第15课 类与封装的概念
1. 封装的基本概念
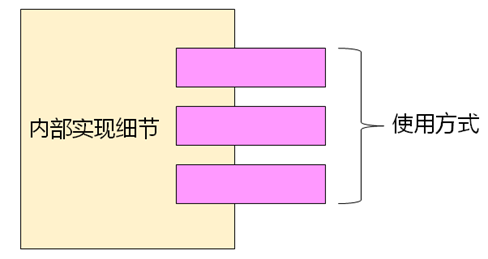
(1)类通常分为两个部分:类的实现细节、类的使用方式。
-
当使用类时,不需要关心其实现细节
-
当创建类时,才需要考虑其内部实现细节
(2)根据经验,并不是类的每个属性都是对外公开的,但一些属性是对外公开的。
(3)必须在类的表示法中定义属性和行为的公开级别:类似文件系统中文件的限制
2. C++中类的封装
(1)成员变量:C++中用于表示类属性的变量
(2)成员函数:C++中用于表示类行为的函数
(3)C++中可以给成员变量和成员函数定义访问级别(如public、private等)
-
public:
-
成员变量和成员函数可以在类的内部和外界访问和调用
-
-
private:
-
成员变量和成员函数只能在类的内部被访问和调用
-
【编程实验】类成员的访问属性 15-1.cpp
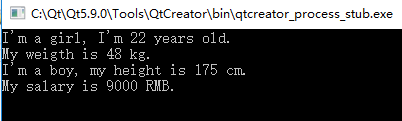
#include <stdio.h> struct Biology { bool living;//生命 }; struct Animal : Biology { bool movable;//可移动 void findFood(){};//找食物 }; struct Plant : Biology { bool growable;//可长大 }; struct Beast : Animal { void sleep(){};//睡觉 }; struct Human : Animal { void sleep(){};//睡觉 void work(){}; //劳动 }; struct Girl : Human { private: int age; //女孩的年龄:private int weight;//女孩的体重:private public: void print() { age = 22; weight = 48; printf("I'm a girl, I'm %d years old.\n", age); printf("My weigth is %d kg.\n", weight); }; }; struct Boy : Human { private: int height; //身高:private int salary; //薪水:private public: int age; int weight; void print() { height = 175; salary = 9000; printf("I'm a boy, my height is %d cm.\n", height); printf("My salary is %d RMB.\n", salary); }; }; int main() { Girl g; Boy b; g.print(); b.age = 19; b.weight = 120; //b.height = 180;//Error: private b.print(); return 0; }
运行结果:
3. 类成员的作用域
(1)类成员的作用域只在类的内部,外部无法直接访问
(2)成员函数可以直接访问成员变量和调用成员函数
(3)类的外部可以通过类变量访问public成员
(4)类成员的作用域与访问级别没有关系。(注意C++中用struct定义的类中所有成员默认为public,而class定义的类成员的默认属性为private)
【编程实验】类成员的作用域 15-2.cpp
#include <stdio.h> int i = 1; struct Test { private: int i; public: int j; int getI() { i = 3; return i; } }; int main() { int i = 2; Test test; test.j = 4; printf("main: i = %d\n", i); //i = 2; printf("::i = %d\n",::i); //::i = 1; //printf("test.i = %d\n", test.i); //Error printf("test.j = %d\n", test.j); //test.j = 4 printf("test.getI() = %d\n", test.getI()); //test.getI() = 3 return 0; }
运行结果:

4. 小结
(1)类通常可分为使用方式和内部细节两部分
(2)类的封装机制使得使用方式和内部细节相分离
(3)C++中通过定义类成员(成员变量和成员函数)的访问级别实现封装机制
(4)public成员可在类的内部和外界访问和调用
(5)private成员只能在类的内部被访问和调用




