跟着webbench学习C++网络编程(二)
跟着webbench学习C++网络编程(二)
webbench.c是最主要的文件,里面的结构大概如下:
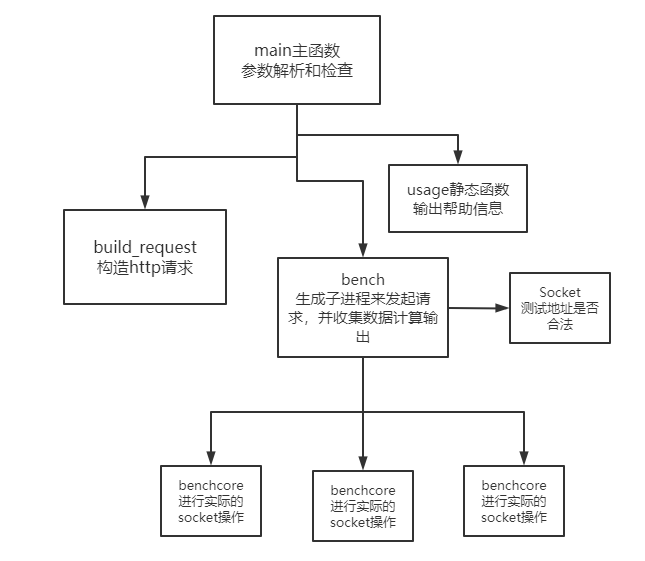
我会用在代码中注释的方式来记录学习的过程:
/*
* (C) Radim Kolar 1997-2004
* This is free software, see GNU Public License version 2 for
* details.
*
* Simple forking WWW Server benchmark:
*
* Usage:
* webbench --help
*
* Return codes:
* 0 - sucess 成功
* 1 - benchmark failed (server is not on-line)
* 2 - bad param 参数错误
* 3 - internal error, fork failed 内部错误,创建进程失败
*
*/
#include "socket.c"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <rpc/types.h>
#include <getopt.h> // getopt_long
#include <strings.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <signal.h>
/* values */
volatile int timerexpired = 0;
int speed = 0;
int failed = 0;
int bytes = 0;
/* 请求方式 */
/* Allow: GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE */
#define METHOD_GET 0
#define METHOD_HEAD 1
#define METHOD_OPTIONS 2
#define METHOD_TRACE 3
#define PROGRAM_VERSION "1.5"
/* 相关参数及其默认设置 */
int http10 = 1; /* 0 - http/0.9, 1 - http/1.0, 2 - http/1.1 */
int method = METHOD_GET; /* GET 方式 */
int clients = 1; /* 只模拟一个客户端 */
int force = 0; /* 等待响应 */
int force_reload = 0; /* 失败时重新请求 */
int proxyport = 80; /* 默认访问端口 */
char* proxyhost = NULL; /* 代理服务器 */
int benchtime = 30; /* 模拟请求时间 */
/* internal */
int mypipe[2]; /* 管道 */
char host[MAXHOSTNAMELEN]; /* 网络地址 */
#define REQUEST_SIZE 2048
char request[REQUEST_SIZE]; /* 请求 */
static const struct option long_options[] =
{
{"force",no_argument,&force,1},
{"reload",no_argument,&force_reload,1},
{"time",required_argument,NULL,'t'},
{"help",no_argument,NULL,'?'},
{"http09",no_argument,NULL,'9'},
{"http10",no_argument,NULL,'1'},
{"http11",no_argument,NULL,'2'},
{"get",no_argument,&method,METHOD_GET},
{"head",no_argument,&method,METHOD_HEAD},
{"options",no_argument,&method,METHOD_OPTIONS},
{"trace",no_argument,&method,METHOD_TRACE},
{"version",no_argument,NULL,'V'},
{"proxy",required_argument,NULL,'p'},
{"clients",required_argument,NULL,'c'},
{NULL,0,NULL,0}
};
/* prototypes */
static void benchcore(const char* host, const int port, const char* request);
static int bench(void);
static void build_request(const char* url);
static void alarm_handler(int signal)
{
timerexpired = 1;
}
/* 静态函数:输出 help 信息 */
static void usage(void)
{
fprintf(stderr,
"webbench [option]... URL\n"
" -f|--force Don't wait for reply from server.\n"
" -r|--reload Send reload request - Pragma: no-cache.\n"
" -t|--time <sec> Run benchmark for <sec> seconds. Default 30.\n"
" -p|--proxy <server:port> Use proxy server for request.\n"
" -c|--clients <n> Run <n> HTTP clients at once. Default one.\n"
" -9|--http09 Use HTTP/0.9 style requests.\n"
" -1|--http10 Use HTTP/1.0 protocol.\n"
" -2|--http11 Use HTTP/1.1 protocol.\n"
" --get Use GET request method.\n"
" --head Use HEAD request method.\n"
" --options Use OPTIONS request method.\n"
" --trace Use TRACE request method.\n"
" -?|-h|--help This information.\n"
" -V|--version Display program version.\n"
);
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int opt = 0;
int options_index = 0;
char* tmp = NULL;
/* 不带参数时直接输出 help 信息 */
if (argc == 1)
{
usage();
return 2;
}
/* getopt_long 为命令行参数解析的库函数,可通过 man 3 getopt_long 查看 */
/* getopt_long 详解可见https://blog.csdn.net/cashey1991/article/details/7942809 */
while ((opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, "912Vfrt:p:c:?h", long_options, &options_index)) != EOF)
{
/* 如果有返回对应的命令行参数 */
switch (opt)
{
case 0: break;
case 'f': force = 1; break;
case 'r': force_reload = 1; break;
case '9': http10 = 0; break;
case '1': http10 = 1; break;
case '2': http10 = 2; break;
case 'V':
printf(PROGRAM_VERSION"\n");
exit(0);
case 't':
benchtime = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'p':
/* proxy server parsing server:port */
/*strrchr 在参数所指向的字符串中搜索最后一次出现字符 c(一个无符号字符)的位置*/
tmp = strrchr(optarg, ':');
proxyhost = optarg;
/* 参数错误,不符合 域名:端口号 的格式*/
if (tmp == NULL)
{
break;
}
/* 没有输入域名参数 */
if (tmp == optarg)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error in option --proxy %s: Missing hostname.\n", optarg);
return 2;
}
/* 没有输入端口参数 */
if (tmp == optarg + strlen(optarg) - 1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error in option --proxy %s Port number is missing.\n", optarg);
return 2;
}
*tmp = '\0';
proxyport = atoi(tmp + 1);
break;
case ':':
case 'h':
case '?': usage(); return 2; break;
case 'c': clients = atoi(optarg); break;
}
}
/* optind 被 getopt_long 设置为命令行参数中未读取的下一个元素下标值 */
/* agrc表示参数的个数,但其值是比实际参数的个数多一个的,因为argv[0]表示程序运行的全路径名。
如果未读取的下一个参数为空,则说明没有输入url*/
if (optind == argc)
{
fprintf(stderr, "webbench: Missing URL!\n");
usage();
return 2;
}
/* 不能指定客户端数和请求时间为 0 */
if (clients == 0) clients = 1;
if (benchtime == 0) benchtime = 60;
/* Copyright */
fprintf(stderr, "Webbench - Simple Web Benchmark "PROGRAM_VERSION"\n"
"Copyright (c) Radim Kolar 1997-2004, GPL Open Source Software.\n"
);
/* 构造 HTTP 请求到 request 数组 */
build_request(argv[optind]);
/* 以下到函数结束为输出提示信息 */
/* print bench info */
printf("\nBenchmarking: ");
switch (method)
{
case METHOD_GET:
default:
printf("GET"); break;
case METHOD_OPTIONS:
printf("OPTIONS"); break;
case METHOD_HEAD:
printf("HEAD"); break;
case METHOD_TRACE:
printf("TRACE"); break;
}
printf(" %s", argv[optind]);
switch (http10)
{
case 0: printf(" (using HTTP/0.9)"); break;
case 2: printf(" (using HTTP/1.1)"); break;
}
printf("\n");
if (clients == 1) printf("1 client");
else
printf("%d clients", clients);
printf(", running %d sec", benchtime);
if (force) printf(", early socket close");
if (proxyhost != NULL) printf(", via proxy server %s:%d", proxyhost, proxyport);
if (force_reload) printf(", forcing reload");
printf(".\n");
/* 开始压力测试,返回 bench 函数执行结果 */
return bench();
}
//检查url参数,构造请求头
void build_request(const char* url)
{
char tmp[10]; //后面用来暂时存放端口号
int i; //存储主机名开始的位置
/* 初始化 */
/* 此处学习bzero和memset()的区别 */
bzero(host, MAXHOSTNAMELEN);
bzero(request, REQUEST_SIZE);
/* 判断应该使用的 HTTP 协议 */
// HTTP/0.9 GET
// HTTP/1.0 GET POST HEAD
// HTTP/1.1 GET POST HEAD PUT PATCH OPTIONS DELETE
if (force_reload && proxyhost != NULL && http10 < 1) http10 = 1;
if (method == METHOD_HEAD && http10 < 1) http10 = 1;
if (method == METHOD_OPTIONS && http10 < 2) http10 = 2;
if (method == METHOD_TRACE && http10 < 2) http10 = 2;
/*填写 method 方法 */
switch (method)
{
default:
case METHOD_GET: strcpy(request, "GET"); break;
case METHOD_HEAD: strcpy(request, "HEAD"); break;
case METHOD_OPTIONS: strcpy(request, "OPTIONS"); break;
case METHOD_TRACE: strcpy(request, "TRACE"); break;
}
strcat(request, " ");
/* URL 合法性判断 */
/* strstr 查找传入字符串中第一次出现指定子字符串的位置,不包括终止符'\0' */
if (NULL == strstr(url, "://"))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: is not a valid URL.\n", url);
exit(2);
}
if (strlen(url) > 1500)
{
fprintf(stderr, "URL is too long.\n");
exit(2);
}
if (proxyhost == NULL)
/*
表头文件:#include <string.h>
函数 定义:int strncasecmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n)
函数 说明:strncasecmp()用来比较参数s1和s2字符串前n个字符,比较时会自动忽略大小写的差异。
返回值 :若参数s1和s2字符串相同,则返回0; 若s1大于s2,则返回大于0的值; 若s1小于s2,则返回小于0的值
*/
if (0 != strncasecmp("http://", url, 7))
{
/* 只支持 HTTP 地址 */
fprintf(stderr, "\nOnly HTTP protocol is directly supported, set --proxy for others.\n");
exit(2);
}
/* 找到主机名开始的地方 */
/* protocol/host delimiter */
i = strstr(url, "://") - url + 3;
/* url必须以 / 结束*/
/* char *strchr(const char *str, int c) 在参数 str 所指向的字符串中搜索第一次出现字符 c(一个无符号字符)的位置。 */
if (strchr(url + i, '/') == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "\nInvalid URL syntax - hostname don't ends with '/'.\n");
exit(2);
}
if (proxyhost == NULL)
{
/* get port from hostname */
/* char *index(const char *s, int c) 找出参数s字符串中第一个出现参数c的地址,然后将该字符串出现的地址返回。字符串结束字符(NULL)也视为字符串的一部分。
如果找到指定的字符,则返回字符所在地址,否则返回NULL*/
if (index(url + i, ':') != NULL && index(url + i, ':') < index(url + i, '/'))
{
strncpy(host, url + i, strchr(url + i, ':') - url - i);
/* 端口 */
bzero(tmp, 10);
strncpy(tmp, index(url + i, ':') + 1, strchr(url + i, '/') - index(url + i, ':') - 1);
/* 设置端口 */
proxyport = atoi(tmp);
if (proxyport == 0)
proxyport = 80;
}
//域名后没有接端口号的情况,只提取域名
else {
/* size_t strcspn(const char *str1, const char *str2) 检索字符串 str1 开头连续有几个字符都不含字符串 str2 中的字符。*/
strncpy(host, url + i, strcspn(url + i, "/"));
}
//printf("host:%s\tport:%d\n",host,proxyport);
//这一步是在request头中加上具体路径,比如http://www.baidu.com/test/ 就是 /test/
strcat(request + strlen(request), url + i + strcspn(url + i, "/"));
}
else {
// printf("ProxyHost=%s\nProxyPort=%d\n",proxyhost,proxyport);
strcat(request, url);
}
if (http10 == 1)
strcat(request, " HTTP/1.0");
else if (http10 == 2)
strcat(request, " HTTP/1.1");
strcat(request, "\r\n");
if (http10 > 0)
strcat(request, "User-Agent: WebBench "PROGRAM_VERSION"\r\n");
if (proxyhost == NULL && http10 > 0)
{
strcat(request, "Host: ");
strcat(request, host);
strcat(request, "\r\n");
}
if (force_reload && proxyhost != NULL)
{
strcat(request, "Pragma: no-cache\r\n");
}
if (http10 > 1)
strcat(request, "Connection: close\r\n");
/* add empty line at end */
if (http10 > 0) strcat(request, "\r\n");
printf("Req=%s\n",request);
}
/* vraci system rc error kod */
static int bench(void)
{
int i, j, k;
pid_t pid = 0;
FILE* f;
/* 作为测试地址是否合法 */
/* check avaibility of target server */
i = Socket(proxyhost == NULL ? host : proxyhost, proxyport);
if (i < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "\nConnect to server failed. Aborting benchmark.\n");
return 1;
}
close(i);
/* 建立管道 */
/* create pipe */
if (pipe(mypipe))
{
perror("pipe failed.");
return 3;
}
/* not needed, since we have alarm() in childrens */
/* wait 4 next system clock tick */
/*
* cas=time(NULL);
* while(time(NULL)==cas)
* sched_yield();
* */
/* 派生子进程 */
/* fork childs */
for (i = 0; i < clients; i++)
{
pid = fork();
if (pid <= (pid_t)0)
{
/* child process or error*/
sleep(1); /* make childs faster */
break; /* 子进程立刻跳出循环,要不就子进程继续 fork 了 */
}
}
if (pid < (pid_t)0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "problems forking worker no. %d\n", i);
perror("fork failed.");
return 3;
}
/*
void perror(const char *s)
perror( ) 用来将上一个函数发生错误的原因输出到标准设备(stderr)。参数 s 所指的字符串会先打印出,后面再加上错误原因字符串。此错误原因依照全局变量errno 的值来决定要输出的字符串。
在库函数中有个errno变量,每个errno值对应着以字符串表示的错误类型。当你调用"某些"函数出错时,该函数已经重新设置了errno的值。perror函数只是将你输入的一些信息和现在的errno所对应的错误一起输出。
*/
if (pid == (pid_t)0)
{
/* 子进程发出实际请求 */
/* I am a child */
if (proxyhost == NULL)
benchcore(host, proxyport, request);
else
benchcore(proxyhost, proxyport, request);
/* 打开管道写 */
/* write results to pipe */
f = fdopen(mypipe[1], "w");
if (f == NULL)
{
perror("open pipe for writing failed.");
return 3;
}
/* fprintf(stderr,"Child - %d %d\n",speed,failed); */
fprintf(f, "%d %d %d\n", speed, failed, bytes);
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
else {
/* 父进程打开管道读 */
f = fdopen(mypipe[0], "r");
if (f == NULL)
{
perror("open pipe for reading failed.");
return 3;
}
setvbuf(f, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
speed = 0; /* 传输速度 */
failed = 0; /* 失败请求数 */
bytes = 0; /* 传输字节数 */
while (1)
{
pid = fscanf(f, "%d %d %d", &i, &j, &k);
/* 如果成功,函数fscanf返回成功匹配和赋值的个数。如果到达文件末尾或发生读错误,则返回 EOF。 */
if (pid < 2)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Some of our childrens died.\n");
break;
}
speed += i;
failed += j;
bytes += k;
/* fprintf(stderr,"*Knock* %d %d read=%d\n",speed,failed,pid); */
/* 子进程是否读取完 */
if (--clients == 0) break;
}
fclose(f);
/* 结果计算 */
printf("\nSpeed=%d pages/min, %d bytes/sec.\nRequests: %d susceed, %d failed.\n",
(int)((speed + failed) / (benchtime / 60.0f)),
(int)(bytes / (float)benchtime),
speed,
failed);
}
return i;
}
void benchcore(const char* host, const int port, const char* req)
{
int rlen;
char buf[1500];
int s, i;
struct sigaction sa;
/*安装信号 */
/* setup alarm signal handler */
sa.sa_handler = alarm_handler;
sa.sa_flags = 0;
if (sigaction(SIGALRM, &sa, NULL))
exit(3);
/* 设置闹钟函数 */
alarm(benchtime);
rlen = strlen(req);
nexttry:
while (1) {
/* 收到信号则 timerexpired = 1 */
if (timerexpired)
{
if (failed > 0)
{
/* fprintf(stderr,"Correcting failed by signal\n"); */
failed--;
}
return;
}
/* 建立 socket, 进行 HTTP 请求 */
s = Socket(host, port);
if (s < 0)
{
failed++;
continue;
}
/* write返回读取到的字节数 */
if (rlen != write(s, req, rlen))
{
failed++;
close(s);
continue;
}
/* HTTP 0.9 的处理 */
if (http10 == 0)
/* 如果关闭不成功 */
if (shutdown(s, 1))
{
failed++;
close(s);
continue;
}
/* -f 选项时不读取服务器回复 */
if (force == 0)
{
/* read all available data from socket */
while (1)
{
if (timerexpired) break;
i = read(s, buf, 1500);
/* fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",i); */
if (i < 0)
{
failed++;
close(s);
goto nexttry;
}
else
if (i == 0) break;
else bytes += i;
}
}
if (close(s))
{
failed++;
continue;
}
speed++;
}
}




