Python多线程编程-GIL
Python GIL:global interpreter lock (cpython)
1、python中一个线程对应于c语言中的一个线程
2、gil使得同一个时刻只有一个线程在一个cpu上执行字节码, 无法将多个线程映射到多个cpu上执行
3、gil会根据执行的字节码行数以及时间片释放gil,gil在遇到io的操作时候主动释放
查看Python的字节码文件
import dis def fun(a): a = a + 1 return a print(dis.dis(fun))
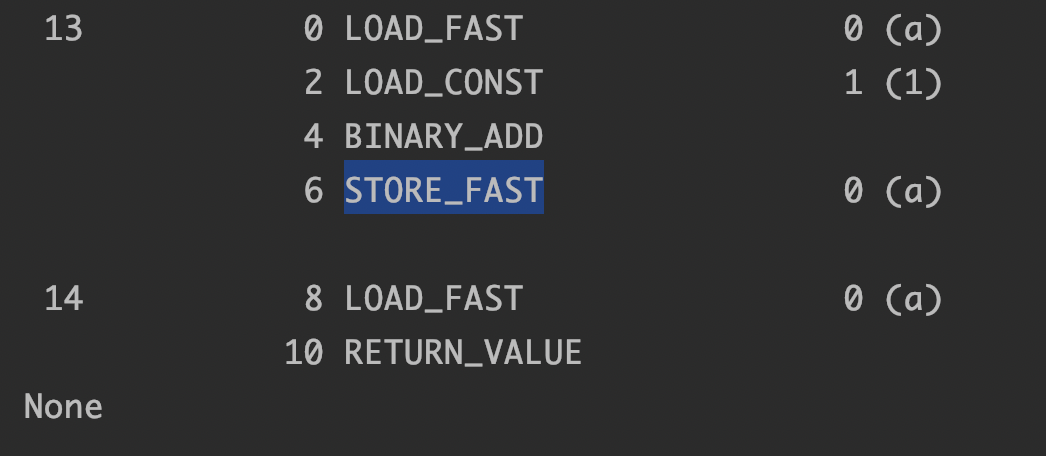
对于第三点的解释:当我们对同一个变量(total)进行加减操作时,会发现最后的运算结果实际上每次都是不一样的,原因在于gil释放锁的时间有区别
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | total = 0def add(): global total for i in range(1000000): total += 1def desc(): global total for i in range(1000000): total -= 1import threadingthread1 = threading.Thread(target=add)thread2 = threading.Thread(target=desc)thread1.start()thread2.start()thread1.join()thread2.join()print(total) |
Python 多线程编程
对于io操作来说,多线程和多进程性能差别不大
Python中使用多线程的方式
1.通过Thread类实例化

1 import threading 2 import time 3 4 5 def get_detail_html(url): 6 print("get detail html started") 7 time.sleep(3) # 处理业务 8 print("get detail html end ") 9 10 11 def get_detail_html_url(): 12 print("get detail html url started") 13 time.sleep(3) # 处理业务 14 print("get detail html url end ") 15 16 17 thread1 = threading.Thread(target=get_detail_html_url, args=("",)) 18 thread2 = threading.Thread(target=get_detail_html, args=("",)) 19 thread1.start() 20 thread2.start() 21 thread2.setDaemon(True) # 设置守护线程 22 thread1.join() # 等待线程执行完成在执行后续主线程 23 thread2.join()
setDaemon 设置线程为守护线程时:主线程结束,子线程也会结束
join 设置jion时,表示子线程未运行完成,主线程不会执行jion后的代码
当二者都不设置时,主线和子线程会并行,且即使主线程运行完成子线程未处理完成会继续运行
2.继承Thread类完成

1 class GetDetailHtml(threading.Thread): 2 def __init__(self, name): 3 super().__init__(name=name) 4 5 def run(self): 6 print("get detail html started") 7 time.sleep(2) 8 print("get detail html end") 9 10 11 class GetDetailUrl(threading.Thread): 12 def __init__(self, name): 13 super().__init__(name=name) 14 15 def run(self): 16 print("get detail url started") 17 time.sleep(4) 18 print("get detail url end") 19 20 if __name__ == "__main__": 21 thread1 = GetDetailHtml("get_detail_html") 22 thread2 = GetDetailUrl("get_detail_url") 23 start_time = time.time() 24 thread1.start() 25 thread2.start() 26 27 thread1.join() 28 thread2.join()
重载run方法,适用与比较复杂的线程
多线程通信
1、多线程可以通过共享变量进行通信 (多进程是不行的)
- 全局变量
- 不具备线程安全
- 队列
- 具备线程安全(Python 双端队列)
线程同步
1、使用threading 中Lock锁
1 lock = Lock() 2 lock.acquire() 3 共享变量 4 lock.release()
使用锁会影响程序的性能,引发死锁的原因:资源竞争、循环等待
当一个线程内要多次锁进行资源绑定时,可以使用Python的可从入锁RLock,但是acquire和release次数要相等
2、使用条件变量(condiction),用于Python复杂线程的通信

1 import threading 2 3 #条件变量, 用于复杂的线程间同步 4 # class XiaoAi(threading.Thread): 5 # def __init__(self, lock): 6 # super().__init__(name="小爱") 7 # self.lock = lock 8 # 9 # def run(self): 10 # self.lock.acquire() 11 # print("{} : 在 ".format(self.name)) 12 # self.lock.release() 13 # 14 # self.lock.acquire() 15 # print("{} : 好啊 ".format(self.name)) 16 # self.lock.release() 17 # 18 # class TianMao(threading.Thread): 19 # def __init__(self, lock): 20 # super().__init__(name="天猫精灵") 21 # self.lock = lock 22 # 23 # def run(self): 24 # 25 # self.lock.acquire() 26 # print("{} : 小爱同学 ".format(self.name)) 27 # self.lock.release() 28 # 29 # self.lock.acquire() 30 # print("{} : 我们来对古诗吧 ".format(self.name)) 31 # self.lock.release() 32 33 #通过condition完成协同读诗 34 35 class XiaoAi(threading.Thread): 36 def __init__(self, cond): 37 super().__init__(name="小爱") 38 self.cond = cond 39 40 def run(self): 41 with self.cond: 42 self.cond.wait() 43 print("{} : 在 ".format(self.name)) 44 self.cond.notify() 45 46 self.cond.wait() 47 print("{} : 好啊 ".format(self.name)) 48 self.cond.notify() 49 50 self.cond.wait() 51 print("{} : 君住长江尾 ".format(self.name)) 52 self.cond.notify() 53 54 self.cond.wait() 55 print("{} : 共饮长江水 ".format(self.name)) 56 self.cond.notify() 57 58 self.cond.wait() 59 print("{} : 此恨何时已 ".format(self.name)) 60 self.cond.notify() 61 62 self.cond.wait() 63 print("{} : 定不负相思意 ".format(self.name)) 64 self.cond.notify() 65 66 class TianMao(threading.Thread): 67 def __init__(self, cond): 68 super().__init__(name="天猫精灵") 69 self.cond = cond 70 71 def run(self): 72 with self.cond: 73 print("{} : 小爱同学 ".format(self.name)) 74 self.cond.notify() 75 self.cond.wait() 76 77 print("{} : 我们来对古诗吧 ".format(self.name)) 78 self.cond.notify() 79 self.cond.wait() 80 81 print("{} : 我住长江头 ".format(self.name)) 82 self.cond.notify() 83 self.cond.wait() 84 85 print("{} : 日日思君不见君 ".format(self.name)) 86 self.cond.notify() 87 self.cond.wait() 88 89 print("{} : 此水几时休 ".format(self.name)) 90 self.cond.notify() 91 self.cond.wait() 92 93 print("{} : 只愿君心似我心 ".format(self.name)) 94 self.cond.notify() 95 self.cond.wait() 96 97 98 99 if __name__ == "__main__": 100 from concurrent import futures 101 cond = threading.Condition() 102 xiaoai = XiaoAi(cond) 103 tianmao = TianMao(cond) 104 105 #启动顺序很重要 106 #在调用with cond之后才能调用wait或者notify方法 107 #condition有两层锁, 一把底层锁会在线程调用了wait方法的时候释放, 上面的锁会在每次调用wait的时候分配一把并放入到cond的等待队列中,等到notify方法的唤醒 108 xiaoai.start() 109 tianmao.start()
wait和notify要成对出现
#在调用with cond之后才能调用wait或者notify方法
#condition有两层锁, 一把底层锁会在线程调用了wait方法的时候释放, 上面的锁会在每次调用wait的时候分配一把并放入到cond的等待队列中,等到notify方法的唤醒
3、信号量

1 #Semaphore 是用于控制进入数量的锁 2 #文件, 读、写, 写一般只是用于一个线程写,读可以允许有多个 3 4 #做爬虫 5 import threading 6 import time 7 8 class HtmlSpider(threading.Thread): 9 def __init__(self, url, sem): 10 super().__init__() 11 self.url = url 12 self.sem = sem 13 14 def run(self): 15 time.sleep(2) 16 print("got html text success") 17 self.sem.release() 18 19 class UrlProducer(threading.Thread): 20 def __init__(self, sem): 21 super().__init__() 22 self.sem = sem 23 24 def run(self): 25 for i in range(20): 26 self.sem.acquire() 27 html_thread = HtmlSpider("https://baidu.com/{}".format(i), self.sem) 28 html_thread.start() 29 30 if __name__ == "__main__": 31 sem = threading.Semaphore(3) 32 url_producer = UrlProducer(sem) 33 url_producer.start()
4、Semaphore 并发控制

1 #Semaphore 是用于控制进入数量的锁 2 #文件, 读、写, 写一般只是用于一个线程写,读可以允许有多个 3 4 #做爬虫 5 import threading 6 import time 7 8 class HtmlSpider(threading.Thread): 9 def __init__(self, url, sem): 10 super().__init__() 11 self.url = url 12 self.sem = sem 13 14 def run(self): 15 time.sleep(2) 16 print("got html text success") 17 self.sem.release() 18 19 class UrlProducer(threading.Thread): 20 def __init__(self, sem): 21 super().__init__() 22 self.sem = sem 23 24 def run(self): 25 for i in range(20): 26 self.sem.acquire() 27 html_thread = HtmlSpider("https://baidu.com/{}".format(i), self.sem) 28 html_thread.start() 29 30 if __name__ == "__main__": 31 sem = threading.Semaphore(3) 32 url_producer = UrlProducer(sem) 33 url_producer.start()





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现