算法题速查手册
杂
Boyer-Moore 投票算法
初始化m*n二维数组:dp = [[1]*n for _ in range(m)]
每个key的value都是list的dict:tree = collections.defaultdict(list)
dict 计数:mydict[x] = mydict.get(x, 0) + 1
dict 排序: mylist = sorted(mydict.items(), key = lambda kv:(kv[1], kv[0]))
ASCII值:ord("A")
避免浮点数运算: math.floor( (x + (n-1)) / n ) = math.ceil( x / n ) = (x + (n-1)) // n
位运算
位运算符:
& 且
| 或
~ 非
^ 异或
<< 左移
>> 右移
Brian Kernighan 算法:令 x = x & (x-1),该运算将 x 的二进制表示的最后一个 1 变成 0.
排序
# 库函数
people.sort(key=lambda x: (-x[0], x[1])) # 按x[0]降序,x[1]升序
归并排序:
def MergeSort(nums):
if len(nums) <= 1:
return nums
mid = len(nums) // 2
left = MergeSort(nums[:mid])
right = MergeSort(nums[mid:])
return Merge(left, right)
def Merge(left, right):
r, l=0, 0
result=[]
while l<len(left) and r<len(right):
if left[l] <= right[r]:
result. Append(left[l])
l += 1
else:
result. Append(right[r])
r += 1
result += list(left[l:])
result += list(right[r:])
return result
print MergeSort([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 90, 21, 23, 45])
堆排序:https://aijishu.com/a/1060000000090217
import heapq
def HeapSort(nums):
heap, res = [], []
for num in nums:
heapq.heappush(heap, num)
while heap:
res.append(heapq.heappop(heap))
return res
def HeapSort(nums):
heap, res = nums, []
heapq.heapify(heap)
while heap:
res.append(heapq.heappop(heap))
return res
print(HeapSort([6,8,1,6,4,9]))
# 'heap' is a heap at all indices >= startpos, except possibly for pos. pos
# is the index of a leaf with a possibly out-of-order value. Restore the
# heap invariant.
def _siftdown(heap, startpos, pos):
newitem = heap[pos]
# Follow the path to the root, moving parents down until finding a place
# newitem fits.
while pos > startpos:
parentpos = (pos - 1) >> 1
parent = heap[parentpos]
if newitem < parent:
heap[pos] = parent
pos = parentpos
continue
break
heap[pos] = newitem
def _siftup(heap, pos):
endpos = len(heap)
startpos = pos
newitem = heap[pos]
# Bubble up the smaller child until hitting a leaf.
childpos = 2*pos + 1 # leftmost child position
while childpos < endpos:
# Set childpos to index of smaller child.
rightpos = childpos + 1
if rightpos < endpos and not heap[childpos] < heap[rightpos]:
childpos = rightpos
# Move the smaller child up.
heap[pos] = heap[childpos]
pos = childpos
childpos = 2*pos + 1
# The leaf at pos is empty now. Put newitem there, and bubble it up
# to its final resting place (by sifting its parents down).
heap[pos] = newitem
_siftdown(heap, startpos, pos)
def heapify(x):
"""Transform list into a heap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time."""
n = len(x)
# Transform bottom-up. The largest index there's any point to looking at
# is the largest with a child index in-range, so must have 2*i + 1 < n,
# or i < (n-1)/2. If n is even = 2*j, this is (2*j-1)/2 = j-1/2 so
# j-1 is the largest, which is n//2 - 1. If n is odd = 2*j+1, this is
# (2*j+1-1)/2 = j so j-1 is the largest, and that's again n//2-1.
for i in reversed(range(n//2)):
_siftup(x, i)
def heappush(heap, item):
"""Push item onto heap, maintaining the heap invariant."""
heap.append(item)
_siftdown(heap, 0, len(heap)-1)
def heappop(heap):
"""Pop the smallest item off the heap, maintaining the heap invariant."""
lastelt = heap.pop() # raises appropriate IndexError if heap is empty
if heap:
returnitem = heap[0]
heap[0] = lastelt
_siftup(heap, 0)
return returnitem
return lastelt
class Solution(object):
def heap_sort(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
self.nums = nums
# 初始化大顶堆
for i in range(n//2-1, -1, -1):
self.build_heap(i, n-1)
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
nums[0], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[0] # 交换
self.build_heap(0, i-1) # 调整大顶堆
return nums
def build_heap(self, i, n):
nums = self.nums
left, right = 2*i+1, 2*i+2 # 左右子节点的下标
large_index = left
if right <= n and nums[left] < nums[right]:
large_index = right
if nums[i] > nums[large_index]:
large_index = i
if large_index != i:
nums[i], nums[large_index] = nums[large_index], nums[i]
self.build_heap(large_index, n)
回溯
1. 求所有子集:https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai-5/
时间复杂度 \(O(n×2^n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n)\)
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
# 库函数
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)+1):
for tmp in itertools.combinations(nums, i): # 长度为i的所有子集
res.append(tmp)
return res
# 迭代
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = [[]]
for x in nums:
res = res + [[x] + sub for sub in res]
return res
[] 000
[1] 001 (往前面的加上001的1这一位)
[2] 010 (往前面的加上010的1这一位)
[2, 1] 011
[3] 100 (往前面的加上100的1这一位)
[3, 1] 101
[3, 2] 110
[3, 2, 1] 111
# 递归
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
n = len(nums)
res = []
def helper(i, tmp):
res.append(tmp)
for j in range(i+1, n):
helper(j, tmp+[nums[j]])
helper(-1, [])
return res
[] 000
[1] 001 [2] 010 [3] 100 ([]最高位000,遍历001,010,100)
[1, 2] 011 [1, 3] 101 ([1]最高位001,遍历010, 100) [2, 3] 110 ([2]最高位010,遍历100)
[1, 2, 3] 111 ([1, 2]最高位010,遍历100)
2. 求全排列:https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-by-powcai-2/
时间复杂度 \(O(n*n!)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n)\).
# 库函数
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
return list(itertools.permutations(nums))
# 递归
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
def helper(candidates, tmp):
if not candidates:
res.append(tmp)
for i in range(len(candidates)):
helper(candidates[:i]+candidates[i+1:], tmp+[candidates[i]])
helper(nums, [])
return res
# 递归,两两交换
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def backtrack(first = 0):
# 所有数都填完了
if first == n:
res.append(nums[:])
for i in range(first, n):
# 动态维护数组
nums[first], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[first]
# 继续递归填下一个数
backtrack(first + 1)
# 撤销操作
nums[first], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[first]
n = len(nums)
res = []
backtrack()
return res
链表
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = None, next = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def create_link(link):
root = Node(link[0])
pre = root
for i in range(1, len(link)):
p = Node(link[i])
pre.next = p
pre = p
return root
def print_link(root):
p = root
while p:
print(p.val, end=",")
p = p.next
print()
link = [1, 3, 9, 2]
link_root = create_link(link)
print_link(link_root)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
二叉树
前序:中左右;
中序:左中右;
后序:左右中;
层次。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self. Right = right
并查集
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self):
"""
记录每个节点的父节点
"""
self.father = {}
def add(self, x):
"""
添加新节点
"""
if x not in self.father:
self.father[x] = None
def find(self, x):
"""
查找根节点
路径压缩
"""
root = x
while self.father[root] != None:
root = self.father[root]
# 路径压缩
while x != root:
original_father = self.father[x]
self.father[x] = root
x = original_father
return root
def merge(self, x, y):
"""
合并两个节点
"""
root_x,root_y = self.find(x),self.find(y)
if root_x != root_y:
self.father[root_x] = root_y
def is_connected(self,x,y):
"""
判断两节点是否相连
"""
return self.find(x) == self. Find(y)
牛顿-拉弗森法求根号2
求多项式 f(x) = x^2-n = x^2-2 = 0 的根 k
k_better = k - f(k) / f'(k) = k - (k^2-2) / (2*k)
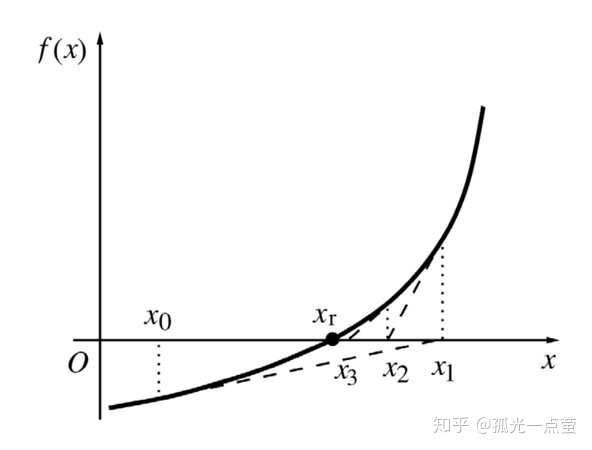
def newton_raphson(k, epsilon, n=2):
while abs(k * k - n) >= epsilon:
k = k - ((k * k - n) / (n * k))
return k
print(newton_raphson(2, 0.00001))
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43031313/article/details/125469836


