c++ 行为型模式_状态(State)
1) 意图
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它的类
2) 结构
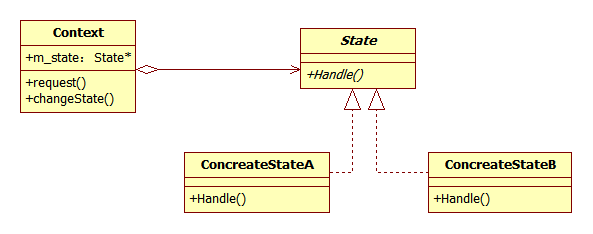
其中:
- Context定义客户感兴趣的接口,维护一个ConcreteState子类的实例,这个实例定义当前状态
- State定义一个接口以封装与Context的一个特定状态相关的行为
- ConcreteState每个子类实现与Context的一个状态相关的行为
3) 适用性
- 一个对象的行为决定于它的状态,并且它必须在运行时刻根据状态改变它的行为
- 一个操作中含有庞大的多分支的条件语句,且这些分支依赖于该对象的状态
4) 举例
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <list> 3 class State; 4 class Context 5 { 6 public: 7 Context(State* state):m_state(state) {} 8 virtual ~Context() 9 { 10 if (m_state) 11 { 12 delete m_state; 13 } 14 } 15 void request(); 16 void changeState(State* state) 17 { 18 if (m_state) delete m_state; 19 m_state = state; 20 } 21 void show(); 22 private: 23 State* m_state; 24 }; 25 class State 26 { 27 public: 28 State(){} 29 virtual ~State() {} 30 virtual void Handle(Context* pContext) = 0; 31 virtual void printState() = 0; 32 }; 33 34 class ConcreateStateA : public State 35 { 36 public: 37 ConcreateStateA() {} 38 virtual ~ConcreateStateA() {} 39 virtual void Handle(Context* pContext); 40 virtual void printState() 41 { 42 std::cout << "state is ConcreateStateA" << std::endl; 43 } 44 }; 45 class ConcreateStateB : public State 46 { 47 public: 48 ConcreateStateB() {} 49 virtual ~ConcreateStateB() {} 50 virtual void Handle(Context* pContext); 51 virtual void printState() 52 { 53 std::cout << "state is ConcreateStateB" << std::endl; 54 } 55 }; 56 void Context::request() 57 { 58 m_state->Handle(this); 59 } 60 void Context::show() 61 { 62 m_state->printState(); 63 } 64 void ConcreateStateA::Handle(Context* pContext) 65 { 66 pContext->changeState(new ConcreateStateB()); 67 } 68 void ConcreateStateB::Handle(Context* pContext) 69 { 70 pContext->changeState(new ConcreateStateA()); 71 } 72 int main() 73 { 74 State* pStateA = new ConcreateStateA(); 75 Context* pContext = new Context(pStateA); 76 pContext->show(); 77 78 pContext->request(); 79 pContext->show(); 80 81 pContext->request(); 82 pContext->show(); 83 84 pContext->request(); 85 pContext->show(); 86 87 delete pContext; 88 system("pause"); 89 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号