Spring_Spring与IoC_基于XML的DI
一、注入分类
bean实例在调用无参构造器创建空值对象后,就要对Bean对象的属性进行初始化。初始化时由容器自动完成的,称为注入。根据注入方式的不同,常用的有2类:设值注入、构造注入。(还有一种,实现特定接口注入,采用侵入式编程,污染了代码,几乎不用)。
二、设值注入

1 public class Student { 2 private String name; 3 private int age; 4 private School school; 5 public void setName(String name) { 6 this.name = name; 7 } 8 public void setAge(int age) { 9 this.age = age; 10 } 11 12 public void setSchool(School school) { 13 this.school = school; 14 } 15 @Override 16 public String toString() { 17 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", school=" + school + "]"; 18 } 19 20 21 }

1 public class School { 2 private String name; 3 4 public void setName(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public String toString() { 10 return "School [name=" + name + "]"; 11 } 12 13 }

1 public class MyTest { 2 3 @Test 4 public void test01() { 5 //创建容器对象 6 String resource = "com/jmu/di01/applicationContext.xml"; 7 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource); 8 Student student = (Student) ac.getBean("myStudent"); 9 System.out.println(student); 10 } 11 12 }

1 <bean id="mySchool" class="com.jmu.di01.School"> 2 <property name="name" value="清华大学"></property> 3 </bean> 4 <bean id="myStudent" class="com.jmu.di01.Student"> 5 <property name="name" value="张三"></property> 6 <property name="age" value="20"></property> 7 <property name="school" ref="mySchool"></property> 8 </bean>
三、构造注入

1 public class Student { 2 private String name; 3 private int age; 4 private School school; 5 6 public Student() { 7 super(); 8 } 9 public Student(String name, int age, School school) { 10 super(); 11 this.name = name; 12 this.age = age; 13 this.school = school; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String toString() { 18 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", school=" + school + "]"; 19 } 20 21 22 }

1 public class School { 2 private String name; 3 4 public void setName(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public String toString() { 10 return "School [name=" + name + "]"; 11 } 12 13 }

1 <bean id="mySchool" class="com.jmu.di02.School"> 2 <property name="name" value="清华大学"></property> 3 </bean> 4 <bean id="myStudent" class="com.jmu.di02.Student"> 5 <constructor-arg name="name" value="李四"/> 6 <constructor-arg name="age" value="24"/> 7 <constructor-arg name="school" ref="mySchool"/> 8 </bean>
四、P命名空间设值注入
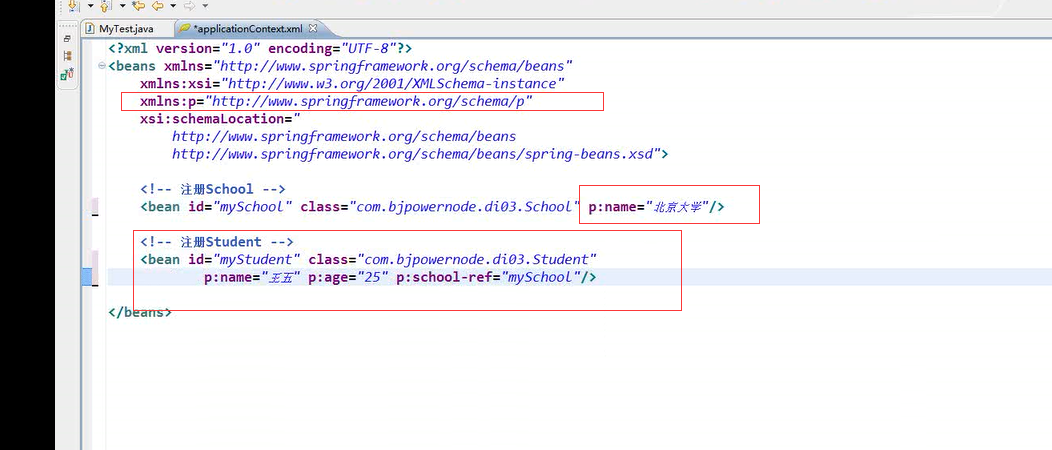
五、C命名空间构造注入

六、数组、集合属性注入

1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Map; 4 import java.util.Properties; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 public class Some { 8 private School[] schools; 9 private String[] myStrs; 10 private List<String> myList; 11 private Set<String> mySet; 12 private Map<String, Object> myMap; 13 private Properties myPros;//key、value均为字符串 14 public void setSchools(School[] schools) { 15 this.schools = schools; 16 } 17 public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) { 18 this.myStrs = myStrs; 19 } 20 public void setMyList(List<String> myList) { 21 this.myList = myList; 22 } 23 public void setMySet(Set<String> mySet) { 24 this.mySet = mySet; 25 } 26 public void setMyMap(Map<String, Object> myMap) { 27 this.myMap = myMap; 28 } 29 public void setMyPros(Properties myPros) { 30 this.myPros = myPros; 31 } 32 @Override 33 public String toString() { 34 return "Some [schools=" + Arrays.toString(schools) + ", myStrs=" + Arrays.toString(myStrs) + ", myList=" 35 + myList + ", mySet=" + mySet + ", myMap=" + myMap + ", myPros=" + myPros + "]"; 36 } 37 38 }

1 public class School { 2 private String name; 3 4 public void setName(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public String toString() { 10 return "School [name=" + name + "]"; 11 } 12 13 }

1 <bean id="mySchool" class="com.jmu.di03.School"> 2 <property name="name" value="清华大学"></property> 3 </bean> 4 <bean id="mySchool2" class="com.jmu.di03.School"> 5 <property name="name" value="北京大学"></property> 6 </bean> 7 <bean id="mySome" class="com.jmu.di03.Some"> 8 <property name="schools"> 9 <array> 10 <ref bean="mySchool"/> 11 <ref bean="mySchool2"/> 12 13 </array> 14 </property> 15 16 <property name="myStrs"> 17 <array> 18 <value>中国</value> 19 <value>福建</value> 20 </array> 21 </property> 22 23 <property name="myList"> 24 <list> 25 <value>厦门</value> 26 <value>泉州</value> 27 </list> 28 </property> 29 30 <property name="mySet"> 31 <set> 32 <value>唐朝</value> 33 <value>宋朝</value> 34 </set> 35 </property> 36 37 <property name="myMap"> 38 <map> 39 <entry key="mobile" value="2132124"></entry> 40 <entry key="QQ" value="12424532"></entry> 41 </map> 42 </property> 43 44 <property name="myPros"> 45 <props> 46 <prop key="education">大学</prop> 47 <prop key="gender">男</prop> 48 </props> 49 </property> 50 </bean>

1 import org.junit.Test; 2 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 3 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 4 5 public class MyTest { 6 7 @Test 8 public void test01() { 9 //创建容器对象 10 String resource = "com/jmu/di03/applicationContext.xml"; 11 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource); 12 Some some=(Some) ac.getBean("mySome"); 13 System.out.println(some); 14 } 15 16 }
输出:

Some [schools=[School [name=清华大学], School [name=北京大学]], myStrs=[中国, 福建], myList=[厦门, 泉州], mySet=[唐朝, 宋朝], myMap={mobile=2132124, QQ=12424532}, myPros={gender=男, education=大学}]
简写:

1 <property name="myStrs" value="中国,福建" /> 2 <property name="myList" value="厦门,泉州" /> 3 <property name="mySet" value="唐朝,宋朝" />
七、对于域属性的自动注入
1、autowire="byName"会从容器中查找与实体类的域属性同名的Bean的id,并将该Bean对象自动注入给该域属性
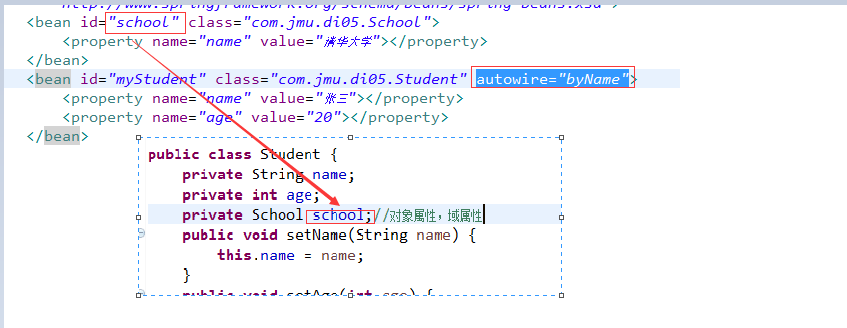
2、autowire="byType"会从容器中查找与实体类的域属性类型具有is-a关系的Bean,并将该Bean对象自动注入给该域属性

1 <!-- <bean id="mySchool" class="com.jmu.di06.School"> 2 <property name="name" value="集美大学"></property> 3 </bean> --> 4 <bean id="myPrimarySchool" class="com.jmu.di06.PrimarySchool"> 5 <property name="address" value="集美区"></property> 6 </bean> 7 <bean id="myStudent" class="com.jmu.di06.Student" autowire="byType"> 8 <property name="name" value="张三"></property> 9 <property name="age" value="20"></property> 10 </bean>

1 public class PrimarySchool extends School { 2 private String address; 3 4 public void setAddress(String address) { 5 this.address = address; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public String toString() { 10 return "PrimarySchool [address=" + address + "]"; 11 } 12 13 }
输出:

Student [name=张三, age=20, school=PrimarySchool [address=集美区]]
八、使用SPEL注入
SPEL,Spring Expression Language,即Spring EL表达式语言。在Spring配置文件中为Bean的属性注入时,可直接使用SPEL表达式计算的结果。

1 <bean id="myPerson" class="com.jmu.di07.Person"> 2 <property name="pname" value="宫本武藏"></property> 3 <property name="page" value="#{T(java.lang.Math).random()*50}"></property> 4 </bean> 5 <bean id="myStudent" class="com.jmu.di07.Student" autowire="byType"> 6 <property name="name" value="#{myPerson.pname}"></property> 7 <property name="age" value="#{myPerson.page>25?25:myPerson.page}"></property> 8 </bean>

1 Person person=(Person) ac.getBean("myPerson"); 2 System.out.println(person); 3 4 Student student = (Student) ac.getBean("myStudent"); 5 System.out.println(student);
输出:

1 Person [pname=宫本武藏, page=15] 2 Student [name=宫本武藏, age=15]

九、内部Bean

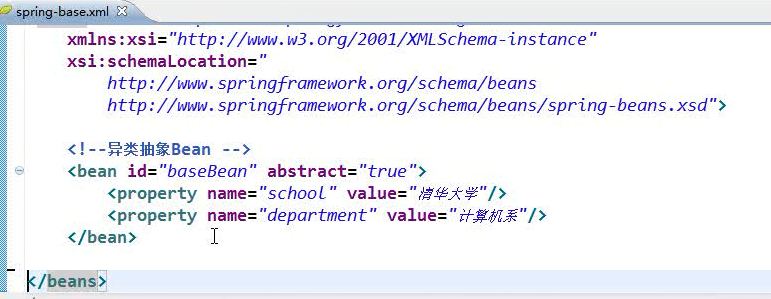
十、同类抽象Bean

十一、异步抽象Bean

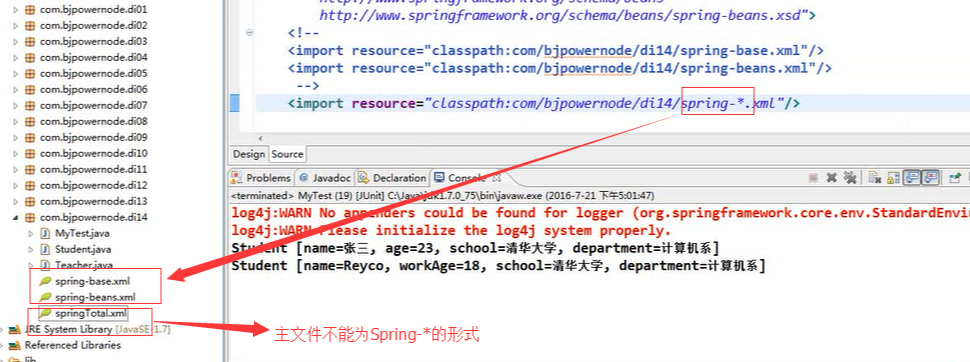
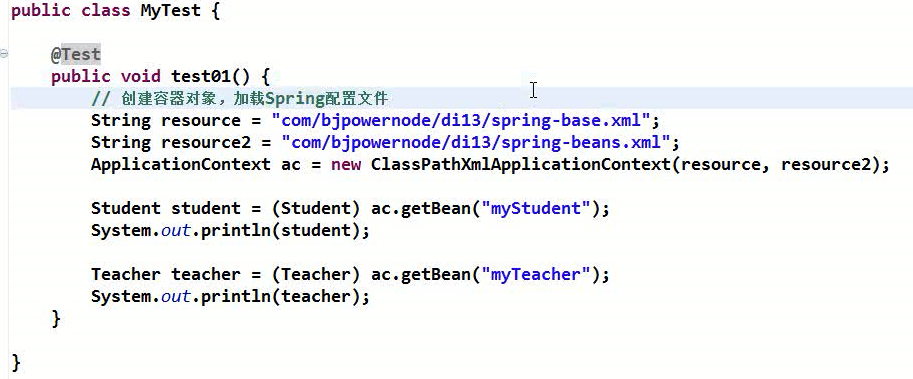
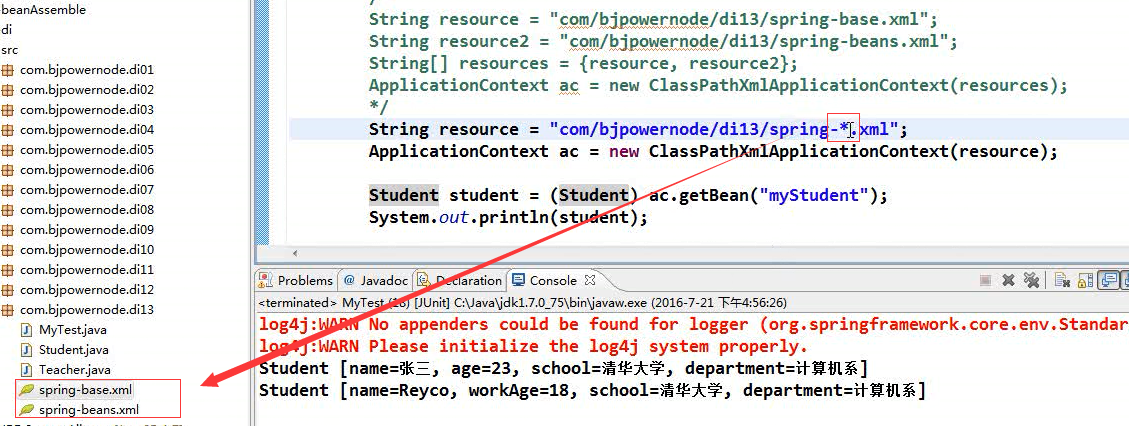
十二、为应用指定多个Spring配置文件
1、平等关系
方式一:

方式二:
二、包含关系