JavaScript 原型
<script type="text/javascript"> function Person(name) { this.name = name; this.sayName = function () { alert("我的名字:" + name); } } var father = new Person("父亲"); console.dir(Person); console.dir(father); </script>

可以看出father没有prototype属性,Person有
按照javascript的说法,function定义的这个Person就是一个Object(对象),而且还是一个很特殊的对象,这个使用function定义的对象与使用new操作符生成的对象之间有一个重要的区别。这个区别就是function定义的对象有一个prototype属性,使用new生成的对象就没有这个prototype属性。
prototype属性又指向了一个prototype对象,注意prototype属性与prototype对象是两个不同的东西,要注意区别。在prototype对象中又有一个constructor属性,这个constructor属性同样指向一个constructor对象,而这个constructor对象恰恰就是这个function函数本身。
<script type="text/javascript"> function Person(name) { this.name = name; this.sayName = function () { alert("我的名字:" + name); } } Person.prototype.country = "中国"; Person.prototype.form = function () { alert("我是中国人"); } var father = new Person("父亲"); console.dir(Person); console.dir(father); </script>
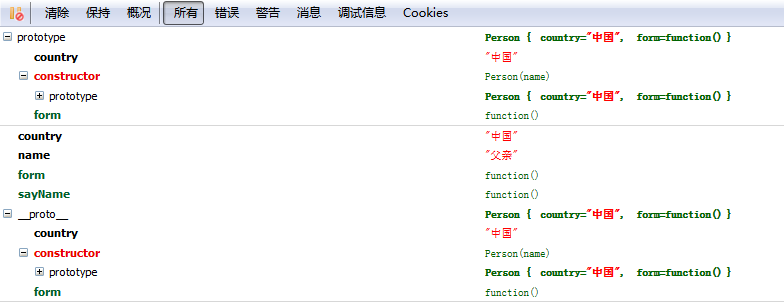
new形式创建对象的过程实际上可以分为三步:
第一步是建立一个新对象father;
第二步将该对象father内置的原型对象设置为构造函数(就是Person)prototype 属性引用的那个原型对象;
第三步就是将该对象father作为this 参数调用构造函数(就是Person),完成成员设置等初始化工作。
其中第二步中出现了一个新名词就是内置的原型对象,注意这个新名词跟prototype对象不是一回事,为了区别我叫它inobj,inobj就指向了函数Person的prototype对象。在person的prototype对象中出现的任何属性或者函数都可以在father对象中直接使用,这个就是javascript中的原型继承了。

继承
继承的实现很简单,只需要把子类的prototype设置为父类的一个对象即可。注意这里说的可是对象哦!
<script type="text/javascript"> function Person(name) { this.name = name; this.sayName = function () { alert("我的名字:" + name); } } Person.prototype.country = "中国"; Person.prototype.form = function () { alert("我是中国人"); } var father = new Person("父亲"); var SubPer = function () { this.phone = "IPhone5"; this.say = function () { alert("Hello!"); } } SubPer.prototype = father; var son = new SubPer(); console.dir(Person); console.dir(father); console.dir(SubPer); console.dir(son); </script>
SubPer对象

Son对象






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)