中替换节点与删除节点均为黑色的情况,双黑标记表明了当前树违背了黑色节点数目一致的原则,需要进行修复。修复双黑就是为了保证红黑树满足上述合法性的操作。
源码
package com.qhong.dataStructures.RBTreeDemo;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
/**
* Java 语言: 红黑树
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
private int size;
private RBTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点
public RBTree() {
mRoot = null;
size = 1;
}
private RBTNode<T> parentOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node != null ? node.parent : null;
}
private boolean colorOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node != null ? node.color : BLACK;
}
private boolean isRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
return (node != null) && (node.color == RED);
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
return !isRed(node);
}
private void setBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node != null) {
node.color = BLACK;
}
}
private void setRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node != null) {
node.color = RED;
}
}
private void setParent(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
if (node != null) {
node.parent = parent;
}
}
private void setColor(RBTNode<T> node, boolean color) {
if (node != null) {
node.color = color;
}
}
/*
* 前序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void preOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 中序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void inOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 后序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void postOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
}
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* (递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> search(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x == null) {
return x;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
return search(x.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
return search(x.right, key);
} else {
return x;
}
}
public RBTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* (非递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x = x.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
x = x.right;
} else {
return x;
}
}
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最小结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> minimum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return null;
}
while (tree.left != null) {
tree = tree.left;
}
return tree;
}
public T minimum() {
RBTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != null) {
return p.key;
}
return null;
}
/*
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最大结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> maximum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return null;
}
while (tree.right != null) {
tree = tree.right;
}
return tree;
}
public T maximum() {
RBTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != null) {
return p.key;
}
return null;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> successor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x.right != null) {
return minimum(x.right);
}
// 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y != null) && (x == y.right)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> predecessor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x.left != null) {
return maximum(x.left);
}
// 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y != null) && (x == y.left)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \ #
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
private void leftRotate(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”;
// 如果y的左孩子非空,将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
// 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = y; // 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
} else {
x.parent.right = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-. / \ #
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \ #
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
private void rightRotate(RBTNode<T> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
RBTNode<T> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”;
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null) {
x.right.parent = y;
}
// 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = x; // 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
} else {
if (y == y.parent.right) {
y.parent.right = x; // 如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
} else {
y.parent.left = x; // (y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}
/*
* 红黑树插入修正函数
*
* 在向红黑树中插入节点之后(失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的z
*/
private void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> parent, gparent;
// 若“父节点存在,并且父节点的颜色是红色”
while (((parent = parentOf(node)) != null) && isRed(parent)) {
gparent = parentOf(parent);
//若“父节点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent.left) {
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.right;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:父子节点左右关系改成左左关系
if (parent.right == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
leftRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:变色并对祖父节点进行右旋
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
} else {
// 父节点为祖父节点的右孩子
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.left;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:父子节点右左关系改成右右关系
if (parent.left == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
rightRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:变色并对祖父节点进行左旋
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
}
}
// 将根节点设为黑色
setBlack(this.mRoot);
}
/*
* 将结点插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的node
*/
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.mRoot;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
node.parent = y;
if (y != null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
y.left = node;
} else {
y.right = node;
}
} else {
this.mRoot = node;
}
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node = new RBTNode<T>(key, BLACK, null, null, null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (node != null) {
insert(node);
}
size++;
}
/*
* 红黑树删除修正函数
*
* 在从红黑树中删除插入节点之后(红黑树失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 待修正的节点,平衡点,remove删除操作,
* 这里的node就是真正的被删除节点的原始位置,二叉树删除操作后该位置新的节点
* 如果被删除节点没有子节点,node为null
* 如果被删除节点的后继节点没有右子节点,node为null
* 反之node九尾被删除节点的后继节点的右子节点
* 嗯,也可以理解为,真正被删除节点的位置,在二叉树删除操作后,该位置的节点
*
* parent为真正被删除节点(被删除节点有子节点,就为后继节点)的父节点
* 但有一种特殊情况,就是后继节点为被删除节点的父节点,此时,定义parent为后继节点
* 嗯,也可以理解为,真正被删除节点的父节点位置,在二叉树删除操作后,该位置的节点。
*/
private void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
RBTNode<T> other;
//node节点不是红色节点
//下面注释中,x为真正被删除节点位置的当前节点
//s节点为x的相邻节点
while ((node == null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.mRoot)) {
System.out.println("removeFixUp方法:node:"+node+",parent:"+parent);
System.out.println("二叉树删除后");
if(mRoot!=null) {
mRoot.print();
}
//除了后继节点是被删除节点的子节点这种情况
if (parent.left == node) {
other = parent.right;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
leftRotate(parent);
other = parent.right;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.left);
setRed(other);
rightRotate(other);
other = parent.right;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.right);
leftRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
} else {
// 被删除节点没有子节点,parent为被删除节点的父节点
// 被删除节点就是后继节点的父节点,那么parent为后继节点
other = parent.left;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
rightRotate(parent);
other = parent.left;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.right);
setRed(other);
leftRotate(other);
other = parent.left;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.left);
rightRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
}
}
if (node != null) {
setBlack(node);
}
}
/*
* 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* node 删除的结点
*/
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ((node.left != null) && (node.right != null)) {
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null) {
replace = replace.left;
}
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
// 更新被删除的节点,替换为其后继节点
if (parentOf(node) != null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node) {
parentOf(node).left = replace;
} else {
parentOf(node).right = replace;
}
} else {
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
this.mRoot = replace;
}
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace.right;
// parent为后继节点的父节点
parent = parentOf(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
// 此时会将parent设置为后继节点,因为父节点会被删掉
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
// child不为空
if (child != null) {
child.parent = parent;
}
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK) {
removeFixUp(child, parent);
}
node = null;
return;
}
// 被删除节点node只有一个子节点child
// 或者没有任何子节点,child为null
if (node.left != null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child != null) {
child.parent = parent;
}
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.left == node) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
} else {
this.mRoot = child;
}
if (color == BLACK) {
removeFixUp(child, parent);
}
node = null;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != null) {
remove(node);
}
size--;
}
/*
* 销毁红黑树
*/
private void destroy(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return;
}
if (tree.left != null) {
destroy(tree.left);
}
if (tree.right != null) {
destroy(tree.right);
}
tree = null;
}
public void clear() {
destroy(mRoot);
mRoot = null;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null) {
mRoot.print();
}
}
private class RBTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
/**
* 宽度间隔(不能小于5,如果key大于1000,请加宽度)
*/
private final int interval = 5;
boolean color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
RBTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
RBTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
private int maxHeight = 0;
private Map<Integer, List<String>> allFieldMap = new HashMap<>();
public RBTNode(T key, boolean color, RBTNode<T> parent, RBTNode<T> left, RBTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public T getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* 当前节点的高度,根节点高度为1
*/
public int getHight() {
int i = 1;
RBTNode<T> node = this;
while (node.parent != null) {
node = node.parent;
i++;
}
return i;
}
public String toString() {
if (key == null) {
return "NIL";
}
if (this.color == RED) {
return "(" + key + ")";
} else {
return "" + key;
}
}
private void getMaxHeight(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
if (tree.getHight() > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = tree.getHight();
}
getMaxHeight(tree.left);
getMaxHeight(tree.right);
}
}
/**
* 获取最深的高度,根节点高度为1
*/
public int getMaxHeight() {
if (mRoot != null) {
getMaxHeight(this);
return maxHeight;
}
return 0;
}
/**
*
*/
private void show(RBTNode<T> tree, int leftWidth, int fixWidth) {
if (tree != null) {
//System.out.println("leftWidth:" + leftWidth+" fixWidth:"+fixWidth+" value:"+tree.key);
String showContent = "";
int ahead = 0;
if (tree.color == RED) {
ahead++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < leftWidth - ahead; i++) {
showContent += " ";
}
showContent += tree;
getFieldList(tree).add(showContent);
show(tree.left, leftWidth - (int) (0.5 * fixWidth), fixWidth / 2);
show(tree.right, leftWidth + (int) (0.5 * fixWidth), fixWidth / 2);
}
}
/**
* 获取对应节点对应高度的数组
*/
private List<String> getFieldList(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (allFieldMap.get(tree.getHight()) == null) {
allFieldMap.put(tree.getHight(), Lists.newArrayList());
}
return allFieldMap.get(tree.getHight());
}
/**
* 打印节点
*/
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null) {
allFieldMap = new HashMap<>();
int fieldWidth = (2 << (mRoot.getMaxHeight() - 1) - 1);
int allWidth = fieldWidth * interval;
int fixWidth = (allWidth - interval) / 2;
show(this, fixWidth, fixWidth);
allFieldMap.entrySet().forEach(x -> {
AtomicReference<String> str = new AtomicReference<>("");
List<String> list = x.getValue();
list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(y -> y.length())).forEach(y -> {
str.set(str + y.substring(str.get().length()));
});
System.out.println(str.get());
});
}
}
}
}
运行调试
public class RBTreeTest {
private static final int[] a = {10, 40, 30, 60, 90, 70, 20, 50, 80, 75,88,87,98,23,44,55,66,77,1,2,3,4,35,36,33,32,31,89,81,82,83,84,85,86,79};
private static final boolean mDebugInsert = false; // "插入"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开)
private static final boolean mDebugDelete = false; // "删除"动作的检测开关(false,关闭;true,打开)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, ilen = a.length;
RBTree<Integer> tree = new RBTree<Integer>();
System.out.printf("== 原始数据: ");
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) {
tree.insert(a[i]);
// 设置mDebugInsert=true,测试"添加函数"
if (mDebugInsert) {
System.out.printf("== 添加节点: %d\n", a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
System.out.println("== 遍历 ");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("== 前序遍历: ");
tree.preOrder();
System.out.printf("\n== 中序遍历: ");
tree.inOrder();
System.out.printf("\n== 后序遍历: ");
tree.postOrder();
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 最小值: %s\n", tree.minimum());
System.out.printf("== 最大值: %s\n", tree.maximum());
System.out.printf("\n");
// tree.remove(60);
// tree.print();
// 设置mDebugDelete=true,测试"删除函数"
if (mDebugDelete) {
for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) {
tree.remove(a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 删除节点: %d\n", a[i]);
System.out.printf("== 树的详细信息: \n");
tree.print();
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
// 销毁二叉树
tree.clear();
}
}
被删除节点没有子节点,不存在后继节点
== 原始数据: 1 4 5 3 6 7 8 9 10
== 遍历
6
(4) (8)
1 5 7 9
(3) (10)
二叉树删除 5
6
(4) (8)
1 7 9
(3) (10)
平衡修正后:
6
(3) (8)
1 4 7 9
(10)
removeFixUp方法的node为null,parent为4
后继节点为被删除节点子节点:
== 原始数据: 1 4 5 3 6 7 8 9 10
== 遍历
6
(4) (8)
1 5 7 9
(3) (10)
二叉树删除 8
6
(4) (9)
1 5 7 (10)
(3)
平衡修正后:
6
(4) (9)
1 5 7 10
(3)
removeFixUp方法的node为10,parent为9
后继节点不是被删除节点子节点:
== 原始数据: 1 4 5 3 6 7 8 9 10
== 遍历
6
(4) (8)
1 5 7 9
(3) (10)
二叉树删除 6
7
(4) (8)
1 5 9
(3) (10)
平衡修正后:
7
(4) (9)
1 5 8 10
(3)
removeFixUp方法的node为null,parent为8
特殊场景,平衡点存在左子树
下面的第二次平衡操作,平衡点为86,而86存在左子树
== 遍历
84
79 86
45 (82) 85 89
81 83
== 删除节点: 89
== 树的详细信息:
removeFixUp方法:node:null,parent:86
平衡操作
84
79 86
45 (82) 85
81 83
removeFixUp方法:node:86,parent:84
平衡操作
84
79 86
45 (82) (85)
81 83
== 平衡调整后
82
79 84
45 81 83 86
(85)
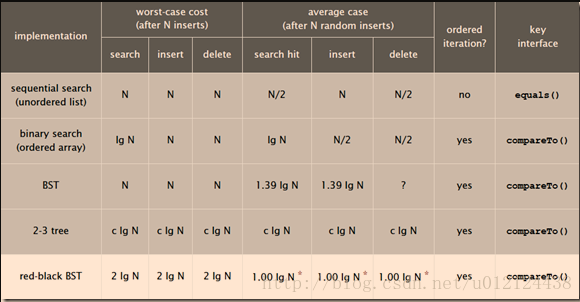
各种树的操作时间复杂度



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2019-01-08 Intellij IDEA 设置启动JVM参数