Head First Python-python面向对象
与大多数其他的编程语言一样,Python容许创建并定义面向对象的类,类可以将代码与代码处理的数据相关联。
对于更加复杂的数据,一般的列表已经不能满足需求了。
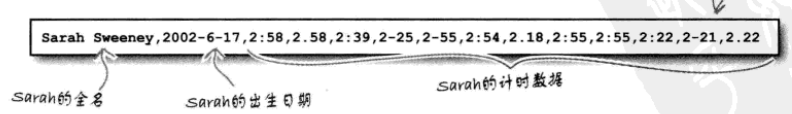
我们可以使用字典dict将数据值与键相关联。
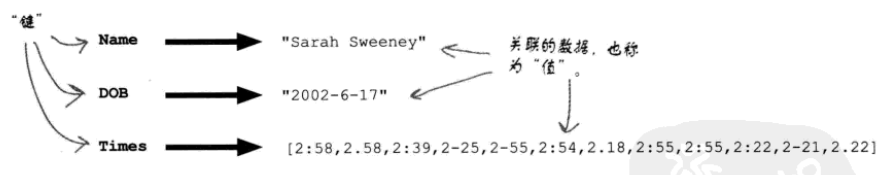
1,使用dict来完成处理
相关处理代码如下:
#DICT def sanitize(time_string): if '-' in time_string: spliter='-' elif ':' in time_string: spliter=':' else: return time_string (mins,secs)=time_string.split(spliter) return mins+'.'+secs def get_coach_data(filename): james_data = {} try: with open(filename) as f: data=f.readline() temp_data=data.strip().split(',') #f_data=[sanitize(i) for i in temp_data] james_data = {'Name':temp_data.pop(0),'Bir':temp_data.pop(0),'Times':str(sorted([sanitize(i) for i in temp_data])[0:3])} return james_data except IOError as Ierror: print('read file error: '+str(Ierror)) return None james=get_coach_data('./data/james2.txt') print(james['Name']+"'s fastest times are: "+james['Times'])
2,使用python类:
在面向对象的世界里,代码通常称为类的方法,数据通常称为类的属性。实例化数据对象通常称为实例。
#class class Athlete(object): def __init__(self,name,bir=None,times=[]): self.name=name self.bir=bir self.times=times def top3(self): return sorted(set([sanitize(i) for i in self.times]))[0:3] def add_time(self,a_time): self.times.append(a_time) def add_times(self,b_time): self.times.extend(b_time) def sanitize(time_string): if '-' in time_string: spliter='-' elif ':' in time_string: spliter=':' else: return time_string (mins,secs)=time_string.split(spliter) return mins+'.'+secs def get_coach_data(filename): try: with open(filename) as f: data=f.readline() temp_data=data.strip().split(',') return Athlete(temp_data.pop(0),temp_data.pop(0),temp_data) except IOError as ioerror: print('file open fail:' + str(ioerror)) return None james=get_coach_data('./data/james2.txt') james.add_times(['1-1','1:2']) print(james.name+"'s fastest times are: "+str(james.top3()))
如果你真心觉得文章写得不错,而且对你有所帮助,那就不妨小小打赏一下吧,如果囊中羞涩,不妨帮忙“推荐"一下,您的“推荐”和”打赏“将是我最大的写作动力!
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号