1.基本介绍
LINQ(Language Integrated Query)即语言集成查询。
LINQ是一组语言特性和API,使得你可以使用统一的方式编写各种查询。用于保存和检索来自不同数据源的数据,从而消除了编程语言和数据库之间的不匹配,以及为不同类型的数据源提供单个查询接口。
LINQ总是使用对象,因此你可以使用相同的查询语法来查询和转换XML、对象集合、SQL数据库、ADO.NET数据集以及任何其他可用的LINQ提供程序格式的数据。
LINQ to Object 多用于映射数据库的查询,LINQ to XML 用于查询 XML 元素数据。使用 LINQ 查询的前提是对象必须是一个 IEnumerable 集合
LINQ主要包含以下三部分:
LINQ to Objects 主要负责对象的查询。
LINQ to XML 主要负责XML的查询。
LINQ to ADO.NET 主要负责数据库的查询。
LINQ to SQL
LINQ to DataSet
LINQ to Entities
2.Linq的操作语法
LINQ查询时有两种语法可供选择:查询表达式语法(Query Expression)和方法语法(Fluent Syntax)。
2.1 查询表达式语法
from<range variable> in <IEnumerable<T> or IQueryable<T> Collection> <Standard Query Operators> <lambda expression> <select or groupBy operator> <result formation>
Linq查询表达式
约束:Linq表达式必须以from子句开头,以select或group语句结束
| 关键字 | 功能 |
| from... in.. | 指定要查询的数据源以及范围变量,多个from子句则表示从多个数据源查找数据。注意:C#编译器会把“复合from子句”的查询表达式转换为SelectMany()扩展方法。 |
| join…in…on…equals… | 指定多个数据源的关联方式 |
| let | 引入用于存储查询表达式中子表达式结果的范围变量。通常能达到层次感会更好,使代码更易于阅读。 |
| orderby、descending | 指定元素的排序字段和排序方式。当有多个排序字段时,由字段顺序确定主次关系,可指定升序和降序两种排序方式 |
| where | 指定元素的筛选条件。多个where子句则表示了并列条件,必须全部都满足才能入选。每个where子句可以使用谓词&&、||连接多个条件表达式。 |
| group | 指定元素的分组字段。 |
| select | 指定查询要返回的目标数据,可以指定任何类型,甚至是匿名类型。(目前通常被指定为匿名类型) |
| into |
提供一个临时的标识符。该标识可以引用join、group和select子句的结果。 1) 直接出现在join子句之后的into关键字会被翻译为GroupJoin。(into之前的查询变量可以继续使用) 2) select或group子句之后的into它会重新开始一个查询,让我们可以继续引入where, orderby和select子句,它是对分步构建查询表达式的一种简写方式。(into之前的查询变量都不可再使用) |
案例:查询一个整数数组中的偶数
int[] ints = { 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 10 }; var result = from i in ints where i % 2 == 0 select i;
取出数组中平方值大于平均值的数字:
int[] ints = { 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 10 }; var result = from i in ints let squared = Math.Pow(i, 2) let average = ints.Average() where squared > average select i;
LINQ to XML 的示例,假如我们有如下 XML 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <Employees> <Employee> <EmpId>1</EmpId> <Name>Hobe</Name> <Sex>男</Sex> </Employee> <Employee> <EmpId>2</EmpId> <Name>Lily</Name> <Sex>女</Sex> </Employee> <Employee> <EmpId>3</EmpId> <Name>Jack</Name> <Sex>男</Sex> </Employee> </Employees>
使用 LINQ to XML 查询所有含有指定节点值的元素:
引用命名空间:using System.Xml.Linq;
XElement xelement = XElement.Load("Employees.xml"); var els = from el in xelement.Elements("Employee") where el.Element("Sex").Value == "男" select el; foreach (XElement item in els) { string id = item.Element("EmpId").Value; string name = item.Element("Name").Value; Console.WriteLine($"id:{id},姓名:{name},性别:男"); }
2.2 方法语法
方法语法(也称为流利语法)主要利用System.Linq.Enumerable类中定义的扩展方法和Lambda表达式方式进行查询,类似于如何调用任何类的扩展方法。
案例:
int[] ints = { 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 10 }; var result = ints.Where(i => i % 2 == 0).ToArray();
查询数组中偶数的元素及其在数组中的索引
int[] ints = { 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 10 }; var res = ints.Select((item, index) => new { Item = item, Index = index }); var result = res.Where(p => p.Item % 2 == 0).Select(p => p); foreach (var item in result) { Console.WriteLine($"item:{item.Item},index:{item.Index}"); }
3.集合的一些Linq操作
3.1 Except取差集
LINQ 的 Except 方法用来取差集,即取出集合中与另一个集合所有元素不同的元素。
int[] first = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; int[] second = { 0, 2, 3, 5 }; var result = first.Except(second); // result = { 1, 4 }
注意 Except 方法会去除重复元素:
int[] second = { 0, 2, 3, 5 }; int[] third = { 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4 }; var result = third.Except(second); // result = { 1, 4 }
自定义类型或复合类型取差集,此时需要自定义类型实现IEquatable<T>接口
public class User : IEquatable<User> { public int UserID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string Sex { get; set; } public bool Equals([AllowNull] User other) { return Name == other.Name; } public override int GetHashCode() { return Name?.GetHashCode() ?? 0; } }
var list1 = new List<User> { new User{UserID=1, Name = "User1",Sex="Male"}, new User{UserID=2, Name = "User2",Sex="Female"}, }; var list2 = new List<User> { new User{ UserID=2, Name = "User2",Sex="Female"}, new User{ UserID=3, Name = "User3",Sex="Female"}, }; var result = list1.Except(list2).ToList(); result.ForEach(u => Console.WriteLine(u.Name)); // 输出:User1
3.2 SelectMany集合降维
SelectMany 可以把多维集合降维,比如把二维的集合平铺成一个一维的集合。
var collection = new int[][] { new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {4, 5, 6}, }; var result = collection.SelectMany(x => x); // result = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
举个更贴合实际应用的例子。例如有如下实体类(一个部门有多个员工):
class Department { public Employee[] Employees { get; set; } } class Employee { public string Name { get; set; } }
此时,我们拥有一个这样的数据集合:
var departments = new[] { new Department() { Employees = new [] { new Employee { Name = "Bob" }, new Employee { Name = "Jack" } } }, new Department() { Employees = new [] { new Employee { Name = "Jim" }, new Employee { Name = "John" } } } };
现在我们可以使用 SelectMany 把各部门的员工查询到一个结果集中:
var allEmployees = departments.SelectMany(x => x.Employees); foreach (var emp in allEmployees) { Console.WriteLine(emp.Name); } // 依次输出:Bob Jack Jim John
3.3 SelectMany笛卡尔积运算
SelectMany 不光适用于单个包含多维集合对象的降维,也适用于多个集合之前的两两相互操作,比如进行迪卡尔积运算。比如我们有这样两个集合:
var list1 = new List<string> { "a1", "a2" }; var list2 = new List<string> { "b1", "b2", "b3" };
现在我们需要把它进行两两组合
var result = list1.SelectMany(x => list2.Select(y => $"{x}{y}")); // result = ["a1b1", "a1b2", "a1b3", "a2b1", "a2b2", "a2b3"]
如何对 N 个集合进行迪卡尔积运算呢,比如有这样的集合数据:
var arrList = new List<string[]> { new string[] { "a1", "a2" }, new string[] { "b1", "b2", "b3" }, new string[] { "c1" }, // ... };
下面是一个使用 SelectMany 的实现,需要用到递归:
static void Main(string[] args) { var arrList = new List<string[]> { new string[] { "a1", "a2" }, new string[] { "b1", "b2", "b3" }, new string[] { "c1" }, // ... }; var result = Recursion(arrList, 0, new List<string>()); result.ForEach(x => Console.WriteLine(x)); } static List<string> Recursion(List<string[]> list, int start, List<string> result) { if (start >= list.Count) return result; if (result.Count == 0) result = list[start].ToList(); else result = result.SelectMany(x => list[start].Select(y => x + y)).ToList(); result = Recursion(list, start + 1, result); return result; }
返回结果
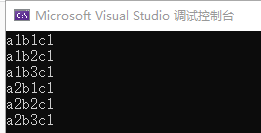
类似这种集合的迪卡尔积运算操作,也可以用 LINQ to Object 来代替 SelectMany 实现:
result = result.SelectMany(x => list[start].Select(y => x + y)).ToList(); // 等同使用扩展方法: result = (from a in result from b in list[start] select a + b).ToList();
3.4 Aggregate聚合
Aggregate 扩展方法可以对一个集合依次执行类似累加器的操作,就像滚雪球一样把数据逐步聚集在一起。比如实现从 1 加到 10,用 Aggregate 扩展方法就很方便:
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; int sum = numbers.Aggregate((prevSum, current) => prevSum + current); // sum = 55
再来看一个字符串的例子加深理解:
string[] stringList = { "Hello", "World", "!" }; string joinedString = stringList.Aggregate((prev, current) => prev + " " + current); // joinedString = "Hello World !"
Aggregate 还有一个重载方法,可以指定累加器的初始值。我们来看一个比较综合的复杂例子。
假如我们有如下 1-12 的一个数字集合:
现在我们想做如下计算:
-
计算集合元素的总数个数
-
计算值为偶数的元素个数
-
收集每第 4 个元素
var result = items.Aggregate(new { Total = 0, Even = 0, FourthItems = new List<int>() }, (accum, item) => new { Total = accum.Total + 1, Even = accum.Even + (item % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 0), FourthItems = (accum.Total + 1) % 4 == 0 ? new List<int>(accum.FourthItems) { item } : accum.FourthItems } ); // result: // Total = 12 // Even = 6 // FourthItems = [4, 8, 12]
3.5 Join关联查询
和 SQL 查询一样,LINQ 同样支持 Inner Join、Left Join、Right Join、Cross Join 和 Full Outer Join,有时候你可能看到不同的写法,其实是同一个意思,比如 Left Outer Join 就是 Left Join,Join 是 Inner Join 省略了 Inner 等。
var first = new List<string>() { "a","b","c" }; // 左边 var second = new List<string>() { "a", "c", "d" }; // 右边
Inner Join
var result = from f in first join s in second on f equals s select new { f, s }; // 等同使用扩展方法: var result = first.Join(second, f => f, s => s, (f, s) => new { f, s }); // result: {"a","a"} // {"c","c"}
Left Join
var result = from f in first join s in second on f equals s into temp from t in temp.DefaultIfEmpty() select new { First = f, Second = t }; // 或者: var result = from f in first from s in second.Where(x => x == f).DefaultIfEmpty() select new { First = f, Second = s }; // 等同使用扩展方法: var result = first.GroupJoin(second, f => f, s => s, (f, s) => new { First = f, Second = s }) .SelectMany(temp => temp.Second.DefaultIfEmpty(), (f, s) => new { First = f.First, Second = s }); // result: {"a","a"} // {"b", null} // {"c","c"}
Right Join
var result = from s in second join f in first on s equals f into temp from t in temp.DefaultIfEmpty() select new { First = t, Second = s }; // 其它和 Left Join 类似 // result: {"a","a"} // {"c","c"} // {null,"d"}
Cross Join
var result = from f in first from s in second select new { f, s }; // result: {"a","a"} // {"a","c"} // {"a","d"} // {"b","a"} // {"b","c"} // {"b","d"} // {"c","a"} // {"c","c"} // {"c","d"}
Full Outer Join
var leftJoin = from f in first join s in second on f equals s into temp from t in temp.DefaultIfEmpty() select new { First = f, Second = t }; var rightJoin = from s in second join f in first on s equals f into temp from t in temp.DefaultIfEmpty() select new { First = t, Second = s }; var fullOuterJoin = leftJoin.Union(rightJoin);
根据多个键关联
在 SQL 中,表与表进行关联查询时 on 条件可以指定多个键的逻辑判断,用 and 或 or 连接。但 C# 的 LINQ 不支持 and 关键字,若要根据多键关联,需要把要关联的键值分别以相同的属性名放到匿名对象中,然后使用 equals 比较两个匿名对象是否相等。示例:
var stringProps = typeof(string).GetProperties(); var builderProps = typeof(StringBuilder).GetProperties(); var query = from s in stringProps join b in builderProps on new { s.Name, s.PropertyType } equals new { b.Name, b.PropertyType } select new { s.Name, s.PropertyType };
3.6 Zip拉链
Zip 扩展方法操作的对象是两个集合,它就像拉链一样,根据位置将两个系列中的每个元素依次配对在一起。其接收的参数是一个 Func 实例,该 Func 实例允许我们成对在处理两个集合中的元素。如果两个集合中的元素个数不相等,那么多出来的将会被忽略。
示例:
int[] numbers = { 3, 5, 7 }; string[] words = { "three", "five", "seven", "ignored" }; IEnumerable<string> zip = numbers.Zip(words, (n, w) => n + "=" + w); foreach (string s in zip) { Console.WriteLine(s); }
输出:
3=three
5=five
7=seven
3.7 ToLookUp索引式查找
ToLookup 扩展方法返回的是可索引查找的数据结构,它是一个 ILookup 实例,所有元素根据指定的键进行分组并可以按键进行索引。这样说有点抽象,来看具体示例:
string[] array = { "one", "two", "three" }; // 根据元素字符串长度创建一个查找对象 var lookup = array.ToLookup(item => item.Length); // 查找字符串长度为 3 的元素 var result = lookup[3]; // result: one,two
再来一个示例:
int[] array = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 }; // 创建一个奇偶查找(键为 0 和 1) var lookup = array.ToLookup(item => item % 2); // 查找偶数 var even = lookup[0]; // even: 2,4,6,8 // 查找奇数 var odd = lookup[1]; // odd: 1,3,5,7
3.8 Distinct去重
简单类型的集合调用 Distinct 方法使用的是默认的比较器,Distinct 方法用此比较器来判断元素是否与其它元素重复,但对于自定义类型要实现去重则需要自定义比较器。示例:
public class IdEqualityComparer : IEqualityComparer<Person> { public bool Equals(Person x, Person y) => x.Id == y.Id; public int GetHashCode(Person p) => p.Id; } public class Person { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var people = new List<Person>(); var distinct = people.Distinct(new IdEqualityComparer()); } }
3.9 字典转换
ToDictionary 扩展方法可以把集合 IEnumerable<TElement> 转换为 Dictionary<TKey, TValue> 结构的字典,它接收一个 Func<TSource, TKey> 参数用来返回每个元素指定的键与值。示例:
IEnumerable<User> users = GetUsers(); Dictionary<int, User> usersById = users.ToDictionary(x => x.Id);
上面 ToDictionary 返回的字典数据中的值是整个元素,你也可以通过它的第二个参数来自定义字典的值。示例:
Dictionary<int, string> userNamesById = users.ToDictionary(x => x.Id, x => x.Name);
你也可以为转换的字典指定其键是否区分大小写,即自定义字典的 IComparer,示例:
Dictionary<string, User> usersByCaseInsenstiveName = users.ToDictionary(x =>x.Name, StringComparer.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase); var user1 =usersByCaseInsenstiveName["liam"]; var user2 =usersByCaseInsenstiveName["LIAM"]; user1 == user2; // true
注意,字典类型要求所有键不能重复,所以在使用 ToDictionary 方法时要确保作为字典的键的元素属性不能有重复值,否则会抛出异常。
3.10 其他常见方法
Range 和 Repeat
Range 和 Repeat 用于生成简单的数字或字符串系列。示例:
// 生成 1-100 的数字,即结果为 [1, 2, ..., 99, 100] var range = Enumerable.Range(1, 100); // 生成三个重复的字符串“a”,即结果为 ["a", "a", "a"] var repeatedValues = Enumerable.Repeat("a", 3);
Any 和 All
Any 用来判断集合中是否存在任一一个元素符合条件,All 用来判断集合中是否所有元素符合条件。示例:
var numbers = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; bool result = numbers.Any(); // true bool result = numbers.Any(x => x == 6); // false bool result = numbers.All(x => x > 0); // true bool result = numbers.All(x => x > 1); // false
Concat 和 Union
Concat 用来拼接两个集合,不会去除重复元素,示例:
List<int> foo = newList<int> { 1, 2, 3 }; List<int> bar = newList<int> { 3, 4, 5 }; // 通过 Enumerable 类的静态方法 var result = Enumerable.Concat(foo, bar).ToList(); // 1,2,3,3,4,5 // 通过扩展方法 var result = foo.Concat(bar).ToList(); // 1,2,3,3,4,5
Union 也是用来拼接两个集合,与 Concat 不同的是,它会去除重复项,示例:
var result = foo.Union(bar); // 1,2,3,4,5
GroupBy 分组
GroupBy 扩展方法用来对集合进行分组,下面是一个根据奇偶进行分组的示例:
var list = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; var grouped = list.GroupBy(x => x % 2 == 0); // grouped: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 和 [2, 4, 6, 8]
还可以根据指定属性进行分组:
public class Person { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } var people = new List<Person>(); var query = people .GroupBy(x => x.Age) .Select(g => { Age = g.Key, Count = g.Count() });
DefaultIfEmpty 空替换
在上面的关联查询中我们使用了 DefaultIfEmpty 扩展方法,它表示在没有查询到指定条件的元素时使用元素的默认值代替。其实 DefaultIfEmpty 还可以指定其它的默认值,示例:
var chars = new List<string>() { "a", "b", "c", "d" }; chars.Where(s => s.Length > 1).DefaultIfEmpty().First(); // 返回 null chars.DefaultIfEmpty("N/A").FirstOrDefault(); // 返回 "a" chars.Where(s => s.Length > 1).DefaultIfEmpty("N/A").FirstOrDefault(); // 返回 "N/A"
SequenceEqual 集合相等
SequenceEqual 扩展方法用于比较集合系列各个相同位置的元素是否相等。示例:
int[] a = new int[] {1, 2, 3}; int[] b = new int[] {1, 2, 3}; int[] c = new int[] {1, 3, 2}; bool result1 = a.SequenceEqual(b); // true bool result2 = a.SequenceEqual(c); // false
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/dotnet261010/p/8279256.html,https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/echHLYV9s65oS-1u1NnEVw


