反射那点基础-Method
@
Method 类描述的是类对象的方法信息。 其中包含了被反射方法的信息, 访问信息。在运行时, 我们可以通过该类进行方法的调用。
1 获取 Method
1.1 方法
因为 Java 中的 java.lang.reflect 包下所有类的构造函数都不为 public, 同时类都是 final 类型的, 因此, 不能直接通过外部 new 来获取该方法。
获取所有的 public 方法,包括其父类, 接口的
public Method[] getMethods();
获取指定参数的 public 方法, 包括其父类, 接口的
public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes);
获取声明(public, private, protected, friendly)的所有普通方法
public Method[] getDeclaredMethods();
获取声明(public, private, protected, friendly)的指定参数的普通方法
public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes);
1.2 实例
该实例称为实例1。
定义父类
public class ParentClass {
private String privateMethod(){
return "ParentClass::privateMethod";
}
String defaultMethod(){
return "ParentClass::defaultMethod";
}
protected String protectedMethod(){
return "ParentClass::protectedMethod";
}
public String publicMethod(){
return "ParentClass::public";
}
}
定义子类
public class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
private String childPrivateMethod(){
return "ChildClass::childPrivateMethod";
}
String childDefaultMethod(){
return "ChildClass::childDefaultMethod";
}
protected String childProtectedMethod(){
return "ChildClass::childProtectedMethod";
}
public String childPublicMethod(){
return "ChildClass::childPublicMethod";
}
测试类
public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<ChildClass> childClass = ChildClass.class;
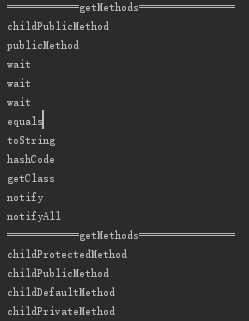
Method[] methods = childClass.getMethods();
System.out.println("============getMethods================");
for (Method method:methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
Method[] dMethods = childClass.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println("============getMethods================");
for (Method method:dMethods) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
}
}
输出
2 Method 的方法
Method 是存储方法相关的信息, 因此, 其方法及属性都跟这些相关。
2.1 Java 方法基础知识
下面是一个方法的属性:
- 修饰符:修饰符,这是可选的,告诉编译器如何调用该方法。定义了该方法的访问类型。
- 返回值 :方法可能会返回值。returnValueType 是方法返回值的数据类型。有些方法执行所需的操作,但没有返回值。在这种情况下,returnValueType 是关键字void。
- 方法名:是方法的实际名称。方法名和参数表共同构成方法签名。
- 参数:参数像是一个占位符。当方法被调用时,传递值给参数。这个值被称为实参或变量。参数列表是指方法的参数类型、顺序和参数的个数。参数是可选的,方法可以不包含任何参数。
- 异常:方法中抛出的异常类型。
- 注解:方法上的注解。
2.2 修饰符相关方法
在 Java 中, 修饰符以数字的形式存在, 通过 int 存储了32位的数字, 就可以存储多个数值, 此种存储方式在Modifier 中会进行讲解。
2.2.1 获取修饰符
public int getModifiers() {
return modifiers;
}
同样以之前 [实例1] 的代码进行测试, 重写写一个测试方法
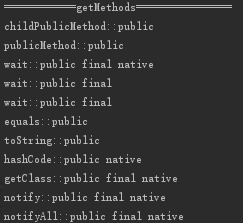
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<ChildClass> childClass = ChildClass.class;
Method[] methods = childClass.getMethods();
System.out.println("============getMethods================");
for (Method method:methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName()+"::"+Modifier.toString(method.getModifiers()));
}
}
结果
2.2.2 判断是否为 default 方法
public boolean isDefault() {
// Default methods are public non-abstract instance methods
// declared in an interface.
return ((getModifiers() & (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) ==
Modifier.PUBLIC) && getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
这是 Java 8 中引入的概念:默认方法是在接口中声明的, public, 非 abstract 的实体方法(实体方法即不是 static 方法)。
在此处不展开。
2.2.3 判断是否为 bridge 方法
public boolean isBridge() {
return (getModifiers() & Modifier.BRIDGE) != 0;
}
判断是否为桥接方法。
2.2.4 判断是否为 synthetic 方法
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return super.isSynthetic();
}
判断是否为 synthetic 方法。
2.3 获取返回值类型
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
2.4 获取方法名
public String getName() {
return name;
}
2.5 获取返回值
2.5.1 方法
获取返回值的类型有两种:
获取到返回值的 Class类型的对象
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
获取到返回值的 Type类型的对象
public Type getGenericReturnType() {
if (getGenericSignature() != null) {
return getGenericInfo().getReturnType();
} else { return getReturnType();}
}
2.5.2 测试
定义类
public class Animal {
private Map<String,Animal> friends = new HashMap<>();
public void addFriend(String name, Animal animal){
friends.put(name,animal);
}
public Animal callFriend(String name){
return friends.get(name);
}
public<T extends Animal> T callFriend(String name, T unusedTypeObj){
return (T)friends.get(name);
}
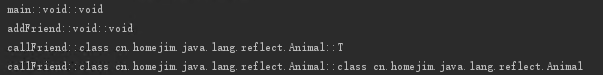
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Animal> clazz = Animal.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method:methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName()+"::"+method.getReturnType()+"::"+method.getGenericReturnType());
}
}
}
输出
2.6 参数
获取所有的参数, 返回值是 Class 数组
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes()
获取所有参数, 返回值是 Type 数组
public Type[] getGenericParameterTypes()
获取参数的所有注解
public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations()
2.7 异常
2.7.1 方法
获取所有的异常, 返回值是 Class 数组
public Class<?>[] getExceptionTypes()
获取所有的异常, 返回值是 Type 数组
public Type[] getGenericExceptionTypes()
获取注解异常
public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedExceptionTypes()
2.7.2 测试
public class ExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method m = ExceptionExample.class.getMethod("method");
System.out.println(m.getGenericExceptionTypes()[0]);
System.out.println(m.getExceptionTypes()[0]);
}
public static <T extends Throwable> void method() throws T {}
}
输出

2.8 注解
获取声明的所有注解
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations()
2.9 调用相关
2.9.1 访问权限控制
抑制Java的权限控制检查:在针对非public时方法时, 可以考虑这么用
public void setAccessible(boolean flag)
2.9.2 方法调用
方法调用
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
2.9.3 测试
使用示例1中的代码
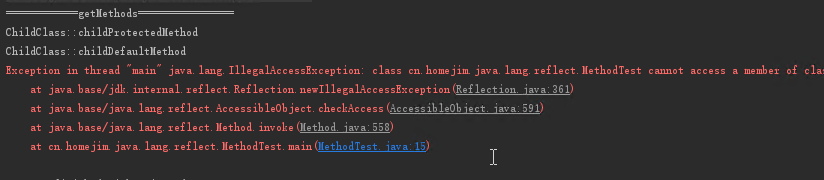
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<ChildClass> childClass = ChildClass.class;
Method[] methods = childClass.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println("============getMethods================");
ChildClass child = new ChildClass();
for (Method method:methods) {
method.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(method.invoke(child));
}
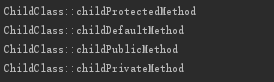
如果注释权限控制, 输出如下
取消注释之后





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?