Java 多线程(三)之线程状态及其验证
@
目录
线程状态 Thread.State
状态类型
在指定的时间点, 一个线程有且只有一种状态。 这些状态是 JVM 的状态, 他们并没有反映操作系统的状态。
定义
Thread 的状态是定义在 Thread 内部的枚举类型。
public enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
}
在定义中, 我们知道共有 6 种类型。
说明
| 状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NEW | 至今尚未启动的线程处于这种状态 |
| RUNNABLE | 正在 Java 虚拟机中执行的线程处于这种状态。 因为可能在等待其他的资源, 比如处理器。 |
| BLOCKED | 受阻塞并等待某个监视器锁的线程处于这种状态 |
| WAITING | 无限期地等待另一个线程来执行。某一特定操作的线程处于这种状态 |
| TIMED_WAITING | 等待另一个线程来执行。取决于指定等待时间的操作的线程处于这种状态 |
| TERMINATED | 已退出的线程处于这种状态 |
状态转换
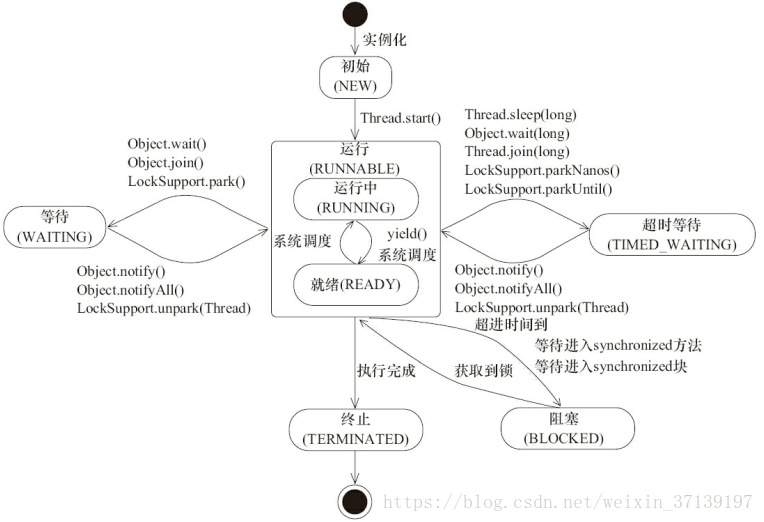
借用 《Java 并发编程的艺术》图一张
从以上的图可以看出,
- 线程创建后未启动未 「NEW」 状态, 通过 start() 函数转换为 「RUNNABLE」状态。
- 「RUNNABLE」 状态通过各函数, 可以与「WAITING」、「TIMED-WAITING」、「BLOCKED」 进行双向切换。
- 「RUNNABLE」 状态在线程结束后转换为 「TERMINATED」 状态。
也就是说, 全部的状态是以 「RUNNABLE」 为中心的。
状态验证
「NEW」-> 「RUNNABLE」 -> 「TERMINATED」
创建一个实现 Runnable 的类
public class StateTestThread implements Runnable{
public StateTestThread() {
// 此时的线程还是 main
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" state in Constructor:"+
Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" state in Run:"+
Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
}
创建一个测试类
public class ThreadStateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StateTestThread stateTestThread = new StateTestThread();
Thread thread = new Thread(stateTestThread);
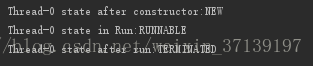
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state after constructor:"
+thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state after run:"
+thread.getState());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果
「RUNNABLE」 -> 「TIMED_WAITING」
public class ThreadStateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 25); i++) {
int j = (int) Math.sqrt(i);
// 该条件永远不成立, 只是为了计算
if (j * j > i) {
break;
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("calculate end:"+(end - begin));
try {
System.out.println("begin sleep");
Thread.sleep(5000L);
System.out.println("end sleep");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
try {
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(100L);
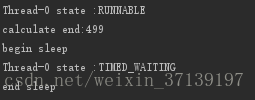
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"
+thread.getState());
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"
+thread.getState());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果如下:
Thread-0 的状态从 「RUNNABLE」 转化为 「TIMED_WAITING」
「RUNNABLE」 -> 「WAITING」
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
final Object lock = new Object();
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"
+thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"
+thread.getState());
}
运行结果
「RUNNABLE」 -> 「BLOCKED」
先创建一个 Runnable 子类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
final Object lock = new Object();
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"+thread.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(thread.getName()+" state :"+thread.getState());
}
测试方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockedStateRun blockedStateRun = new BlockedStateRun();
Thread thread1= new Thread(blockedStateRun);
Thread thread2= new Thread(blockedStateRun);
thread1.setName("First");
thread1.start();
thread2.setName("Second");
thread2.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(200L);
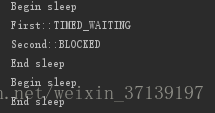
System.out.println(thread1.getName()+"::"+thread1.getState());
System.out.println(thread2.getName()+"::"+thread2.getState());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
最后的运行结果:
作者:阿进的写字台
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义